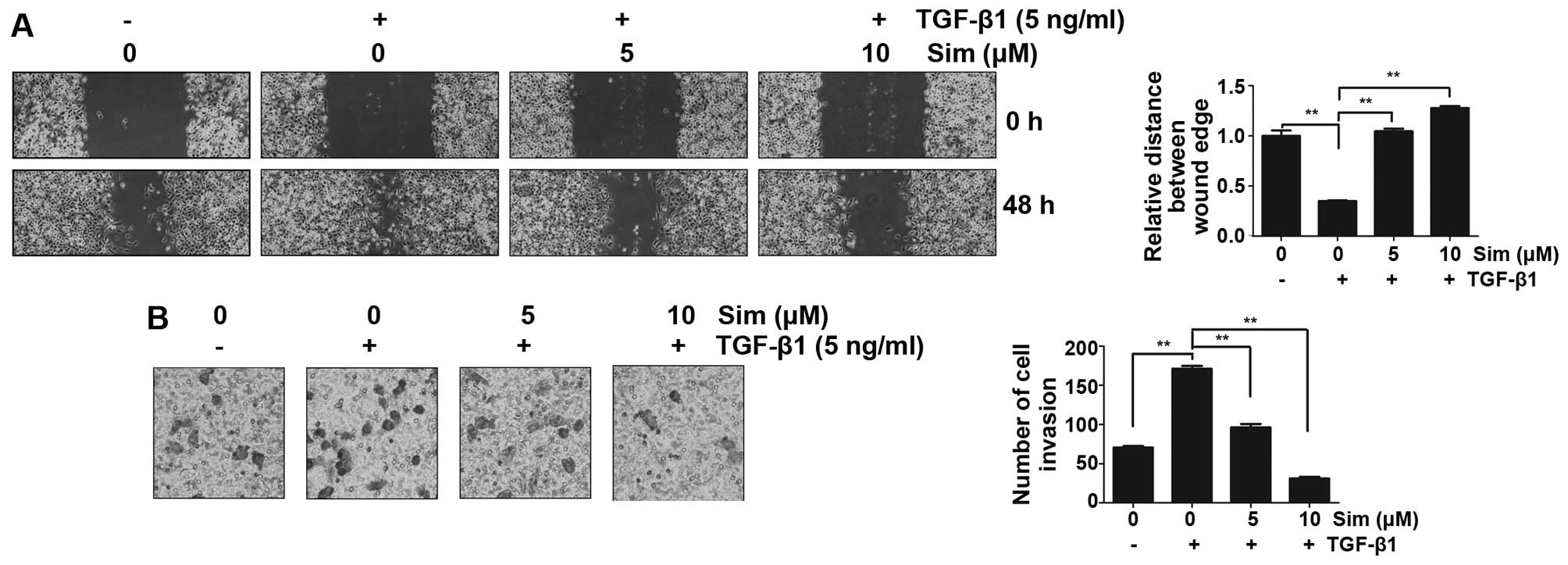
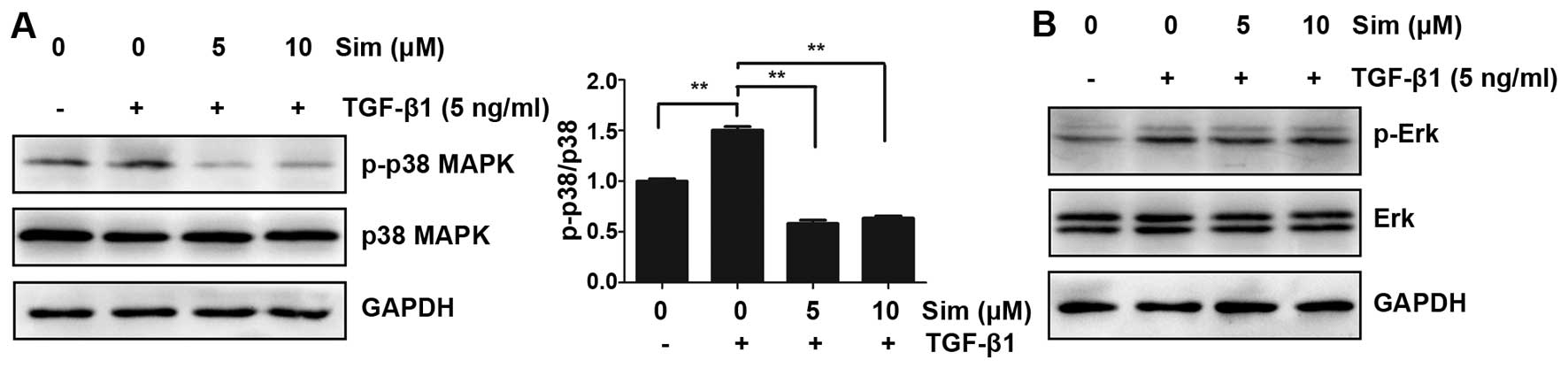
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Platz EA, Leitzmann MF, Visvanathan K,
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC and Giovannucci E: Statin drugs
and risk of advanced prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1819–1825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loeb S, Kan D, Helfand BT, Nadler RB and
Catalona WJ: Is statin use associated with prostate cancer
aggressiveness? BJU Int. 105:1222–1225. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park YH, Seo SY, Lee E, Ku JH, Kim HH and
Kwak C: Simvastatin induces apoptosis in castrate resistant
prostate cancer cells by deregulating nuclear factor-κB pathway. J
Urol. 189:1547–1552. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yokomizo A, Shiota M, Kashiwagi E, Kuroiwa
K, Tatsugami K, Inokuchi J, Takeuchi A and Naito S: Statins reduce
the androgen sensitivity and cell proliferation by decreasing the
androgen receptor protein in prostate cancer cells. Prostate.
