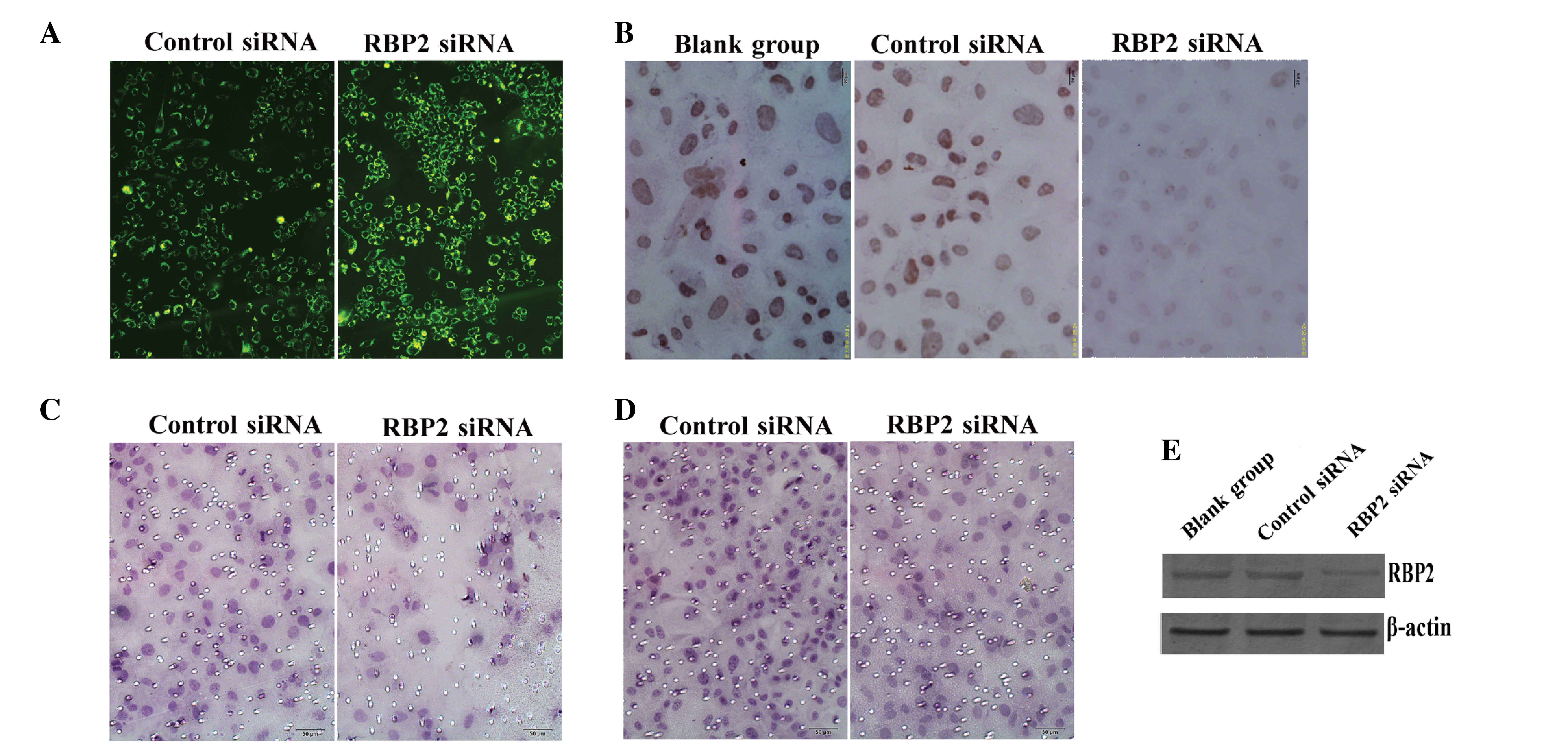
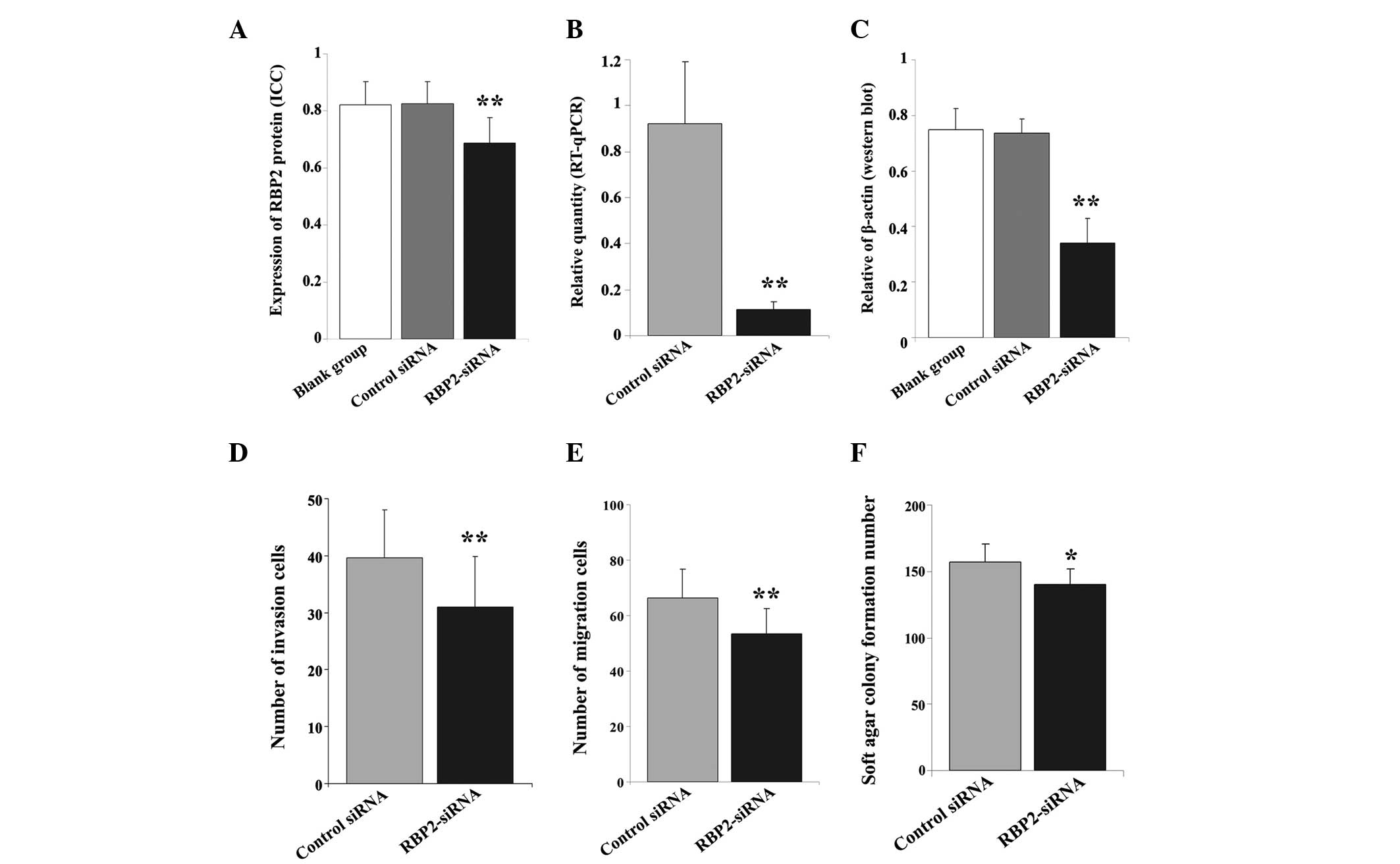
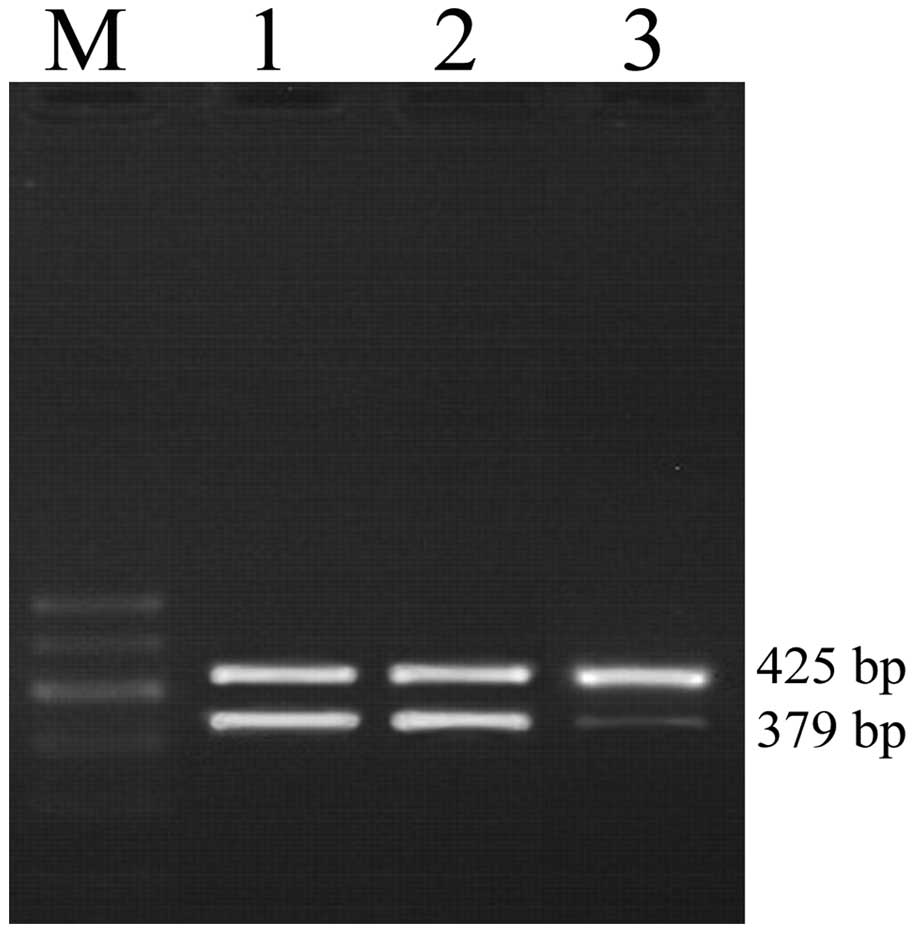
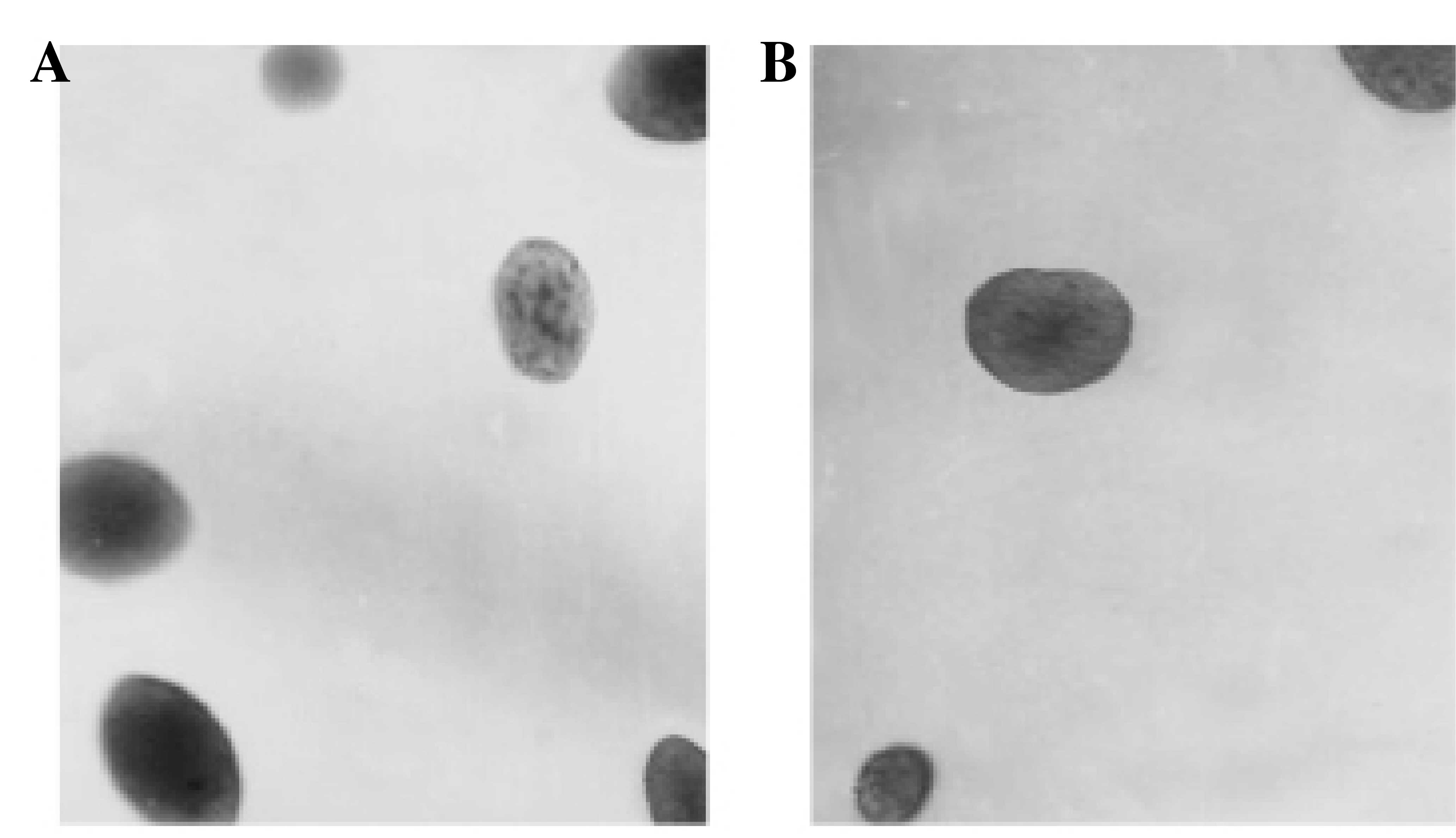
|
1
|
Sherman SI: Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet.
361:501–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davies L and Welch HG: Current thyroid
cancer trends in the United States. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 40:317–322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Moura MA, Bergmann A, Aguiar SS and Thuler
LC: The magnitude of the association between smoking and the risk
of developing cancer in Brazil: A multicenter study. BMJ Open.
