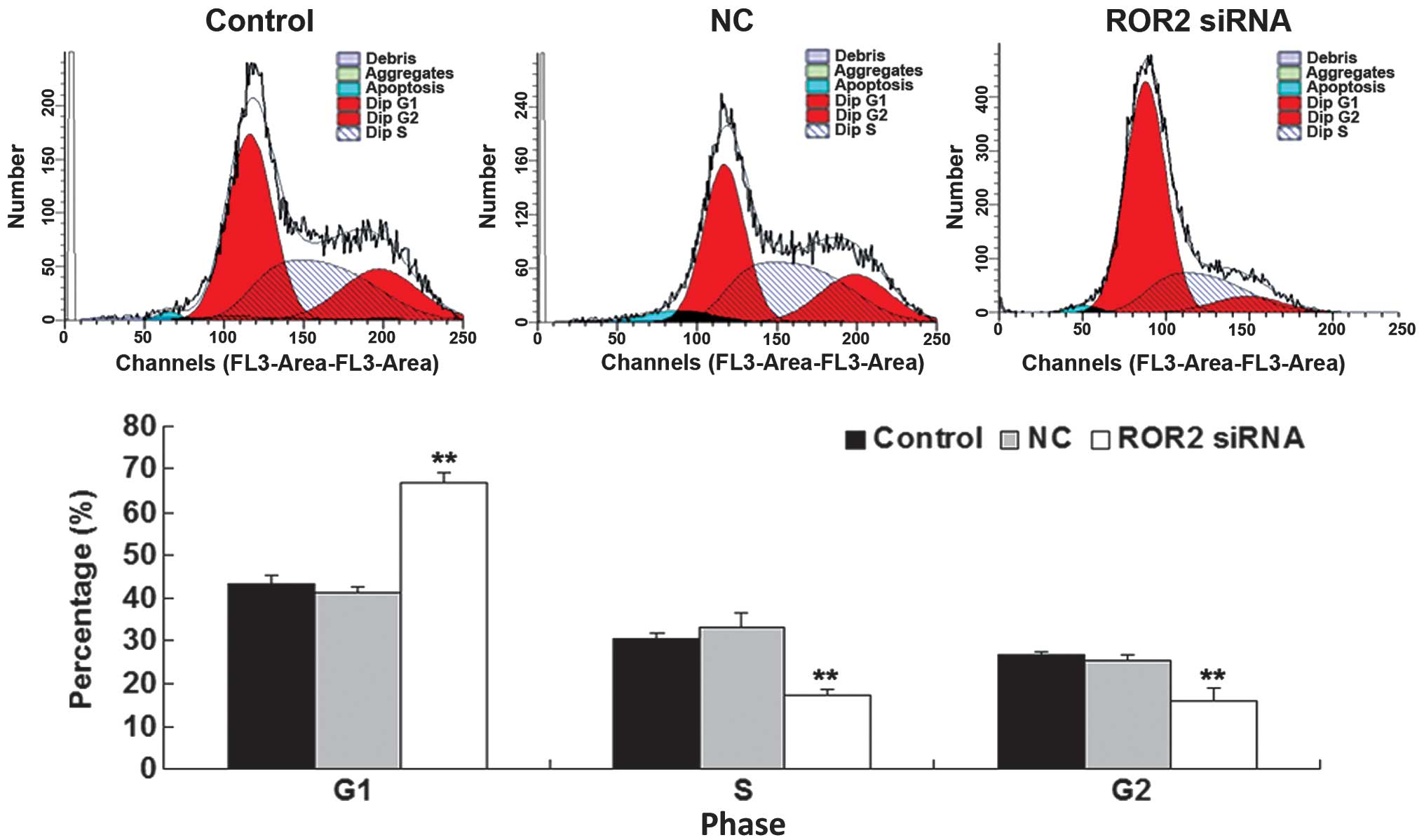
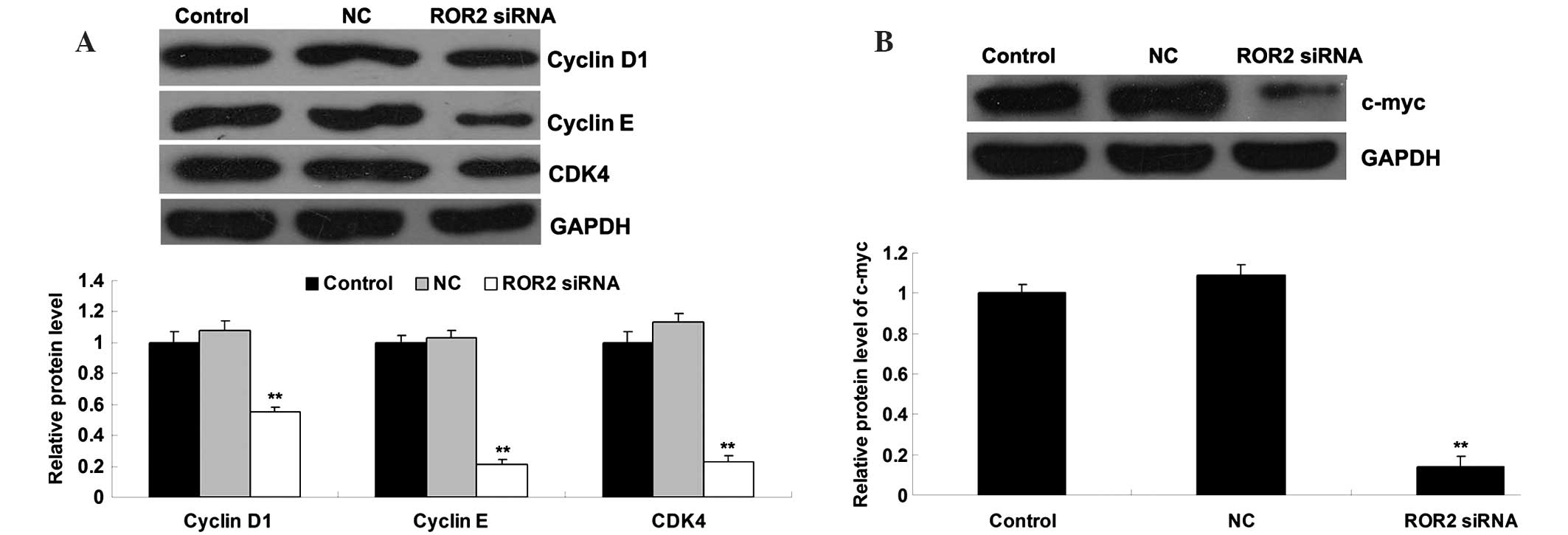
|
1
|
Valery PC, Laversanne M and Bray F: Bone
cancer incidence by morphological subtype: A global assessment.
Cancer Causes Control. 26:1127–1139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrari S, Smeland S, Mercuri M, Bertoni
F, Longhi A, Ruggieri P, Alvegard TA, Picci P, Capanna R, Bernini
G, et al: Italian and Scandinavian Sarcoma Groups: Neoadjuvant
chemotherapy with high-dose Ifosfamide, high-dose methotrexate,
cisplatin, and doxorubicin for patients with localized osteosarcoma
of the extremity: A joint study by the Italian and Scandinavian
Sarcoma Groups. J Clin Oncol. 23:8845–8852. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mialou VI, Philip T, Kalifa C, Perol D,
Gentet JC, Marec-Berard P, Pacquement H, Chastagner P, Defaschelles
AS and Hartmann O: Metastatic osteosarcoma at diagnosis: prognostic
factors and long-term outcome - the French pediatric experience.
Cancer. 104:1100–1109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson LD: Osteosarcoma. Ear Nose Throat
J. 92:288–290. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
PosthumaDeBoer J, Witlox MA, Kaspers GJ
and van Royen BJ: Molecular alterations as target for therapy in
metastatic osteosarcoma: A review of literature. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 28:493–503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sundaram MV: Canonical RTK-Ras-ERK
signaling and related alternative pathways. WormBook. 1:1–38. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jiménez G, Shvartsman SY and Paroush Z:
