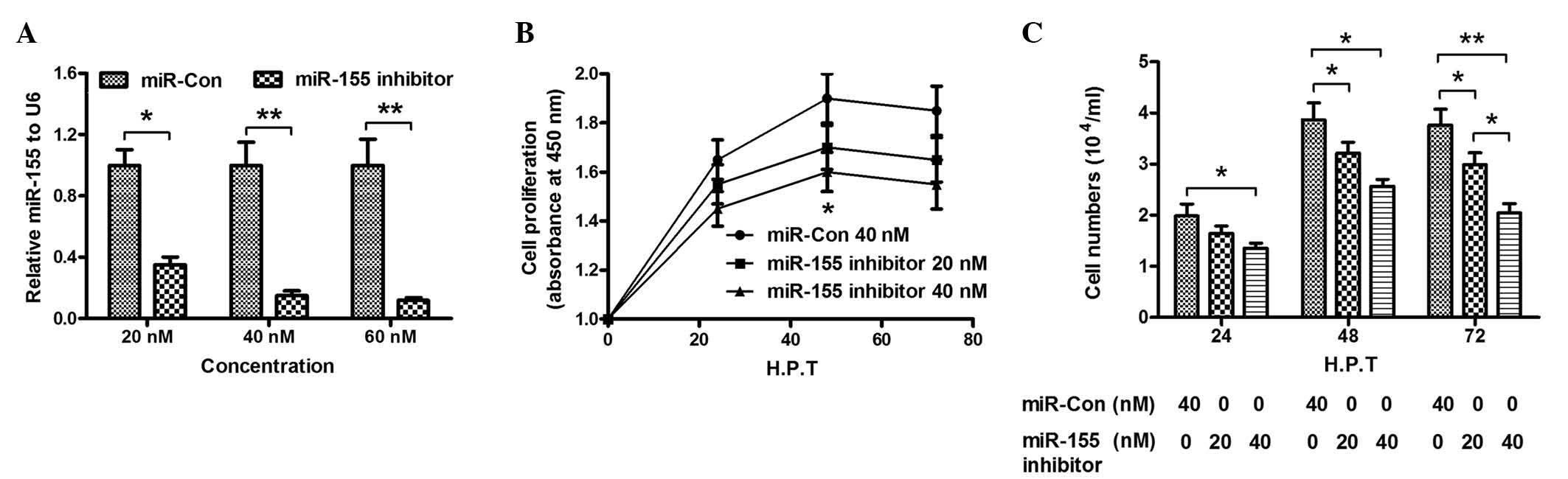
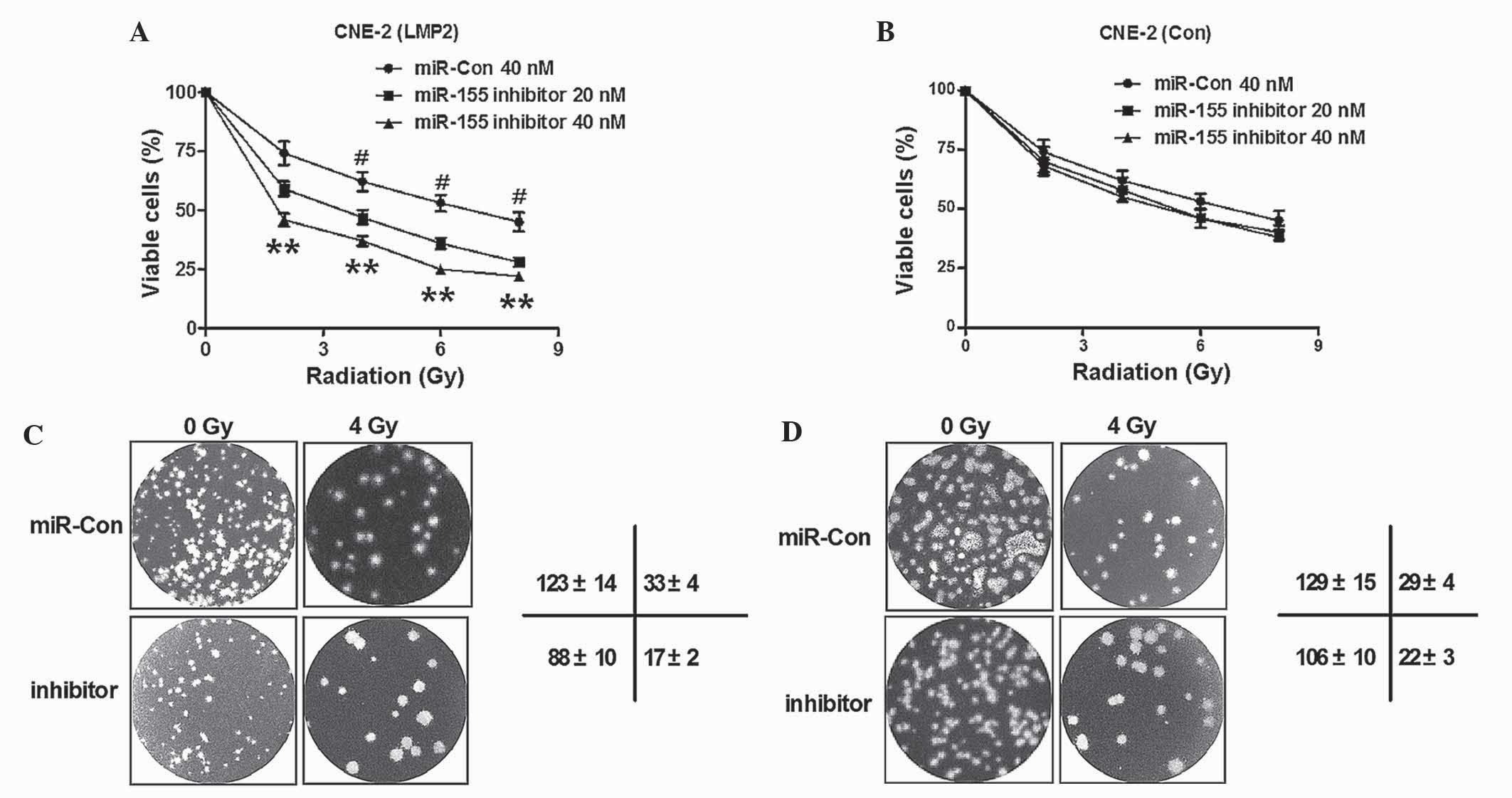
|
1
|
Guo X, O'Brien SJ, Zeng Y, Nelson GW and
Winkler CA: GSTM1 and GSTT1 gene deletions and the risk for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Han Chinese. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 17:1760–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolf H, zur Hausen H and Becker V: EB
viral genomes in epithelial nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Nat New
Biol. 244:245–247. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Y, Shi Y, Yuan Q, Liu X, Yan B, Chen L,
Tao Y and Cao Y: Epstein-Barr Virus encoded LMP1 regulates cyclin
D1 promoter activity by nuclear EGFR and STAT3 in CNE1 cells. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 32:902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zeng S and Hu X: LMP1
expression is positively associated with metastasis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Evidence from a meta-analysis. J Clin
Pathol. 65:41–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Niu Q, Qian M, Liu G, Yang F and Teng Y: A
genome-wide identification and characterization of microRNAs and
their targets in ‘Suli’ pear (Pyrus pyrifolia white pear
group). Planta (Sep). 8:2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
7
|
Wang HY, Li YY, Fu S, Wang XP, Huang MY,
Zhang X, Shao Q, Deng L, Zeng MS, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA-30a
promotes invasiveness and metastasis in vitro and in
vivo through epithelial-mesenchymal transition and results in
poor survival of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 239:891–898. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu J, Luo H, Liu X, Peng Y, Zhang B, Wang
L, Xu X, Peng X, Li G, Tian W, et al: miR-9 targets CXCR4 and
functions as a potential tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 35:554–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li G, Wu Z, Peng Y, Liu X, Lu J, Wang L,
Pan Q, He ML and Li XP: MicroRNA-10b induced by Epstein-Barr
virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 promotes the metastasis of
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 299:29–36. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu X, Wang Y, Sun Y, Zheng J and Zhu D:
MiR-155 up-regulation by LMP1 DNA contributes to increased
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 271:1939–1945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Freimoser FM, Jakob CA, Aebi M and Tuor U:
The MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium
bromide] assay is a fast and reliable method for colorimetric
determination of fungal cell densities. Appl Environ Microbiol.
65:3727–3729. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang JM, Ma XM, Hou YL, Dai LY, Cao HB, Ye
M and Bai YR: Analysis of simultaneous modulated accelerated
radiotherapy (SMART) for nasopharyngeal carcinomas. J Radiat Res.
55:794–802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hua YJ, Han F, Lu LX, Mai HQ, Guo X, Hong
