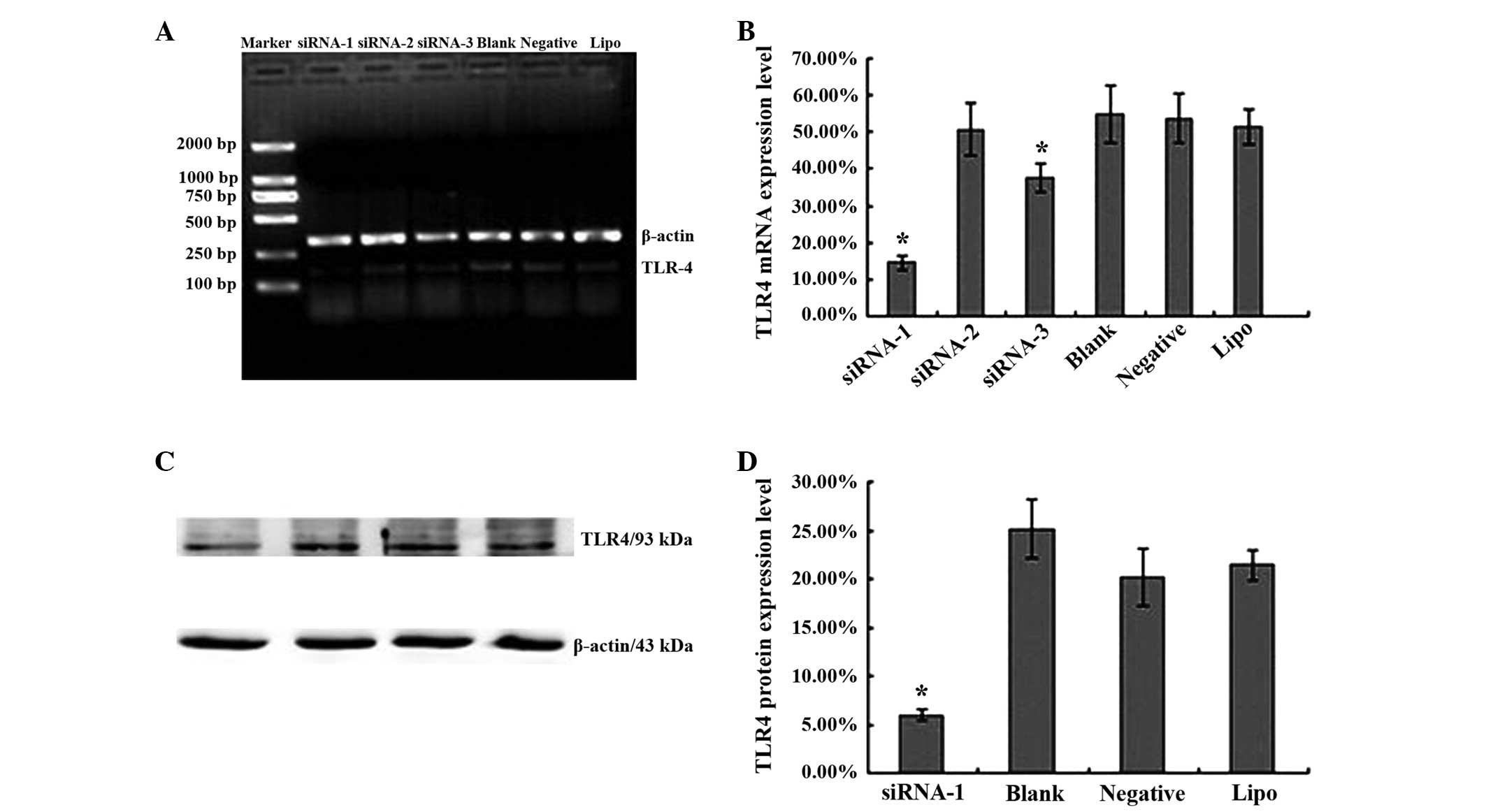
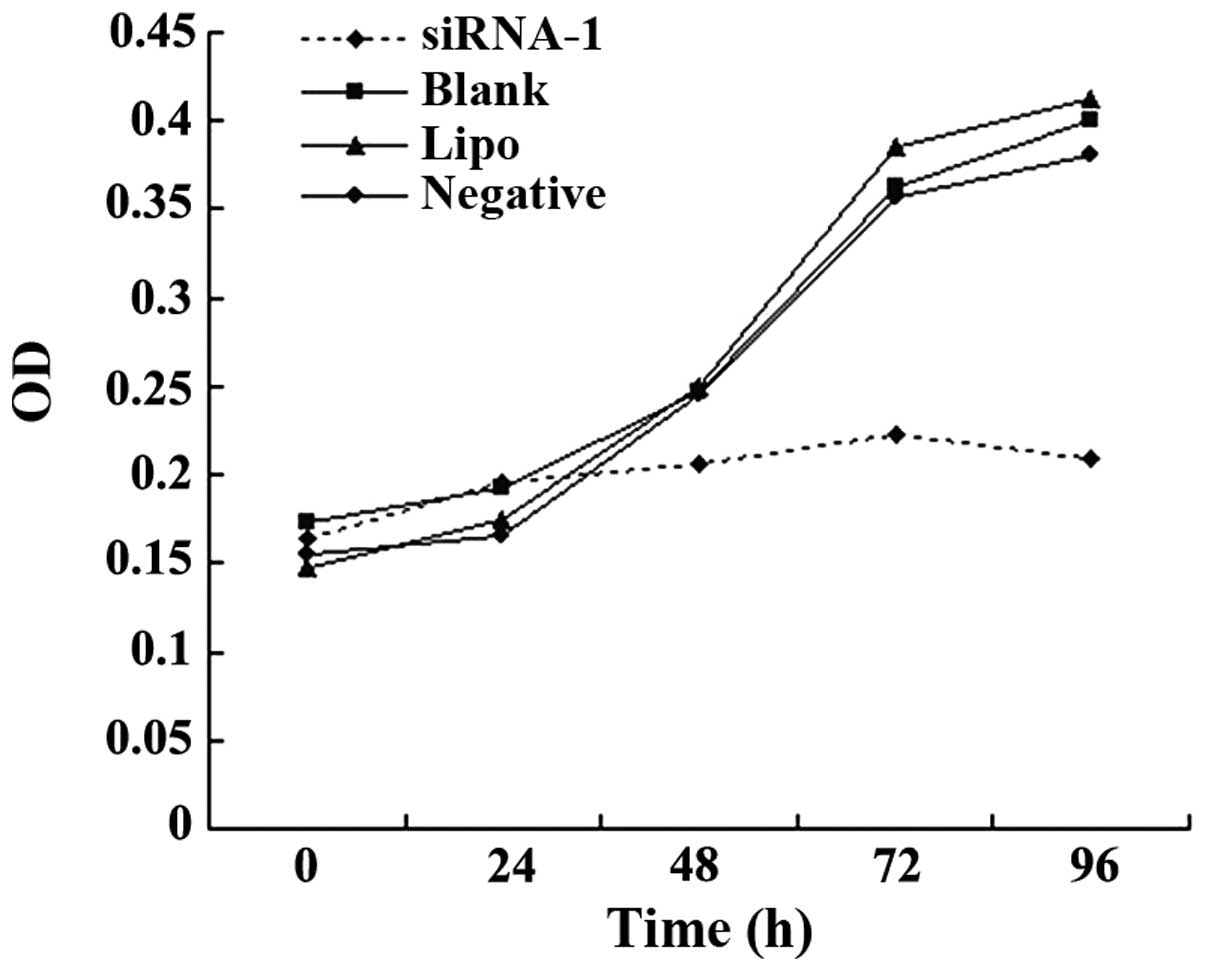
|
1
|
Baffy G, Brunt EM and Caldwell SH:
Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An
emerging menace. J Hepatol. 56:1384–1391. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Li G, Wu
L and He J: The incidences and mortalities of major cancers in
China, 2009. Chin J Cancer. 32:106–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang J, Yan L and Wang W: Current status
of multimodal & combination therapy for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Indian J Med Res. 136:391–403. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muccioli M, Sprague L, Nandigam H, Pate M
and Benencia F: Toll-like receptors as novel therapeutic targets
for ovarian cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2012:6421412012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang D, Kang R, Carolyn CB, Zeh HJ and
Lotze MT: PAMPs and DAMPs: Signal 0s that spur autophagy and
immunity. Immunol Rev. 249:158–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee CH, Wu CL and Shiau AL: Toll-like
receptor 4 signaling promotes tumor growth. J Immunother. 33:73–82.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M,
Elishaev E, Mandapathil M, Nowak-Markwitz E, Spaczynski M and
Whiteside TL: TLR4 signaling induced by lipopolysacharide or
paclitaxel regulates tumor survival and chemoresistance in ovarian
cancer. Oncogene. 28:4353–4363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Killeen SD, Wang JH, Andrews EJ and
Redmond HP: Bacterial endotoxin enhances colorectal cancer cell
adhesion and invasion through TLR-4 and NF-kappaB-dependent
activation of the urokinase plasminogen activator system. Br J
Cancer. 100:1589–1602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hua D, Liu MY, Cheng ZD, Qin XJ, Zhang HM,
Chen Y, Qin GJ, Liang G, Li JN, Han XF and Liu DX: Small
interfering RNA-directed targeting of Toll-like receptor 4 inhibits
human prostate cancer cell invasion, survival and tumorigenicity.
