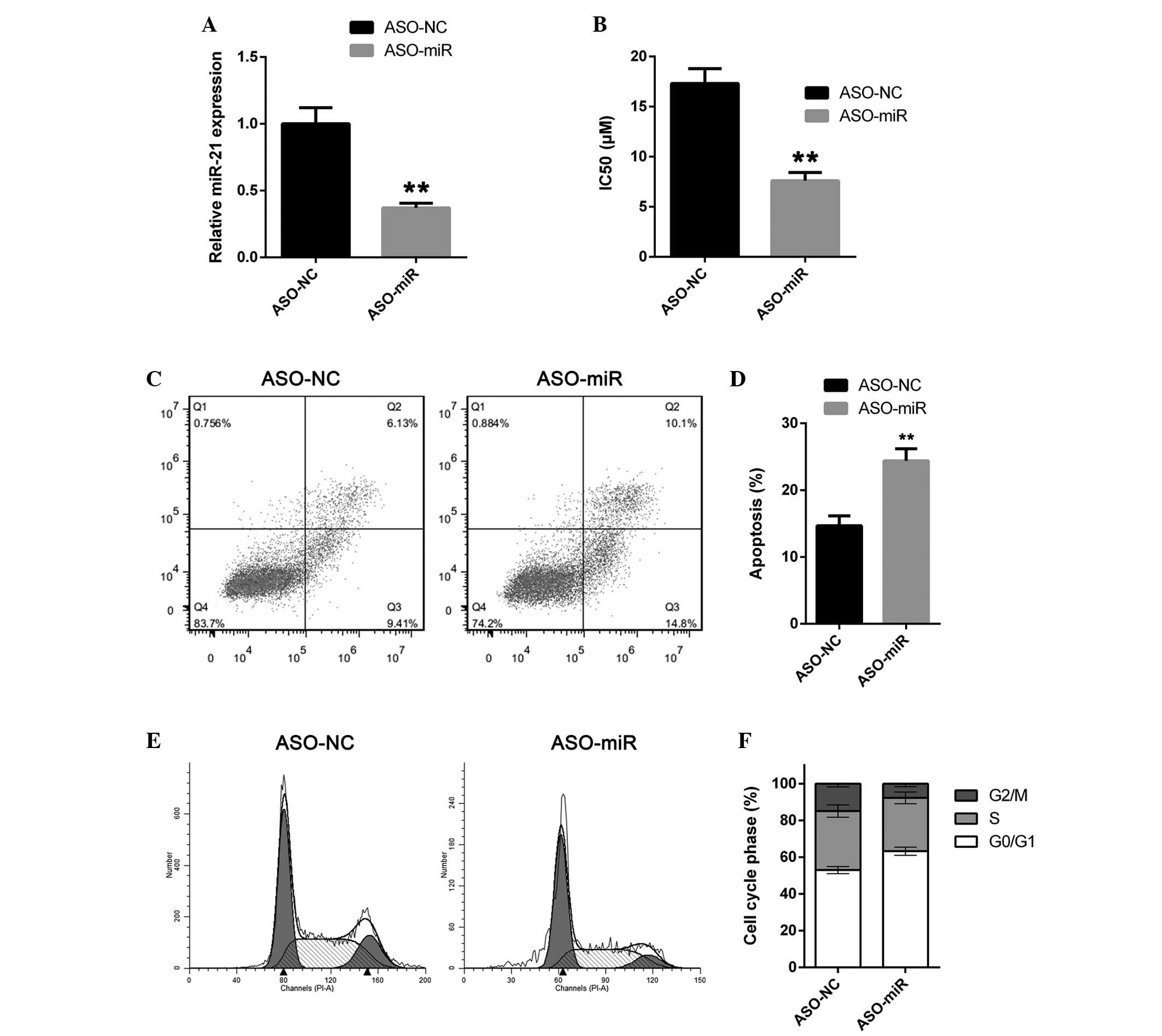
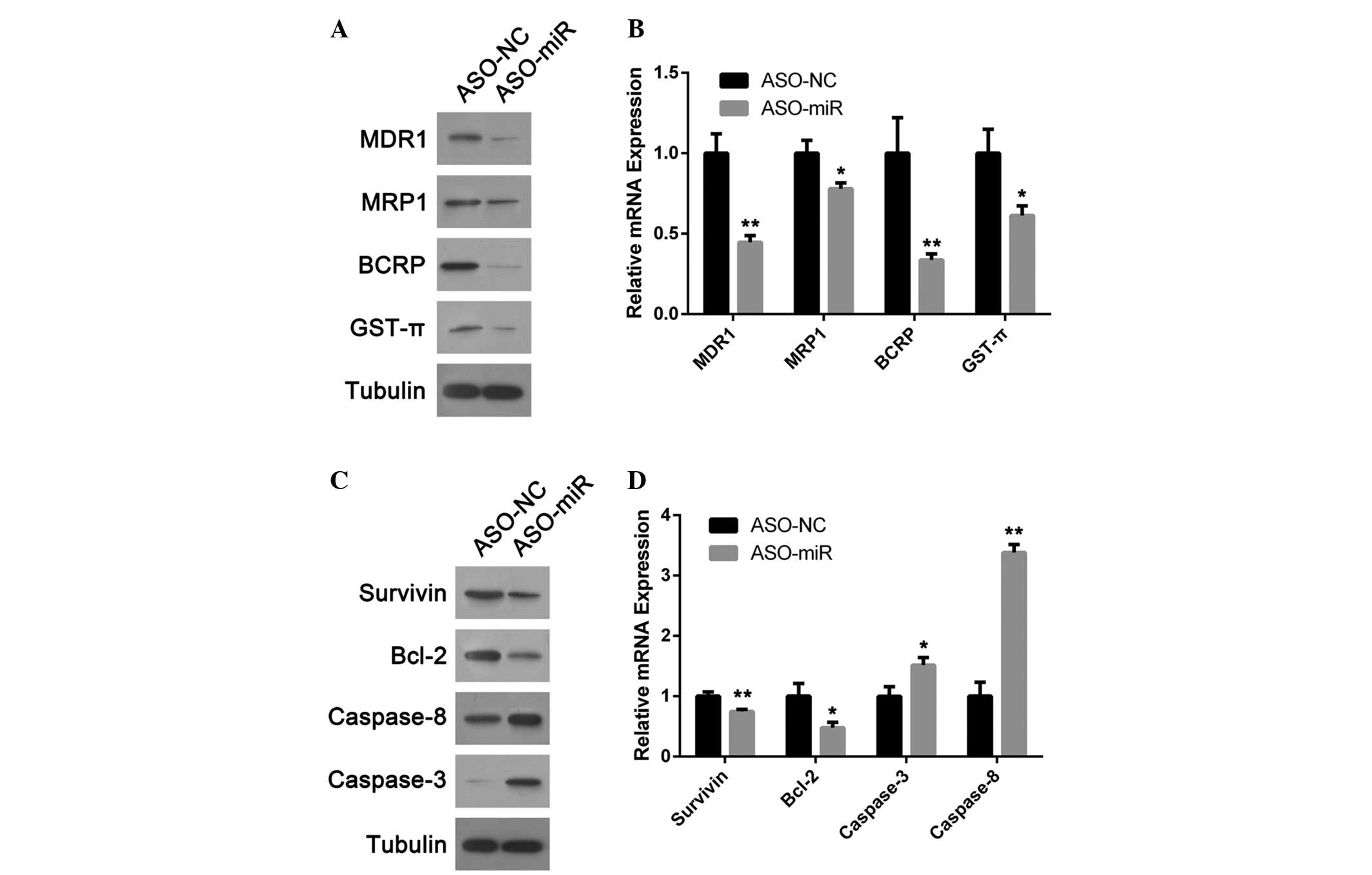
|
1
|
Niu X, Liu S, Jia L and Chen J: Role of
MiR-3619-5p in β-catenin-mediated non-small cell lung cancer growth
and invasion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 4:1527–1536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Won YK, Lee JY, Kang YN, Jang JS, Kang JH,
Jung SL, Sung SY, Jo IY, Park HH, Lee DS, et al: Stereotactic
radiosurgery for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Radiat Oncol J. 3:207–216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hoffman PC, Mauer AM and Vokes EE: Lung
cancer. Lancet. 355:479–485. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer, Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Janku F, Stewart DJ and Kurzrock R:
Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer-is it becoming a
reality? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:401–414. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV,
Chernova OB and Stark GR: The p53 network. J Biol Chem. 273:1–4.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Müller I, Niethammer D and Bruchelt G:
Anthracycline-derived chemotherapeutics in apoptosis and free
radical cytotoxicity (Review). Int J Mol Med. 1:491–494.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu T, Li LL, Xiao GF, Luo QZ, Liu QZ, Yao
KT and Xiao GH: Berberine increases doxorubicin sensitivity by
suppressing STAT3 in lung cancer. Am J Chin Med. 27:1–16. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Li ZL, Chen C, Yang Y, Wang C, Yang T,
Yang X and Liu SC: Gamma secretase inhibitor enhances sensitivity
to doxorubicin in MDA-MB-231 cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
5:4378–4387. 2015.
|
|
11
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan Y, Yao YF, Hu SN, Gao J and Zhang LL:
MiR-133a is functionally involved in doxorubicin-resistance in
