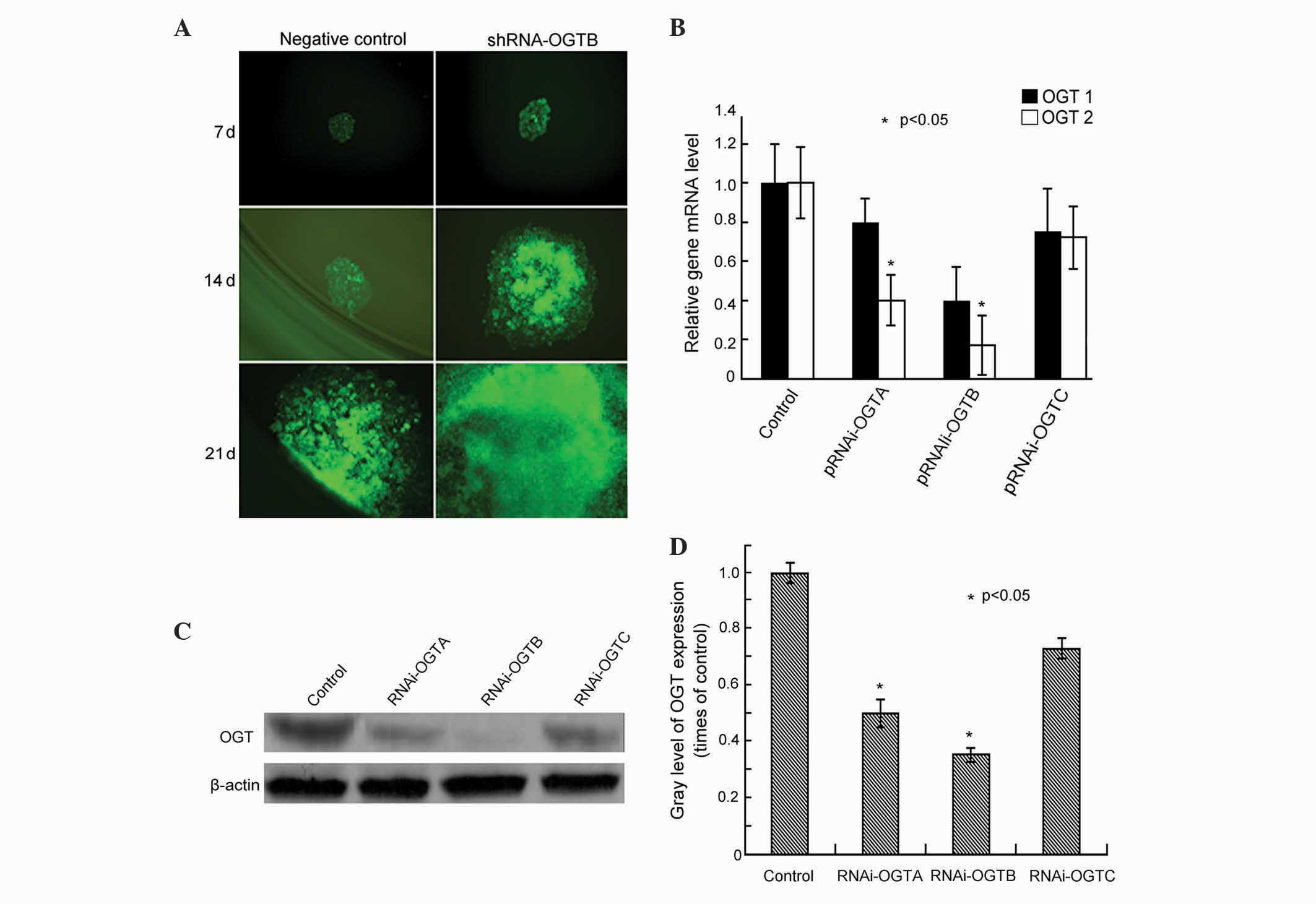
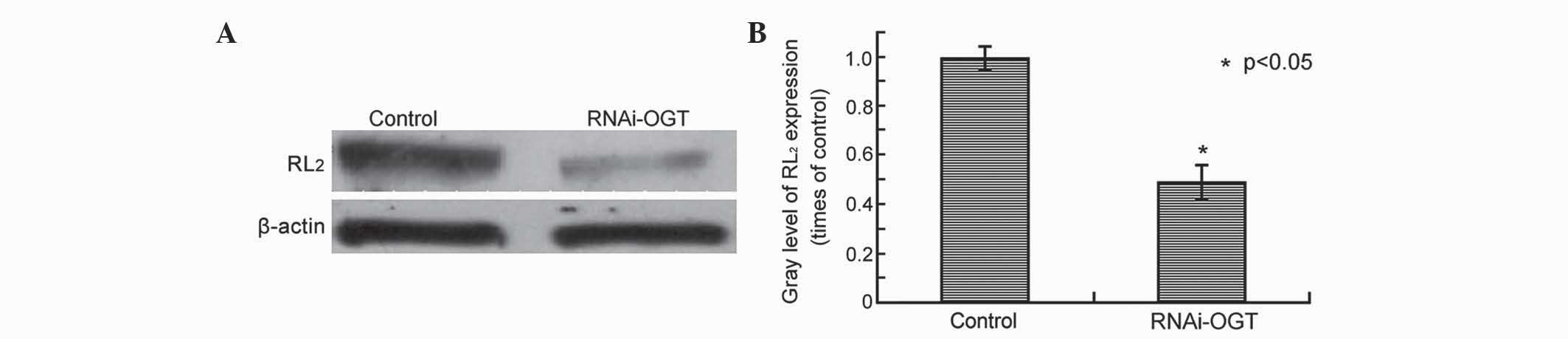
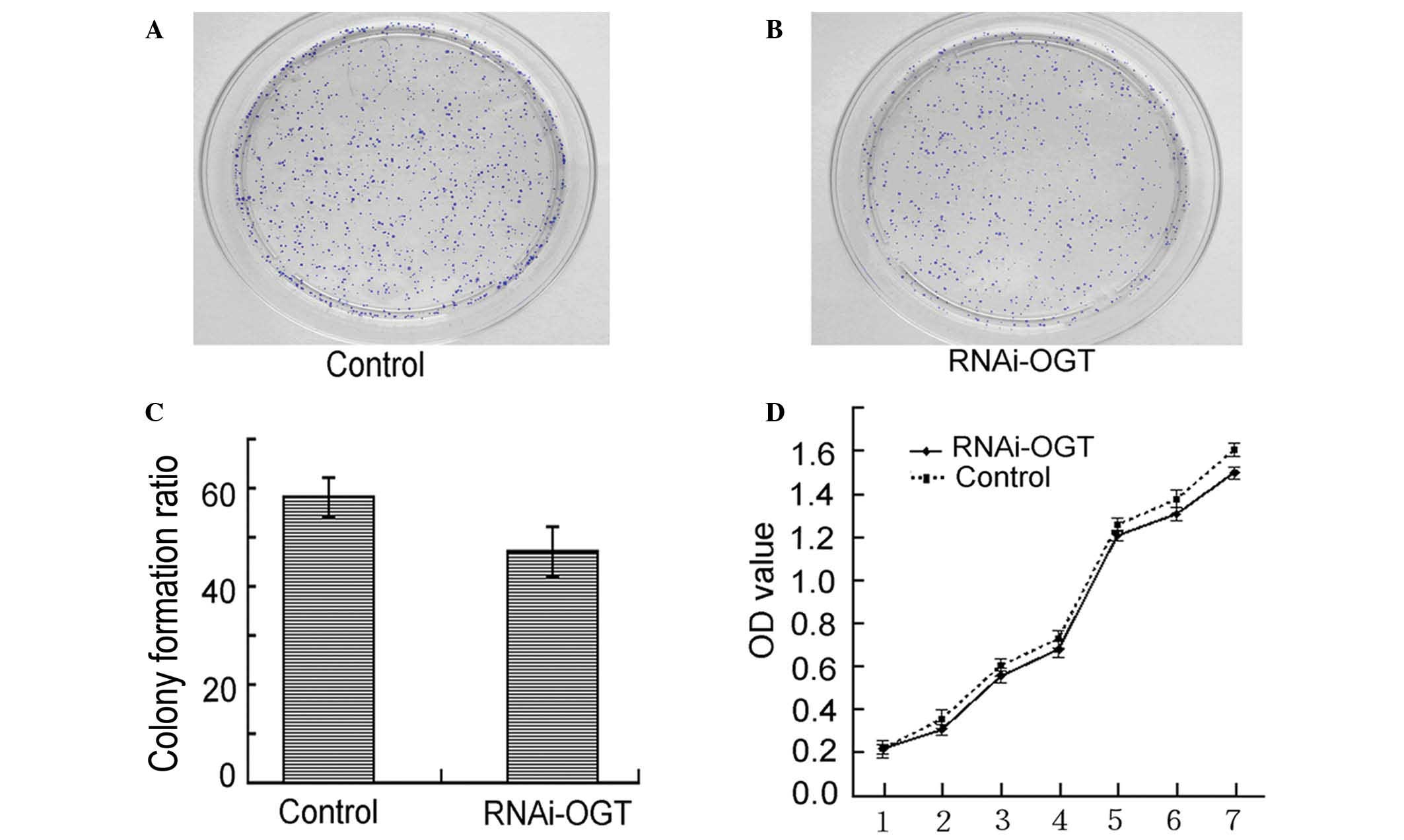
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pakzad R, Mohammadian-Hafshejani A,
Khosravi B, Soltani S, Pakzad I, Mohammadian M, Salehiniya H and
Momenimovahed Z: The incidence and mortality of esophageal cancer
and their relationship to development in Asia. Ann Transl Med.
4:292016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM, Bray FI and Devesa SS: Cancer
burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer. 37(Suppl
8): S4–S66. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Rensburg SJ: Esophageal cancer,
micronutrient malnutrition, and silica fragments. Lancet.
2:1098–1099. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network:
NCCN Guidelines and Clinical Resources: Guidelines for Treatment of
Cancer by Site. Version 7. 2015.
|
|
6
|
Brescia AA, Broderick SR, Crabtree TD,
Puri V, Musick JF, Bell JM, Kreisel D, Krupnick AS, Patterson GA
and Meyers BF: Adjuvant therapy for positive nodes after induction
therapy and resection of esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg.
101:200–210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L, Ma J, Han Y, Liu J, Zhou W, Hong
L and Fan D: Targeted therapy in esophageal cancer. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. Feb 19–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeidan Q and Hart GW: The intersections
