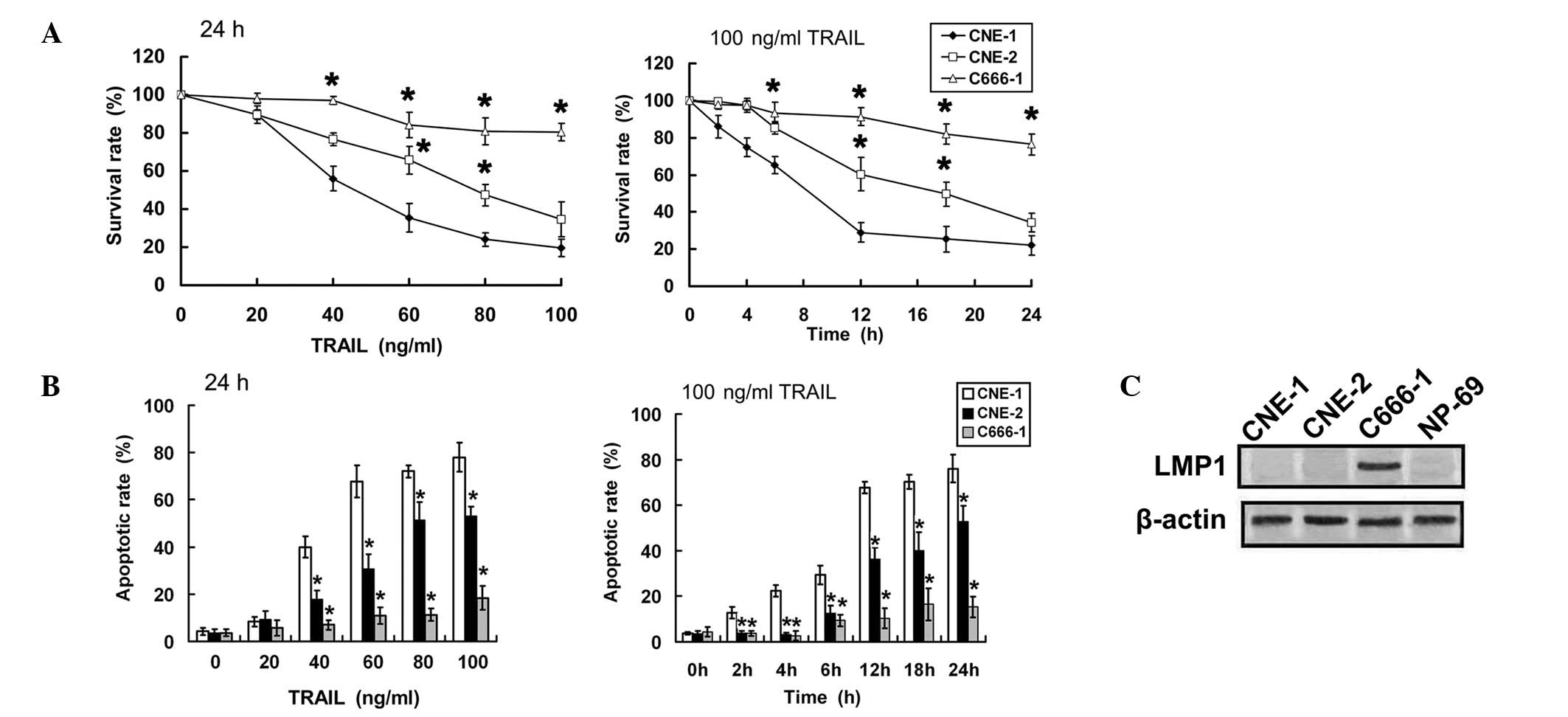
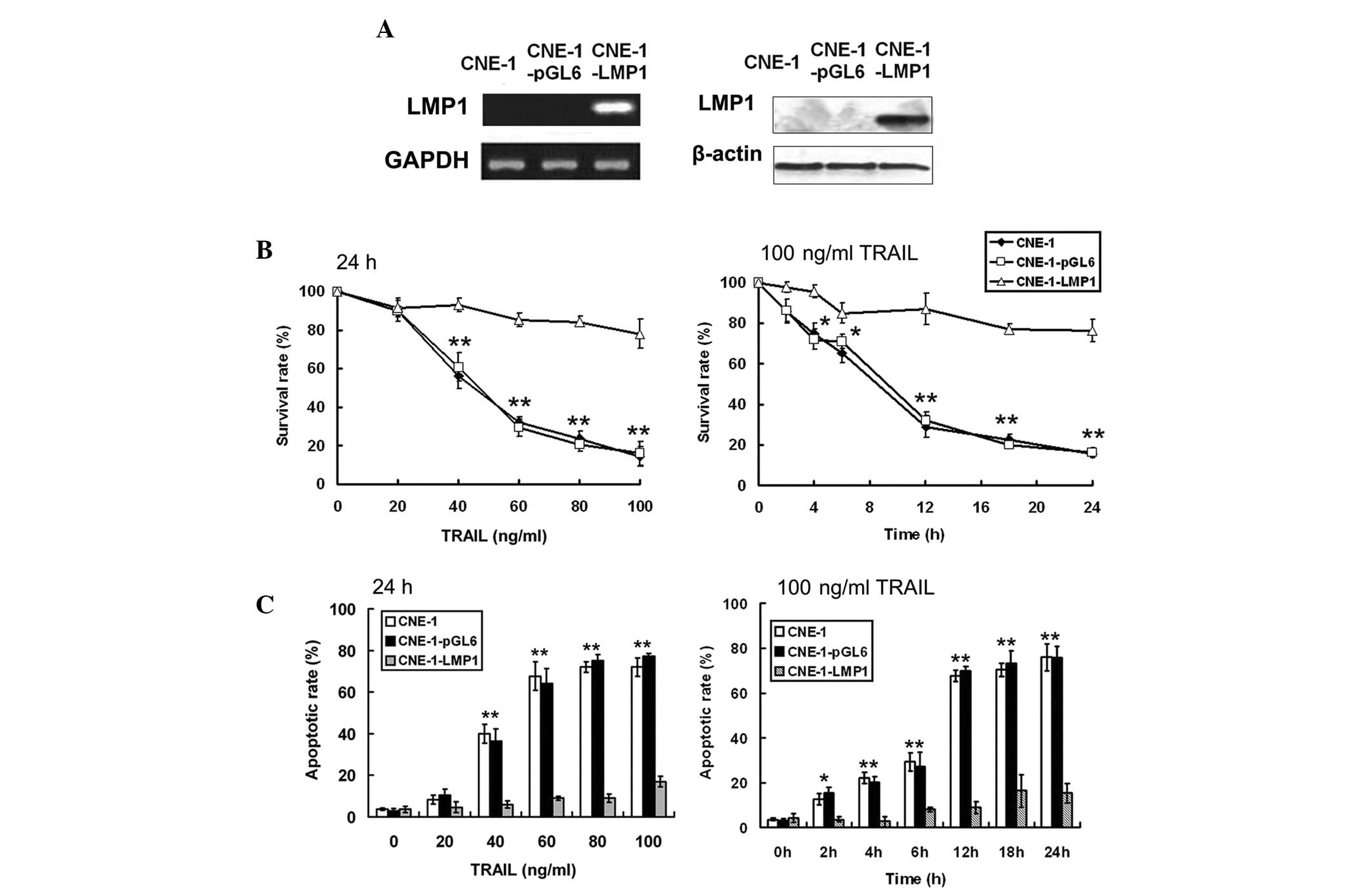
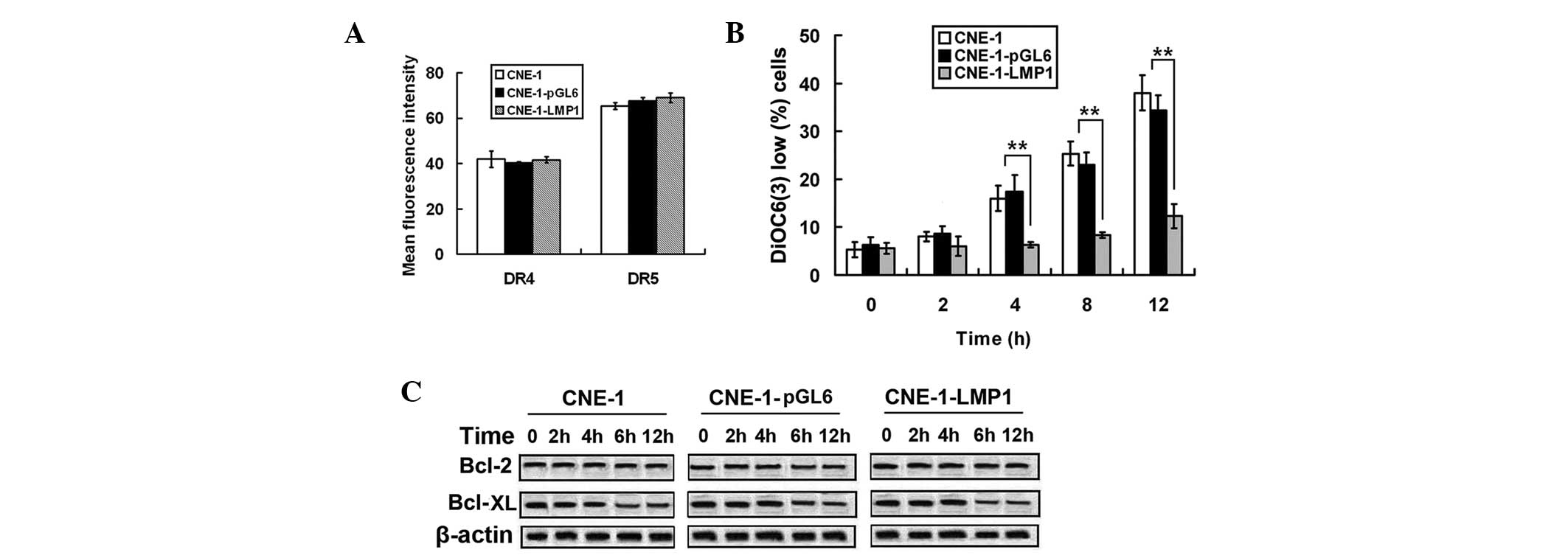
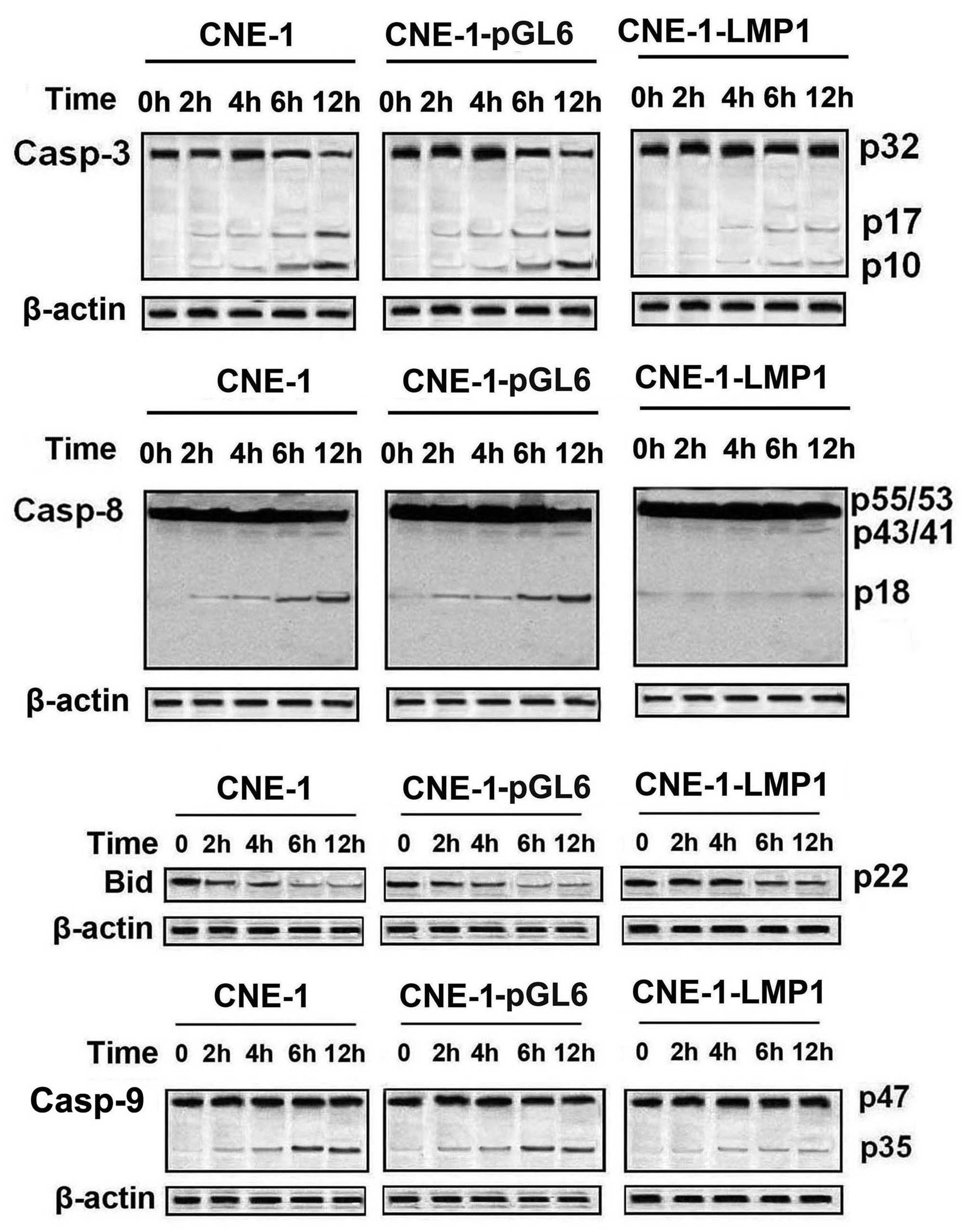
|
1
|
Walczak H and Krammer PH: The CD95
(APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems. Exp Cell Res.
256:58–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R and
Dixit VM: An antagonist decoy receptor and a death
domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science. 277:815–818. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl-2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siddiqui IA, Malik A, Adhami VM, Asim M,
Hafeez BB, Sarfaraz S and Mukhtar H: Green tea polyphenol EGCG
sensitizes human prostate carcinoma LNCaP cells to TRAIL-mediated
apoptosis and synergistically inhibits biomarkers associated with
angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene. 27:2055–2063. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamaguchi K, Uzzo RG, Pimkina J, Makhov P,
Golovine K, Crispen P and Kolenko VM: Methylseleninic acid
sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis.
Oncogene. 24:5868–5877. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang L, Mao Y, Liu L, Liang S, Chen Y, Sun
Y, Liao X, Lin A, Liu M, Li L and Ma J: The volume to be irradiated
during selective neck irradiation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Analysis of the spread patterns in lymph nodes by magnetic
resonance imaging. Cancer. 115:680–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Isobe K, Ito H, Shigematsu N, Kawada T,
Yasuda S, Hara R, Machida N, Takano H, Uchida Y, Uno T, et al:
Advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with chemotherapy and
radiotherapy: Distant metastasis and local recurrence. Int J Oncol.
