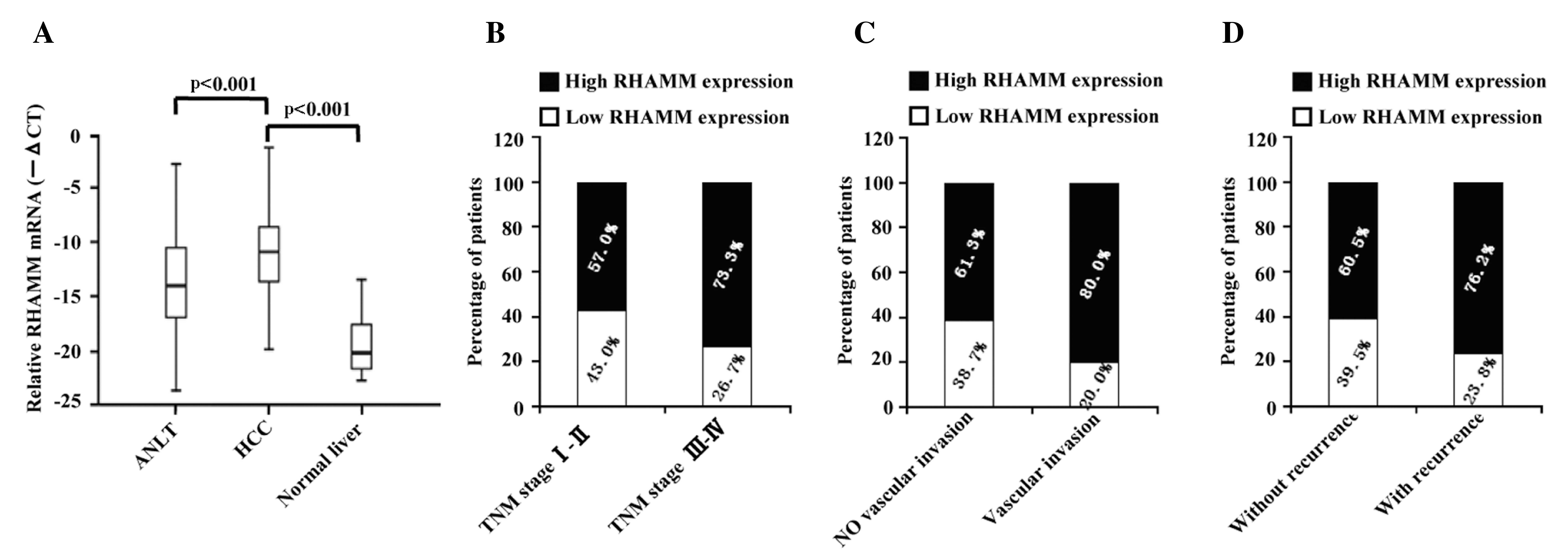
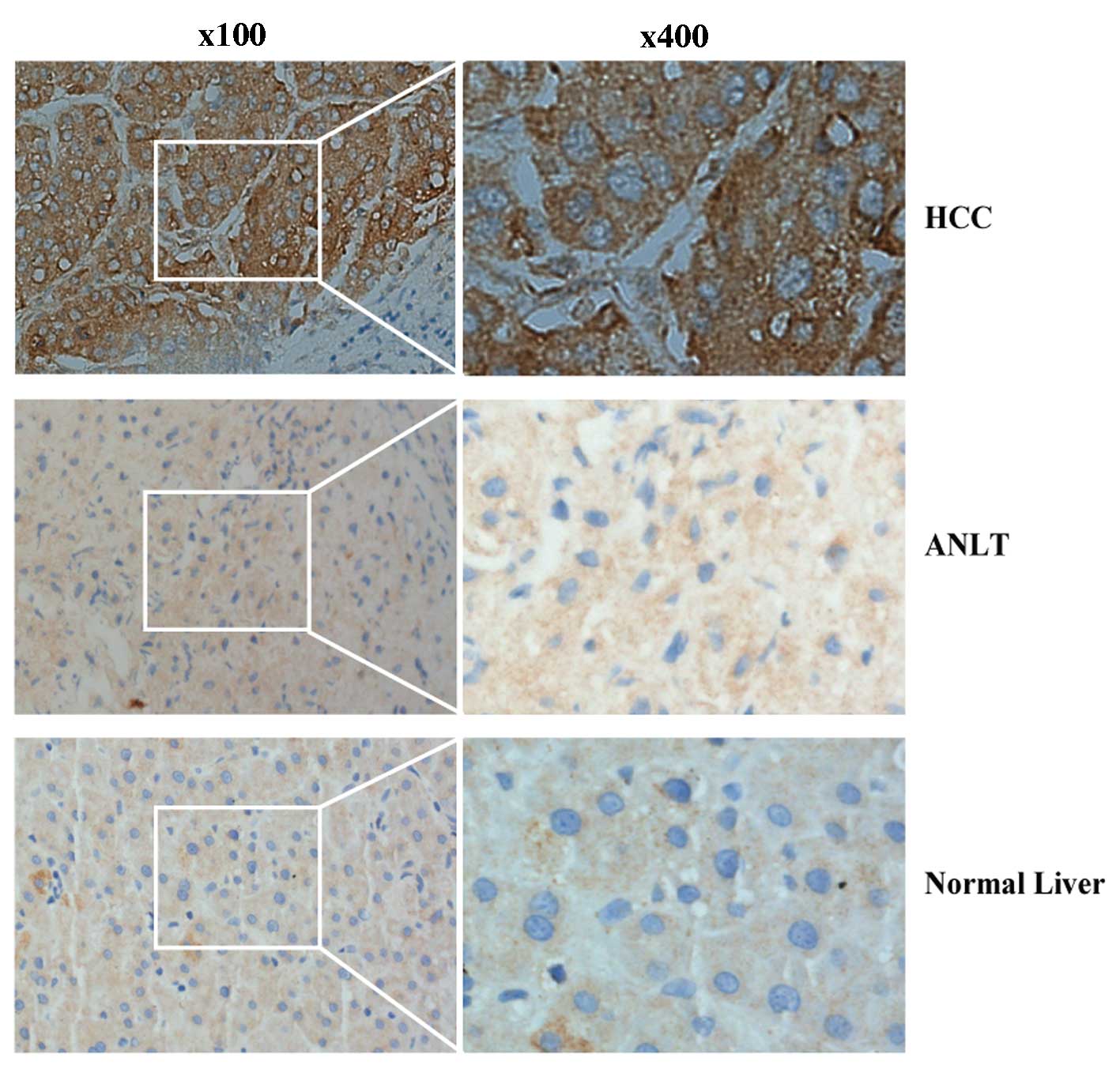
|
1
|
Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA,
Hutin YJF and Bell BP: The contributions of hepatitis B virus and
hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer
worldwide. J Hepatol. 45:529–538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferenci P, Fried M, Labrecque D, Bruix J,
Sherman M, Omata M, Heathcote J, Piratsivuth T, Kew M, Otegbayo JA,
et al: World Gastroenterology Organisation Guidelines and
Publications Committee: World Gastroenterology Organisation
Guideline. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): A global perspective. J
Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 19:311–317. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiao WK, Chen D, Li SQ, Fu SJ, Peng BG and
Liang LJ: Prognostic significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in
hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 4:117–126.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin SL, Chang D and Ying SY: Hyaluronan
stimulates transformation of androgen-independent prostate cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 28:310–320. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stojkovic M, Krebs O, Kölle S, et al:
Developmental regulation of hyaluronan-binding protein
(RHAMM/IHABP) expression in early bovine embryos. Biol Reprod.
68:60–66. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park D, Kim Y, Kim H, Kim K, Lee YS, Choe
J, Hahn JH, Lee H, Jeon J, Choi C, et al: Hyaluronic acid promotes
angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFβ receptor interaction via
CD44-PKCδ. Mol Cells. 33:563–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shigeishi H, Higashikawa K and Takechi M:
Role of receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM) in human