between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: Implications for
multiple signaling pathways. J Cell Sci. 123:13–22. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marshall S, Bacote V and Traxinger RR:
Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced
desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine
biosynthesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem.
266:4706–4712. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Copeland RJ, Bullen JW and Hart GW:
Cross-talk between GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: Roles in
insulin resistance and glucose toxicity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 295:E17–E28. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Housley MP, Rodgers JT, Udeshi ND, Kelly
TJ, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Puigserver P and Hart GW: O-GlcNAc
regulates FoxO activation in response to glucose. J Biol Chem.
283:16283–16292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vosseller K, Wells L, Lane MD and Hart GW:
Elevated nucleocytoplasmic glycosylation by O-GlcNAc results in
insulin resistance associated with defects in Akt activation in
3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:5313–5318. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang JY, Gu JL, Shi JH, Liu F and Shen Q:
The inhibitory effect of OGT gene expression on the level of tau
phosphorylation. Prog Biochem Biophys. 36:346–352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vervoorts J, Lüscher-Firzlaff J and
Lüscher B: The ins and outs of MYC regulation by posttranslational
mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 281:34725–34729. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang WH, Kim JE, Nam HW, Ju JW, Kim HS,
Kim YS and Cho JW: Modification of p53 with O-linked
N-acetylglucosamine regulates p53 activity and stability. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:1074–1083. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barone BB, Yeh HC, Snyder CF, Peairs KS,
Stein KB, Derr RL, Wolff AC and Brancati FL: Long-term all-cause
mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama. 300:2754–2764. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Torres CR and Hart GW: Topography and
polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues
on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes. Evidence for O-linked
GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 259:3308–3317. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hart GW, Housley MP and Slawson C: Cycling
of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins.