breast cancer cells MCF-7 via its regulation of the expression of
uncoupling protein 2. PLoS One. 6:e01298432015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gandellini P, Profumo V, Folini M and
Zaffaroni N: MicroRNAs as new therapeutic targets and tools in
cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:265–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trang P, Weidhaas JB and Slack FJ:
MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene. 27((Suppl
2)): S52–S57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang F, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Cheng L,
Bai Y and Ma H: The value of microRNA-155 as a prognostic factor
for survival in non-small cell lung cancer, A meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 8:e01368892015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sochor M, Basova P, Pesta M, Dusilkova N,
Bartos J, Burda P, Pospisil V and Stopka T: Oncogenic microRNAs,
MiR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b and miR-24 enable monitoring of early
breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer. 14:4482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yan Z, Che S, Wang J, Jiao Y, Wang C and
Meng Q: miR-155 contributes to the progression of glioma by
enhancing Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Tumour Biol. 7:5323–5331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hongliang C, Shaojun H, Aihua L and Hua J:
Correlation between expression of miR-155 in colon cancer and serum
carcinoembryonic antigen level and its contribution to recurrence
and metastasis forecast. Saudi Med J. 35:547–553. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li T, Yang J, Lv X, Liu K, Gao C, Xing Y
and Xi T: MiR-155 regulates the proliferation and cell cycle of
colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2. Biotechnol Lett.