head and neck cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:1629–1640.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Assmann V, Jenkinson D, Marshall JF and
Hart IR: The intracellular hyaluronan receptor RHAMM/IHABP
interacts with microtubules and actin filaments. J Cell Sci.
112:3943–3954. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koelzer VH, Huber B, Mele V, Iezzi G,
Trippel M, Karamitopoulou E, Zlobec I and Lugli A: Expression of
the hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor RHAMM in tumor budding
cells identifies aggressive colorectal cancers. Hum Pathol. Jul
29–2015.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.07.010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Savani RC, Cao G, Pooler PM, Zaman A, Zhou
Z and DeLisser HM: Differential involvement of the hyaluronan (HA)
receptors CD44 and receptor for HA-mediated motility in endothelial
cell function and angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 276:36770–36778. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Forteza R, Lieb T, Aoki T, Savani RC,
Conner GE and Salathe M: Hyaluronan serves a novel role in airway
mucosal host defense. FASEB J. 15:2179–2186. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin SL, Chang D, Chiang A and Ying SY:
Androgen receptor regulates CD168 expression and signaling in
prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 29:282–290. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heldin P, Basu K, Olofsson B, Porsch H,
Kozlova I and Kahata K: Deregulation of hyaluronan synthesis,
degradation and binding promotes breast cancer. J Biochem.
154:395–408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ishigami S, Ueno S, Nishizono Y, Matsumoto
M, Kurahara H, Arigami T, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T, Arima H, Yoshiaki
K, et al: Prognostic impact of CD168 expression in gastric cancer.
