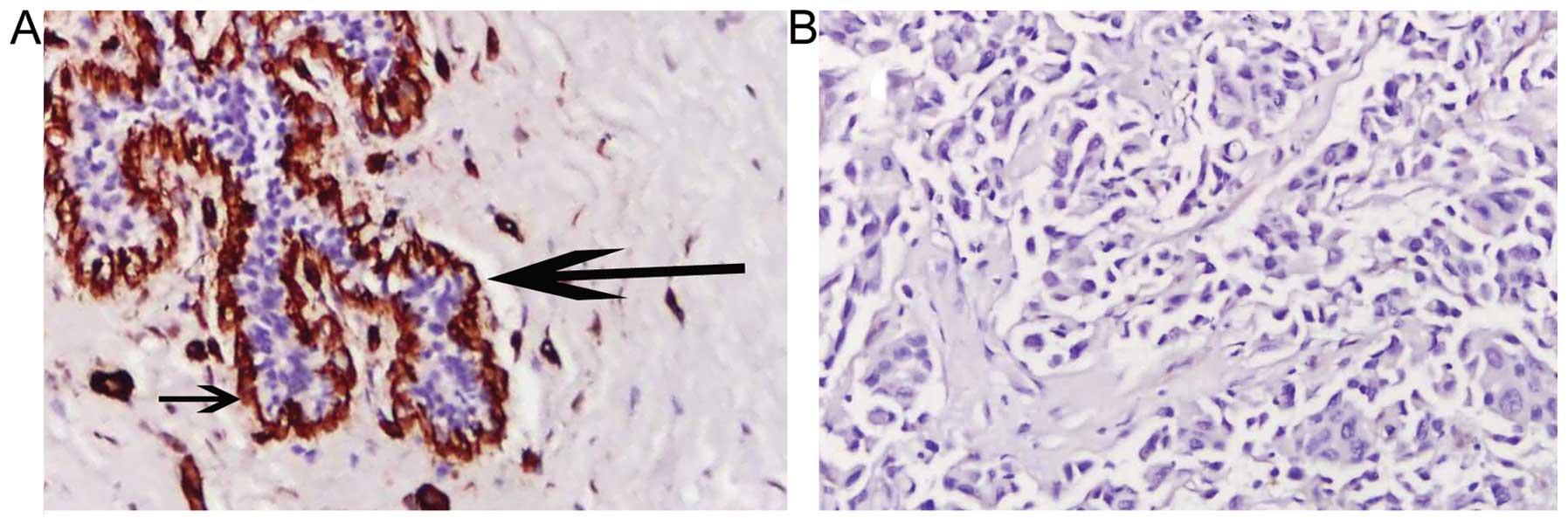
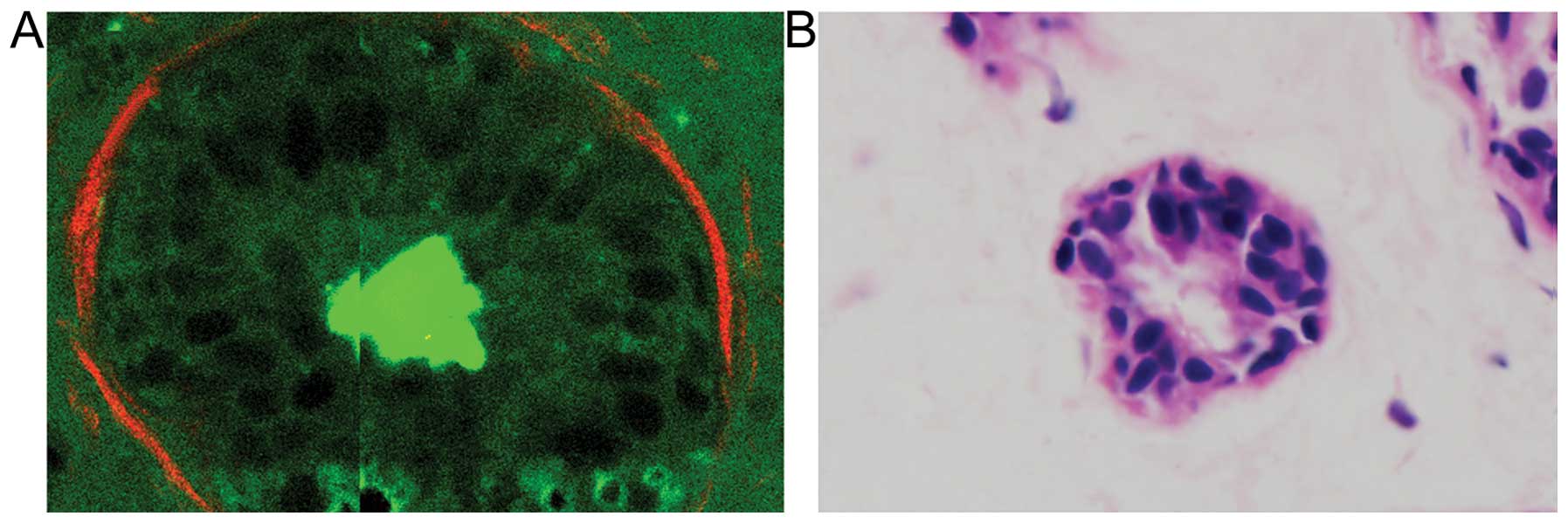
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eifel P, Axelson JA, Costa J, Crowley J,
Curran WJ Jr, Deshler A, Fulton S, Hendricks CB, Kemeny M,
Kornblith AB, et al: National institutes of health consensus
development conference statement: adjuvant therapy for breast
cancer, November 1–3, 2000. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:979–989. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abdelkarim M, Vintonenko N, Starzec A,
Robles A, Aubert J, Martin ML, Mourah S, Podgorniak MP,
Rodrigues-Ferreira S, Nahmias C, et al: Invading basement membrane
matrix is sufficient for MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells to develop
a stable in vivo metastatic phenotype. PLoS One. 6:e233342011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Plodinec M, Loparic M, Monnier CA,
Obermann EC, Zanetti-Dallenbach R, Oertle P, Hyotyla JT, Aebi U,
Bentires-Alj M, Lim RY and Schoenenberger CA: The nanomechanical
signature of breast cancer. Nat Nanotechnol. 7:757–765. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lipponen P, Ji H, Aaltomaa S and Syrjänen
K: Tumour vascularity and basement membrane structure in breast
cancer as related to tumour histology and prognosis. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 120:645–650. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gusterson BA, Warburton MJ, Mitchell D,
Ellison M, Neville AM and Rudland PS: Distribution of myoepithelial
cells and basement membrane proteins in the normal breast and in
benign and malignant breast diseases. Cancer Res. 42:4763–4770.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zipfel WR, Williams RM, Christie R,
Nikitin AY, Hyman BT and Webb WW: Live tissue intrinsic emission
microscopy using multiphoton-excited native fluorescence and second
harmonic generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7075–7080. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Campagnola PJ and Loew LM: Second-harmonic
imaging microscopy for visualizing biomolecular arrays in cells,
tissues and organisms. Nat Biotechnol. 21:1356–1360. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhuo S, Zheng L, Chen J, Xie S, Zhu X and
Jiang X: Depth-cumulated epithelial redox ratio and stromal
collagen quantity as quantitative intrinsic indicators for
differentiating normal, inflammatory and dysplastic epithelial
tissues. Appl Phys Lett. 97:1737012010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu X, Zhuo S, Chen J and Liu N: Real-time
in vivo imaging collagen in lymphedematous skin using multiphoton
