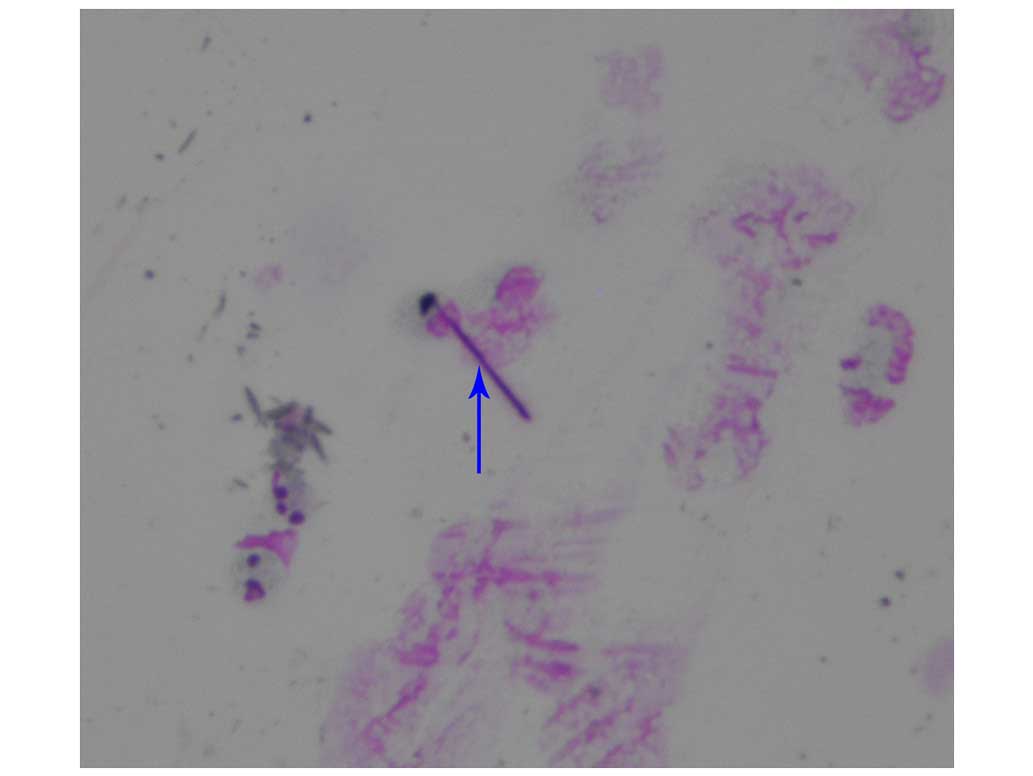
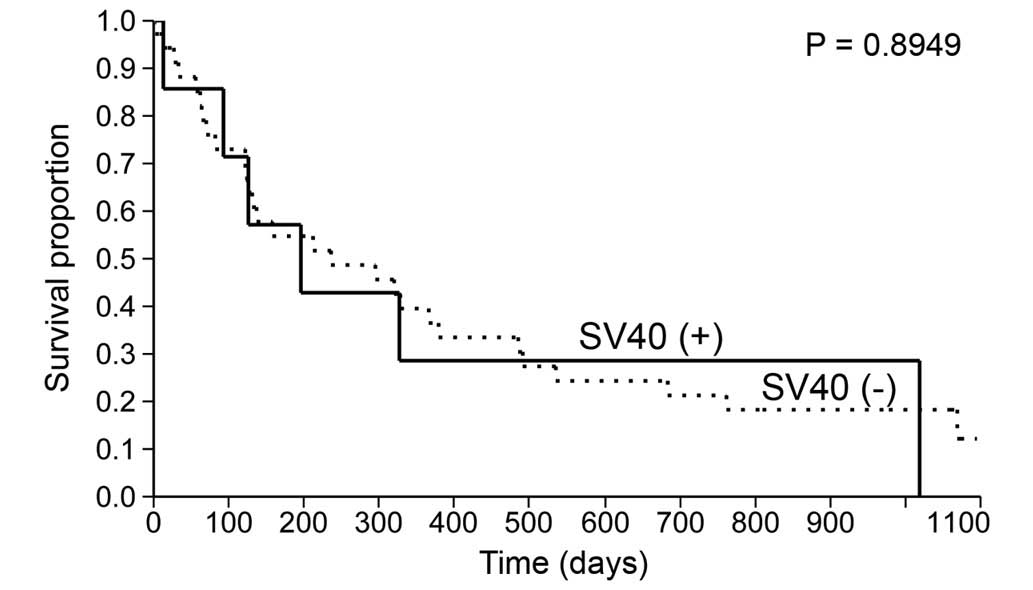
|
1
|
Robinson BM: Malignant pleural
mesothelioma: An epidemiological perspective. Ann Cardiothorac
Surg. 1:491–496. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Robinson BW, Musk AW and Lake RA:
Malignant mesothelioma. Lancet. 366:397–408. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cugell DW and Kamp DW: Asbestos and the
pleura: A review. Chest. 125:1103–1117. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang H, Testa JR and Carbone M:
Mesothelioma epidemiology, carcinogenesis, and pathogenesis. Curr
Treat Options Oncol. 9:147–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carbone M, Pannuti A, Zhang L, Testa JR
and Bocchetta M: A novel mechanism of late gene silencing drives
SV40 transformation of human mesothelial cells. Cancer Res.
