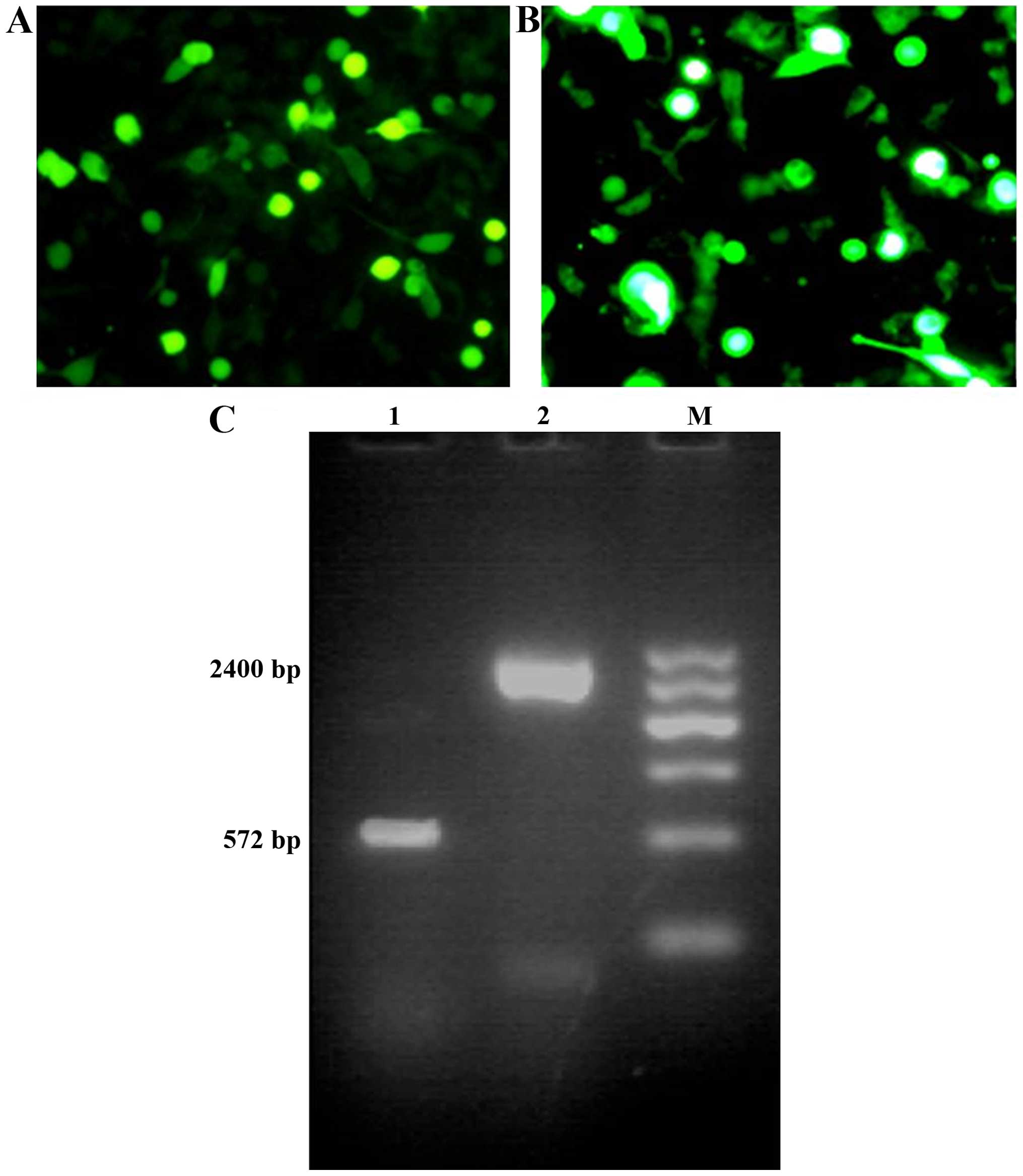
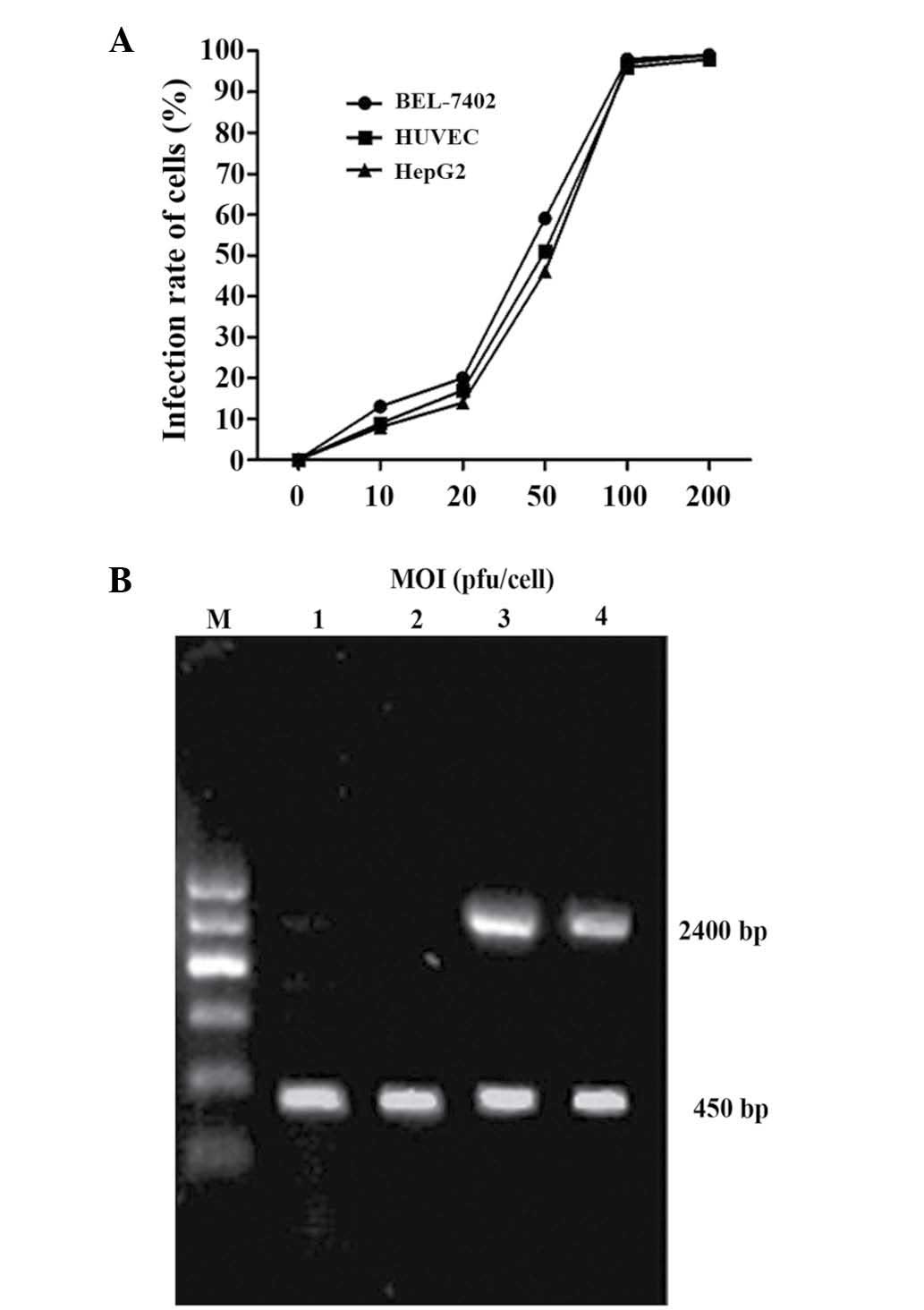
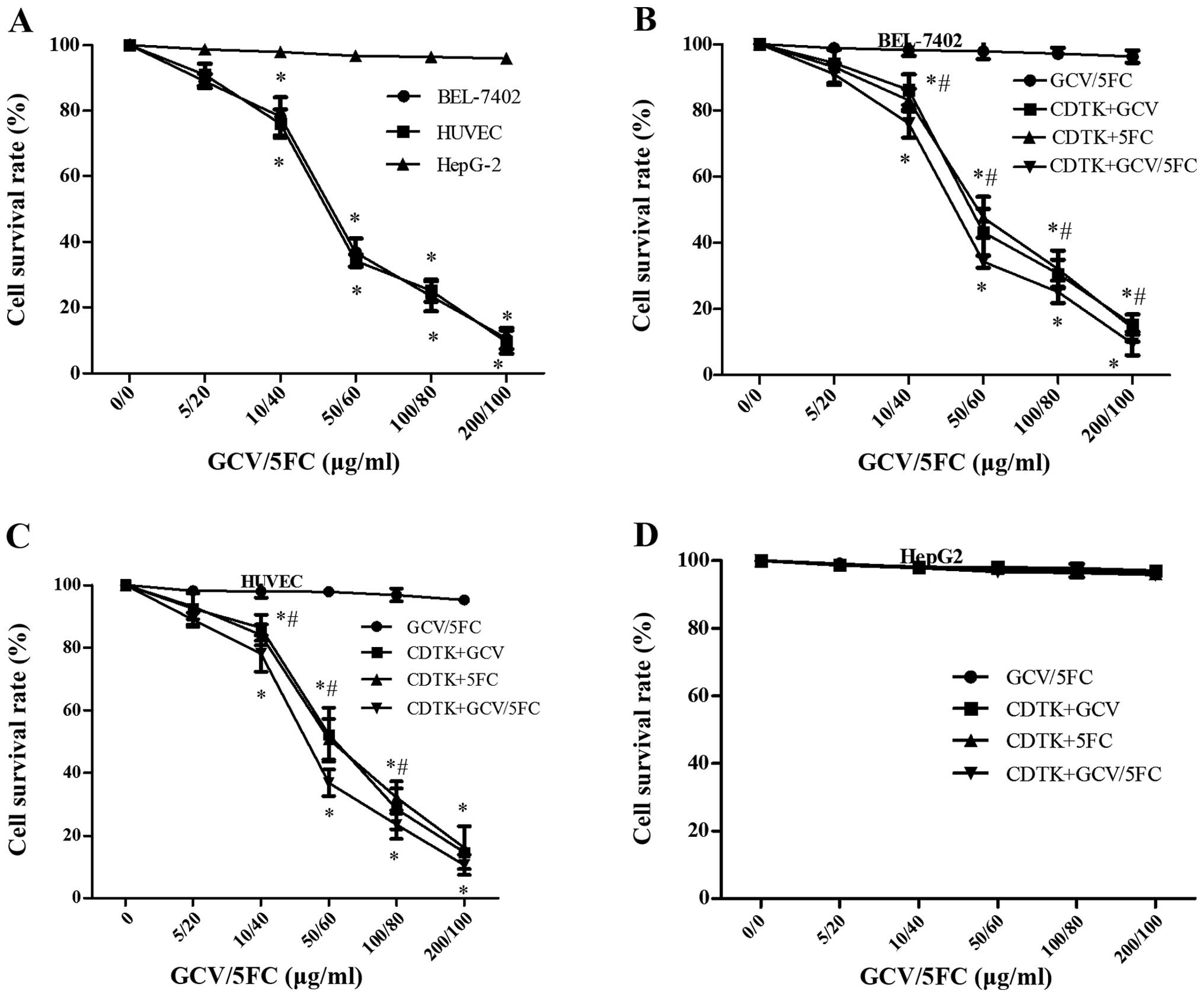
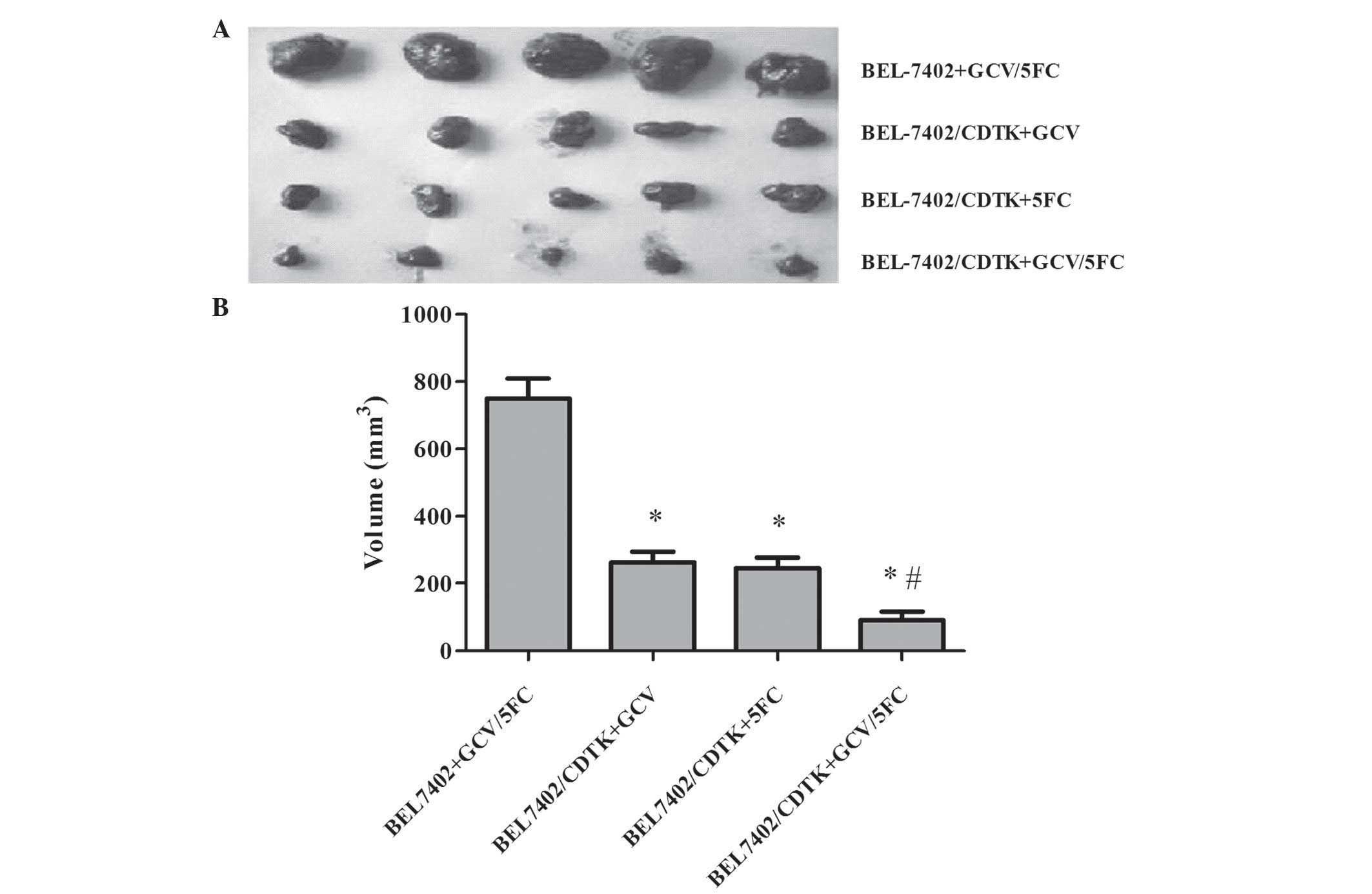
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M and Llovet JM:
Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 5:215–219. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang CH, Wey KC, Mo LR, Chang KK, Lin RC
and Kuo JJ: Current trends and recent advances in diagnosis,
therapy, and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:3595–3604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhayani NH, Jiang Y, Hamed O, Kimchi ET,
Staveley-O'Carroll KF and Gusani NJ: Advances in the pharmacologic
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Clin Pharmacol.
