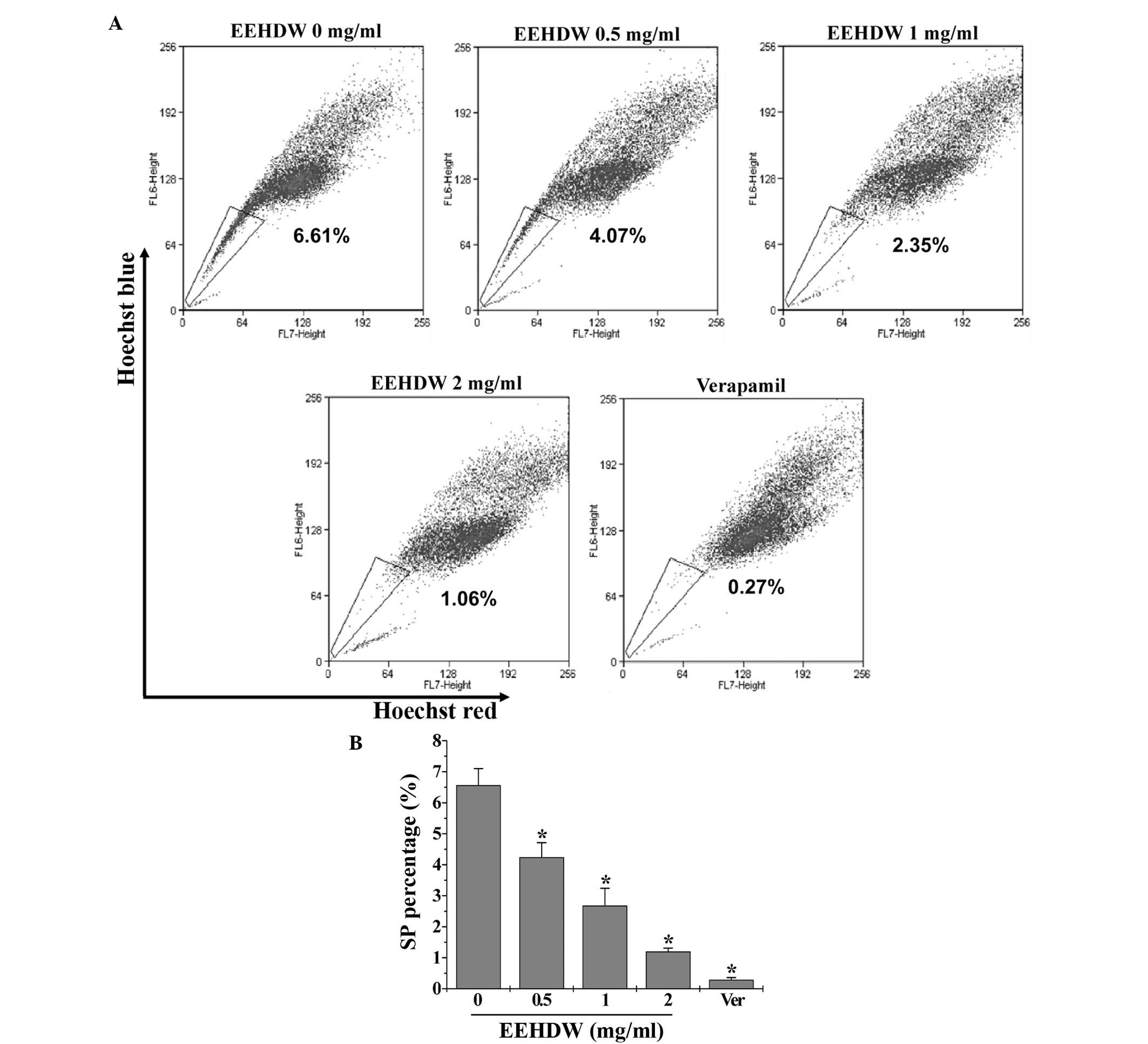
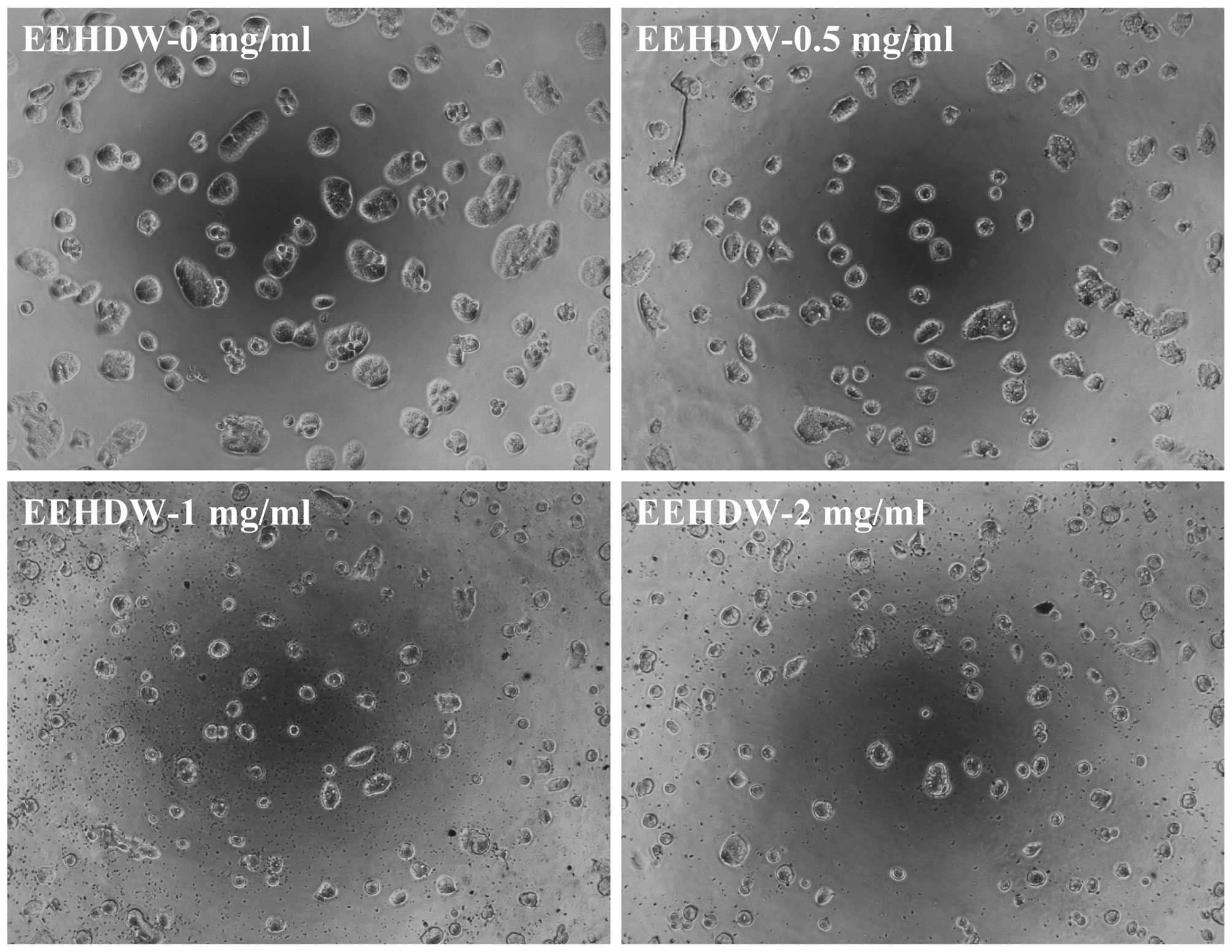
|
1
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Markowitz SD and Bertagnolli MM: Molecular
origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J
Med. 361:2449–2460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Montagnani F, Chiriatti A, Turrisi G,
Francini G and Fiorentini G: A systematic review of FOLFOXIRI
chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer: Improved efficacy at the cost of increased toxicity.