4:e0037362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pilli T, Prasad KV, Jayarama S, Pacini F
and Prabhakar BS: Potential utility and limitations of thyroid
cancer cell lines as models for studying thyroid cancer. Thyroid.
19:1333–1342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Medici M, Porcu E, Pistis G, Teumer A,
Brown SJ, Jensen RA, Rawal R, Roef GL, Plantinga TS, Vermeulen SH,
et al: Identification of novel genetic loci associated with thyroid
peroxidase antibodies and clinical thyroid disease. PLoS Genet.
10:e10041232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Akeno N, Miller AL, Ma X and
Wikenheiser-Brokamp KA: p53 suppresses carcinoma progression by
inhibiting mTOR pathway activation. Oncogene. 34:589–99. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moretti S, Menicali E, Voce P, Morelli S,
Cantarelli S, Sponziello M, Colella R, Fallarino F, Orabona C,
Alunno A, et al: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is
up-regulated in thyroid carcinoma and drives the development of an
immunosuppressant tumor microenvironment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
99:E832–E840. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy.
Nature. 429:457–463. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tiwari N, Tiwari VK, Waldmeier L, Balwierz
PJ, Arnold P, Pachkov M, Meyer-Schaller N, Schübeler D, van
Nimwegen E and Christofori G: Sox4 is a master regulator of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by controlling Ezh2 expression
and epigenetic reprogramming. Cancer Cell. 23:768–783. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Enkhbaatar Z, Terashima M, Oktyabri D,
Tange S, Ishimura A, Yano S and Suzuki T: KDM5B histone demethylase
controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells by
regulating the expression of the microRNA-200 family. Cell Cycle.