The Capicua repressor-a general sensor of RTK signaling in
development and disease. J Cell Sci. 125:1383–1391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Batchu SN and Korshunov VA: Novel tyrosine
kinase signaling pathways: Implications in vascular remodeling.
Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 21:122–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Katoh M: WNT signaling pathway and stem
cell signaling network. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4042–4045. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Green JL, Kuntz SG and Sternberg PW: Ror
receptor tyrosine kinases: Orphans no more. Trends Cell Biol.
18:536–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Bhat RA, Seestaller-Wehr LM,
Fukayama S, Mangine A, Moran RA, Komm BS, Bodine PV and Billiard J:
The orphan receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 promotes osteoblast
differentiation and enhances ex vivo bone formation. Mol
Endocrinol. 21:376–387. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
DeChiara TM, Kimble RB, Poueymirou WT,
Rojas J, Masiakowski P, Valenzuela DM and Yancopoulos GD: Ror2,
encoding a receptor-like tyrosine kinase, is required for cartilage
and growth plate development. Nat Genet. 24:271–274. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mehawej C, Chouery E, Maalouf D, Baujat G,
Le Merrer M, Cormier-Daire V and Mégarbané A: Identification of a
novel causative mutation in the ROR2 gene in a Lebanese family with
a mild form of recessive Robinow syndrome. Eur J Med Genet.
