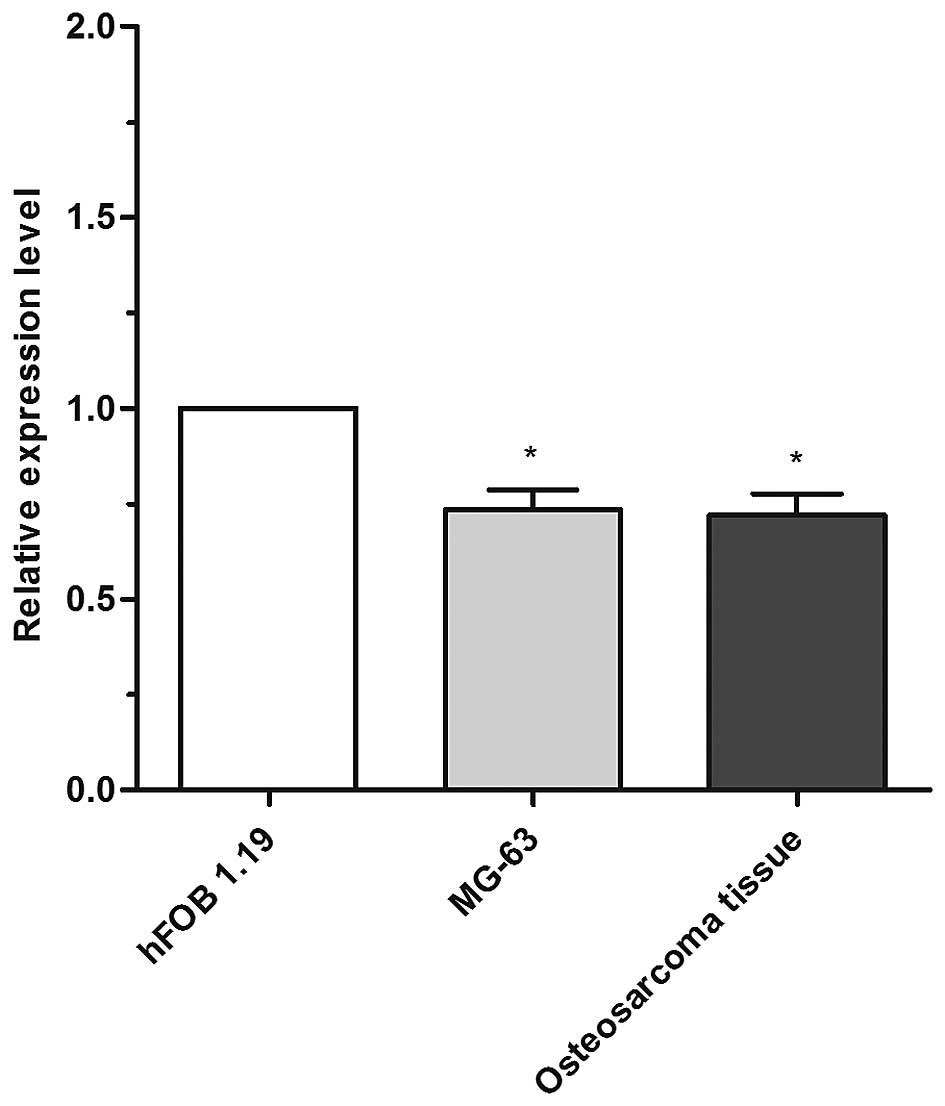
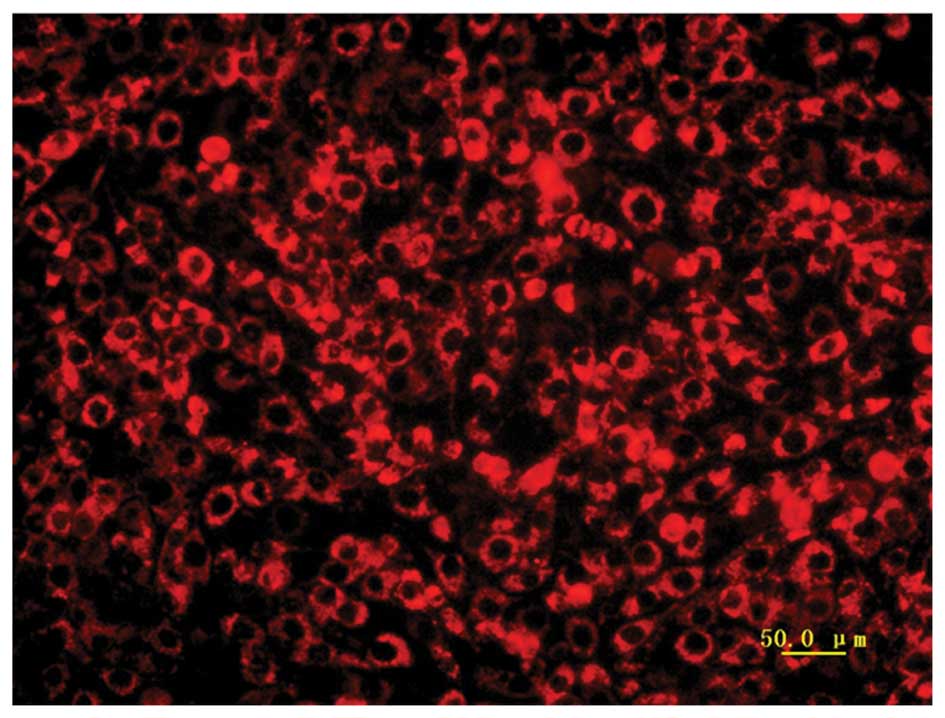
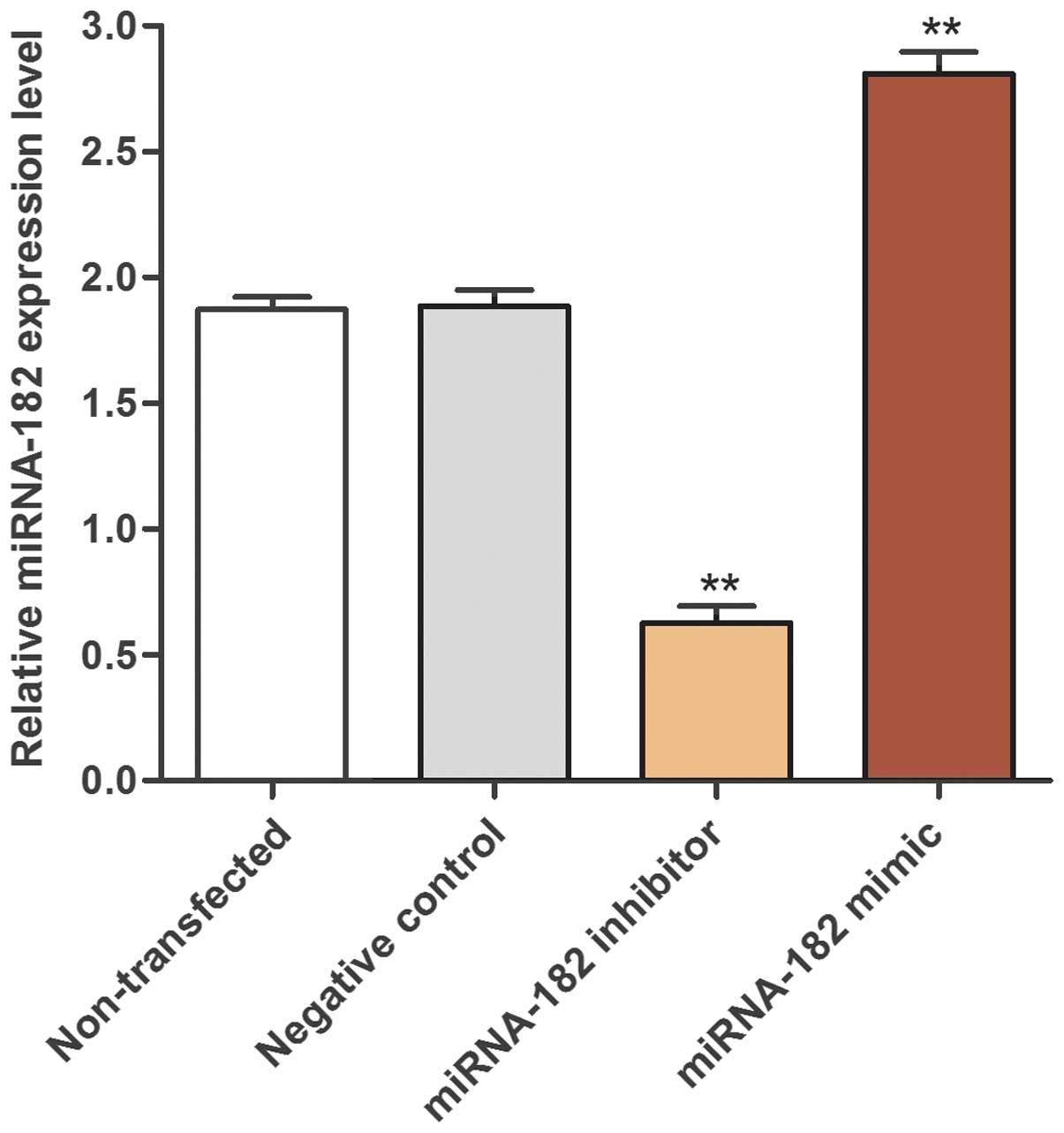
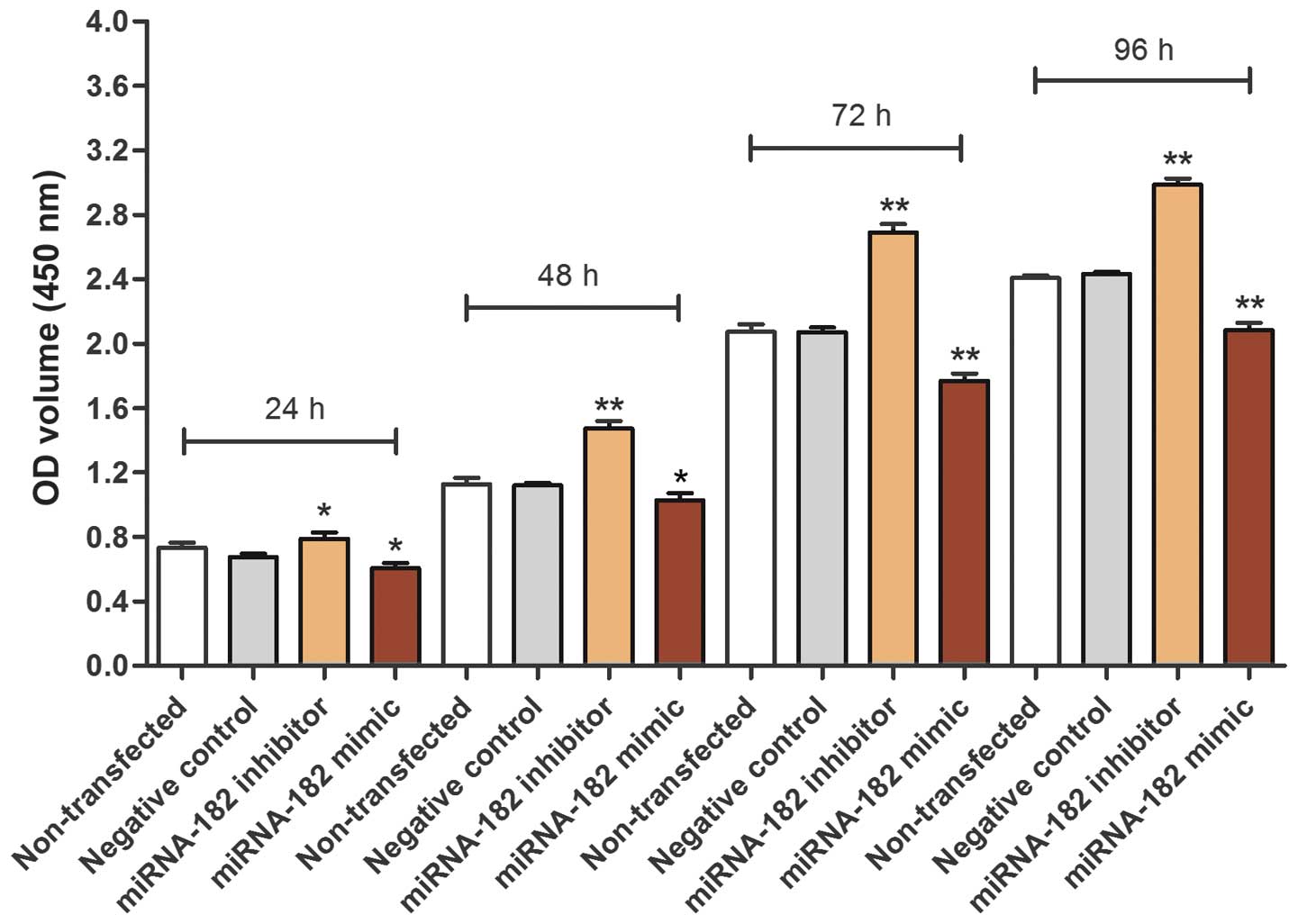
|
1
|
Bramwell VH: Osteosarcomas and other
cancers of bone. Curr Opin Oncol. 12:330–336. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kobayashi E, Hornicek FJ and Duan Z:
MicroRNA involvement in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma. 2012:3597392012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hartford CM, Wodowski KS, Rao BN, Khoury
JD, Neel MD and Daw NC: Osteosarcoma among children aged 5 years or
younger: The St. Jude children's research hospital experience. J
Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 28:43–47. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognosticfactors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marina N, Gebhardt M, Teot L and Gorlick
