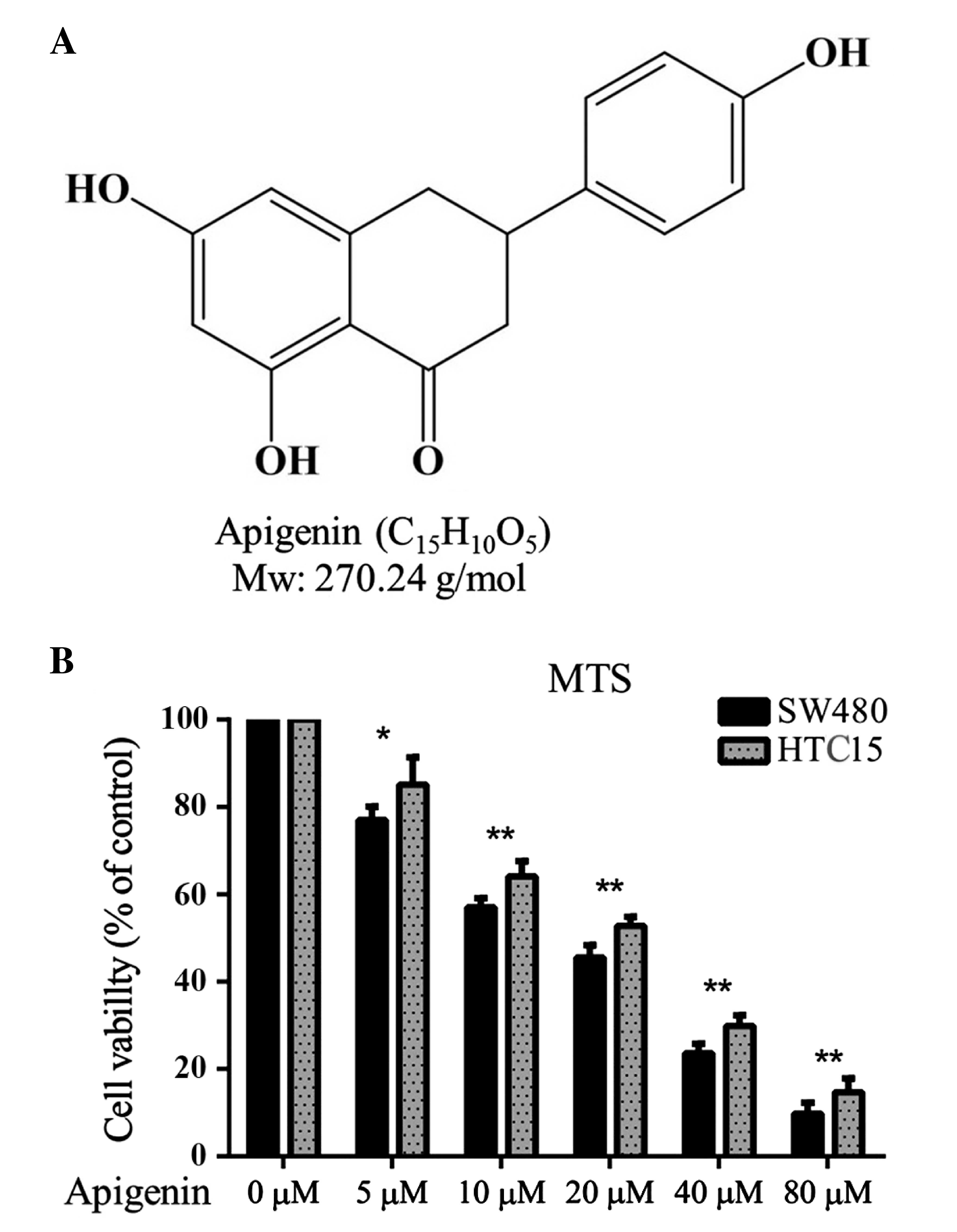
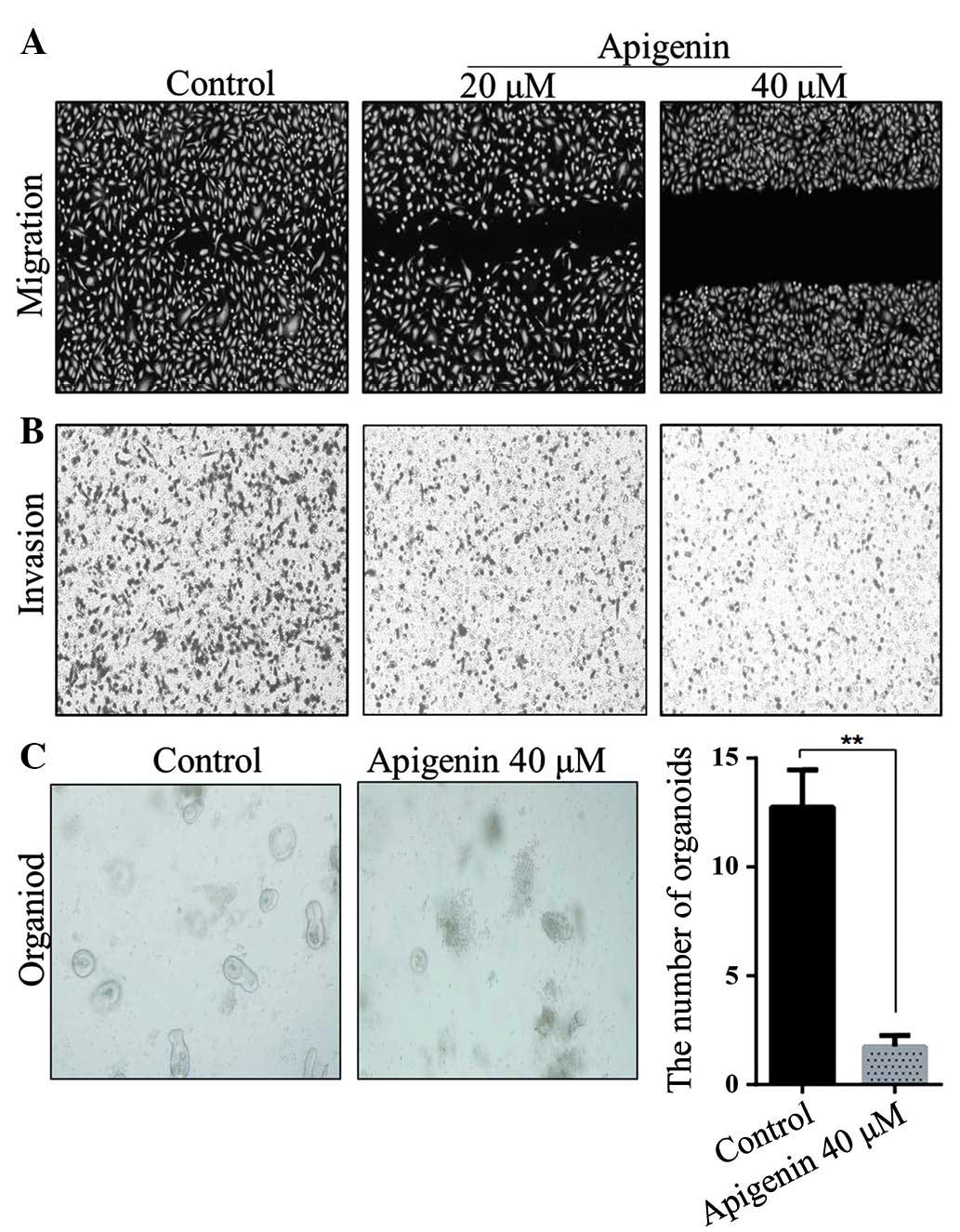
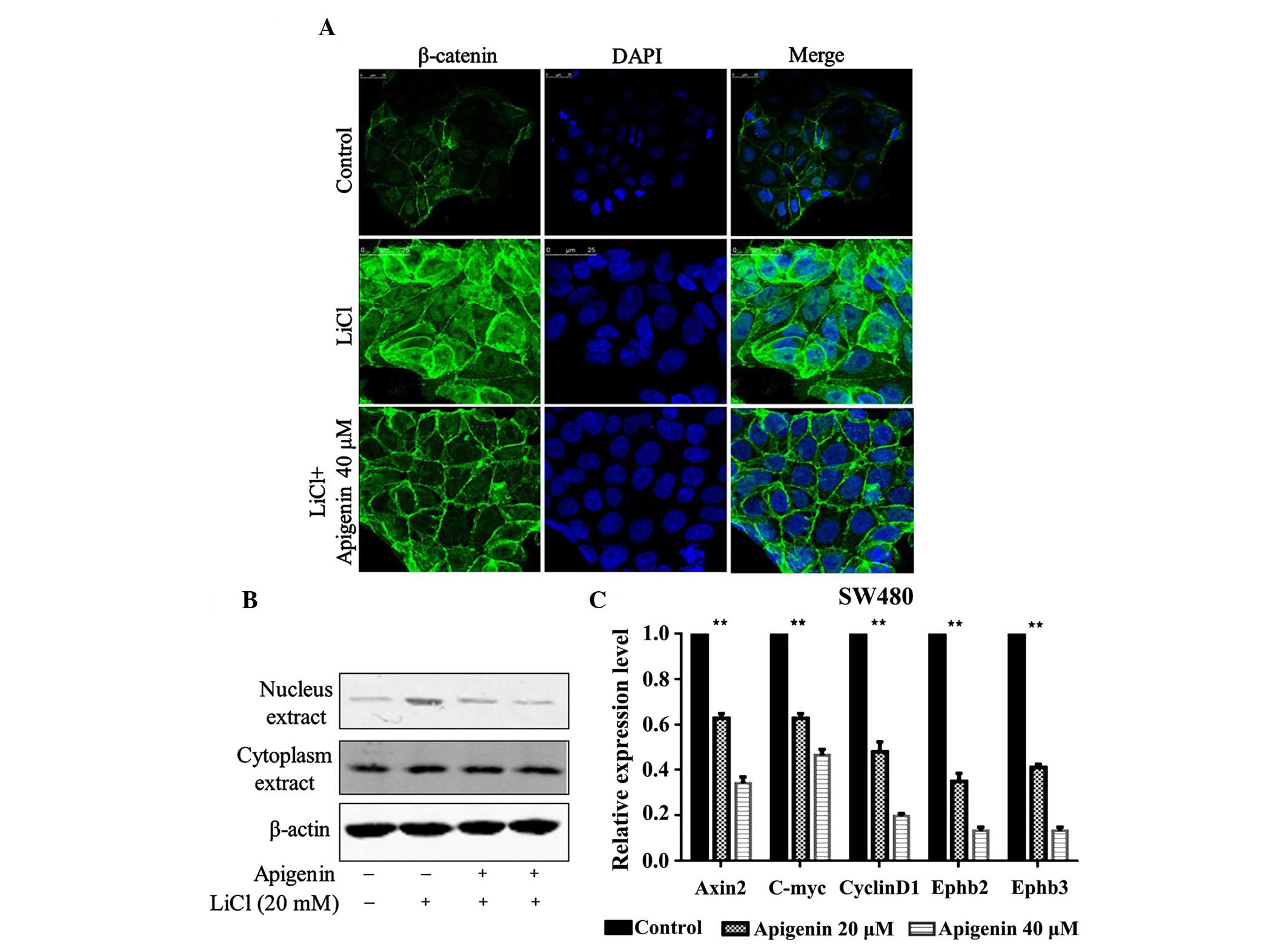
|
1
|
Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM Jr
and Buchsbaum DJ: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A
review. Gynecol Oncol. 131:772–779. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Noguti J, De Moura CF, Hossaka TA, Franco
M, Oshima CT, Dedivitis RA and Ribeiro DA: The role of canonical
WNT signaling pathway in oral carcinogenesis: A comprehensive
review. Anticancer Res. 32:873–878. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pecina-Slaus N: Wnt signal transduction
pathway and apoptosis: A review. Cancer Cell Int. 10:222010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moon RT, Brown JD and Torres M: WNTs
modulate cell fate and behavior during vertebrate development.
Trends Genet. 13:157–162. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Behrens J: Control of beta-catenin
signaling in tumor development. Ann NY Acad Sci. 910:21–35. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chesire DR, Ewing CM, Sauvageot J, Bova GS