55:103–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Debebe Z and Rathmell WK: Ror2 as a
therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 150:143–148. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rebagay G, Yan S, Liu C and Cheung NK:
ROR1 and ROR2 in human malignancies: Potentials for targeted
therapy. Front Oncol. 2:342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Ying J, Tong X, Zhong L, Su X, Xiang
T, Shu X, Rong R, Xiong L, Li H, et al: Epigenetic identification
of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 as a functional
tumor suppressor inhibiting β-catenin and AKT signaling but
frequently methylated in common carcinomas. Cell Mol Life Sci.
71:2179–2192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu BJ, Wang YQ, Wei XJ, Rong LQ, Wei D,
Yan CM, Wang DJ and Sun JY: Expression of WNT-5a and ROR2
correlates with disease severity in osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep.
5:1033–1036. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ren D, Minami Y and Nishita M: Critical
role of Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in motility and invasiveness of
carcinoma cells following Snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Genes Cells. 16:304–315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Enomoto M, Hayakawa S, Itsukushima S, Ren
DY, Matsuo M, Tamada K, Oneyama C, Okada M, Takumi T, Nishita M and
Minami Y: Autonomous regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasiveness
by Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling. Oncogene. 28:3197–3208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stricker S and Mundlos S: FGF and ROR2
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in human skeletal development.
Curr Top Dev Biol. 97:179–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamagata K, Li X, Ikegaki S, Oneyama C,
Okada M, Nishita M and Minami Y: Dissection of Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling
leading to matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-13) expression. J Biol
Chem. 287:1588–1599. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang HR, Lian JD, Lo CW, Chang YC, Yang
MY and Wang CJ: Induction of urothelial proliferation in rats by
aristolochic acid through cell cycle progression via activation of
cyclin D1/cdk4 and cyclin E/cdk2. Food Chem Toxicol. 44:28–35.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li C, Chen H, Hu L, Xing Y, Sasaki T,
Villosis MF, Li J, Nishita M, Minami Y and Minoo P: Ror2 modulates
the canonical Wnt signaling in lung epithelial cells through
cooperation with Fzd2. BMC Mol Biol. 9:112008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lerner UH and Ohlsson C: The WNT system:
Background and its role in bone. J Intern Med. 277:630–649. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ford CE, Ma Qian SS, Quadir A and Ward RL:
The dual role of the novel Wnt receptor tyrosine kinase, ROR2, in
human carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 133:779–787. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wright TM, Brannon AR, Gordan JD, Mikels
AJ, Mitchell C, Chen S, Espinosa I, van de Rijn M, Pruthi R, Wallen
E, et al: Ror2, a developmentally regulated kinase, promotes tumor
growth potential in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 28:2513–2523.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geng M, Cao YC, Chen YJ, Jiang H, Bi LQ
and Liu XH: Loss of Wnt5a and Ror2 protein in hepatocellular
carcinoma associated with poor prognosis. World J Gastroenterol.
18:1328–1338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Connell MP, Fiori JL, Xu M, Carter AD,
Frank BP, Camilli TC, French AD, Dissanayake SK, Indig FE, Bernier
M, et al: The orphan tyrosine kinase receptor, ROR2, mediates Wnt5A
signaling in metastatic melanoma. Oncogene. 29:34–44. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wright TM, Brannon AR, Gordan JD, Mikels
AJ, Mitchell C, Chen S, Espinosa I, van de Rijn M, Pruthi R, Wallen
E, et al: Ror2, a developmentally regulated kinase, promotes tumor
growth potential in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 28:2513–2523.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kobayashi M, Shibuya Y, Takeuchi J, Murata
M, Suzuki H, Yokoo S, Umeda M, Minami Y and Komori T: Ror2
expression in squamous cell carcinoma and epithelial dysplasia of
the oral cavity. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
107:398–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morioka K, Tanikawa C, Ochi K, Daigo Y,
Katagiri T, Kawano H, Kawaguchi H, Myoui A, Yoshikawa H, Naka N, et
al: Orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ROR2 as a potential therapeutic
target for osteosarcoma. Cancer Sci. 100:1227–1233. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheng BQ, Jiang Y, Zhu Q and Lin WG:
Wnt/β-catenin aids in regulating the proliferation of hepG2 cells
mediated by thy-1. Genet Mol Res. 13:5115–5127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|