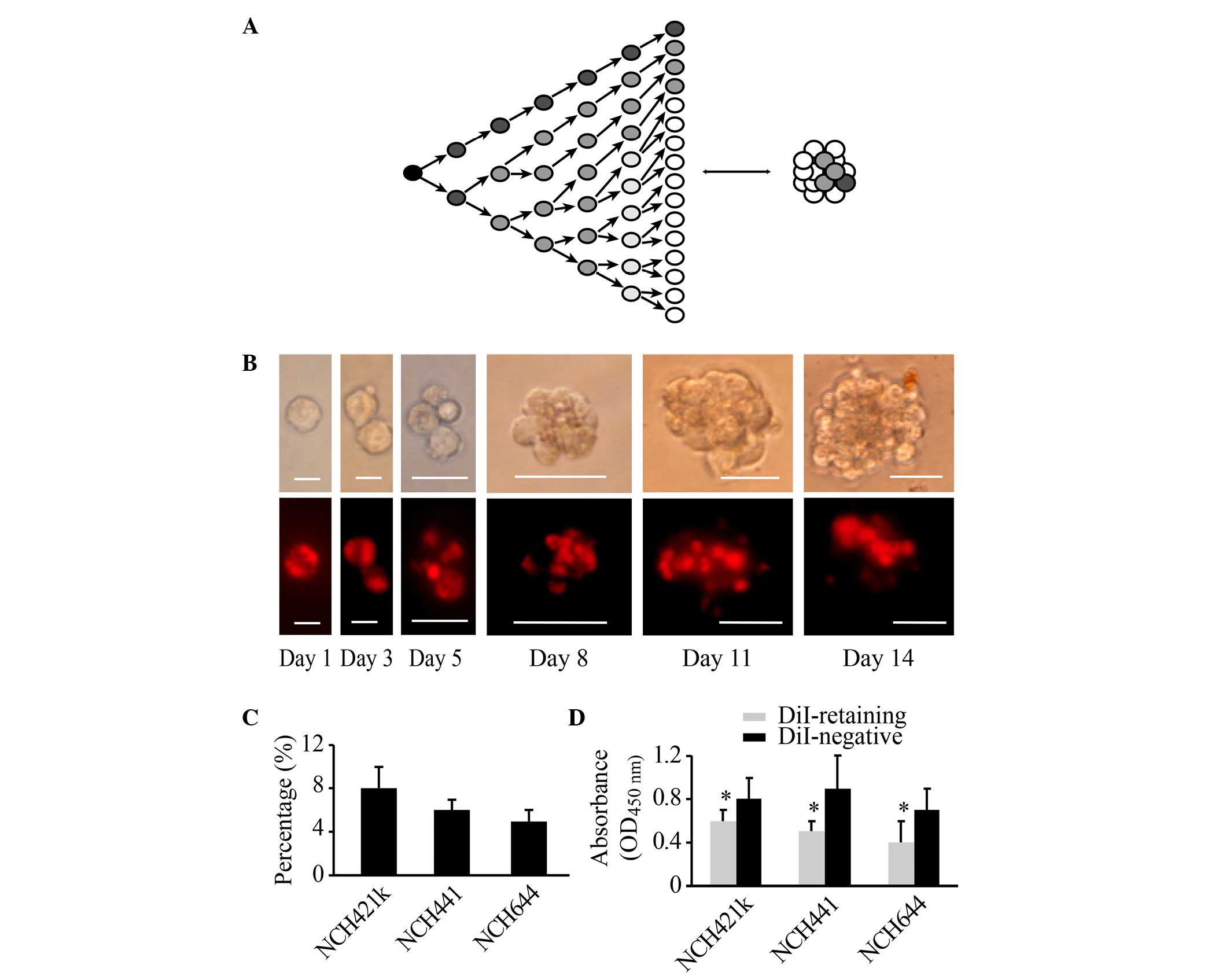
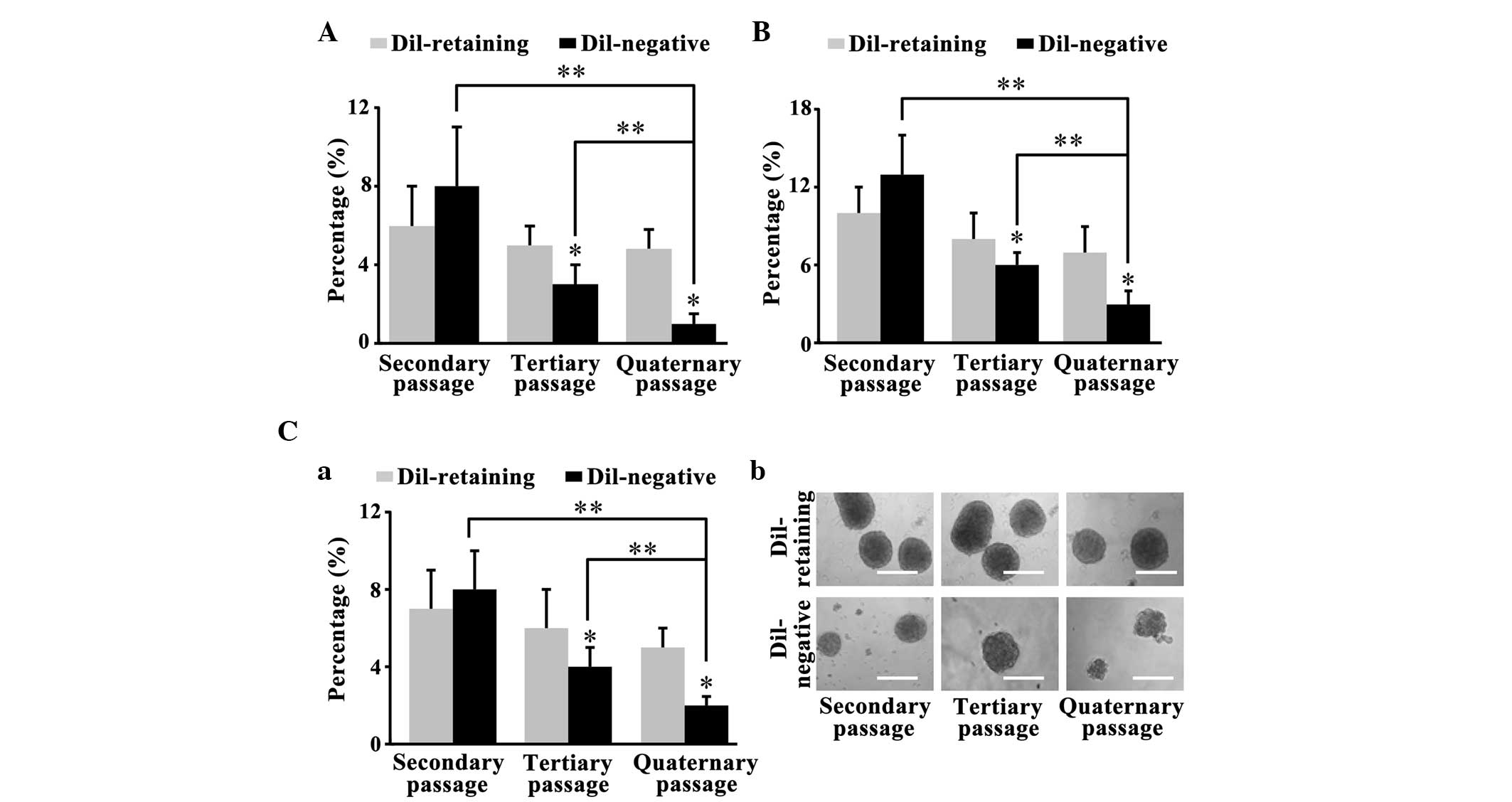
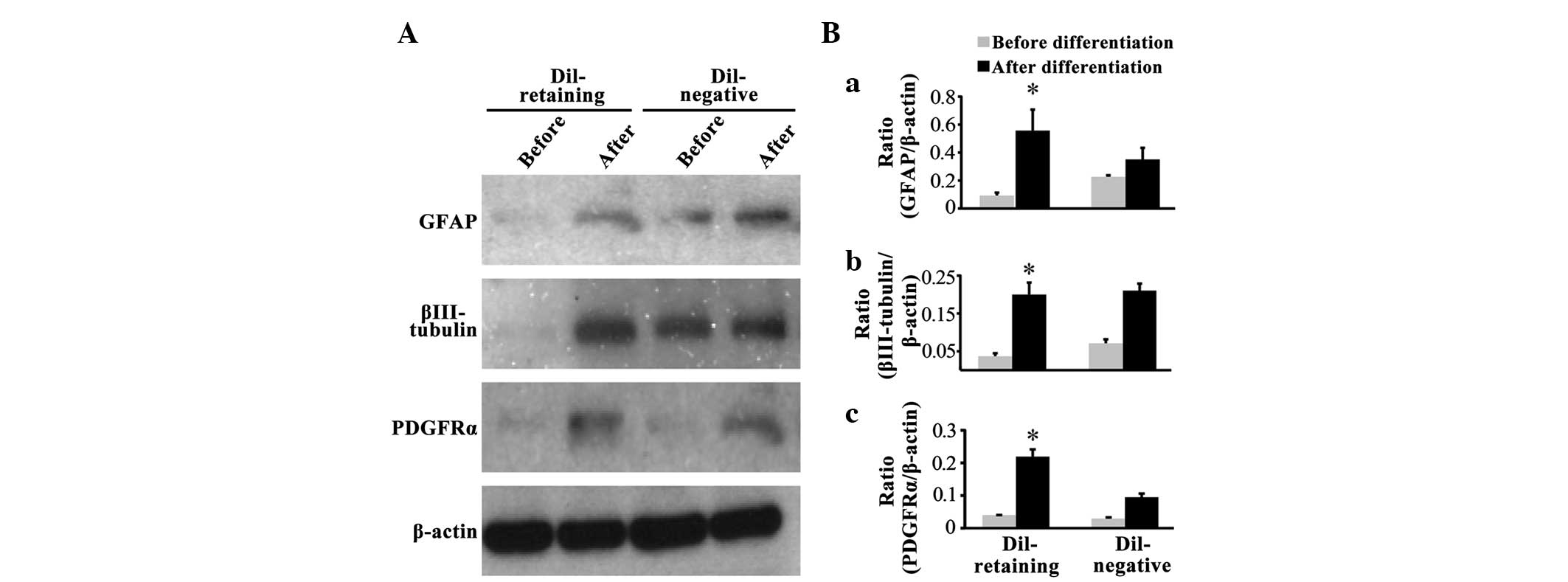
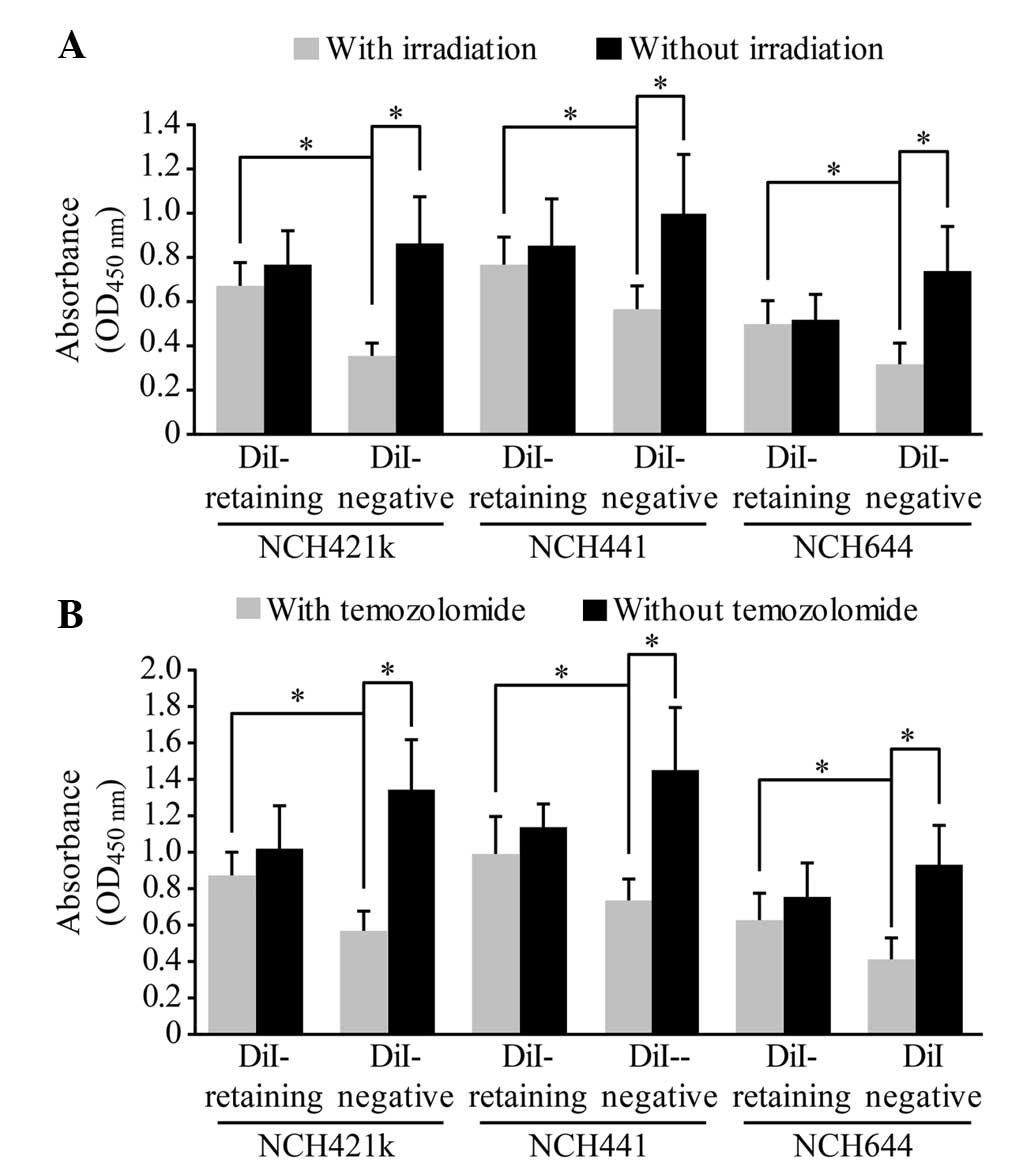
|
1
|
Rock K, McArdle O, Forde P, Dunne M,
Fitzpatrick D, O'Neill B and Faul C: A clinical review of treatment
outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme - the validation in a non-trial
population of the results of a randomised Phase III clinical trial:
Has a more radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol.
85:e729–e733. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jackson M, Hassiotou F and Nowak A:
Glioblastoma stem-like cells: At the root of tumor recurrence and a
therapeutic target. Carcinogenesis. 36:177–185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stopschinski BE, Beier CP and Beier D:
