|
1
|
Zeng ST, Guo L, Liu SK, Wang DH, Xi J,
Huang P, Liu DT, Gao JF, Feng J and Zhang L: Egg consumption is
associated with increased risk of ovarian cancer: Evidence from a
meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin Nutr. 34:635–641.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ahmed N, Abubaker K and Findlay JK:
Ovarian cancer stem cells: Molecular concepts and relevance as
therapeutic targets. Mol Aspects Med. 39:110–125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lengyel E: Ovarian cancer development and
metastasis. Am J Pathol. 177:1053–1064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kipps E, Tan DS and Kaye SB: Meeting the
challenge of ascites in ovarian cancer: New avenues for therapy and
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:273–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conic I, Dimov I, Tasic-Dimov D,
Djordjevic B and Stefanovic V: Ovarian epithelial cancer stem
cells. ScientificWorldJournal. 11:1243–1269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bristow RE, Puri I and Chi DS:
Cytoreductive surgery for recurrent ovarian cancer: A
meta-analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 112:265–274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forstner R, Sala E, Kinkel K and Spencer
JA: European Society of Urogenital Radiology: ESUR guidelines:
Ovarian cancer staging and follow-up. Eur Radiol. 20:2773–2780.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kumar Dhingra V, Kand P and Basu S: Impact
of FDG-PET and -PET/CT imaging in the clinical decision-making of
ovarian carcinoma: An evidence-based approach. Women's Health (Lond
Engl). 8:191–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
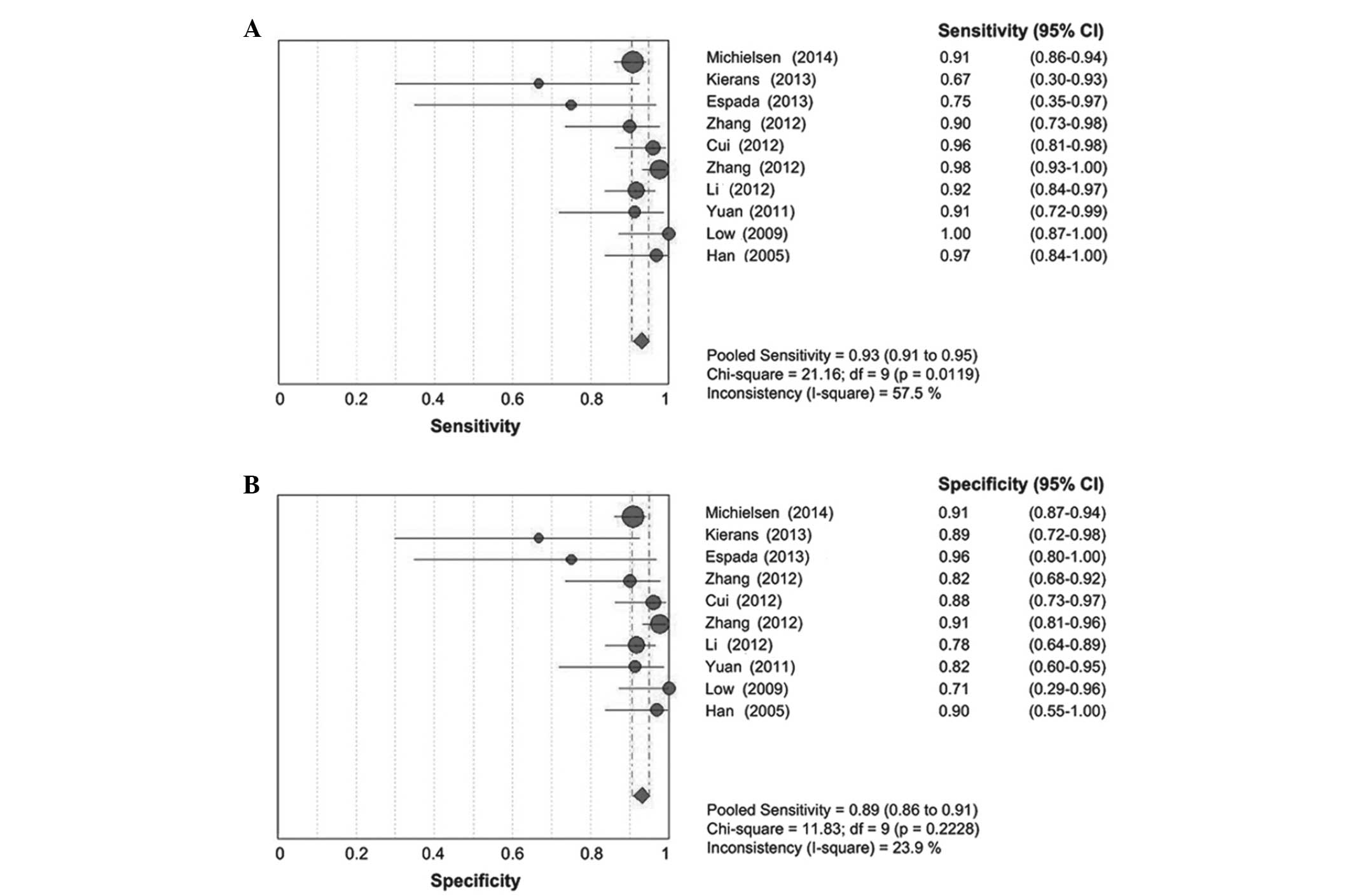
Michielsen K, Vergote I, de Op Beeck K,
Amant F, Leunen K, Moerman P, Deroose C, Souverijns G, Dymarkowski
S, De Keyzer F and Vandecaveye V: Whole-body MRI with
diffusion-weighted sequence for staging of patients with suspected
ovarian cancer: A clinical feasibility study in comparison to CT
and FDG-PET/CT. Eur Radiol. 24:889–901. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Low RN and Gurney J: Diffusion-weighted
MRI (DWI) in the oncology patient: Value of breathhold DWI compared
to unenhanced and gadolinium-enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging.
