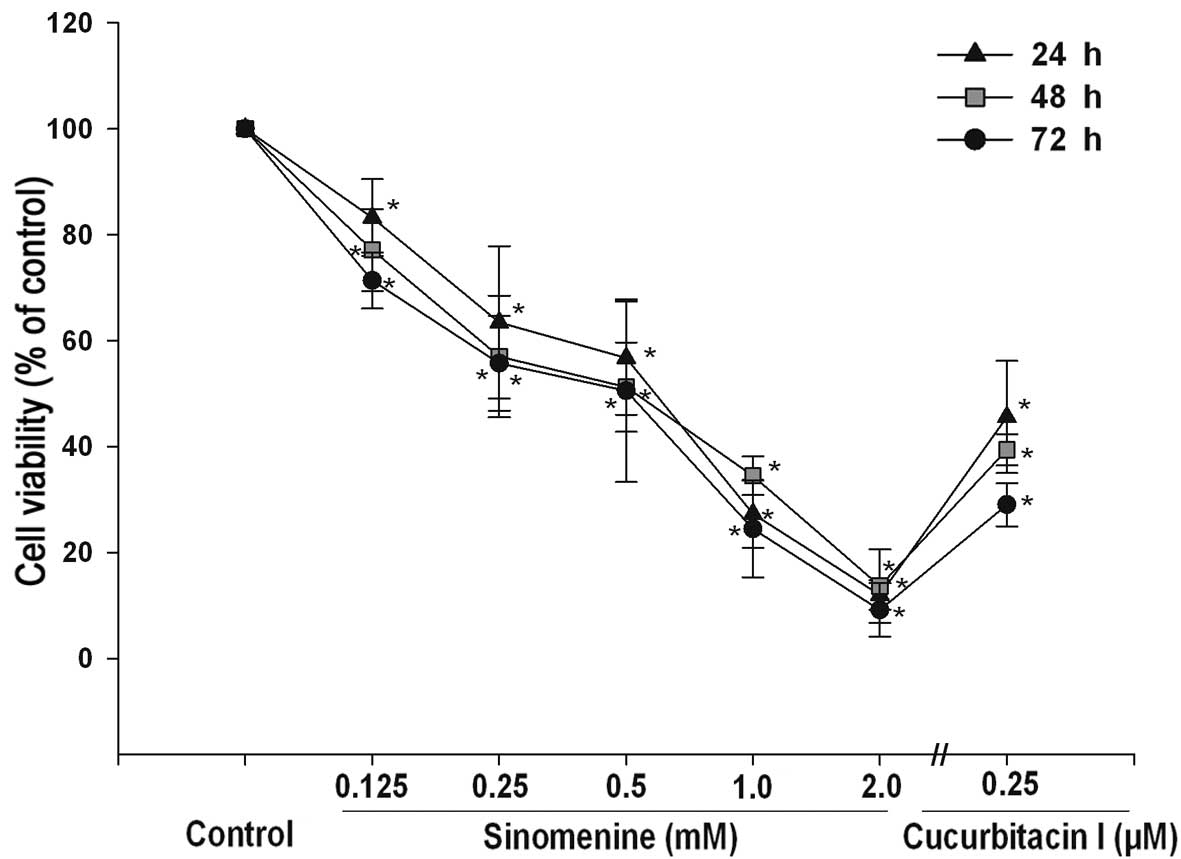
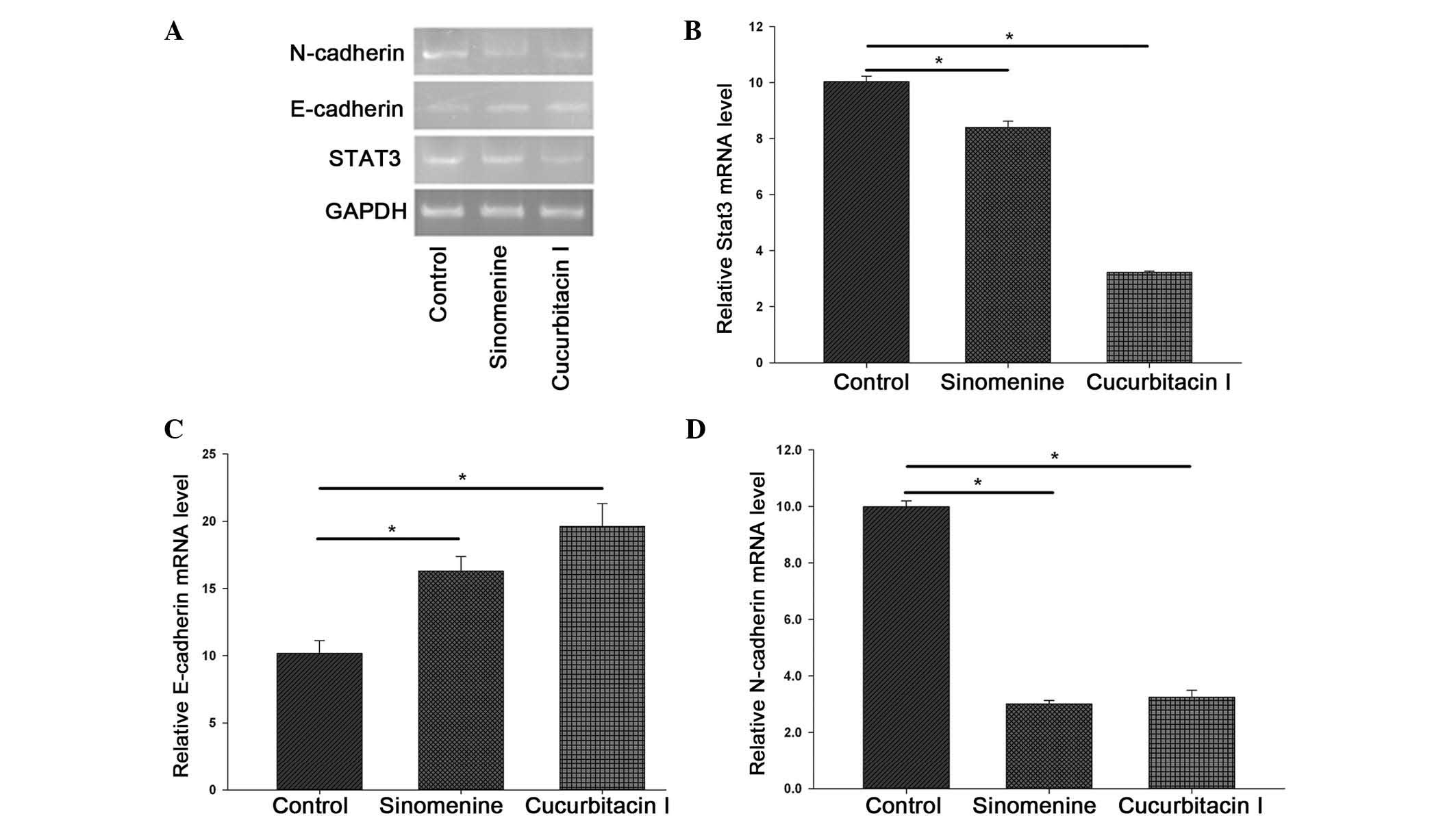
|
1
|
Yano T, Okamoto T, Fukuyama S and Maehara
Y: Therapeutic strategy for postoperative recurrence in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:1048–1054.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pirker R: Adjuvant chemotherapy in
patients with completely resected non-small cell lung cancer.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:305–310. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L:
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions: The
IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Byron E and Pinder-Schenck M: Systemic and
targeted therapies for early-stage lung cancer. Cancer Control.
21:21–31. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Akbari-Birgani S, Paranjothy T, Zuse A,
Janikowski T, Cieślar-Pobuda A, Likus W, Urasińska E, Schweizer F,
Ghavami S, Klonisch T and Łos MJ: Cancer stem cells,
cancer-initiating cells and methods for their detection. Drug
Discov Today. 21:836–842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brower V: Back to nature: Extinction of
medicinal plants threatens drug discovery. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:838–839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li JW and Vederas JC: Drug discovery and
natural products: End of an era or an endless frontier? Science.
325:161–165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu Q, Sun Y, Zhu J, Fang T, Zhang W and
Li JX: Antinociceptive effects of sinomenine in a rat model of
neuropathic pain. Sci Rep. 4:72702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qian L, Xu Z, Zhang W, Wilson B, Hong JS
and Flood PM: Sinomenine, a natural dextrorotatory morphinan
analog, is anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective through inhibition
of microglial NADPH oxidase. J Neuroinflammation. 4:232007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kok TW, Yue PY, Mak NK, Fan TP, Liu L and
Wong RN: The anti-angiogenic effect of sinomenine. Angiogenesis.
8:3–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li XJ, Yue PY, Ha WY, Wong DY, Tin MM,
Wang PX, Wong RN and Liu L: Effect of sinomenine on gene expression
of the IL-1 beta-activated human synovial sarcoma. Life Sci.