Glioblastoma cancer stem cells - from concept to clinical
application. Cancer Lett. 338:32–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Sakariassen PØ, Tsinkalovsky O,
Immervoll H, Bøe SO, Svendsen A, Prestegarden L, Røsland G, Thorsen
F, Stuhr L, et al: CD133 negative glioma cells form tumors in nude
rats and give rise to CD133 positive cells. Int J Cancer.
122:761–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, Lohmeier A,
Wischhusen J, Oefner PJ, Aigner L, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U and Beier
CP: CD133(+) and CD133(−) glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cells
show differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles.
Cancer Res. 67:4010–4015. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ogden AT, Wziri AE, Lochhead RA, Fusco D,
Lopez K, Ellis JA, Kang J, Assanah M, McKhann GM, Sisti MB, et al:
Identification of A2B5+CD133-tumor-initiating cells in adult human
gliomas. Neurosurgery. 62:505–514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mao XG, Zhang X, Xue XY, Guo G, Wang P,
Zhang W, Fei Z, Zhen HN, You SW and Yang H: Brain tumor stem-like
cells identified by neural stem cell marker CD15. Transl Oncol.
2:247–257. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma I and Allan AL: The role of human
aldehyde dehydrogenase in normal and cancer stem cells. Stem Cell
Rev. 7:292–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meyer M, Reimand J, Lan X, Head R, Zhu X,
Kushida M, Bayani J, Pressey JC, Lionel AC, Clarke ID, et al:
Single cell-derived clonal analysis of human glioblastoma links
functional and genomic heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:851–856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clément V, Marino D, Cudalbu C, Hamou MF,
Mlynarik V, de Tribolet N, Dietrich PY, Gruetter R, Hegi ME and
Radovanovic I: Marker-independent identification of
glioma-initiating cells. Nat Methods. 7:224–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilson A, Laurenti E, Oser G, van der Wath
RC, Blanco-Bose W, Jaworski M, Offner S, Dunant CF, Eshkind L,
Bockamp E, et al: Hematopoietic stem cells reversibly switch from
dormancy to self-renewal during homeostasis and repair. Cell.
