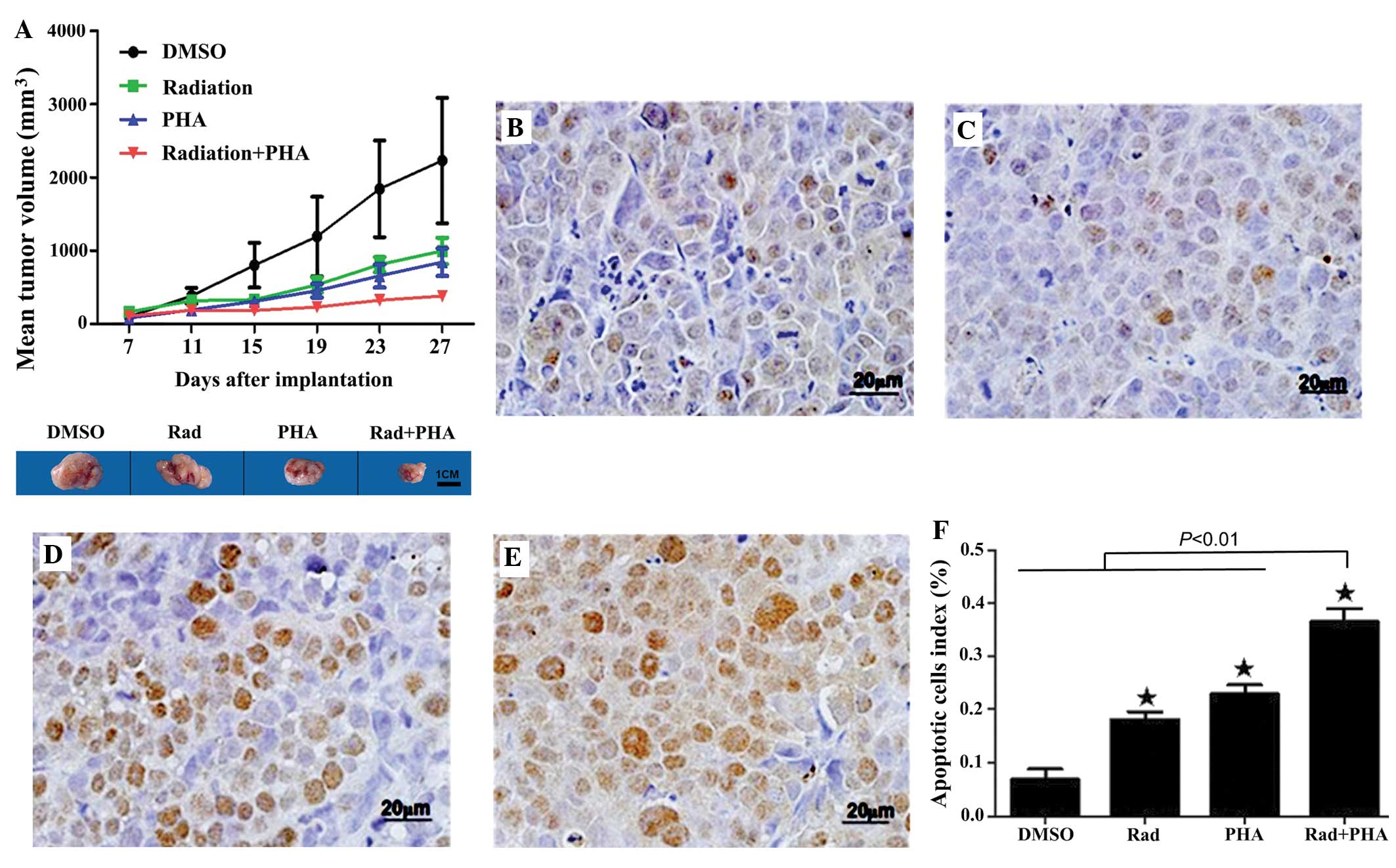
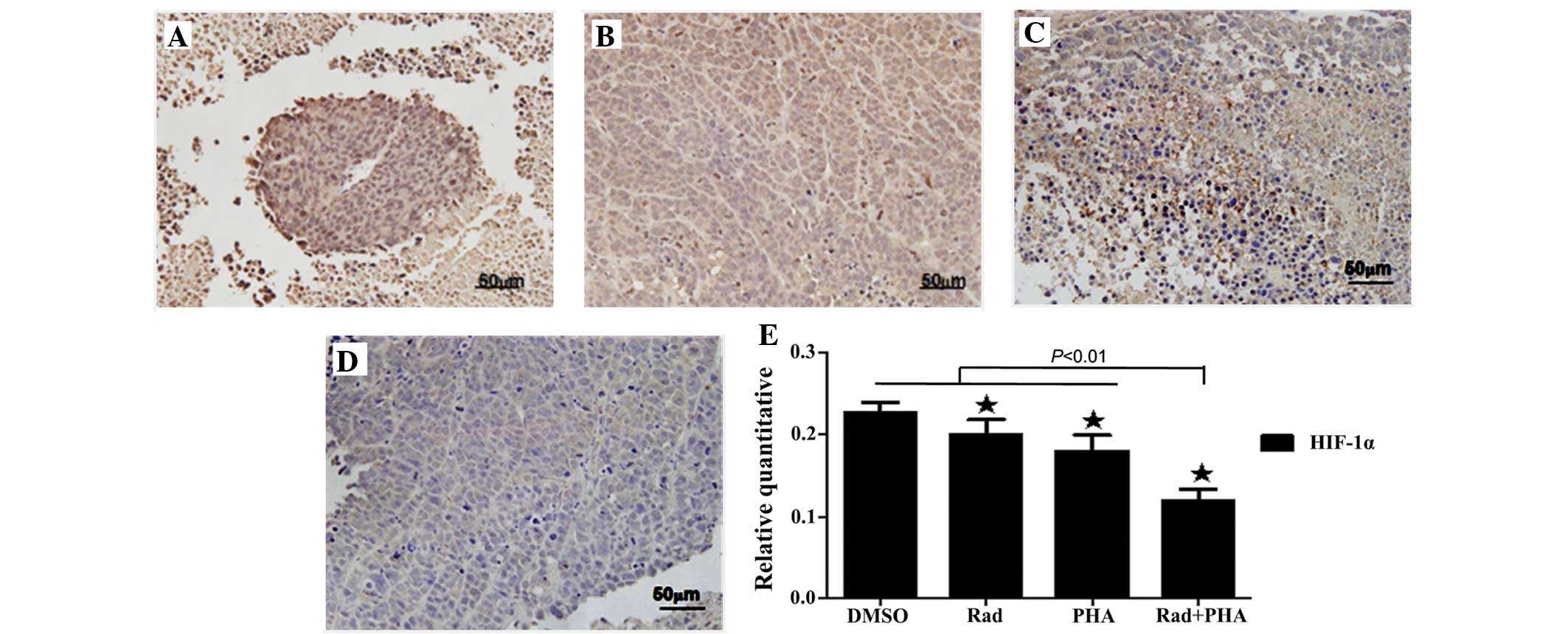
|
1
|
Robbins AS, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Racial
disparities in stage-specific colorectal cancer mortality rates
from 1985 to 2008. J Clin Oncol. 30:401–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bosset JF, Collette L, Calais G, Mineur L,
Maingon P, Radosevic-Jelic L, Daban A, Bardet E, Beny A and Ollier
JC: EORTC Radiotherapy Group Trial 22921: Chemotherapy with
preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
355:1114–1123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gérard JP, Conroy T, Bonnetain F, Bouché
O, Chapet O, Closon-Dejardin MT, Untereiner M, Leduc B, Francois E,
Maurel J, et al: Preoperative radiotherapy with or without
concurrent fluorouracil and leucovorin in T3–4 rectal cancers:
Results of FFCD 9203. J Clin Oncol. 24:4620–4625. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dhadda AS, Dickinson P, Zaitoun AM, Gandhi
N and Bessell EM: Prognostic importance of Mandard tumour
regression grade following pre-operative chemo/radiotherapy for
locally advanced rectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 47:1138–1145. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu T, Yao Y, Yu S, Guo H, Han L, Wang W,
Tian T, Hao Y, Liu Z, Nan K and Wang S: Clinicopathologic
significance of CXCR4 and Nrf2 in colorectal cancer. J Biomed Res.
27:283–290. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scarpino S, d'Alena Cancellario F, Di
