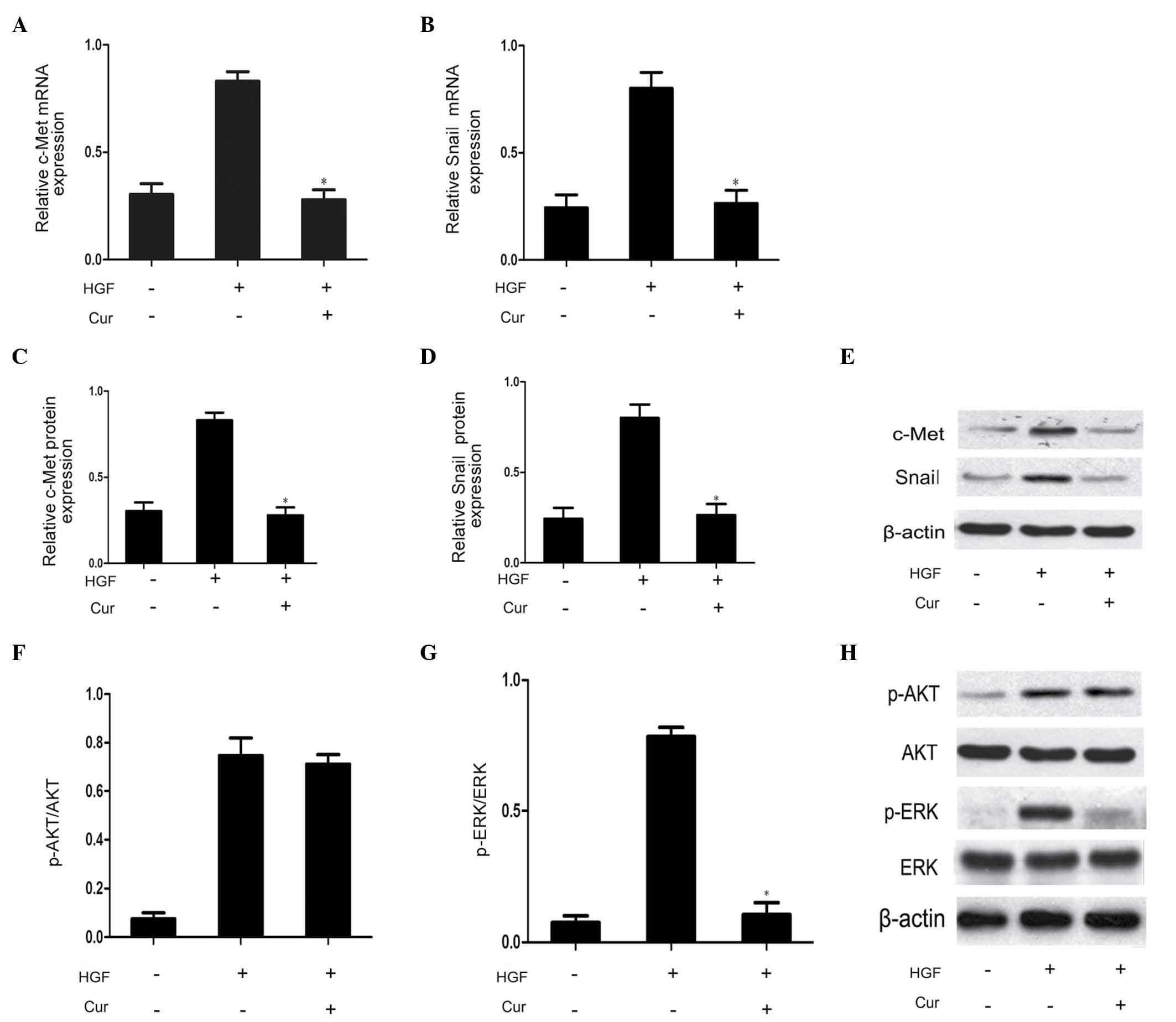
|
1
|
Sturge J, Caley MP and Waxman J: Bone
metastasis in prostate cancer: Emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 8:357–368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parikh RA, Wang P, Beumer JH, Chu E and
Appleman LJ: The potential roles of hepatocyte growth factor
(HGF)-MET pathway inhibitors in cancer treatment. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:969–983. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Elliott BE, Hung WL, Boag AH and Tuck AB:
The role of hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor) in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 80:91–102. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Graveel CR, Tolbert D and Van de Woude GF:
MET: A critical player in tumorigenesis and therapeutic target.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0092092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Varkaris A, Corn PG, Gaur S, Dayyani F,
Logothetis CJ and Gallick GE: The role of HGF/c-Met signaling in
prostate cancer progression and c-Met inhibitors in clinical
trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 20:1677–1684. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu P, Chung LW, Berel D, Frierson HF, Yang
H, Liu C, Wang R, Li Q, Rogatko A and Zhau HE: Convergent RANK- and
c-Met-mediated signaling components predict survival of patients
with prostate cancer: An interracial comparative study. PLoS One.