10:299–304. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boucher PD, Im MM, Freytag SO and Shewach
DS: A novel mechanism of synergistic cytotoxicity with
5-fluorocytosine and ganciclovir in double suicide gene therapy.
Cancer Res. 66:3230–3237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fogar P, Greco E, Basso D, Navaglia F,
Plebani M and Pedrazzoli S: Killer genes in pancreatic cancer
therapy. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 51:61–76. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su GQ, Su G and Huang ZH:
Adenovirus-mediated tissue-targeted expression of the CDglyTk gene
for the treatment of breast cancer. Mol Med Rep. 6:321–329.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu F, Li S, Li XL, Guo Y, Zou BY, Xu R,
Liao H, Zhao HY, Zhang Y, Guan ZZ and Zhang L: Phase I and
biodistribution study of recombinant adenovirus vector-mediated
herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene and ganciclovir
administration in patients with head and neck cancer and other
malignant tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 16:723–730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rainov NG: A phase III clinical evaluation
of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and ganciclovir
gene therapy as an adjuvant to surgical resection and radiation in
adults with previously untreated glioblastoma multiforme. Hum Gene
Ther. 11:2389–2401. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kong H, Tao L, Qi K, Wang Y, Li Q, Du J
and Huang Z: Thymidine kinase/ganciclovir and cytosine
deaminase/5-fluorocytosine suicide gene therapy-induced cell
apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 30:1209–1214.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qu L, Wang Y, Gong L, Zhu J, Gong R and Si
J: Suicide gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
survivin promoter-driven expression of the herpes simplex virus
thymidine kinase gene. Oncol Rep. 29:1435–1440. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sia D, Alsinet C, Newell P and Villanueva
A: VEGF signaling in cancer treatment. Curr Pharm Des.
20:2834–2842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bertolini F, Shaked Y, Mancuso P and
Kerbel RS: The multifaceted circulating endothelial cell in cancer:
Towards marker and target identification. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:835–845. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Suh YG, Lee EJ, Cha H, Yang SH and Seong
J: Prognostic values of vascular endothelial growth factor and
matrix metalloproteinase-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma after
radiotherapy. Dig Dis. 32:725–732. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bupathi M, Kaseb A and Janku F:
Angiopoietin 2 as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma
treatment: Current perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1927–1932.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Detwiller KY, Fernando NT, Segal NH, Ryeom
SW, D'Amore PA and Yoon SS: Analysis of hypoxia-related gene
expression in sarcomas and effect of hypoxia on RNA interference of
vascular endothelial cell growth factor A. Cancer Res.
65:5881–5889. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Siemann DW and Shi W: Efficacy of combined
antiangiogenic and vascular disrupting agents in treatment of solid
tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 60:1233–1240. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huber BE, Austin EA, Good SS, Knick VC,
Tibbels S and Richards CA: In vivo antitumor activity of
5-fluorocytosine on human colorectal carcinoma cells genetically
modified to express cytosine deaminase. Cancer Res. 53:4619–4626.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua
P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S and Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis:
A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in
early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:1875–1887.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scripture CD and Figg WD: Drug
interactions in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:546–558. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K, Sakkas A,
Yarmus L, Huang H, Li Q, Freitag L, Zarogoulidis K and Malecki M:
Suicide gene therapy for cancer - current strategies. J Genet Syndr
Gene Ther. 4:2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rogulski KR, Wing MS, Paielli DL, Gilbert
JD, Kim JH and Freytag SO: Double suicide gene therapy augments the
antitumor activity of a replication-competent lytic adenovirus
through enhanced cytotoxicity and radiosensitization. Hum Gene
Ther. 11:67–76. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fischer U, Steffens S, Frank S, Rainov NG,
Schulze-Osthoff K and Kramm CM: Mechanisms of thymidine
kinase/ganciclovir and cytosine deaminase/5-fluorocytosine suicide
gene therapy-induced cell death in glioma cells. Oncogene.