79:665–673. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang T, Zhou L, Zhang W, Qu D, Xu X, Yang
Y and Li S: Effects of sinomenine on proliferation and apoptosis in
human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460 in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
3:51–56. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu XL, Zeng J, Chen YL, He PM, Wen MX, Ren
MD, Hu YN, Lu GF and He SX: Sinomenine hydrochloride inhibits human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in
vivo: Involvement of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction.
Int J Oncol. 42:229–238. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuraishy A, Karin M and Grivennikov SI:
Tumor promotion via injury- and death-induced inflammation.
Immunity. 35:467–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He G and Karin M: NF-κB and STAT3 - key
players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 21:159–168.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bosch-Barrera J and Menendez JA: Silibinin
and STAT3: A natural way of targeting transcription factors for
cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:540–546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Ma G, Lu D, Lin F, Xu HJ, Liu J and
Arlinghaus RB: Bcr: A negative regulator of the Bcr-Abl
oncoprotein. Oncogene. 18:4416–4424. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Z, Duan ZJ, Chang JY, Zhang ZF, Chu R,
Li YL, Dai KH, Mo GQ and Chang QY: Sinomenine sensitizes
multidrug-resistant colon cancer cells (Caco-2) to doxorubicin by
downregulation of MDR-1 expression. PLoS One. 9:e985602014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Wang K, Ren Y, Zhang L, Tang XJ,
Zhang HM, Zhao CQ, Liu PJ, Zhang JM and He JJ: MAPK signaling
mediates sinomenine hydrochloride-induced human breast cancer cell
death via both reactive oxygen species-dependent and -independent
pathways: An in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang JX, Yang ZR, Wu DD, Song J, Guo XF,
Wang J and Dong WG: Suppressive effect of sinomenine combined with
5-fluorouracil on colon carcinoma cell growth. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:6737–6743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spitzner M, Ebner R, Wolff HA, Ghadimi BM,
Wienands J and Grade M: STAT3: A novel molecular mediator of
resistance to chemoradiotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 6:1986–2011.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, Dai X, Zhang
J, Kumar AP, Tan BK, Sethi G and Bishayee A: Targeting the STAT3
signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural
inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:136–154. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishida F, Matsuda K, Sekiguchi N,
Makishima H, Taira C, Momose K, Nishina S, Senoo N, Sakai H, Ito T
and Kwong YL: STAT3 gene mutations and their association with pure
red cell aplasia in large granular lymphocyte leukemia. Cancer Sci.
105:342–346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geletu M, Guy S and Raptis L: Effects of
SRC and STAT3 upon gap junctional, intercellular communication in
lung cancer lines. Anticancer Res. 33:4401–4410. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ramakrishna G, Rastogi A, Trehanpati N,
Sen B, Khosla R and Sarin SK: From cirrhosis to hepatocellular
carcinoma: New molecular insights on inflammation and cellular
senescence. Liver Cancer. 2:367–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsu FN, Chen MC, Lin KC, Peng YT, Li PC,
Lin E, Chiang MC, Hsieh JT and Lin H: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5
modulates STAT3 and androgen receptor activation through
phosphorylation of Ser727 on STAT3 in prostate cancer
cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 305:E975–E986. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ibrahim SA, Hassan H, Vilardo L, Kumar SK,
Kumar AV, Kelsch R, Schneider C, Kiesel L, Eich HT, Zucchi I, et
al: Syndecan-1 (CD138) modulates triple-negative breast cancer stem
cell properties via regulation of LRP-6 and IL-6-mediated STAT3
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e857372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao Y, Li J, Yu K, Liu Y and Chen X:
Sinomenine inhibits maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells
through blocking activation of NF-kappa B. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:637–645. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Simone V, Franzè E, Ronchetti G,
Colantoni A, Fantini MC, Di Fusco D, Sica GS, Sileri P, MacDonald
TT, Pallone F, et al: Th17-type cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-α
synergistically activate STAT3 and NF-κB to promote colorectal
cancer cell growth. Oncogene. 34:3493–3503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Levy DE and Darnell JE Jr: Stats:
Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 3:651–662. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rho JK, Choi YJ, Lee JK, Ryoo BY, Na II,
Yang SH, Kim CH and Lee JC: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
derived from repeated exposure to gefitinib determines the
sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in A549, a non-small cell lung
cancer cell line. Lung Cancer. 63:219–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, Rapa
I, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M and Allgayer H: Loss of miR-200c
expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant
phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
8:1207–1216. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1658–1667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Peinado H, Portillo F and Cano A:
Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and
carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 48:365–375. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|