Napoli A, Pasquini A, Marzullo A and Ruco LP: Increased expression
of Met protein is associated with up-regulation of hypoxia
inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) in tumour cells in papillary carcinoma
of the thyroid. J Pathol. 202:352–358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Wever O, Nguyen QD, Van Hoorde L,
Bracke M, Bruyneel E, Gespach C and Mareel M: Tenascin-C and SF/HGF
produced by myofibroblasts in vitro provide convergent
pro-invasive signals to human colon cancer cells through RhoA and
Rac. FASEB J. 18:1016–1018. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park MK, Kim DK and Lee HJ: Adenoviral
mediated hepatocyte growth factor gene attenuates hyperglycemia and
beta cell destruction in overt diabetic mice. Exp Mol Med.
35:494–500. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Comoglio PM and Trusolino L: Invasive
growth: From development to metastasis. J Clin Invest. 109:857–862.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stellrecht CM and Gandhi V: MET receptor
tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic anticancer target. Cancer Lett.
280:1–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kammula US, Kuntz EJ, Francone TD, Zeng Z,
Shia J, Landmann RG, Paty PB and Weiser MR: Molecular co-expression
of the c-Met oncogene and hepatocyte growth factor in primary colon
cancer predicts tumor stage and clinical outcome. Cancer Lett.