Nature. 446:1017–1022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiao Z, Dang C, Zhou B, Li S, Zhang W,
Jiang J, Zhang J, Kong R and Ma Y: O-linked N-acetylglucosamine
transferase (OGT) is overexpressed and promotes O-linked protein
glycosylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Biomed Res.
26:268–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Love DC and Hanover JA: The hexosamine
signaling pathway: Deciphering the ‘O-GlcNAc code’. Sci STKE.
2005:re132005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haltiwanger RS, Holt GD and Hart GW:
Enzymatic addition of O-GlcNAc to nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins.
Identification of a uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine: Peptide
beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 265:2563–2568.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong DL and Hart GW: Purification and
characterization of an O-GlcNAc selective
N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase from rat spleen cytosol. J Biol
Chem. 269:19321–19330. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cetinbas N, Macauley MS, Stubbs KA,
Drapala R and Vocadlo DJ: Identification of Asp174 and Asp175 as
the key catalytic residues of human O-GlcNAcase by functional
analysis of site-directed mutants. Biochemistry. 45:3835–3844.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao Y, Wells L, Comer FI, Parker GJ and
Hart GW: Dynamic O-glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins:
Cloning and characterization of a neutral, cytosolic
beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from human brain. J Biol Chem.
276:9838–9845. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rogacka D, Piwkowska A, Jankowski M,
Kocbuch K, Dominiczak MH, Stepiński JK and Angielski S: Expression
of GFAT1 and OGT in podocytes: Transport of glucosamine and the
implications for glucose uptake into these cells. J Cell Physiol.
225:577–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mi W, Gu Y, Han C, Liu H, Fan Q, Zhang X,
Cong Q and Yu W: O-GlcNAcylation is a novel regulator of lung and
colon cancer malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812:514–519. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caldwell SA, Jackson SR, Shahriari KS,
Lynch TP, Sethi G, Walker S, Vosseller K and Reginato MJ: Nutrient
sensor O-GlcNAc transferase regulates breast cancer tumorigenesis
through targeting of the oncogenic transcription factor FoxM1.
Oncogene. 29:2831–2842. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ngoh GA, Facundo HT, Zafir A and Jones SP:
O-GlcNAc signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res.
107:171–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Slawson C, Copeland RJ and Hart GW:
O-GlcNAc signaling: A metabolic link between diabetes and cancer?
Trends Biochem Sci. 35:547–555. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gu Y, Mi W, Ge Y, Liu H, Fan Q, Han C,
Yang J, Han F, Lu X and Yu W: GlcNAcylation plays an essential role
in breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 70:6344–6351. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Akter H, Park M, Kwon OS, Song EJ, Park WS
and Kang MJ: Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by
neurotensin promotes cell invasion and migration through ERK
pathway in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:6053–6062. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song J, Wu C, Korpos E, Zhang X, Agrawal
SM, Wang Y, Faber C, Schäfers M, Körner H, Opdenakker G, et al:
Focal MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity at the blood-brain barrier promotes
chemokine-induced leukocyte migration. Cell Rep. 10:1040–1054.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Slawson C, Pidala J and Potter R:
Increased N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase activity in primary breast
carcinomas corresponds to a decrease in N-acetylglucosamine
containing proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1537:147–157. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang YZ, Wu JN, Sun RQ and Wu WX:
Expression of MMP-9 and MMP-9 mRNA in esophageal carcinoma its
correlation with antioncogene p53. Jiang Su Da Xue Xue Bao.
2:113–116. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Kneass ZT and Marchase RB: Protein
O-GlcNAc modulates motility-associated signaling intermediates in
neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 280:14579–14585. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hong S, Park KK, Magae J, Ando K, Lee TS,
Kwon TK, Kwak JY, Kim CH and Chang YC: Ascochlorin inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by suppressing activator
protein-1-mediated gene expression through the erk1/2 signaling
pathway: Inhibitory effects of ascochlorin on the invasion of renal
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 280:25202–25209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Westermarck J and Kähäri VM: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. Faseb J.
13:781–792. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|