68:9488–9496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carbone M, Pass HI, Miele L and Bocchetta
M: Novel developments about the association of SV40 with human
mesothelioma. Oncogene. 22:5173–5180. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jaurand MC and Fleury-Feith J:
Pathogenesis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Respirology.
10:2–8. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Comar M, Rizzardi C, de Zotti R, Melato M,
Bovenzi M, Butel JS and Campello C: SV40 multiple tissue infection
and asbestos exposure in a hyperendemic area for malignant
mesothelioma. Cancer Res. 67:8456–8459. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin M, Sawa H, Suzuki T, Shimizu K, Makino
Y, Tanaka S, Nojima T, Fujioka Y, Asamoto M, Suko N, et al:
Investigation of simian virus 40 large T antigen in 18 autopsied
malignant mesothelioma patients in Japan. J Med Virol. 74:668–676.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Testa JR, Carbone M, Hirvonen A, Khalili
K, Krynska B, Linnainmaa K, Pooley FD, Rizzo P, Rusch V and Xiao
GH: A multi-institutional study confirms the presence and
expression of simian virus 40 in human malignant mesotheliomas.
Cancer Res. 58:4505–4509. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aoe K, Hiraki A, Murakami T, Toyooka S,
Shivapurkar N, Gazdar AF, Sueoka N, Taguchi K, Kamei T, Takeyama H,
et al: Infrequent existence of simian virus 40 large T antigen DNA
in malignant mesothelioma in Japan. Cancer Sci. 97:292–295. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hirvonen A, Mattson K, Karjalainen A,
Ollikainen T, Tammilehto L, Hovi T, Vainio H, Pass HI, Di Resta I,
Carbone M and Linnainmaa K: Simian virus 40 (SV40)-like DNA
sequences not detectable in finnish mesothelioma patients not
exposed to SV40-contaminated polio vaccines. Mol Carcinog.
26:93–99. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
López-Ríos F, Illei PB, Rusch V and
Ladanyi M: Evidence against a role for SV40 infection in human
mesotheliomas and high risk of false-positive PCR results owing to
presence of SV40 sequences in common laboratory plasmids. Lancet.
364:1157–1166. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pilatte Y, Vivo C, Renier A, Kheuang L,
Greffard A and Jaurand MC: Absence of SV40 large T-antigen
expression in human mesothelioma cell lines. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 23:788–793. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Rienzo A, Tor M, Sterman DH, Aksoy F,
Albelda SM and Testa JR: Detection of SV40 DNA sequences in
malignant mesothelioma specimens from the United States, but not
from Turkey. J Cell Biochem. 84:455–459. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kushitani K, Takeshima Y, Amatya VJ,
Furonaka O, Sakatani A and Inai K: Immunohistochemical marker
panels for distinguishing between epithelioid mesothelioma and lung
adenocarcinoma. Pathol Int. 57:190–199. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sandeck HP, Røe OD, Kjærheim K, Willén H
and Larsson E: Re-evaluation of histological diagnoses of malignant
mesothelioma by immunohistochemistry. Diagn Patho. 5:472010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M and Clark
GM: Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by
immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 11:155–168.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nguyen GK and Kline TS: Cytology
laboratory and quality assurance practice. Essentials of
Exfoliative Cytology (New York, NY). Igaku-Shoin Medical
Publishers, Inc. 6–13. 1992.
|
|
20
|
De Vuyst P, Dumortier P, Moulin E,
Yourassowsky N, Roomans P, de Francquen P and Yernault JC: Asbestos
bodies in bronchoalveolar lavage reflect lung asbestos body
concentration. Eur Respir J. 1:362–367. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cutrone R, Lednicky J, Dunn G, Rizzo P,
Bocchetta M, Chumakov K, Minor P and Carbone M: Some oral
poliovirus vaccines were contaminated with infectious SV40 after
1961. Cancer Res. 65:10273–10279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martini F, Corallini A, Balatti V,
Sabbioni S, Pancaldi C and Tognon M: Simian virus 40 in humans.
Infect Agent Cancer. 2:132007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xaubet A, Rodriguez-Roisín R, Bombí JA,
Marín A, Roca J and Agustí-Vidal A: Correlation of bronchoalveolar
lavage and clinical and functional findings in asbestosis. Am Rev
Respir Dis. 133:848–854. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kroczynska B, Cutrone R, Bocchetta M, Yang
H, Elmishad AG, Vacek P, Ramos-Nino M, Mossman BT, Pass HI and
Carbone M: Crocidolite asbestos and SV40 are cocarcinogens in human
mesothelial cells and in causing mesothelioma in hamsters. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:14128–14133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cicala C, Pompetti F and Carbone M: SV40
induces mesotheliomas in hamsters. Am J Pathol. 142:1524–1533.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Milano MT and Zhang H: Malignant pleural
mesothelioma: A population-based study of survival. J Thorac Oncol.
5:1841–1848. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van der Bij S, Koffijberg H, Burgers JA,
Baas P, van de Vijver MJ, de Mol BA and Moons KG: Prognosis and
prognostic factors of patients with mesothelioma: A
population-based study. Br J Cancer. 107:161–164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|