8:e730812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee RJ and Smith MR: Targeting MET and
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling in
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer J. 19:90–98. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghalandarlaki N, Alizadeh AM and
Ashkani-Esfahani S: Nanotechnology-applied curcumin for different
diseases therapy. Biomed Res Int. 2014:3942642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dulbecco P and Savarino V: Therapeutic
potential of curcumin in digestive diseases. World J Gastroenterol.
19:9256–9270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dorai T, Diouri J, O'Shea O and Doty SB:
Curcumin inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis by up-regulating
bone morphogenic protein-7 in vivo. J Cancer Ther.
5:369–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin XL, He XL, Zeng JF, Zhang H, Zhao Y,
Tan JK and Wang Z: FGF21 increases cholesterol efflux by
upregulating ABCA1 through the ERK1/2-PPARγ-LXRα pathway in THP1
macrophage-derived foam cells. DNA Cell Biol. 33:514–521. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chang HY, Kao MC, Way TD, Ho CT and Fu E:
Diosgenin suppresses hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by down-regulation of Mdm2 and
vimentin. J Agric Food Chem. 59:5357–5363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hung CM, Kuo DH, Chou CH, Su YC, Ho CT and
Way TD: Osthole suppresses hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via repression of the
c-Met/Akt/mTOR pathway in human breast cancer cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:9683–9690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Książkiewicz M, Markiewicz A and Zaczek
AJ: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A hallmark in metastasis
formation linking circulating tumor cells and cancer stem cells.
Pathobiology. 79:195–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nishimura K, Kitamura M, Takada S,
Nonomura N, Tsujimura A, Matsumiya K, Miki T, Matsumoto K and
Okuyama A: Regulation of invasive potential of human prostate
cancer cell lines by hepatocyte growth factor. Int J Urol.
5:276–281. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grotegut S, von Schweinitz D, Christofori
G and Lehembre P: Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering
through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J.
25:3534–3545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nieto MA: The snail superfamily of
zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:155–166. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van Leenders G, van Balken B, Aalders T,
de Hulsbergen-van Kaa C, Ruiter D and Schalken P: Intermediate
cells in normal and malignant prostate epithelium express c-MET:
Implications for prostate cancer invasion. Prostate. 51:98–107.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Davies G, Watkins G, Mason MD and Jiang
WG: Targeting the HGF/SF receptor c-met using a hammerhead ribozyme
transgene reduces in vitro invasion and migration in
prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 60:317–324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park W, Amin AR, Chen ZG and Shin DM: New
perspectives of curcumin in cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 6:387–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen HW, Lee JY, Huang JY, Wang CC, Chen
WJ, Su SF, Huang CW, Ho CC, Chen JJ, Tsai MF, et al: Curcumin
inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis through the tumor
suppressor HLJ1. Cancer Res. 68:7428–7438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sakulterdkiat T, Srisomsap C,
Udomsangpetch R, Svasti J and Lirdprapamongkol K: Curcumin
resistance induced by hypoxia in HepG2 cells is mediated by
multidrug-resistance-associated proteins. Anticancer Res.
32:5337–5342. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seol DW, Chen Q and Zarnegar R:
Transcriptional activation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor
(c-met) gene by its ligand (hepatocyte growth factor) is mediated
through AP-1. Oncogene. 19:1132–1137. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duhon D, Bigelow RL, Coleman DT, Steffan
JJ, Yu C, Langston W, Kevil CG and Cardelli JA: The polyphenol
epigallocatechin-3-gallate affects lipid rafts to block activation
of the c-Met receptor in prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
49:739–749. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|