Colorectal Dis. 13:846–852. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lippman SM: The dilemma and promise of
cancer chemoprevention. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 3:5232006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Longley DB, Allen WL and Johnston PG: Drug
resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:184–196. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alison MR, Lin WR, Lim SM and Nicholson
LJ: Cancer stem cells: In the line of fire. Cancer Treat Rev.
38:589–598. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumour stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou BB, Zhang H, Damelin M, Geles KG,
Grindley JC and Dirks PB: Tumour-initiating cells: Challenges and
opportunities for anticancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:806–823. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin JM, Wei LH, Chen YQ, Liu XX, Hong ZF,
Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang induced apoptosis in human
colon cancer HT-29 cells is associated with regulation of the Bcl-2
family and activation of caspase 3. Chin J Integr Med. 17:685–690.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen AL, Hong F, Liu LY, Lin JM, Zhuang
QC, Hong ZF and Peng J: Effects of Pien Tze Huang on angiogenesis
in vivo and in vitro. Chin J Integr Med. 18:431–436.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Shen A, Sferra TJ,
Hong Z and Peng J: Ursolic acid promotes colorectal cancer cell
apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation via modulation of
multiple signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 43:1235–1243.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin J, Wei L, Shen A, Cai Q, Xu W, Li H,
Zhan Y, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract
suppresses Sonic hedgehog signaling leading to the inhibition of
colorectal cancer angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 42:651–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhan
Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa
Willd inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via
inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–6128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Chen X, Xu W, Hong
Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract
induces apoptosis via activation of the mitochondrion-dependent
pathway in human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 37:1331–1338.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei L, Chen P, Chen Y, Shen A, Chen H, Lin
W, Hong Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang suppresses the
stem-like side population in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Med Rep.
9:261–266. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B,
Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, Minden M, Paterson B, Caligiuri MA and
Dick JE: A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after
transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 367:645–648. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Efferth T: Stem cells, cancer stem-like
cells, and natural products. Planta Med. 78:935–942. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Golebiewska A, Brons NH, Bjerkvig R and
Niclou SP: Critical appraisal of the side population assay in stem
cell and cancer stem cell research. Cell Stem Cell. 8:136–147.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou S, Schuetz JD, Bunting KD, Colapietro
AM, Sampath J, Morris JJ, Lagutina I, Grosveld GC, Osawa M,
Nakauchi H and Sorrentino BP: The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is
expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular
determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat Med. 7:1028–1034.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Robey RW, To KK, Polgar O, Dohse M, Fetsch
P, Dean M and Bates SE: ABCG2: A perspective. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
61:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun T,
Schneider-Broussard R, Zhou J, Claypool K and Tang DG: Side
population is enriched in tumorigenic, stem-like cancer cells,
whereas ABCG2+ and ABCG2- cancer cells are similarly tumorigenic.
Cancer Res. 65:6207–6219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bleau AM, Hambardzumyan D, Ozawa T,
Fomchenko EI, Huse JT, Brennan CW and Holland EC: PTEN/PI3K/Akt
pathway regulates the side population phenotype and ABCG2 activity
in glioma tumor stem-like cells. Cell Stem Cell. 4:226–235. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chiba T, Kita K, Zheng YW, Yokosuka O,
Saisho H, Iwama A, Nakauchi H and Taniguchi H: Side population
purified from hepatocellular carcinoma cells harbors cancer stem
cell-like properties. Hepatology. 44:240–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haraguchi N, Utsunomiya T, Inoue H, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Barnard GF and Mori M: Characterization of a side
population of cancer cells from human gastrointestinal system. Stem
Cells. 24:506–513. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ho MM, Ng AV, Lam S and Hung JY: Side
population in human lung cancer cell lines and tumors is enriched
with stem-like cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:4827–4833. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Wnt signaling
and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:387–398. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Komiya Y and Habas R: Wnt signal
transduction pathways. Organogenesis. 4:68–75. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rao TP and Kühl M: An updated overview on
Wnt signaling pathways: A prelude for more. Circ Res.
106:1798–1806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|