24:1231–1243. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiu Y, Peng GL, Liu QC, Li FL, Zou XS and
He JX: Selective killing of lung cancer cells using
carcinoembryonic antigen promoter and double suicide genes,
thymidine kinase and cytosine deaminase (pCEA-TK/CD). Cancer Lett.
316:31–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fillat C, Carrió M, Cascante A and Sangro
B: Suicide gene therapy mediated by the Herpes Simplex virus
thymidine kinase gene/Ganciclovir system: Fifteen years of
application. Curr Gene Ther. 3:13–26. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang NH, Hwang KA, Yi BR, Lee HJ, Jeung
EB, Kim SU and Choi KC: Human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells
expressing cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase inhibits the
growth of breast cancer cells in cellular and xenograft mouse
models. Cancer Gene Ther. 19:412–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Konopka K, Spain C, Yen A, Overlid N,
Gebremedhin S and Düzgüneş N: Correlation between the levels of
survivin and survivin promoter-driven gene expression in cancer and
non-cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 14:70–89. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tan HY, Wang N, Tsao SW, Zhang Z and Feng
Y: Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor via
inactivation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 by alkaloids in
Coptidis rhizome in hepatocellular carcinoma. Integr Cancer Ther.
13:425–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li XM, Tang ZY, Zhou G, Lui YK and Ye SL:
Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression
in invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 17:13–17. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ranieri G, Ammendola M, Marech I, Laterza
A, Abbate I, Oakley C, Vacca A, Sacco R and Gadaleta CD: Vascular
endothelial growth factor and tryptase changes after
chemoembolization in hepatocarcinoma patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:6018–6025. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suzuki K, Hayashi N, Miyamoto Y, Yamamoto
M, Ohkawa K, Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Yamaguchi Y, Nakase H, Noda K, et al:
Expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial
growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
56:3004–3009. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhan P, Qian Q and Yu LK: Serum VEGF level
is associated with the outcome of patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2:209–215.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cipriani G and Mazzanti R: Treatment with
inhibitors of angiogenesis in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A
new tool in our hands or simply a hope? Dig Liver Dis. 37:230–231.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma J, Li M, Mei L, Zhou Q, Liu L, Yu X and
Che G: Double suicide genes driven by kinase domain insert
containing receptor promoter selectively kill human lung cancer
cells. Genet Vaccines Ther. 9:62011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang JH, Wan MX, Yuan JY and Pan BR: Do
there exist synergistic antitumor effects by coexpression of herpes
simplex virus thymidine kinase with cytokine genes on human gastric
cancer cell line SCG7901? World J Gastroenterol. 10:147–151.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qiang L, Yanping L, Zonghai H, Fei C, Zhou
L and Jinlong Y: Study of the mechanism of bystander effect of
KDR-CDglyTK system mediated by adenovirus for the treatment of
gastric cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:1021–1027. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang W, Zhao CG, Sun HY, Zheng WE and
Chen H: Expression characteristics of KAI1 and vascular endothelial
growth factor and their diagnostic value for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gut Liver. 8:536–542. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhai LL, Wu Y, Huang DW and Tang ZG:
Increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and reduced tissue
factor pathway inhibitor-2 expression correlate with angiogenesis
and early postoperative recurrence of pancreatic carcinoma. Am J
Transl Res. 7:2412–2422. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zou Y, Guo CG and Zhang MM: Inhibition of
human hepatocellular carcinoma tumor angiogenesis by siRNA
silencing of VEGF via hepatic artery perfusion. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 19:4751–4761. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang J, Ma X, Chen X, Liu X, Zhang B,
Minmin L, Nie W, Zhang L and Liu L: Microvessel density as a
prognostic factor in bladder cancer: A systematic review of
literature and meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark. 14:505–514.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|