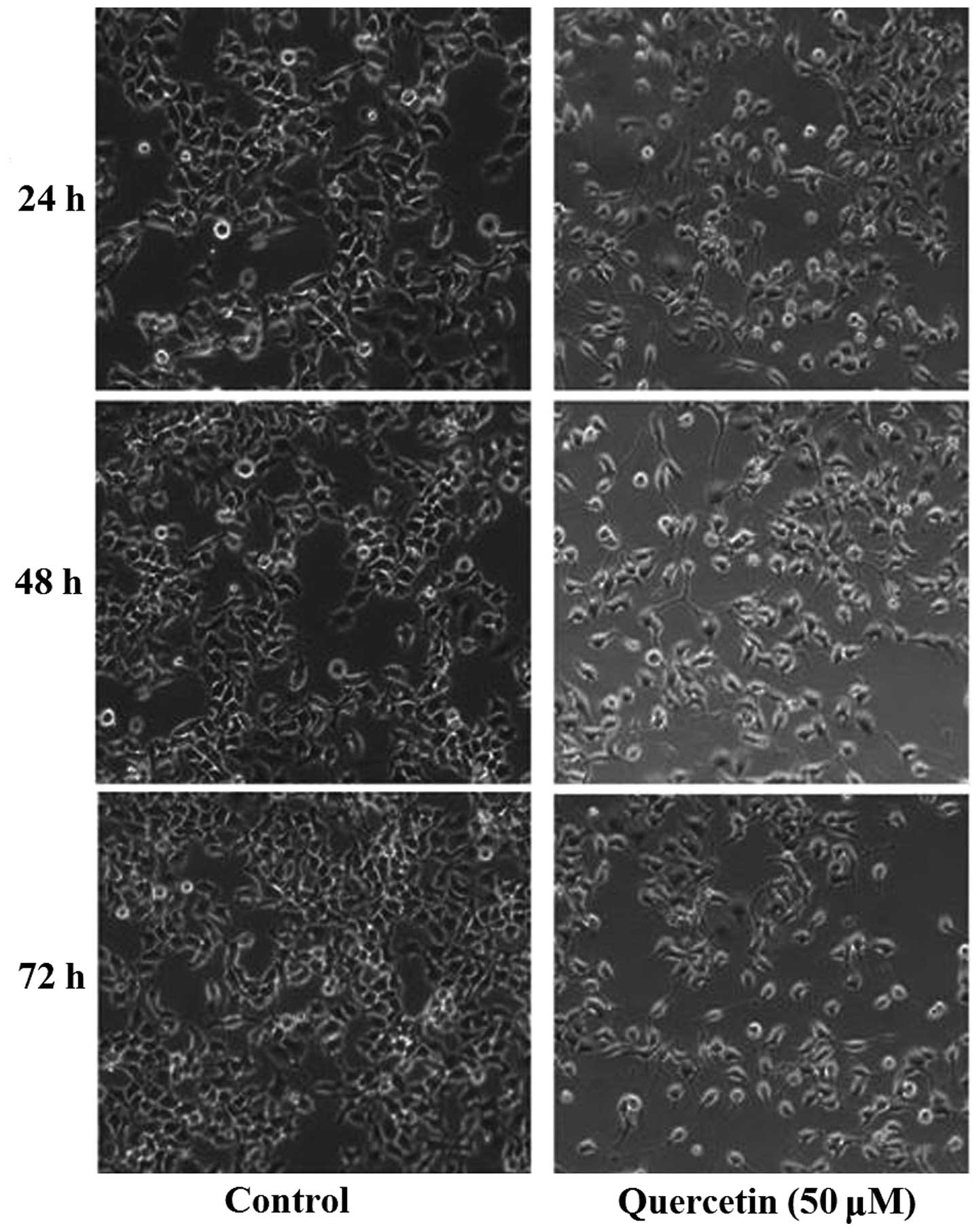
|
1
|
Linsalata M, Orlando A, Messa C, Refolo MG
and Russo F: Quercetin inhibits human DLD-1 colon cancer cell
growth and polyamine biosynthesis. Anticancer Res. 30:3501–3507.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guazelli CF, Fattori V, Colombo BB,
Georgetti SR, Vicentini FT, Casagrande R, Baracat MM and Verri WA
Jr: Quercetin-loaded microcapsules ameliorate experimental colitis
in mice by anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms. J Nat
Prod. 76:200–208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu H, Xue JX, Li X, Ao R and Lu Y:
Quercetin liposomes protect against radiation-induced pulmonary
injury in a murine model. Oncol Lett. 6:453–459. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chuang-Xin L, Wen-Yu W, Yao C, Xiao-Yan L
and Yun Z: Quercetin enhances the effects of
5-fluorouracil-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis of
esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting NF-κB. Oncol Lett. 4:775–778.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ong SE, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I,
Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A and Mann M: Stable isotope
labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and
accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics.
