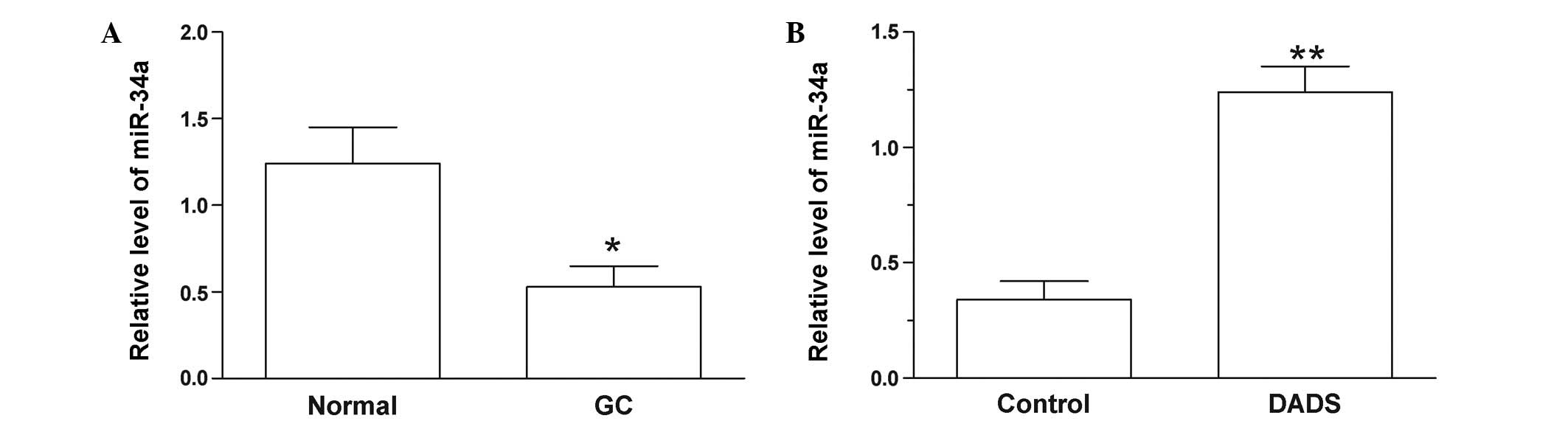
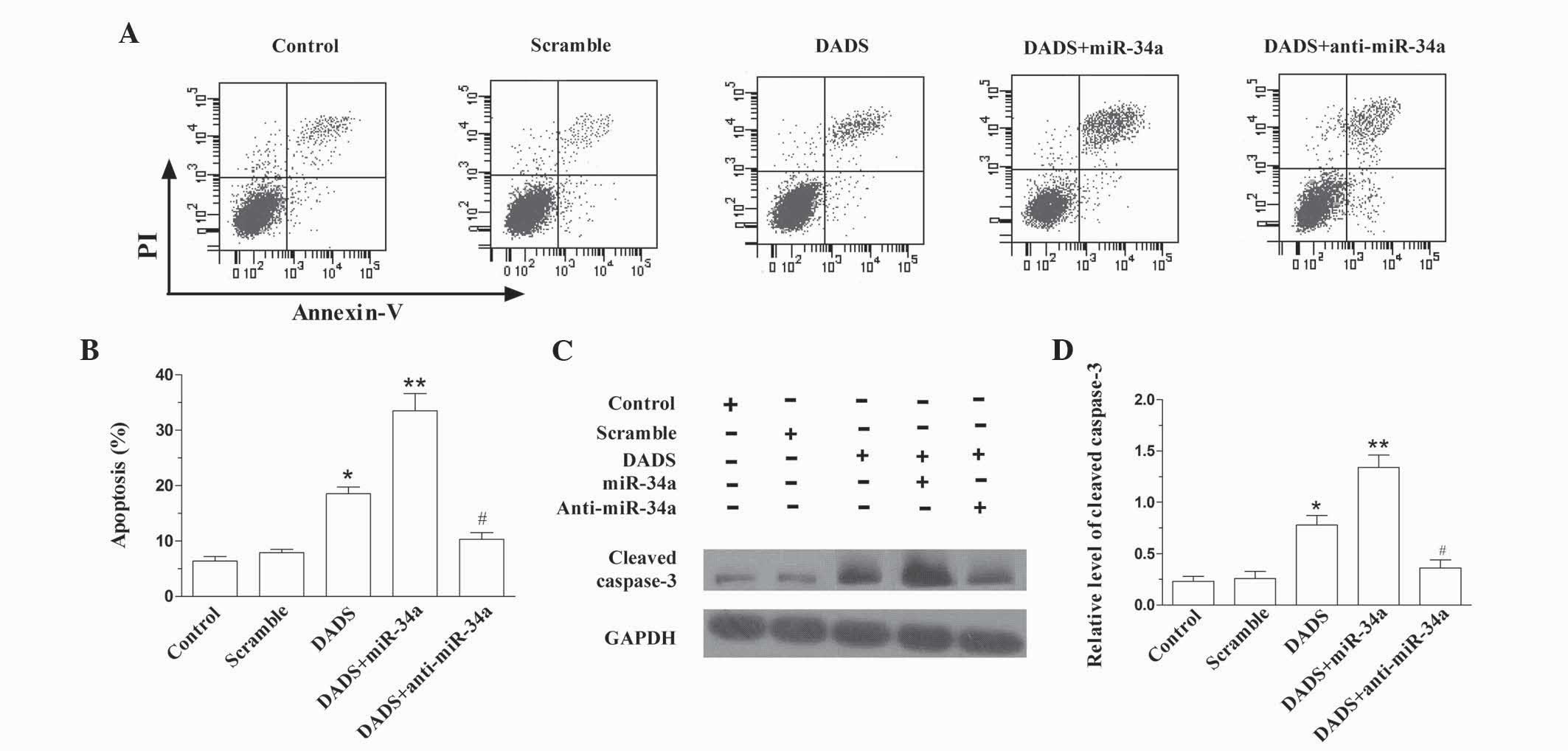
|
1
|
Cao W, Fan R, Wang L, Cheng S, Li H, Jiang
J, Geng M, Jin Y and Wu Y: Expression and regulatory function of
miRNA-34a in targeting survivin in gastric cancer cells. Tumor
Biol. 34:963–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Xie B, Zhou J, Shu G, Liu DC, Zhou J, Chen
J and Yuan L: Restoration of klotho gene expression induces
apoptosis and autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Tumor suppressive
role of klotho in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 13:182013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Wang Y, Dong S, Ge C, Xiao Y, Li R,
Ma X, Xue Y, Zhang Q, Lv J, et al: Association of CXCR1 and 2
expressions with gastric cancer metastasis in ex vivo and
tumor cell invasion in vitro. Cytokine. 69:6–13. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan JP, Wang GH, Ling H, Su Q, Yang YH,
Song Y, Tang RJ, Liu Y and Huang C: Diallyl disulfide-induced G2/M
arrest of human gastric cancer MGC803 cells involves activation of
p38 MAP kinase pathways. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2731–2734. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang XD, Shu YQ, Liang J, Zhang FC, Ma
XZ, Huang JJ, Chen L, Shi GM, Cao WG, Guo CY, et al: Combination
chemotherapy with paclitaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil for
patients with advanced and metastatic gastric or esophagogastric
junction adenocarcinoma: A multicenter prospective study. Chin J
Cancer Res. 24:291–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Liu Q, Fan Y, Wang S, Liu X, Zhu L,
Liu M and Tang H: Downregulation of PPP2R5E expression by miR-23a
suppresses apoptosis to facilitate the growth of gastric cancer
cells. FEBS Lett. 588:3160–3169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao D, Lew KL, Kim YA, Zeng Y, Hahm ER,
Dhir R and Singh SV: Diallyl trisulfide suppresses growth of PC-3
human prostate cancer xenograft in vivo in association with
Bax and Bak induction. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6836–6843. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lei XY, Yao SQ, Zu XY, Huang ZX, Liu LJ,
Zhong M, Zhu BY, Tang SS and Liao DF: Apoptosis induced by diallyl
disulfide in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 29:1233–1239. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Robert V, Mouillé B, Mayeur C, Michaud M
and Blachier F: Effects of the garlic compound diallyl disulfide on
the metabolism, adherence and cell cycle of HT-29 colon carcinoma
cells: Evidence of sensitive and resistant sub-populations.