BMC Cancer. 11:106–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giannopoulos K, Li L, Bojarska-Junak A,
Rolinski J, Dmoszynska A, Hus I, Greiner J, Renner C, Döhner H and
Schmitt M: Expression of RHAMM/CD168 and other tumor-associated
antigens in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int
J Oncol. 29:95–103. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Verslype C, Rosmorduc O and Rougier P:
ESMO Guidelines Working Group: Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO-ESDO
Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
follow-up. Ann Oncol. 23(Suppl 7): vii41–vii48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liao W, Liu W, Yuan Q, Liu X, Ou Y, He S,
Yuan S, Qin L, Chen Q, Nong K, et al: Silencing of DLGAP5 by siRNA
significantly inhibits the proliferation and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLOS One. 8:e80789–e80797. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang YC, Xu Z, Zhang TF and Wang YL:
Circulating microRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic tools for
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:9853–9862.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong X, He H, Zhang W, Yu D, Wang X and
Chen Y: Combination of serum RASSF1A methylation and AFP is a
promising non-invasive biomarker for HCC patient with chronic HBV
infection. Diagn Pathol. 10:1332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Godar S and Weinberg RA: Filling the
mosaic of p53 actions: p53 represses RHAMM expression. Cell Cycle.
7:3479–3480. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Assmann V, Marshall JF, Fieber C, Hofmann
M and Hart IR: The human hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is expressed as
an intracellular protein in breast cancer cells. J Cell Sci.
111:1685–1694. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lynn BD, Turley EA and Nagy JI:
Subcellular distribution, calmodulin interaction, and mitochondrial
association of the hyaluronan-binding protein RHAMM in rat brain. J
Neurosci Res. 65:6–16. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stojkovic M, Machado SA, Stojkovic P,
Zakhartchenko V, Hutzler P, Gonçalves PB and Wolf E: Mitochondrial
distribution and adenosine triphosphate content of bovine oocytes
before and after in vitro maturation: Correlation with
morphological criteria and developmental capacity after in vitro
fertilization and culture. Biol Reprod. 64:904–909. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang C, Thor AD, Moore DH II, Zhao Y,
Kerschmann R, Stern R, Watson PH and Turley EA: The overexpression
of RHAMM, a hyaluronan-binding protein that regulates ras
signaling, correlates with overexpression of mitogen-activated
protein kinase and is a significant parameter in breast cancer
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 4:567–576. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nedvetzki S, Gonen E, Assayag N, Reich R,
Williams RO, Thurmond RL, Huang JF, Neudecker BA, Wang FS, Turley
EA, et al: RHAMM, a receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility,
compensates for CD44 in inflamed CD44-knockout mice: A different
interpretation of redundancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:18081–18086. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li H, Guo L, Li JW, Liu N, Qi R and Liu J:
Expression of hyaluronan receptors CD44 and RHAMM in stomach
cancers: relevance with tumor progression. Int J Oncol. 17:927–932.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mima K, Beppu T, Ishiko T, Chikamoto A,
Nakagawa S, Hayashi H, Watanabe M, Sakamaki K and Baba H:
Preoperative serum hyaluronic acid level as a prognostic factor in
patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Br J Surg. 101:269–276. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bourguignon LY, Gilad E, Peyrollier K,
Brightman A and Swanson RA: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction stimulates
Rac1 signaling and PKN gamma kinase activation leading to
cytoskeleton function and cell migration in astrocytes. J
Neurochem. 101:1002–1017. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Contreras EG, Gaete M, Sánchez N, Carrasco
H and Larraín J: Early requirement of Hyaluronan for tail
regeneration in Xenopus tadpoles. Development. 136:2987–2996. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Washio A, Kitamura C, Jimi E, Terashita M
and Nishihara T: Mechanisms involved in suppression of NGF-induced
neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells by hyaluronic acid. Exp Cell
Res. 315:3036–3043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim Y, Lee YS, Choe J, Lee H, Kim YM and
Jeoung D: CD44-epidermal growth factor receptor interaction
mediates hyaluronic acid-promoted cell motility by activating
protein kinase C signaling involving Akt, Rac1, Phox, reactive
oxygen species, focal adhesion kinase, and MMP-2. J Biol Chem.
283:22513–22528. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Koyama H, Hibi T, Isogai Z, Yoneda M,
Fujimori M, Amano J, Kawakubo M, Kannagi R, Kimata K, Taniguchi S,
et al: Hyperproduction of hyaluronan in neu-induced mammary tumor
accelerates angiogenesis through stromal cell recruitment: Possible
involvement of versican/PG-M. Am J Pathol. 170:1086–1099. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Golshani R, Lopez L, Estrella V, Kramer M,
Iida N and Lokeshwar VB: Hyaluronic acid synthase-1 expression
regulates bladder cancer growth, invasion, and angiogenesis through
CD44. Cancer Res. 68:483–491. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|