1:376–386. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou J, Liang S, Fang L, et al:
Quantitative proteomic analysis of HepG2 cells treated with
quercetin suggests IQGAP1 involved in quercetin-induced regulation
of cell proliferation and migration. OMICS. 13:93–103. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hengstschläger M, Braun K, Soucek T,
Miloloza A and Hengstschläger-Ottnad E: Cyclin-dependent kinases at
the G1-S transition of the mammalian cell cycle. Mutat Res.
436:1–9. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee MH and Yang HY: Regulators of G1
cyclin-dependent kinases and cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
22:435–449. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He Y, Franco OE, Jiang M, Williams K, Love
HD, Coleman IM, Nelson PS and Hayward SW: Tissue-specific
consequences of cyclin D1 overexpression in prostate cancer
progression. Cancer Res. 67:8188–8197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mylona E, Tzelepis K, Theohari I,
Giannopoulou I, Papadimitriou C and Nakopoulou L: Cyclin D1 in
invasive breast carcinoma: Favourable prognostic significance in
unselected patients and within subgroups with an aggressive
phenotype. Histopathology. 62:472–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El-Hafez AA, El Aaty Shawky A and Hasan B:
Cyclin D1 overexpression associates with favourable prognostic
factors in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 12:149–154.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weng CJ and Yen GC: Flavonoids, a
ubiquitous dietary phenolic subclass, exert extensive in vitro
anti-invasive and in vivo. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:323–351. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan J, Wong IL, Jiang T, Wang SW, Liu T,
Wen BJ, Chow LM and Wan Sheng B: Synthesis of methylated quercetin
derivatives and their reversal activities on P-gp- and
BCRP-mediated multidrug resistance tumour cells. Eur J Med Chem.
54:413–422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hernández-Ortega LD, Alcántar-Díaz BE,
Ruiz-Corro LA, Sandoval-Rodriguez A, Bueno-Topete M,
Armendariz-Borunda J and Salazar-Montes AM: Quercetin improves
hepatic fibrosis reducing hepatic stellate cells and regulating
pro-fibrogenic/anti-fibrogenic molecules balance. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 27:1865–1872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao P, Mao JM, Zhang SY, Zhou ZQ, Tan Y
and Zhang Y: Quercetin induces HepG2 cell apoptosis by inhibiting
fatty acid biosynthesis. Oncol Lett. 8:765–769. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Youn H, Jeong JC, Jeong YS, Kim EJ and Um
SJ: Quercetin potentiates apoptosis by inhibiting nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling in H460 lung cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:944–951. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Psahoulia FH, Moumtzi S, Roberts ML,
Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S and Pintzas A: Quercetin mediates
preferential degradation of oncogenic Ras and causes autophagy in
Ha-RAS-transformed human colon cells. Carcinogenesis. 28:1021–1031.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pratheeshkumar P, Budhraja A, Son YO, Wang
X, Zhang Z, Ding S, Wang L, Hitron A, Lee JC, Xu M, et al:
Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor
growth by targeting VEGFR-2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling
pathways. PLoS One. 7:e475162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen CY, Chi LM, Chi HC, Tsai MM, Tsai CY,
Tseng YH, Lin YH, Chen WJ, Huang YH and Lin KH: Stable isotope
labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-based
quantitative proteomics study of a thyroid hormone-regulated
secretome in human hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Proteomics.