248:219–228. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kataoka H, Hamasuna R, Itoh H, Kitamura N
and Koono M: Activation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 60:6148–6159. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du Z, Qin R, Wei C, Wang M, Shi C, Tian R
and Peng C: Pancreatic cancer cells resistant to chemoradiotherapy
rich in “stem-cell-like” tumor cells. Dig Dis Sci. 56:741–750.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suárez-Causado A, Caballero-Díaz D,
Bertrán E, Roncero C, Addante A, García-Álvaro M, Fernández M,
Herrera B, Porras A, Fabregat I and Sánchez A: HGF/c-Met signaling
promotes liver progenitor cell migration and invasion by an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-independent, phosphatidyl
inositol-3 kinase-dependent pathway in an in vitro model.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:2453–2463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Bacco F, Luraghi P, Medico E, Reato G,
Girolami F, Perera T, Gabriele P, Comoglio PM and Boccaccio C:
Induction of MET by ionizing radiation and its role in
radioresistance and invasive growth of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:645–661. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Buchanan IM, Scott T, Tandle AT, Burgan
WE, Burgess TL, Tofilon PJ and Camphausen K: Radiosensitization of
glioma cells by modulation of Met signalling with the hepatocyte
growth factor neutralizing antibody, AMG102. J Cell Mol Med.
15:1999–2006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun W, Song L, Ai T, Zhang Y, Gao Y and
Cui J: Prognostic value of MET, cyclin D1 and MET gene copy number
in non-small cell lung cancer. J Biomed Res. 27:220–230. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council of the National
Academies: Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (8th).
The National Academies Press. Washington, D.C., USA: 199–200.
2011.
|
|
19
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh H, Daci K, Petersen LA, Collins C,
Petersen NJ, Shethia A and El-Serag HB: Missed opportunities to
initiate endoscopic evaluation for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Am
J Gastroenterol. 104:2543–2554. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bekaii-Saab T and Wu C: Seeing the forest
through the trees: A systematic review of the safety and efficacy
of combination chemotherapies used in the treatment of metastatic
colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 91:9–34. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Teicher BA: Antiangiogenic agents and
targets: A perspective. Biochem Pharmacol. 81:6–12. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kawamura M, Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Tanaka
K, Okugawa Y, Hiro J, Uchida K, Mohri Y, Inoue Y and Kusunoki M:
Correlation of MACC1 and MET expression in rectal cancer after
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Anticancer Res. 32:1527–1531.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hong TS, Wo JY and Kwak EL: Targeted
therapies with chemoradiation in esophageal cancer: Development and
future directions. Semin Radiat Oncol. 23:31–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akervall J, Nandalur S, Zhang J, Qian CN,
Goldstein N, Gyllerup P, Gardinger Y, Alm J, Lorenc K, Nilsson K,
et al: A novel panel of biomarkers predicts radioresistance in
patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur J
Cancer. 50:570–581. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Medová M, Aebersold DM, Blank-Liss W,
Streit B, Medo M, Aebi S and Zimmer Y: MET inhibition results in
DNA breaks and synergistically sensitizes tumor cells to
DNA-damaging agents potentially by breaching a damage-induced
checkpoint arrest. Genes Cancer. 1:1053–1062. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Medová M, Aebersold DM and Zimmer Y: MET
inhibition in tumor cells by PHA665752 impairs homologous
recombination repair of DNA double strand breaks. Int J Cancer.
130:728–734. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhuang HQ, Bo QF, Yuan ZY, Wang J, Zhao LJ
and Wang P: The different radiosensitivity when combining erlotinib
with radiation at different administration schedules might be
related to activity variations in c-MET-PI3K-AKT signal
transduction. Onco Targets Ther. 6:603–608. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Welsh JW, Mahadevan D, Ellsworth R, Cooke
L, Bearss D and Stea B: The c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor MP470 radiosensitizes glioblastoma cells. Radiat Oncol.
4:692009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jun HT, Sun J, Rex K, Radinsky R, Kendall
R, Coxon A and Burgess TL: AMG 102, a fully human anti-hepatocyte
growth factor/scatter factor neutralizing antibody, enhances the
efficacy of temozolomide or docetaxel in U-87 MG cells and
xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6735–6742. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan S, Wang JA, Yuan RQ, Rockwell S,
Andres J, Zlatapolskiy A, Goldberg ID and Rosen EM: Scatter factor
protects epithelial and carcinoma cells against apoptosis induced
by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene. 17:131–141. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meyn RE, Munshi A, Haymach JV, Milas L and
Ang KK: Receptor signaling as a regulatory mechanism of DNA repair.
Radiother Oncol. 92:316–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abdollahi A and Folkman J: Evading tumor
evasion: Current concepts and perspectives of anti-angiogenic
cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 13:16–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Puri N, Khramtsov A, Ahmed S, Nallasura V,
Hetzel JT, Jagadeeswaran R, Karczmar G and Salgia R: A selective
small molecule inhibitor of c-Met, PHA665752, inhibits
tumorigenicity and angiogenesis in mouse lung cancer xenografts.
Cancer Res. 67:3529–3534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Citrin D, Ménard C and Camphausen K:
Combining radiotherapy and angiogenesis inhibitors: Clinical trial
design. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 64:15–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|