MH, Lu TX and Zhao C: Long-term treatment outcome of recurrent
nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with salvage intensity modulated
radiotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 48:3422–3428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaneda A, Matsusaka K, Aburatani H and
Fukayama M: Epstein-Barr virus infection as an epigenetic driver of
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 72:3445–3450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Murata T, Sato Y and Kimura H: Modes of
infection and oncogenesis by the Epstein-Barr virus. Rev Med Virol.
24:242–253. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dawson CW, Tramountanis G, Eliopoulos AG
and Young LS: Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)
activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway to promote
cell survival and induce actin filament remodeling. J Biol Chem.
278:3694–3704. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao Y, Pang TY, Wang Y, Wang S, Kang HX,
Ding WB, Yong WW, Bie YH, Cheng XG, Zeng C, et al: LMP1 stimulates
the transcription of eIF4E to promote the proliferation, migration
and invasion of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. FEBS J.
281:3004–3018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo Z, Dai Y, Zhang L, Jiang C, Li Z, Yang
J, McCarthy JB, She X, Zhang W, Ma J, et al: miR-18a promotes
malignant progression by impairing microRNA biogenesis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 34:415–425. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu H, Lu J, Zuo L, Yan Q, Yu Z, Li X,
Huang J, Zhao L, Tang H, Luo Z, et al: Epstein-Barr virus
downregulates microRNA 203 through the oncoprotein latent membrane
protein 1: A contribution to increased tumor incidence in
epithelial cells. J Virol. 86:3088–3099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS and Baltimore D:
MicroRNA regulation of inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol.
30:295–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Z, Ma T, Huang C, Hu T and Li J: The
pivotal role of microRNA-155 in the control of cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 229:545–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun S, Sun P, Wang C and Sun T:
Downregulation of microRNA-155 accelerates cell growth and invasion
by targeting c-myc in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
32:951–956. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM and
Callen DF: The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 21:1236–1243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Babar IA, Cheng CJ, Booth CJ, Liang X,
Weidhaas JB, Saltzman WM and Slack FJ: Nanoparticle-based therapy
in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155)-dependent mouse model
of lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E1695–E1704. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|