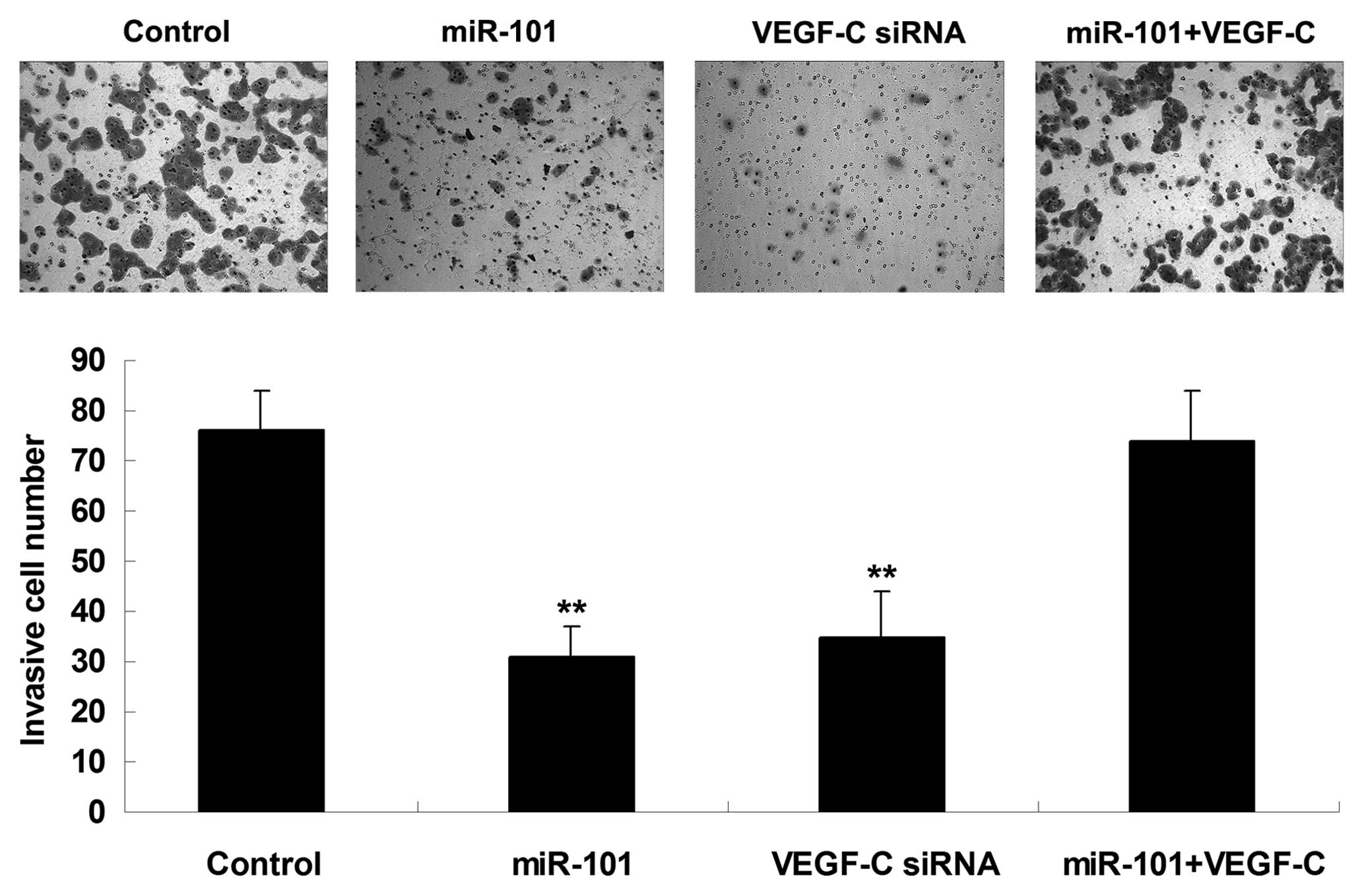
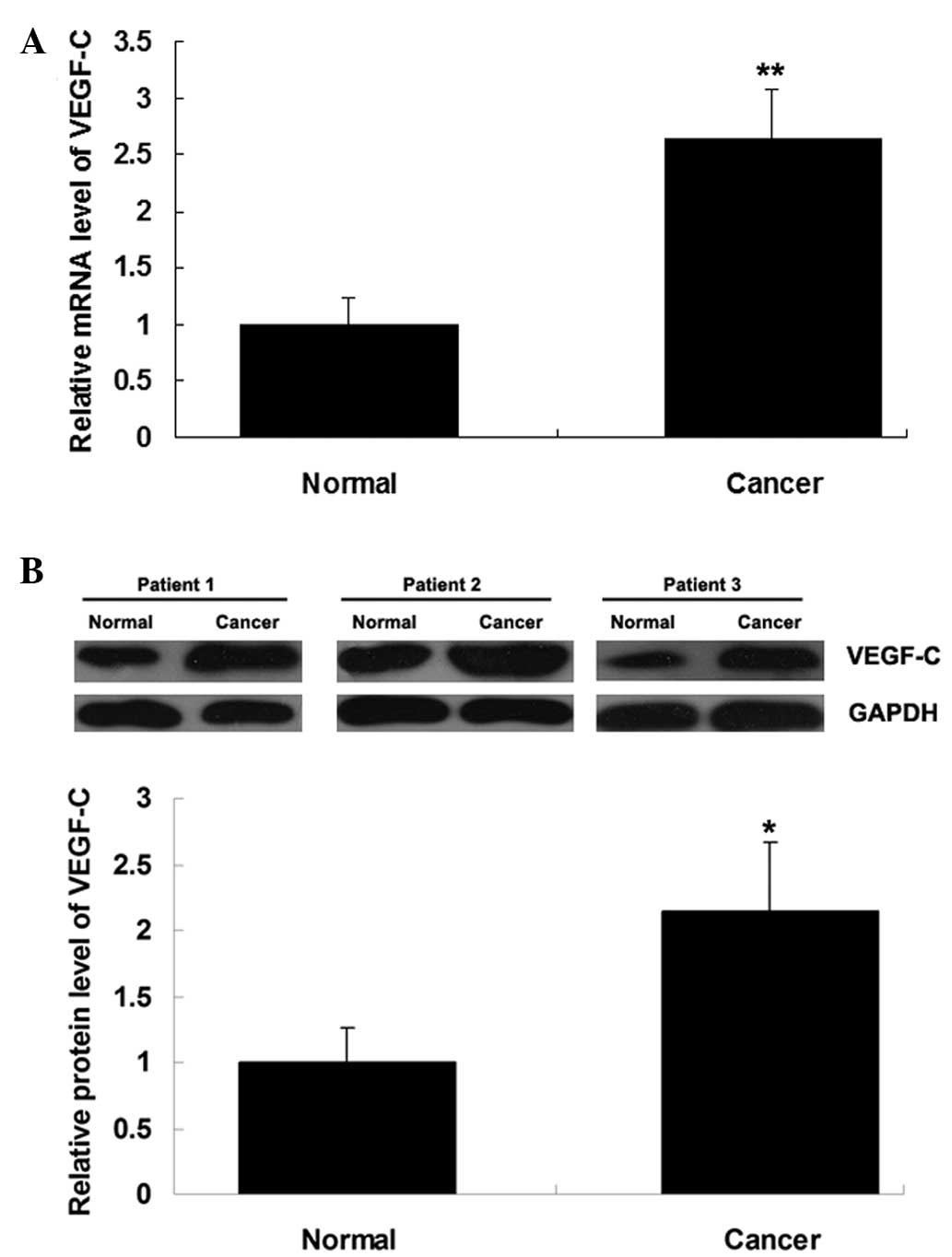
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Li L, Guo R, Li X, Lu Y, Guan X,
Gitau SC, Wang L, Xu C, Yang B, et al: miR-101 promotes breast
cancer cell apoptosis by targeting Janus kinase 2. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:413–422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Konno Y, Dong P, Xiong Y, Suzuki F, Lu J,
Cai M, Watari H, Mitamura T, Hosaka M, Hanley SJ, et al:
MicroRNA-101 targets EZH2, MCL-1 and FOS to suppress proliferation,
invasion and stem cell-like phenotype of aggressive endometrial
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang X, Liu Y, Zeng L, Yu C, Hu Z, Zhou Q
and Yang Z: miR-101 inhibits the G1-to-S phase transition of
cervical cancer cells by targeting Fos. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
24:1165–1172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lei Q, Shen F, Wu J, Zhang W, Wang J and
Zhang L: MiR-101, downregulated in retinoblastoma, functions as a
tumor suppressor in human retinoblastoma cells by targeting EZH2.
