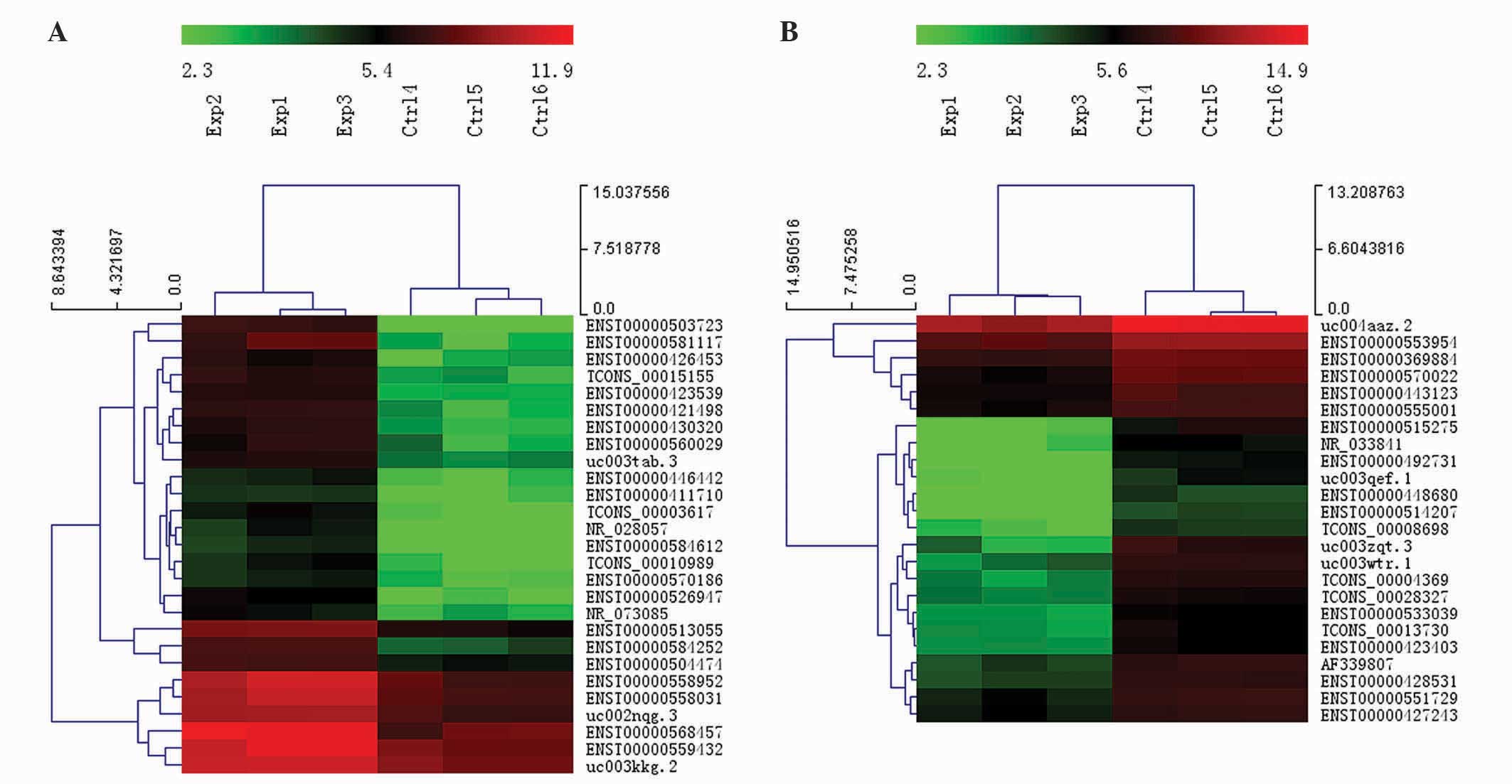
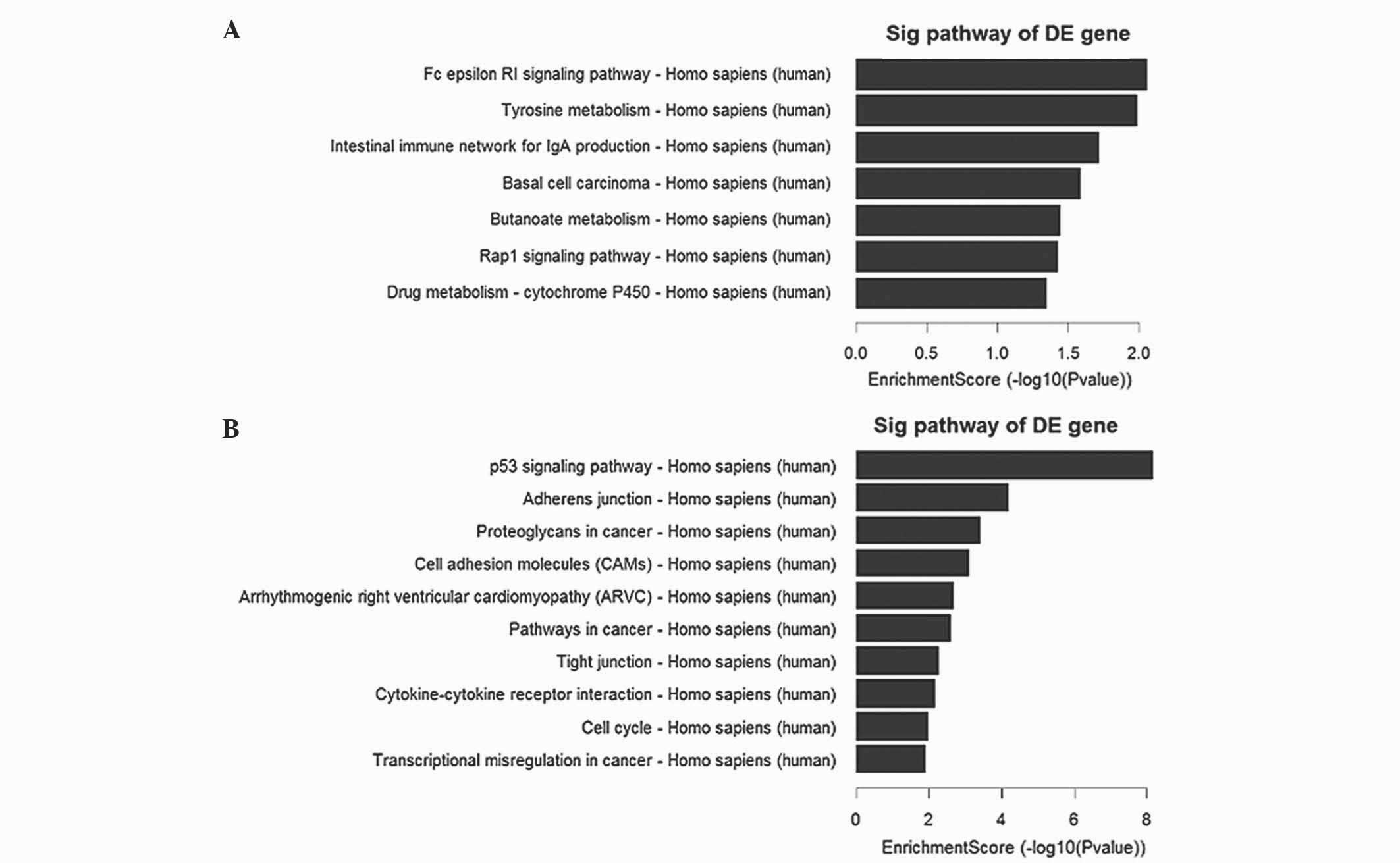
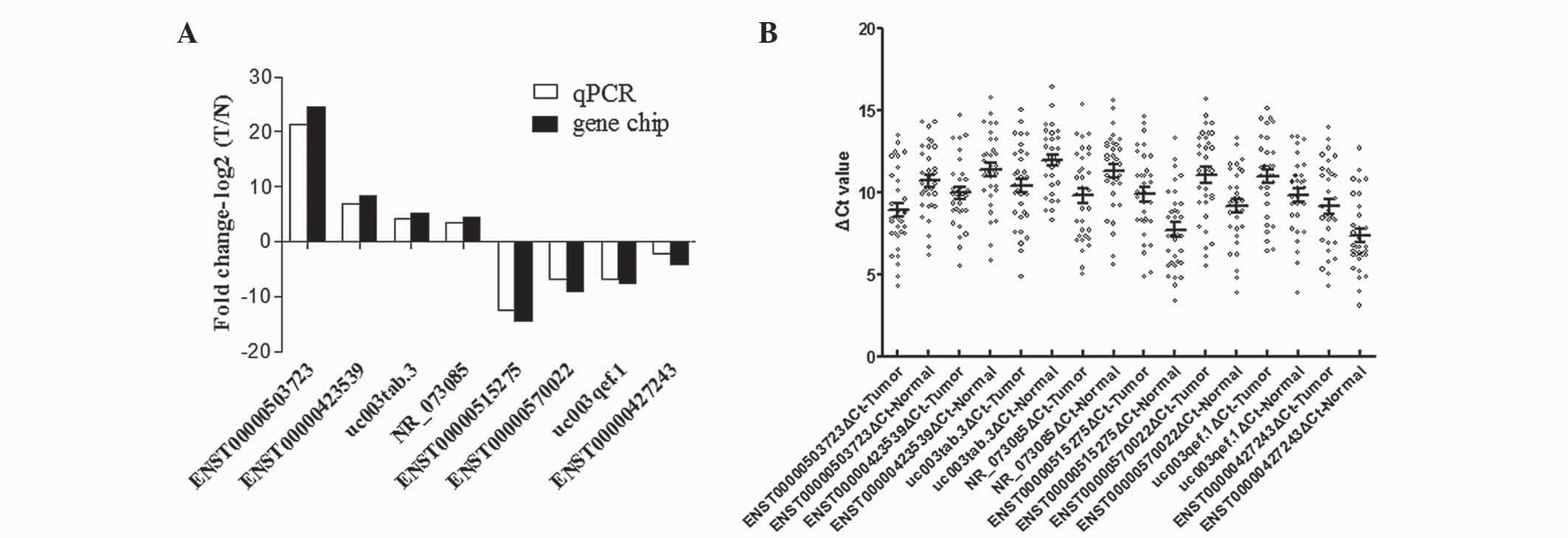
|
1
|
La Vecchia C, Malvezzi M, Bosetti C,
Garavello W, Bertuccio P, Levi F and Negri E: Thyroid cancer
mortality and incidence: A global overview. Int J Cancer.
136:2187–2195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang L, Zheng R, Wang N, Zhang S and Chen
W: Analysis of incidence and mortality of thyroid cancer in China,
2010. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 48:663–668. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pelizzo MR, Boschin Merante I, Toniato A,
Pagetta C, Casal Ide E, Mian C and Rubello D: Diagnosis, treatment,
prognostic factors and long-term outcome in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Minerva Endocrinol. 33:359–379. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Richards ML: Familial syndromes associated
with thyroid cancer in the era of personalized medicine. Thyroid.
20:707–713. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galleani J, Miranda C, Pierotti MA and
Greco A: H2AX phosphorylation and kinetics of radiation-induced DNA
double strand break repair in human primary thyrocytes. Thyroid.
19:257–264. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leux C, Truong T, Petit C,
Baron-Dubourdieu D and Guénel P: Family history of malignant and
benign thyroid diseases and risk of thyroid cancer: A
population-based case-control study in New Caledonia. Cancer Causes