71:298–304. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brown M, Hart C, Tawadros T, et al: The
differential effects of statins on the metastatic behaviour of
prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:1689–1696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zavadil J and Böttinger EP: TGF-beta and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 24:5764–5774.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wikström P, Stattin P, Franck-Lissbrant I,
Damber JE and Bergh A: Transforming growth factor beta1 is
associated with angiogenesis, metastasis and poor clinical outcome
in prostate cancer. Prostate. 37:19–29. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Javelaud D and Mauviel A: Crosstalk
mechanisms between the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways
and Smad signaling downstream of TGF-beta: Implications for
carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 24:5742–5750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bolós V, Peinado H, Pérez-Moreno MA, Fraga
MF, Esteller M and Cano A: The transcription factor Slug represses
E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transitions: A comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell
Sci. 116:499–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier
B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H and Foisner R:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang MH, Hsu DS, Wang HW, et al: Bmi1 is
essential in Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat
Cell Biol. 12:982–992. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
González-Santiago AE, Mendoza-Topete LA,
Sánchez-Llamas F, Troyo-Sanromán R and Gurrola-Díaz CM: TGF-β1
serum concentration as a complementary diagnostic biomarker of lung
cancer: Establishment of a cut-point value. J Clin Lab Anal.
25:238–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren
K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D and van Roy
F: The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1
downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell.
7:1267–1278. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peinado H, Quintanilla M and Cano A:
Transforming growth factor beta-1 induces snail transcription
factor in epithelial cell lines: Mechanisms for epithelial
mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 278:21113–21123. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Janda E, Lehmann K, Killisch I, et al: Ras
and TGF [beta] cooperatively regulate epithelial cell plasticity
and metastasis: Dissection of Ras signaling pathways. J Cell Biol.
156:299–313. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oft M, Heider KH and Beug H: TGFbeta
signaling is necessary for carcinoma cell invasiveness and
metastasis. Curr Biol. 8:1243–1252. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang T, Chen M and Sun T: Simvastatin
attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human alveolar epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:863–874.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Patel S, Mason RM, Suzuki J, et al:
Inhibitory effect of statins on renal epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Am J Nephrol. 26:381–387. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Agrotis A: Simvastatin, an inhibitor of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in experimental
atherosclerotic renovascular disease? J Hypertens. 26:1553–1555.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Urakami C, Kurosaka D, Tamada K, et al:
Lovastatin alters TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in porcine lens epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 37:479–485. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ao M, Williams K, Bhowmick NA and Hayward
SW: Transforming growth factor-beta promotes invasion in
tumorigenic but not in nontumorigenic human prostatic epithelial
cells. Cancer Res. 66:8007–8016. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hotz B, Arndt M, Dullat S, Bhargava S,
Buhr HJ and Hotz HG: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition:
Expression of the regulators snail, slug and twist in pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4769–4776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Non-Smad
TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. 118:3573–3584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Burke JP, Watson RW, Murphy M, Docherty
NG, Coffey JC and O'Connell PR: Simvastatin impairs smad-3
phosphorylation and modulates transforming growth factor
beta1-mediated activation of intestinal fibroblasts. Br J Surg.
96:541–551. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park IH, Park SJ, Cho JS, Moon YM, Moon
JH, Kim TH, Lee SH and Lee HM: Effect of simvastatin on
transforming growth factor beta-1-induced myofibroblast
differentiation and collagen production in nasal polyp-derived
fibroblasts. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 26:7–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu L, Hébert MC and Zhang YE: TGF-beta
receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent
TGF-beta responses. EMBO J. 21:3749–3759. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meyer-Ter-Vehn T, Katzenberger B, Han H,
Grehn F and Schlunck G: Lovastatin inhibits TGF-beta-induced
myofibroblast transdifferentiation in human tenon fibroblasts.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 49:3955–3960. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jacobs EJ, Rodriguez C, Bain EB, Wang Y,
Thun MJ and Calle EE: Cholesterol-lowering drugs and advanced
prostate cancer incidence in a large US cohort. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 16:2213–2217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murtola TJ, Tammela TL, Lahtela J and
Auvinen A: Cholesterol-lowering drugs and prostate cancer risk: A
population-based case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 16:2226–2232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|