135:1118–1129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Radford IR and Lobachevsky PN: An
enteroendocrine cell-based model for a quiescent intestinal stem
cell niche. Cell Prolif. 39:403–414. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Glauche I, Moore K, Thielecke L, Horn K,
Loeffler M and Roeder I: Stem cell proliferation and quiescence -
two sides of the same coin. PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10004472009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hussein D, Punjaruk W, Storer LC, Shaw L,
Othman R, Peet A, Miller S, Bandopadhyay G, Heath R, Kumari R, et
al: Pediatric brain tumor cancer stem cells: Cell cycle dynamics,
DNA repair, and etoposide extrusion. Neuro Oncol. 13:70–83. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis - correlation in invasive
breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Progatzky F, Dallman MJ and Lo Celso C:
From seeing to believing: Labelling strategies for in vivo
cell-tracking experiments. Interface Focus. 3:201300012013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fernandez-Gonzalez R, Illa-Bochaca I,
Shelton DN, Welm BE, Barcellos-Hoff MH and Ortiz-de-Solorzano C:
In situ analysis of cell populations: Long-term
label-retaining cells. Methods Mol Biol. 621:1–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van der Wath RC, Wilson A, Laurenti E,
Trumpp A and Liò P: Estimating dormant and active hematopoietic
stem cell kinetics through extensive modeling of bromodeoxyuridine
label-retaining cell dynamics. PLoS One. 4:e69722009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moore N, Houghton J and Lyle S:
Slow-cycling therapy-resistant cancer cells. Stem Cells Dev.
21:1822–1830. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roesch A, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Schmidt EC,
Zabierowski SE, Brafford PA, Vultur A, Basu D, Gimotty P, Vogt T
and Herlyn M: A temporarily distinct subpopulation of slow-cycling
melanoma cells is required for continuous tumor growth. Cell.
141:583–594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao MQ, Choi YP, Kang S, Youn JH and Cho
NH: CD24+ cells from hierarchically organized ovarian cancer are
enriched in cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 29:2672–2680. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dembinski JL and Krauss S:
Characterization and functional analysis of a slow cycling stem
cell-like subpopulation in pancreas adenocarcinoma. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 26:611–623. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deleyrolle LP, Harding A, Cato K,
Siebzehnrubl FA, Rahman M, Azari H, Olson S, Gabrielli B, Osborne
G, Vescovi A and Reynolds BA: Evidence for label-retaining
tumour-initiating cells in human glioblastoma. Brain.
134:1331–1343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Richichi C, Brescia P, Alberizzi V,
Fornasari L and Pelicci G: Marker-independent method for isolating
slow-dividing cancer stem cells in human glioblastoma. Neoplasia.
15:840–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen R, Nishimura MC, Bumbaca SM,
Kharbanda S, Forrest WF, Kasman IM, Greve JM, Soriano RH, Gilmour
LL, Rivers CS, et al: A hierarchy of self-renewing tumor-initiating
cell types in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 17:362–375. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lottaz C, Beier D, Meyer K, Kumar P,
Hermann A, Schwarz J, Junker M, Oefner PJ, Bogdahn U, Wischhusen J,
et al: Transcriptional profiles of CD133+ and CD133-
glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cell lines suggest different cells
of origin. Cancer Res. 70:2030–2040. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soeda A, Hara A, Kunisada T, Yoshimura S,
Iwama T and Park DM: The evidence of glioblastoma heterogeneity.
Sci Rep. 5:79792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Q, Nguyen DH, Dong Q, Shitaku P, Chung
K, Liu OY, Tso JL, Liu JY, Konkankit V, Cloughesy TF, et al:
Molecular properties of CD133+ glioblastoma stem cells derived from
treatment-refractory recurrent brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 94:1–19.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fillmore CM and Kuperwasser C: Human
breast cancer cell lines contain stem-like cells that self-renew,
give rise to phenotypically diverse progeny and survive
chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R252008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Allan AL, Vantyghem SA, Tuck AB and
Chambers AF: Tumor dormancy and cancer stem cells: Implications for
the biology and treatment of breast cancer metastasis. Breast Dis.
26:87–98. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Udagawa T: Tumor dormancy of primary and
secondary cancers. APMIS. 116:615–628. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK,
Kernie SG and Parada LF: A restricted cell population propagates
glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. 488:522–526. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Trumpp A, Essers M and Wilson A: Awakening
dormant haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:201–209.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wilson A, Laurenti E and Trumpp A:
Balancing dormant and self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 19:461–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schillert A, Trumpp A and Sprick MR: Label
retaining cells in cancer - the dormant root of evil? Cancer Lett.
341:73–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|