Control. 23:745–755. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Santos JC, Bastos AU, Cerutti JM and
Ribeiro ML: Correlation of MLH1 and MGMT expression and promoter
methylation with genomic instability in patients with thyroid
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 13:792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Neta G, Brenner AV, Sturgis EM, Pfeiffer
RM, Hutchinson AA, Aschebrook-Kilfoy B, Yeager M, Xu L, Wheeler W,
Abend M, et al: Common genetic variants related to genomic
integrity and risk of papillary thyroid cancer. Carcinogenesis.
32:1231–1237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M and
Mattick JS: Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. J Pathol.
220:126–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A,
Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F,
et al: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature.
489:101–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jendrzejewski J, He H, Radomska HS, Li W,
Tomsic J, Liyanarachchi S, Davuluri RV, Nagy R and de la Chapelle
A: The polymorphism rs944289 predisposes to papillary thyroid
carcinoma through a large intergenic noncoding RNA gene of tumor
suppressor type. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:8646–8651. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Guo Q, Zhao Y, Chen J, Wang S, Hu
J and Sun Y: BRAF-activated long non-coding RNA contributes to cell
proliferation and activates autophagy in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 8:1947–1952. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dinger ME, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Crowe ML,
Grimmond SM and Mattick JS: NRED: A database of long noncoding RNA
expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database Issue): D122–D126. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu M, Chen Q, Liu X, Sun Q, Zhao X, Deng
R, Wang Y, Huang J, Xu M, Yan J and Yu J: lncRNA H19/miR-675 axis
represses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting TGFBI. FEBS J.
281:3766–3775. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ørom UA, Derrien T, Beringer M, Gumireddy
K, Gardini A, Bussotti G, Lai F, Zytnicki M, Notredame C, Huang Q,
et al: Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human
cells. Cell. 143:46–58. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Faghihi MA and Wahlestedt C: Regulatory
roles of natural antisense transcripts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:637–643. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cabili MN, Trapnell C, Goff L, Koziol M,
Tazon-Vega B, Regev A and Rinn JL: Integrative annotation of human
large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and
specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 25:1915–1927. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu G, Chen J, Pan Q, Huang K, Pan J, Zhang
W, Chen J, Yu F, Zhou T and Wang Y: Long noncoding RNA expression
profiles of lung adenocarcinoma ascertained by microarray analysis.