11:M1112012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zanini C, Giribaldi G, Mandili G, Carta F,
Crescenzio N, Bisaro B, Doria A, Foglia L, di Montezemolo LC,
Timeus F and Turrini F: Inhibition of heat shock proteins (HSP)
expression by quercetin and differential doxorubicin sensitization
in neuroblastoma and Ewing's sarcoma cell lines. J Neurochem.
103:1344–1354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tashiro E, Tsuchiya A and Imoto M:
Functions of cyclin D1 as an oncogene and regulation of cyclin D1
expression. Cancer Sci. 98:629–635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saini SS and Klein MA: Targeting cyclin D1
in non-small cell lung cancer and mesothelioma cells by antisense
oligonucleotides. Anticancer Res. 31:3683–3690. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shih LC, Tsai CW, Tsai MH, Tsou YA, Chang
WS, Li FJ, Lee MH and Bau DT: Association of cyclin D1 genotypes
with nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk. Anticancer Res. 32:1093–1098.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jares P, Campo E, Pinyol M, Bosch F,
Miquel R, Fernandez PL, Sanchez-Beato M, Soler F, Perez-Losada A,
Nayach I, et al: Expression of retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) in
mantle cell lymphomas. Correlation with cyclin D1 (PRAD1/CCND1)
mRNA levels and proliferative activity. Am J Pathol. 148:1591–1600.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Coupland SE, Bechrakis N, Schüler A,
Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel M, Bornfeld N and Stein H: Expression
patterns of cyclin D1 and related proteins regulating G1-S phase
transition in uveal melanoma and retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol.
82:961–970. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi EJ, Bae SM and Ahn WS:
Antiproliferative effects of quercetin through cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells. Arch Pharm
Res. 31:1281–1285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Priyadarsini Vidya R, Senthil Murugan R,
Maitreyi S, Ramalingam K, Karunagaran D and Nagini S: The flavonoid
quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53
induction and NF-κB inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:84–91. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong JH, An JY, Kwon YT, Rhee JG and Lee
YJ: Effects of low dose quercetin: Cancer cell-specific inhibition
of cell cycle progression. J Cell Biochem. 106:73–82. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamak A, Temsah R, Maharsy W, Caron S,
Paradis P, Aries A and Nemer M: Cyclin D2 rescues size and function
of GATA4 haplo-insufficient hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 303:H1057–H1066. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jena N, Deng M, Sicinska E, Sicinski P and
Daley GQ: Critical role for cyclin D2 in BCR/ABL-induced
proliferation of hematopoietic cells. Cancer Res. 62:535–541.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takano Y, Kato Y, Masuda M, Ohshima Y and
Okayasu I: Cyclin D2, but not cyclin D1, overexpression closely
correlates with gastric cancer progression and prognosis. J Pathol.
189:194–200. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Filipits M, Jaeger U, Pohl G, Stranzl T,
Simonitsch I, Kaider A, Skrabs C and Pirker R: Cyclin D3 is a
predictive and prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 8:729–733. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
García-Morales P, Hernando E,
Carrasco-García E, Menéndez-Gutierrez MP, Saceda M and
Martínez-Lacaci I: Cyclin D3 is down-regulated by rapamycin in
HER-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:2172–2181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Q, Sakamoto K, Liu C, Triplett AA,
Lin WC, Rui H and Wagner KU: Cyclin D3 compensates for the loss of
cyclin D1 during ErbB2-induced mammary tumor initiation and
progression. Cancer Res. 71:7513–7524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akli S, Van Pelt CS, Bui T, Multani AS,
Chang S, Johnson D, Tucker S and Keyomarsi K: Overexpression of the
low molecular weight cyclin E in transgenic mice induces metastatic
mammary carcinomas through the disruption of the ARF-p53 pathway.
Cancer Res. 67:7212–7222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|