Carcinogenesis. 22:1155–1161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Knowles LM and Milner JA: Diallyl
disulfide induces ERK phosphorylation and alters gene expression
profiles in human colon tumor cells. J Nutr. 133:2901–2906.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gunadharini DN, Arunkumar A,
Krishnamoorthy G, Muthuvel R, Vijayababu MR, Kanagaraj P,
Srinivasan N, Aruldhas MM and Arunakaran J: Antiproliferative
effect of diallyl disulfide (DADS) on prostate cancer cell line
LNCaP. Cell Biochem Funct. 24:407–412. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wen J, Zhang Y, Chen X, Shen L, Li GC and
Xu M: Enhancement of diallyl disulfide-induced apoptosis by
inhibitors of MAPKs in human HepG2 hepatoma cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 68:323–331. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tu F, Pan ZX, Yao Y, Liu HL, Liu SR, Xie Z
and Li QF: miR-34a targets the inhibin β B gene, promoting
granulosa cell apoptosis in the porcine ovary. Genet Mol Res.
13:2504–2512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Forte E, Salinas RE, Chang C, Zhou T,
Linnstaedt SD, Gottwein E, Jacobs C, Jima D, Li QJ, Dave SS and
Luftig MA: The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced tumor suppressor
microRNA MiR-34a is growth promoting in EBV-infected B cells. J
Virol. 86:6889–6898. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer.
94:776–780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, Yasui W, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z,
Meng D and Wang Y: Differential expression of microRNA species in
human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:652–657. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu R, Zhang C, Hu Z, Li G, Wang C, Yang
C, Huang D, Chen X, Zhang H, Zhuang R, et al: A five-microRNA
signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression
profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis. Eur
J Cancer. 47:784–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McManus MT: MicroRNAs and cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 13:253–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Gong T, Li
M, Sun L, Ji G, Shi Y, Han Z, et al: miRNA-223 promotes gastric
cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor
EPB41L3. Mol Cancer Res. 9:824–833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ambros V: MicroRNA pathways in flies and
worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY and
Yan M: microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 27:1019–1026.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang H, Kong Y, Guo J, Tang Y and Xie X,
Yang L, Su Q and Xie X: Diallyl disulfide suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through Wnt-1
signaling pathway by up-regulation of miR-200b and miR-22. Cancer
Lett. 340:72–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cho WJ, Shin JM, Kim JS, Lee MR, Hong KS,
Lee JH, Koo KH, Park JW and Kim KS: miR-372 regulates cell cycle
and apoptosis of ags human gastric cancer cell line through direct
regulation of LATS2. Mol Cells. 28:521–527. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luo J, Manning BD and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:257–262. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
West KA, Castillo SS and Dennis PA:
Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance.
Drug Resist Updat. 5:234–248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vara Fresno JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang MH, Oh SC, Lee HJ, Kang HN, Kim JL,
Kim JS and Yoo YA: Metastatic function of BMP-2 in gastric cancer
cells: The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK, the NF-κB pathway and MMP-9
expression. Exp Cell Res. 317:1746–1762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yun SM: Abstract 4304: PPP1R1B-STARD3
fusion gene promotes gastric tumorigenesis through activation of
PI3K/Akt signaling. Cancer Res. 73:43042013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shrivastava S, Jeengar MK, Thummuri D and
Naidu VGM: P1 Piperlongumine inhibits growth potential of gastric
cancer cells by targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur J
Cancer. 50:S92014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee IC, Kim SH, Baek HS, Beak HS, Moon C,
Kim SH, Kim YB, Yun WK, Kim HC and Kim JC: Protective effects of
diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity
through activation of Nrf2. Environ Toxicol. 30:538–548. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takahashi S, Hakoi K, Yada H, Hirose M,
Ito N and Fukushima S: Enhancing effects of diallyl sulfide on
hepatocarcinogenesis and inhibitory actions of the related diallyl
disulfide on colon and renal carcinogenesis in rats.
Carcinogenesis. 13:1513–1518. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Druesne N, Pagniez A, Mayeur C, Thomas M,
Cherbuy C, Duée PH, Martel P and Chaumontet C: Diallyl disulfide
(DADS) increases histone acetylation and p21(waf1/cip1) expression
in human colon tumor cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 25:1227–1236.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|