PLoS One. 9:e1040442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kweon SS, Shin MH, Chung IJ, Kim YJ and
Choi JS: Thyroid cancer is the most common cancer in women, based
on the data from population-based cancer registries, South Korea.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 43:1039–1046. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui H, Xie N, Tan Z, Banerjee S,
Thannickal VJ, Abraham E and Liu G: The human long noncoding RNA
lnc-IL7R regulates the inflammatory response. Eur J Immunol.
44:2085–2095. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bhan A, Hussain I, Ansari KI, Bobzean SA,
Perrotti LI and Mandal SS: Bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol
exposure induces the expression of breast cancer associated long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR in vitro and in vivo. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 141:160–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard MR, Hedge
VL, Farzaneh F and Williams GT: GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA,
controls apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene.
28:195–208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wallez Y, Riedl SJ and Pasquale EB:
Association of the breast cancer antiestrogen resistance protein 1
(BCAR1) and BCAR3 scaffolding proteins in cell signaling and
antiestrogen resistance. J Biol Chem. 289:10431–10444. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schrecengost RS, Riggins RB, Thomas KS,
Guerrero MS and Bouton AH: Breast cancer antiestrogen resistance-3
expression regulates breast cancer cell migration through promotion
of p130Cas membrane localization and membrane ruffling. Cancer Res.
67:6174–6182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wilson AL, Schrecengost RS, Guerrero MS,
Thomas KS and Bouton AH: Breast cancer antiestrogen resistance 3
(BCAR3) promotes cell motility by regulating actin cytoskeletal and
adhesion remodeling in invasive breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e656782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo J, Canaff L, Rajadurai C, Fils-Aimé N,
Tian J, Dai M, Korah J, Villatoro M, Park M, Ali S and Lebrun JJ:
Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance-3 inhibits transforming
growth factor-β/Smad signaling and associates with favorable breast
cancer disease outcomes. Breast Cancer Res. 16:4762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wilson IM, Vucic EA, Enfield KS, Thu KL,
Zhang YA, Chari R, Lockwood WW, Radulovich N, Starczynowski DT,
Banáth JP, et al: EYA4 is inactivated biallelically at a high
frequency in sporadic lung cancer and is associated with familial
lung cancer risk. Oncogene. 33:4464–4473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lo PH, Ko JM, Yu ZY, Law S, Wang LD, Li
JL, Srivastava G, Tsao SW, Stanbridge EJ and Lung ML: The LIM
domain protein, CRIP2, promotes apoptosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 316:39–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheung AK, Ko JM, Lung HL, Chan KW,
Stanbridge EJ, Zabarovsky E, Tokino T, Kashima L, Suzuki T, Kwong
DL, et al: Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 2 (CRIP2) acts as a
repressor of NF-kappaB-mediated proangiogenic cytokine
transcription to suppress tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:8390–8395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lan X, Zhang H, Wang Z, Dong W, Sun W,
Shao L, Zhang T and Zhang D: Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding
RNA expression profile in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Gene.
569:109–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McFadden DG, Vernon A, Santiago PM,
Martinez-McFaline R, Bhutkar A, Crowley DM, McMahon M, Sadow PM and
Jacks T: p53 constrains progression to anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
in a Braf-mutant mouse model of papillary thyroid cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:E1600–E1609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liotti F, Visciano C and Melillo RM:
Inflammation in thyroid oncogenesis. Am J Cancer Res. 2:286–297.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiao Y, Jin J, Chang M, Chang JH, Hu H,
Zhou X, Brittain GC, Stansberg C, Torkildsen Ø, Wang X, et al:
Peli1 promotes microglia-mediated CNS inflammation by regulating
Traf3 degradation. Nat Med. 19:595–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marquez RT, Wendlandt E, Galle CS, Keck K
and McCaffrey AP: MicroRNA-21 is upregulated during the
proliferative phase of liver regeneration, targets Pellino-1, and
inhibits NF-kappaB signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 298:G535–G541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang Y, Liao D, Pan L, Ye R, Li X, Wang
S, Ye C and Chen L: Expressions of miRNAs in papillary thyroid
carcinoma and their associations with the BRAFV600E mutation. Eur J
Endocrinol. 168:675–681. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|