and Isaacs WB: Detection and analysis of beta-catenin mutations in
prostate cancer. Prostate. 45:323–334. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Polakis P: The oncogenic activation of
beta-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 9:15–21. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Birt DF, Mitchell D, Gold B, Pour P and
Pinch HC: Inhibition of ultraviolet light induced skin
carcinogenesis in SKH-1 mice by apigenin, a plant flavonoid.
Anticancer Res. 17:85–91. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Caltagirone S, Rossi C, Poggi A,
Ranelletti FO, Natali PG, Brunetti M, Aiello FB and Piantelli M:
Flavonoids apigenin and quercetin inhibit melanoma growth and
metastatic potential. Int J Cancer. 87:595–600. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang IK, Lin-Shiau SY and Lin JK:
Induction of apoptosis by apigenin and related flavonoids through
cytochrome c release and activation of caspase-9 and
caspase-3 in leukaemia HL-60 cells. Eur J Cancer. 35:1517–1525.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang W, Heideman L, Chung CS, Pelling JC,
Koehler KJ and Birt DF: Cell-cycle arrest at G2/M and growth
inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol
Carcinog. 28:102–110. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin F, Giuliano AE, Law RE and Van Herle
AJ: Apigenin inhibits growth and induces G2/M arrest by modulating
cyclin-CDK regulators and ERK MAP kinase activation in breast
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 21:413–420. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu Y, Mao Y, Chen H, Lin Y, Hu Z, Wu J,
Xu X, Xu X, Qin J and Xie L: Apigenin promotes apoptosis, inhibits
invasion and induces cell cycle arrest of T24 human bladder cancer
cells. Cancer Cell Int. 13:542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang YJ, Zhou SM, Xu G and Gao YQ:
Interference of Phenylethanoid Glycosides from Cistanche tubulosa
with the MTT Assay. Molecules. 20:8060–8071. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feliciangeli S, Bendahhou S, Sandoz G,
Gounon P, Reichold M, Warth R, Lazdunski M, Barhanin J and Lesage
F: Does sumoylation control K2P1/TWIK1 background K+ channels?