12:2100–2112. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ramadoss S, Chen X and Wang CY: Histone
demethylase KDM6B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J
Biol Chem. 287:44508–44517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klose RJ, Yan Q, Tothova Z, Yamane K,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Gilliland DG, Zhang Y and Kaelin WG
Jr: The retinoblastoma binding protein RBP2 is an H3K4 demethylase.
Cell. 128:889–900. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Christensen J, Agger K, Cloos PA, Pasini
D, Rose S, Sennels L, Rappsilber J, Hansen KH, Salcini AE and Helin
K: RBP2 belongs to a family of demethylases, specific for tri-and
dimethylated lysine 4 on histone 3. Cell. 128:1063–1076. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Benevolenskaya EV, Murray HL, Branton P,
Young RA and Kaelin WG Jr: Binding of pRB to the PHD protein RBP2
promotes cellular differentiation. Mol Cell. 18:623–635. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, Quinlan MP,
Takahashi F, Maheswaran S, McDermott U, Azizian N, Zou L, Fischbach
MA, et al: A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in
cancer cell subpopulations. Cell. 141:69–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang X, Zeng J, Wang L, Fang M, Wang Q,
Zhao M, Xu X, Liu Z, Li W, Liu S, et al: Histone demethylase
retinoblastoma binding protein 2 is overexpressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma and negatively regulated by hsa-miR-212. PLoS One.
8:e697842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang S, Wang Y, Wu H and Hu L: RBP2
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e847352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao J, Liu Z, Cheung WK, Zhao M, Chen SY,
Chan SW, Booth CJ, Nguyen DX and Yan Q: Histone demethylase RBP2 is
critical for breast cancer progression and metastasis. Cell
Reports. 6:868–877. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiping Z, Ming F, Lixiang W, Xiuming L,
Yuqun S, Han Y, Zhifang L, Yundong S, Shili L, Chunyan C and Jihui
J: MicroRNA-212 inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer by
directly repressing retinoblastoma binding protein 2. J Cell
Biochem. 114:2666–2672. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong L, Zhang G, Wang X, Zhou J, Hou S and
Cui W: Immunohistochemical expression of RBP2 and LSD1 in papillary
thyroid carcinoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 54:499–503.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feinberg AP, Ohlsson R and Henikoff S: The
epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer. Nat Rev Genet.
7:21–33. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Varier RA and Timmers HT: Histone lysine
methylation and demethylation pathways in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1815:75–89. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang Y, Xiao F, An Z and Hao L: Systematic
review on the relationship between genetic polymorphisms of
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1861–1866. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mikkelsen TS, Ku M, Jaffe DB, Issac B,
Lieberman E, Giannoukos G, Alvarez P, Brockman W, Kim TK, Koche RP,
et al: Genome-wide maps of chromatin state in pluripotent and
lineage-committed cells. Nature. 448:553–560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Iwase S, Lan F, Bayliss P, de la
Torre-Ubieta L, Huarte M, Qi HH, Whetstine JR, Bonni A, Roberts TM
and Shi Y: The X-linked mental retardation gene SMCX/JARID1C
defines a family of histone H3 lysine 4 demethylases. Cell.
128:1077–1088. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Defeo-Jones D, Huang PS, Jones RE, Haskell
KM, Vuocolo GA, Hanobik MG, Huber HE and Oliff A: Cloning of cDNAs
for cellular proteins that bind to the retinoblastoma gene product.
Nature. 352:251–254. 1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Teng YC, Lee CF, Li YS, Chen YR, Hsiao PW,
Chan MY, Lin FM, Huang HD, Chen YT, Jeng YM, et al: Histone
demethylase RBP2 promotes lung tumorigenesis and cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 73:4711–4721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Blair LP, Cao J, Zou MR, Sayegh J and Yan
Q: Epigenetic regulation by lysine demethylase 5 (kdm5) enzymes in
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 3:1383–1404. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin N, Du XL, Reitzel LR, Xu L and Strugis
EM: impact of enhanced detection on the increase in thyroid cancer
incidence in the United States: Review of incidence trends by
socioeconomic status within the surveillance, epidemiology, and end
results registry, 1980–2008. Thyroid. 23:103–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|