36:1743–1752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Merhautova J, Hezova R, Poprach A,
Kovarikova A, Radova L, Svoboda M, Vyzula R, Demlova R and Slaby O:
miR-155 and miR-484 are associated with time to progression in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:9419802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu Y, Liu XJ, Yang P, Zhao M, Lv LX,
Zhang GD, Wang Q and Zhang L: Alkylglyceronephosphate synthase
(AGPS) alters lipid signaling pathways and supports chemotherapy
resistance of glioma and hepatic carcinoma cell lines. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3219–3226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fruman DA and Rommel C: PI3K and cancer:
Lessons challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
13:140–156. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hendijani F: JavanmardS hH, Rafiee L and
Sadeghi-Aliabadi H: Effect of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal
stem cell secretome on proliferation, apoptosis and drug resistance
of lung cancer cells. Res Pharm Sci. 2:134–142. 2015.
|
|
26
|
Zhao YY, Yu L, Liu BL, He XJ and Zhang BY:
Downregulation of P-gp, Ras and p-ERK1/2 contributes to the arsenic
trioxide-induced reduction in drug resistance towards doxorubicin
in gastric cancer cell lines. Mol Med Rep. 5:7335–7343. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Keppler D: Multidrug resistance proteins
(MRPs, ABCC s): Importance for pathophysiology and drug therapy.
Handb Exp Pharmacol. 299–323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen S, Jiao JW, Sun KX, Zong ZH and Zhao
Y: MicroRNA-133b targets glutathione S-transferase π expression to
increase ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:5225–5535. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Surowiak P, Materna V, Kaplenko I,
Spaczyński M, Dietel M, Lage H and Zabel M: Augmented expression of
metallothionein and glutathione S-transferase pi as unfavourable
prognostic factors in cisplatin-treated ovarian cancer patients.
Virchows Arch. 447:626–633. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stewart DJ: Mechanisms of resistance to
cisplatin and carboplatin. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 63:12–31. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Moraes Nestal G, Delbue D, Silva KL,
Robaina MC, Khongkow P, Gomes AR, Zona S, Crocamo S, Mencalha AL,
Magalhães LM, Lam EW and Maia RC: FOXM1 targets XIAP and Survivin
to modulate breast cancer survival and chemoresistance. Cell
Signal. 12:2496–2505. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ryan BM, O'Donovan N and Duffy MJ:
Survivin A new target for anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev.
35:553–562. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Altieri DC: Survivin and IAP proteins in
cell-death mechanisms. Biochem J. 430:199–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yip KW and Reed JC: Bcl-2 family proteins
and cancer. Oncogene. 27:6398–6406. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B,
Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ and
Los M: Apoptosis and cancer, Mutations within caspase genes. J Med
Genet. 46:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chakraborty C: GeorgeP riya Doss C and
Bandyopadhyay S: miRNAs in insulin resistance and
diabetes-associated pancreatic cancer: The 'minute and miracle'
molecule moving as a monitor in the 'genomic galaxy'. Curr Drug
Targets. 10:1110–1117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang E and Wu Y: Dual effects of miR-155
on macrophages at different stages of atherosclerosis: LDL is the
key? Med Hypotheses. 83:74–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nitiss JL: Targeting DNA topoisomerase II
in cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:338–350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kong W, He L, Coppola M, Guo J, Esposito
NN, Coppola D and Cheng JQ: MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival,
growth, and chemosensitivity by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer.
J Biol Chem. 23:17869–17879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cai ZK, Chen Q, Chen YB, Gu M, Zheng DC,
Zhou J and Wang Z: microRNA-155 promotes the proliferation of
prostate cancer cells by targeting annexin 7. Mol Med Rep.
1:533–538. 2015.
|
|
41
|
Xue P, Zheng M, Diao Z, Shen L, Liu M,
Gong P, Sun H and Hu Y: miR-155* mediates suppressive effect of
PTEN 3′-untranslated region on AP-1/NF-κB pathway in HTR-8/SVneo
cells. Placenta. 8:650–656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Farooqi AA, Qureshi MZ, Coskunpinar E,
Naqvi SK, Yaylim I and Ismail M: MiR-421, miR-155 and miR-650:
Emerging trends of regulation of cancer and apoptosis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:1909–1912. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gasparini P, Lovat F, Fassan M, Casadei L,
Cascione L, Jacob NK, Carasi S, Palmieri D, Costinean S, Shapiro
CL, et al: Protective role of miR-155 in breast cancer through
RAD51 targeting impairs homologous recombination after irradiation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:4536–4541. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|