Mol Immunol. 46:2876–2884. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Szajnik M,
Harasymczuk M, Boyiadzis M, Kruk-Zagajewska A, Szyfter W, Zeromski
J and Whiteside TL: Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on
human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor
development and protects the tumor from immune attack. Cancer Res.
69:3105–3113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tanimura N, Saitoh S, Matsumoto F,
Akashi-Takamura S and Miyake K: Roles for LPS-dependent interaction
and relocation of TLR4 and TRAM in TRIF-signaling. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 368:94–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Rumpf JJ, Samel D,
Leverkus M, Janssen O, Häcker G, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Kracht M,
Scheurich P and Wajant H: NF-kappaB activation by Fas is mediated
through FADD, caspase-8, and RIP and is inhibited by FLIP. J Cell
Biol. 166:369–380. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sipos F, Fűri I, Constantinovits M,
Tulassay Z and Műzes G: Contribution of TLR signaling to the
pathogenesis of colitis-associated cancer in inflammatory bowel
disease. World J Gastroenterol. 20:12713–12721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang B, Zhao J, Unkeless JC, Feng ZH and
Xiong H: TLR signaling by tumor and immune cells: A double-edged
sword. Oncogene. 27:218–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang B, Zhao J, Li H, He KL, Chen Y, Chen
SH, Mayer L, Unkeless JC and Xiong H: Toll-like receptors on tumor
cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res.
65:5009–5014. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Zhu R, Huang Z, Li H and Zhu H:
Lipopolysaccharide-induced toll-like receptor 4 signaling in cancer
cells promotes cell survival and proliferation in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 58:2223–2236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Balmanno K and Cook SJ: Tumor cell
survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ.
16:368–377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmitz KJ, Wohlschlaeger J, Lang H,
Sotiropoulos GC, Malago M, Steveling K, Reis H, Cicinnati VR,
Schmid KW and Baba HA: Activation of the ERK and AKT signalling
pathway predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and ERK
activation in cancer tissue is associated with hepatitis C virus
infection. J Hepatol. 48:83–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gailhouste L, Ezan F, Bessard A, Frémin C,
Rageul J, Langouët S and Baffet G: RNAi-mediated MEK1 knock-down
prevents ERK1/2 activation and abolishes human hepatocarcinoma
growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 126:1367–1377.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seki E, Brenner DA and Karin M: A liver
full of JNK: Signaling in regulation of cell function and disease
pathogenesis and clinical approaches. Gastroenterology.
143:307–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwabe RF, Bradham CA, Uehara T, Hatano
E, Bennett BL, Schoonhoven R and Brenner DA: c-Jun-N-terminal
kinase drives cyclin D1 expression and proliferation during liver
regeneration. Hepatology. 37:824–832. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karin M and Lin A: NF-kappaB at the
crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maeda S, Kamata H, Luo JL, Leffert H and
Karin M: IKKbeta couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven
compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical
hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell. 121:977–990. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Hogerlinden M, Auer G and Toftgård R:
Inhibition of Rel/Nuclear Factor-kappaB signaling in skin results
in defective DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest and Ha-ras-and
p53-independent tumor development. Oncogene. 21:4969–4977. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|