R: Biology and therapeutic advances for pediatric osteosarcoma.
Oncologist. 9:422–441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Endicott M: Principles of treatment for
osteosarcoma. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 18:110–114. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Szcześniak MW, Owczarkowska E, Gapski J
and Makałowska I: MicroRNA databases. Postepy Biochem. 58:91–99.
2012.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1126–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nikitina EG, Urazova LN and Stegny VN:
MicroRNAs and human cancer. Exp Oncol. 34:2–8. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek
SH and Kim VN: MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
EMBO J. 23:4051–4060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai X, Hagedorn CH and Cullen BR: Human
microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts
that can also function as mRNAs. RNA. 10:1957–1966. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Faller M and Guo F: MicroRNAbiogenesis:
There's more than one way to skin a cat. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1779:663–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Murchison EP and Hannon GJ: MiRNAson the
move: MiRNA biogenesis and the RNAi machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:223–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lund E and Dahlberg JE: Substrate
selectivity of exportin 5 and Dicer in the biogenesis of microRNAs.
Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 71:59–66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang XJ, Reyes JL, Chua NH and Gaasterland
T: Prediction and identification of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs
and their mRNA targets. Genome Biol. 5:R652004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Z, Yao H, Lin S, Zhu X, Shen Z, Lu G,
Poon WS, Xie D, Lin MC and Kung HF: Transcriptional and epigenetic
regulation of human microRNAs. Cancer Lett. 331:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rajewsky N: MicroRNA target predictions in
animals. Nat Genet. 38:S8–S13. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jovanovic M and Hengartner MO: MiRNAs and
apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 25:6176–6187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Babar IA, Slack FJ and Weidhaas JB: MiRNA
modulation of the cellular stress response. Future Oncol.