Cell. 130:563–569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de
Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE, van Es JH, Abo A, Kujala P, Peters
PJ and Clevers H: Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus
structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature.
459:262–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miao L, Xiong X, Lin Y, Cheng Y, Lu J,
Zhang J and Cheng N: MiR-203 inhibits tumor cell migration and
invasion via caveolin-1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
7:658–662. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schuijers J, Junker JP, Mokry M, Hatzis P,
Koo BK, Sasselli V, van der Flier LG, Cuppen E, van Oudenaarden A
and Clevers H: Ascl2 acts as an R-spondin/Wnt-responsive switch to
control stemness in intestinal crypts. Cell stem cell. 16:158–170.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Osada T, Chen M, Yang XY, Spasojevic I,
Vandeusen JB, Hsu D, Clary BM, Clay TM, Chen W, Morse MA and Lyerly
HK: Antihelminth compound niclosamide downregulates Wnt signaling
and elicits antitumor responses in tumors with activating APC
mutations. Cancer Res. 71:4172–4182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen X, Ying H and Yue BY: Wnt activation
by wild type and mutant myocilin in cultured human trabecular
meshwork cells. PLoS One. 7:e449022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haggar FA and Boushey RP: Colorectal
cancer epidemiology: Incidence, mortality, survival and risk
factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 22:191–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blair V, Kahokehr A and Sammour T: Cancer
in Māori: Lessons from prostate, colorectal and gastric cancer and
progress in hereditary stomach cancer in New Zealand. ANZ J Surg.
83:42–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lazarova DL, Chiaro C, Wong T, Drago E,
Rainey A, O'Malley S and Bordonaro M: CBP Activity Mediates Effects
of the histone deacetylase inhibitor butyrate on WNT activity and
apoptosis in colon cancer cells. J Cancer. 4:481–490. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chong KY, Hsu CJ, Hung TH, Hu HS, Huang
TT, Wang TH, Wang C, Chen CM, Choo KB and Tseng CP: Wnt pathway
activation and ABCB1 expression account for attenuation of
proteasome inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in multidrug-resistant
cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:149–159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jang GB, Hong IS, Kim RJ, Lee SY, Park SJ,
Lee ES, Park JH, Yun CH, Chung JU, Lee KJ, et al: Wnt/beta-catenin
small-molecule inhibitor CWP232228 preferentially inhibits the
growth of breast cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 75:1691–1702.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hall CL, Zhang H, Baile S, Ljungman M,
Kuhstoss S and Keller ET: p21CIP-1/WAF-1 induction is required to
inhibit prostate cancer growth elicited by deficient expression of
the Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1. Cancer research. 70:9916–9926. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin C, Lu W, Zhang W, Londoño-Joshi AI,
Buchsbaum DJ, Bu G and Li Y: The C-terminal region Mesd peptide
mimics full-length Mesd and acts as an inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e581022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sack U, Walther W, Scudiero D, Selby M,
Aumann J, Lemos C, Fichtner I, Schlag PM, Shoemaker RH and Stein U:
S100A4-induced cell motility and metastasis is restricted by the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor calcimycin in colon cancer cells.
Mol Biol Cell. 22:3344–3354. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Seo HS, Ku JM, Choi HS, Woo JK, Jang BH,
Shin YC and Ko SG: Induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis by
apigenin by inhibiting STAT3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing
MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 34:2869–2882.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu DG, Yu P, Li JW, Jiang P, Sun J, Wang
HZ, Zhang LD, Wen MB and Bie P: Apigenin potentiates the growth
inhibitory effects by IKK-β-mediated NF-κB activation in pancreatic
cancer cells. Toxicol Lett. 224:157–164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chunhua L, Donglan L, Xiuqiong F, Lihua Z,
Qin F, Yawei L, Liang Z, Ge W, Linlin J, Ping Z, et al: Apigenin
up-regulates transgelin and inhibits invasion and migration of
colorectal cancer through decreased phosphorylation of AKT. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:1766–1775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang QR, Yao XQ, Wen G, Fan Q, Li YJ, Fu
XQ, Li CK and Sun XG: Apigenin suppresses the growth of colorectal
cancer xenografts via phosphorylation and up-regulated FADD
expression. Oncol Lett. 2:43–47. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|