12:1183–1187. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shao JY, Wang HY, Huang XM, Feng QS, Huang
P, Feng BJ, Huang LX, Yu XJ, Li JT, Hu LF, et al: Genome-wide
allelotype analysis of sporadic primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma
from southern China. Int J Oncol. 17:1267–1275. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Teng MS, Brandwein Gensler MS, Teixeira
MS, Martignetti JA and Duffey DC: A Study of TRAIL receptors in
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 131:407–412. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen LC, Chung IC, Hsueh C, Tsang NM, Chi
LM, Liang Y, Chen CC, Wang LJ and Chang YS: The antiapoptotic
protein, FLIP, is regulated by heterogeneous nuclear
ribonucleoprotein K and correlates with poor overall survival of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Cell Death Differ. 17:1463–1473.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ozören N, Fisher MJ, Kim K, Liu CX, Genin
A, Shifman Y, Dicker DT, Spinner NB, Lisitsyn NA and El-Deiry WS:
Homozygous deletion of the death receptor DR4 gene in a
nasopharyngeal cancer cell line is associated with TRAIL
resistance. Int J Oncol. 16:917–925. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li SS, Tang QL, Wang SH, Wang S and Yang
XM: Simultaneously targeting bcl-2 and Akt pathways sensitizes
nasopharyngeal carcinoma to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27:88–95.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kijima T, Kinukawa N, Gooding WE and Uno
M: Association of Epstein-Barr virus with tumor cell proliferation:
Clinical implication in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
18:479–485. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang YL, Lu JH, Cao L, Wu MH, Peng SP,
Zhou HD, Huang C, Yang YX, Zhou YH, Chen Q, et al: Genetic
variations of EBV-LMP1 from nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies:
Potential loss of T cell epitopes. Braz J Med Biol Res. 41:110–116.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Du CW, Wen BG, Li DR, Peng X, Hong CQ,
Chen JY, Lin ZZ, Hong X, Lin YC, Xie LX, et al: Arsenic trioxide
reduces the invasive and metastatic properties of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res. 39:677–685. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mei YP, Zhou JM, Wang Y, Huang H, Deng R,
Feng GK, Zeng YX and Zhu XF: Silencing of LMP1 induces cell cycle
arrest and enhances chemosensitivity through inhibition of AKT
signaling pathway in EBV-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Cell Cycle. 6:1379–1385. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dawson CW, Tramountanis G, Eliopoulos AG
and Young LS: Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)
activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway to promote
cell survival and induce actin filament remodeling. J Biol Chem.
278:3694–7304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Friboulet L, Pioche-Durieu C, Rodriguez S,
Valent A, Souquère S, Ripoche H, Khabir A, Tsao SW, Bosq J, Lo KW
and Busson P: Recurrent overexpression of c-IAP2 in EBV-associated
nasopharyngeal carcinomas: Critical role in resistance to Toll-like
receptor 3-mediated apoptosis. Neoplasia. 10:1183–1194. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hornle M, Peters N, Thayaparasingham B,
Vörsmann H, Kashkar H and Kulms D: Caspase-3 cleaves XIAP in a
positive feedback loop to sensitize melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis. Oncogene. 30:575–587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Snow AL, Vaysberg M, Krams SM and Martinez
OM: EBV B lymphoma cell lines from patients with post-transplant
lymphoproliferative disease are resistant to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis. Am J Transplant. 6:976–985. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hitt MM, Allday MJ, Hara T, Karran L,
Jones MD, Busson P, Tursz T, Ernberg I and Griffin BE: EBV gene
expression in an nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related tumor. EMBO J.
8:2639–2651. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang D, Liebowitz D and Kieff E: An EBV
membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms
established rodent cells. Cell. 43:831–840. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin SY, Tsang NM, Kao SC, Hsieh YL, Chen
YP, Tsai CS, Kuo TT, Hao SP, Chen IH and Hong JH: Presence of
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 gene in the
nasopharyngeal swabs from patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Head Neck. 23:194–200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang X, Sanmun D, Hu L, Fadeel B and
Ernberg I: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 promotes
cisplatin-induced caspase activation through JNK and NF-kappaB
signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360:263–268. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T,
Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and
Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to
mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pratt ZL, Zhang J and Sugden B: The latent
membrane protein 1 (LMP1) oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus can
simultaneously induce and inhibit apoptosis in B cells. J Virol.