Oncol Rep. 32:261–269. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo F, Cogdell D, Hu L, Yang D, Sood AK,
Xue F and Zhang W: MiR-101 suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 in ovarian carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 31:2021–2028. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhang H,
Huang C, Jiang H, Wang X and Li X: miR-101 inhibits autophagy and
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2019–2024. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Guo X, Xiong L, Kong X, Xu Y, Liu
C, Zou L, Li Z, Zhao J and Lin N: MicroRNA-101 suppresses
SOX9-dependent tumorigenicity and promotes favorable prognosis of
human hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 586:4362–4370. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou S, Tan C, Dai Z, Zhu H, Xu M, Zhou Z,
Wang W, Zhao Y, Fu X, Zhou J, et al: Tacrolimus enhances the
invasion potential of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and promotes
lymphatic metastasis in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor-C. Transplant
Proc. 43:2747–2754. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S,
Imoto I and Inazawa J: miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically
silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 31:766–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin X, Guan H, Li H, Liu L, Liu J, Wei G,
Huang Z, Liao Z and Li Y: miR-101 inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting Rac1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Biomed Rep.
2:122–126. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y
and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular
carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer
Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sheng Y, Li J, Zou C, Wang S, Cao Y, Zhang
J, Huang A and Tang H: Downregulation of miR-101-3p by hepatitis B
virus promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by targeting Rab5a. Arch Virol. 159:2397–2410.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee HS, Jun JH, Jung EH, Koo BA and Kim
YS: Epigalloccatechin-3-gallate inhibits ocular neovascularization
and vascular permeability in human retinal pigment epithelial and
human retinal microvascular endothelial cells via suppression of
MMP-9 and VEGF activation. Molecules. 19:12150–12172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao Y, Linden P, Farnebo J, Cao R,
Eriksson A, Kumar V, Qi JH, Claesson-Welsh L and Alitalo K:
Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14389–14394. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, et al:
A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for
the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases.
EMBO J. 15:17511996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kostis G, Ioannis L, Helen K and Helen P:
The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C correlates
with lymphatic microvessel density and lymph node metastasis in
prostate carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study. Urol Ann.
6:224–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peppicelli S, Bianchini F and Calorini L:
Inflammatory cytokines induce vascular endothelial growth factor-C
expression in melanoma-associated macrophages and stimulate
melanoma lymph node metastasis. Oncol Lett. 8:1133–1138.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Li HG, Wen JM, Peng TS, Zeng H and
Wang LY: Expression of CD44v3, erythropoietin and VEGF-C in gastric
adenocarcinomas: correlations with clinicopathological features.
Tumor. 100:321–327. 2014.
|
|
24
|
Omoto I, Matsumoto M, Okumura H, Uchikado
Y, Setoyama T, Kita Y, Owaki T, Kijima Y, Shinchi H, Ishigami S, et
al: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 7:1027–1032. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang ZS, Xu YF, Huang FF and Ding GF:
Associations of nm23H1, VEGF-C and VEGF-3 receptor in human
prostate cancer. Molecules. 19:6851–6862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karaman S and Detmar M: Mechanisms of
lymphatic metastasis. J Clin Invest. 124:922–928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang H, Yin Y, Zhang L, et al: The
effects of vascular endothelial growth factor C knockdown in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:133–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chaudary N, Milosevic M and Hill RP:
Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3
(VEGFR3) and vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) inhibits
hypoxia-induced lymph node metastases in cervix cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 123:393–400. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao ZC, Zheng SS, Wan YL, Jia CK and Xie
HY: The molecular mechanism underlying angiogenesis in
hepatocellular carcinoma: The imbalance activation of signaling
pathways. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2:529–536.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhuang PY, Shen J, Zhu XD, et al:
Prognostic roles of cross-talk between peritumoral hepatocytes and
stromal cells in hepatocellular carcinoma involving peritumoral
VEGF-C, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-3. PLoS One. 8:e645982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|