4:289–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akçakaya P, Ekelund S, Kolosenko I,
Caramuta S, Ozata DM, Xie H, Lindforss U, Olivecrona H and Lui WO:
MiR-185 and miR-133b deregulation is associated with overall
survival and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
39:311–318. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu H and Mo YY: Targeting miR-205 in
breast cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 13:1439–1448. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kiselev FL: MicroRNA and cancer. Mol Biol
(Mosk). 48:232–42. 2014.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mraz M and Pospisilova S: MicroRNAs in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia: From causality to associations and
back. Expert Rev Hematol. 5:579–581. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu H, Wang Y, Li X, Zhang YJ, Li J, Zheng
YQ, Liu M, Song X and Li XR: Expression and regulatory function of
miRNA-182 in triple-negative breast cancer cells through its
targeting of profilin 1. Tumour Biol. 34:1713–1722. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kong WQ, Bai R, Liu T, Cai CL, Liu M, Li X
and Tang H: MicroRNA-182 targets cAMP-responsive element-binding
protein 1 and suppresses cell growth in human gastric
adenocarcinoma. FEBS J. 279:1252–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cekaite L, Rantala JK, Bruun J, Guriby M,
Agesen TH, Danielsen SA, Lind GE, Nesbakken A, Kallioniemi O, Lothe
RA, et al: MiR-9, −31 and −182 deregulation promote proliferation
and tumor cell survival in colon cancer. Neoplasia. 14:868–879.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo D, Li Q, Lv Q, Wei Q, Cao S and Gu J:
MiR-27a targets sFRP1 in hFOB cells to regulate proliferation,
apoptosis and differentiation. PLoS One. 9:e913542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402 4082001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duffy MJ, O'Donovan N and Crown J: Use of
molecular markers for predicting therapy response in cancer
patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 37:151–159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guled M and Knuutila S: MicroRNAs and
cancer. Duodecim. 129:1661–1669. 2013.(In Finnish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ell B and Kang Y: MicroRNAs as regulators
of bone homeostasis and bone metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 3:5492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tang T, Wong HK, Gu W, Yu MY, To KF, Wang
CC, Wong YF, Cheung TH, Chung TK and Choy KW: MicroRNA-182 plays an
onco-miRNA role in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 129:199–208.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yan D, Dong XD, Chen X, Yao S, Wang L,
Wang J, Wang C, Hu DN, Qu J and Tu L: Role of microRNA-182 in
posterior uveal melanoma: Regulation of tumor development through
MITF, BCL2 and cyclin D2. PLOS One. 7:e409672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ning FL, Wang F, Li ML, Yu ZS, Hao YZ and
Chen SS: MicroRNA-182 modulates chemosensitivity of human non-small
cell lung cancer to cisplatin by targeting PDCD4. Diagn Pathol.
9:1432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang MH, Yu J, Jiang DM, Li WL, Wang S and
Ding YQ: MicroRNA-182 targets special AT-rich sequence-binding
protein 2 to promote colorectal cancer proliferation and
metastasis. J Transl Med. 12:1092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo Y, Liao Y, Jia C, Ren J, Wang J and Li
T: MicroRNA-182 promotes tumor cell growth by targeting
transcription elongation factor A-like 7 in endometrial carcinoma.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:581–590. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu R, Li J, Teng Z, Zhang Z and Xu Y:
Overexpressed microRNA-182 promotes proliferation and invasion in
prostate cancer PC-3 cells by down-regulating N-myc downstream
regulated gene 1 (NDRG1). PLOS One. 8:e689822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu X, Chen D, Cui Y, Li Z and Huang J:
Targeting microRNA-23a to inhibit glioma cell invasion via HOXD10.
Sci Rep. 3:34232013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
He Y, Meng C, Shao Z, Wang H and Yang S:
MiR-23a functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 34:1485–1496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Perng DW, Yang DM, Hsiao YH, Lo T, Lee OK,
Wu MT, Wu YC and Lee YC: miRNA-146a expression positively regulates
tumor necrosis factor-α-induced interleukin-8 production in
mesenchymal stem cells and differentiated lung epithelial-like
cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 18:2259–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|