86:4380–4393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee H, Seo SY, Tiwari I and Jang KL:
Epstein-Barr Virus latent membrane protein 1 overcomes all-trans
retinoic acid-induced apoptosis by inhibiting retinoic acid
receptor-β2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
423:313–318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
Enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vier J, Gerhard M, Wagner H and Häcker G:
Enhancement of death-receptor induced caspase-8-activation in the
death-inducing signalling complex by uncoupling of oxidative
phosphorylation. Mol Immunol. 40:661–670. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li SS, Yang S, Wang S, Yang XM, Tang QL
and Wang SH: Latent membrane protein 1 mediates the resistance of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by
activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
26:1573–1579. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Le Clorennec C, Ouk TS, Youlyouz-Marfak I,
Panteix S, Martin CC, Rastelli J, Adriaenssens E, Zimber-Strobl U,
Coll J, Feuillard J and Jayat-Vignoles C: Molecular basis of
cytotoxicity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1
(LMP1) in EBV latency III B cells: LMP1 induces type II
ligand-independent autoactivation of CD95/Fas with caspase
8-mediated apoptosis. J Virol. 82:6721–6733. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Y and Chen XY: Effect of Epstein-Barr
virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) on apoptosis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-1. Ai Zheng. 21:498–503.
2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei Y, Fan T and Yu M: Inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 40:278–288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS and Scott FL:
Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: Why XIAP is the black sheep
of the family. EMBO Rep. 7:988–994. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mizutani Y, Nakanishi H, Li YN, Matsubara
H, Yamamoto K, Sato N, Shiraishi T, Nakamura T, Mikami K, Okihara
K, et al: Overexpression of XIAP expression in renal cell carcinoma
predicts a worse prognosis. Int J Oncol. 30:919–925.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Checinska A, Hoogeland BS, Rodriguez JA,
Giaccone G and Kruyt FA: Role of XIAP in inhibiting
cisplatin-induced caspase activation in non-small cell lung cancer
cells: A small molecule Smac mimic sensitizes for
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis by enhancing caspase-3 activation.
Exp Cell Res. 313:1215–1224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ndozangue-Touriguine O, Sebbagh M, Mérino
D, Micheau O, Bertoglio J and Bréard J: A mitochondrial block and
expression of XIAP lead to resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis
during progression to metastasis of a colon carcinoma. Oncogene.
27:6012–6022. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K,
Salvesen GS and Reed JC: Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis
protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for
caspases. EMBO J. 18:5242–5251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Riedl SJ, Renatus M, Schwarzenbacher R,
Zhou Q, Sun C, Fesik SW, Liddington RC and Salvesen GS: Structural
basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell. 104:791–800.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ferreira KS, Kreutz C, Macnelly S, Neubert
K, Haber A, Bogyo M, Timmer J and Borner C: Caspase-3 feeds back on
caspase-8, Bid and XIAP in type I Fas signaling in primary mouse
hepatocytes. Apoptosis. 17:503–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Feresin GE, Tapia A, Sortino M, Zacchino
S, de Arias AR, Inchausti A, Yaluff G, Rodriguez J, Theoduloz C and
Schmeda-Hirschmann G: Bioactive alkyl phenols and embelin from
Oxalis erythrorhiza. J Ethnopharmacol. 88:241–247. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Xu L, Hu Z, Tomita
Y, Li P, Roller PP, Wang R, Fang X, Guo R, Zhang M, et al:
Discovery of embelin as a cell-permeable, small-molecular weight
inhibitor of XIAP through structure-based computational screening
of a traditional herbal medicine three-dimensional structure
database. J Med Chem. 47:2430–2440. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mori T, Doi R, Kida A, Nagai K, Kami K,
Ito D, Toyoda E, Kawaguchi Y and Uemoto S: Effect of the XIAP
inhibitor Embelin on TRAIL-induced apoptosis of pancreatic cancer
cells. J Surg Res. 142:281–286. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|