microscopy. Scanning. 33:463–467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hovhannisyan VA, Su PJ and Dong CY:
Quantifying thermodynamics of collagen thermal denaturation by
second harmonic generation imaging. Appl Phys Lett. 94:2339022009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Matteini P, Ratto F, Rossi F, Cicchi R,
Stringari C, Kapsokalyvas D, Pavone FS and Pini R:
Photothermally-induced disordered patterns of corneal collagen
revealed by SHG imaging. Opt Express. 17:4868–4878. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhuo S, Chen J, Luo T and Zou D: Multimode
nonlinear optical imaging of the dermis in ex vivo human skin based
on the combination of multichannel mode and Lambda mode. Opt
Express. 14:7810–7820. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brown E, McKee T, diTomaso E, Pluen A,
Seed B, Boucher Y and Jain RK: Dynamic imaging of collagen and its
modulation in tumors in vivo using second harmonic generation. Nat
Med. 9:796–800. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Campagnola PJ and Dong CY: Second harmonic
generation microscopy: principles and applications to disease
diagnosis. Laser Photonics Rev. 5:13–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhuo S, Chen J, Wu G, Xie S, Zheng L,
Jiang X and Zhu X: Quantitatively linking collagen alteration and
epithelial tumor progression by second harmonic generation
microscopy. Appl Phys Lett. 96:2137042010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Place AE, Jin Huh S and Polyak K: The
microenvironment in breast cancer progression: biology and
implications for treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 13:2272011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Georgiou E, Theodossiou T and Hovhannisyan
V: Second and third optical harmonic generation in type I collagen,
by nanosecond laser irradiation, over a broad spectral region. Opt
Commun. 176:253–260. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bao H, Boussioutas A, Jeremy R, Russell S
and Gu M: Second harmonic generation imaging via nonlinear
endomicroscopy. Opt Express. 18:1255–1260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu Y, Xi J, Cobb MJ and Li X: Scanning
fiber-optic nonlinear endomicroscopy with miniature aspherical
compound lens and multimode fiber collector. Opt Lett. 34:953–955.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rivera DR, Brown CM, Ouzounov DG, Pavlova
I, Kobat D, Webb WW and Xu C: Compact and flexible raster scanning
multiphoton endoscope capable of imaging unstained tissue. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:17598–17603. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|