25:848–858. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Low RN, Sebrechts CP, Barone RM and Muller
W: Diffusion-weighted MRI of peritoneal tumors: Comparison with
conventional MRI and surgical and histopathologic findings - a
feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 193:461–470. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Espada M, Garcia-Flores JR, Jimenez M,
Alvarez-Moreno E, De Haro M, Gonzalez-Cortijo L, Hernandez-Cortes
G, Martinez-Vega V and De La Sainz Cuesta R: Diffusion-weighted
magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of intra-abdominal sites of
implants to predict likelihood of suboptimal cytoreductive surgery
in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 23:2636–2642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Low RN and Barone RM: Combined
diffusion-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced MRI can accurately
predict the peritoneal cancer index preoperatively in patients
being considered for cytoreductive surgical procedures. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19:1394–1401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
White NS, McDonald CR, Farid N, Kuperman
JM, Kesari S and Dale AM: Improved conspicuity and delineation of
high-grade primary and metastatic brain tumors using ‘restriction
spectrum imaging’: Quantitative comparison with high B-value DWI
and ADC. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 34:958–964. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Testa ML, Chojniak R, Sene LS, Damascena
AS, Guimarães MD, Szklaruk J and Marchiori E: Is DWI/ADC a useful
tool in the characterization of focal hepatic lesions suspected of
malignancy? PLoS One. 9:e1019442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li SP and Padhani AR: Tumor response
assessments with diffusion and perfusion MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging.
35:745–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Galea N, Cantisani V and Taouli B: Liver
lesion detection and characterization: Role of diffusion-weighted
imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 37:1260–1276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Soussan M, Des Guetz G, Barrau V,
Aflalo-Hazan V, Pop G, Mehanna Z, Rust E, Aparicio T, Douard R,
Benamouzig R, et al: Comparison of FDG-PET/CT and MR with
diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing peritoneal carcinomatosis
from gastrointestinal malignancy. Eur Radiol. 22:1479–1487. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Satoh Y, Ichikawa T, Motosugi U, Kimura K,
Sou H, Sano K and Araki T: Diagnosis of peritoneal dissemination:
Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT, diffusion-weighted MRI, and
contrast-enhanced MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196:447–453. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt
PM and Kleijnen J: The development of QUADAS: A tool for the
quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in
systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 3:252003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pfeiffer KA, McIver KL, Dowda M, Almeida
MJ and Pate RR: Validation and calibration of the Actical
accelerometer in preschool children. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
38:152–157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walter SD: Properties of the summary
receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test
data. Stat Med. 21:1237–1256. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P and Irwig L: The
performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size
effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was
assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:882–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kierans AS, Bennett GL, Mussi TC, Babb JS,
Rusinek H, Melamed J and Rosenkrantz AB: Characterization of
malignancy of adnexal lesions using ADC entropy: Comparison with
mean ADC and qualitative DWI assessment. J Magn Reson Imaging.
37:164–171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang P, Cui Y, Li W, Ren G, Chu C and Wu
X: Diagnostic accuracy of diffusion-weighted imaging with
conventional MR imaging for differentiating complex solid and
cystic ovarian tumors at 1.5T. World J Surg Oncol. 10:2372012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cui YF, Li WH, Zhu MJ, Wang DB, Zhang P,
Zhang ZY and Chu CT: Clinical application and research of diffusion
weighted MR imaging in complex ovarian tumors. Zhongguo Linchuang
Yixue Yingxiang Zazhi. 12(856): 859–869. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Zou S, Shen DH and Tong YX: The
value of MR diffusion-weighted imaging combined with serum CA125 in
the qualitative diagnosis of ovarian occupying lesion. Yixue
Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 8:1348–1353. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Li WH, Chu C, Cui Y, Zhang P and Zhu M:
Diffusion-weighted MRI: A useful technique to discriminate benign
versus malignant ovarian surface epithelial tumors with solid and
cystic components. Abdom Imaging. 37:897–903. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yuan XC, Wang X, Yao G, Zheng L and Hu Y:
The value of 3.0T MRI for the diagnosis of the ovarian tumor.
Shiyong Fangshexue Zazhi. 27(1695): 1698–1712. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Han DM, Yang XP, Wang HP and Li YX:
Comparative study of CT and MRI in the diagnosis of ovarian
neoplasms. Zhongguo Linchuang Yixue Yingxiang Zazhi. 16:441–443.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Ferlay J, Parkin DM and Steliarova-Foucher
E: Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008.
Eur J Cancer. 46:765–781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Decker G, Mürtz P, Gieseke J, Träber F,
Block W, Sprinkart AM, Leitzen C, Buchstab T, Lütter C, Schüller H,
et al: Intensity-modulated radiotherapy of the prostate: dynamic
ADC monitoring by DWI at 3.0 T. Radiother Oncol. 113:115–120. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ginat DT, Mangla R, Yeaney G, Johnson M
and Ekholm S: Diffusion-weighted imaging for differentiating benign
from malignant skull lesions and correlation with cell density. AJR
Am J Roentgenol. 198:W597–601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rechichi G, Galimberti S, Signorelli M,
Franzesi CT, Perego P, Valsecchi MG and Sironi S: Endometrial
cancer: Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient with tumor
grade, depth of myometrial invasion, and presence of lymph node
metastases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 197:256–262. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|