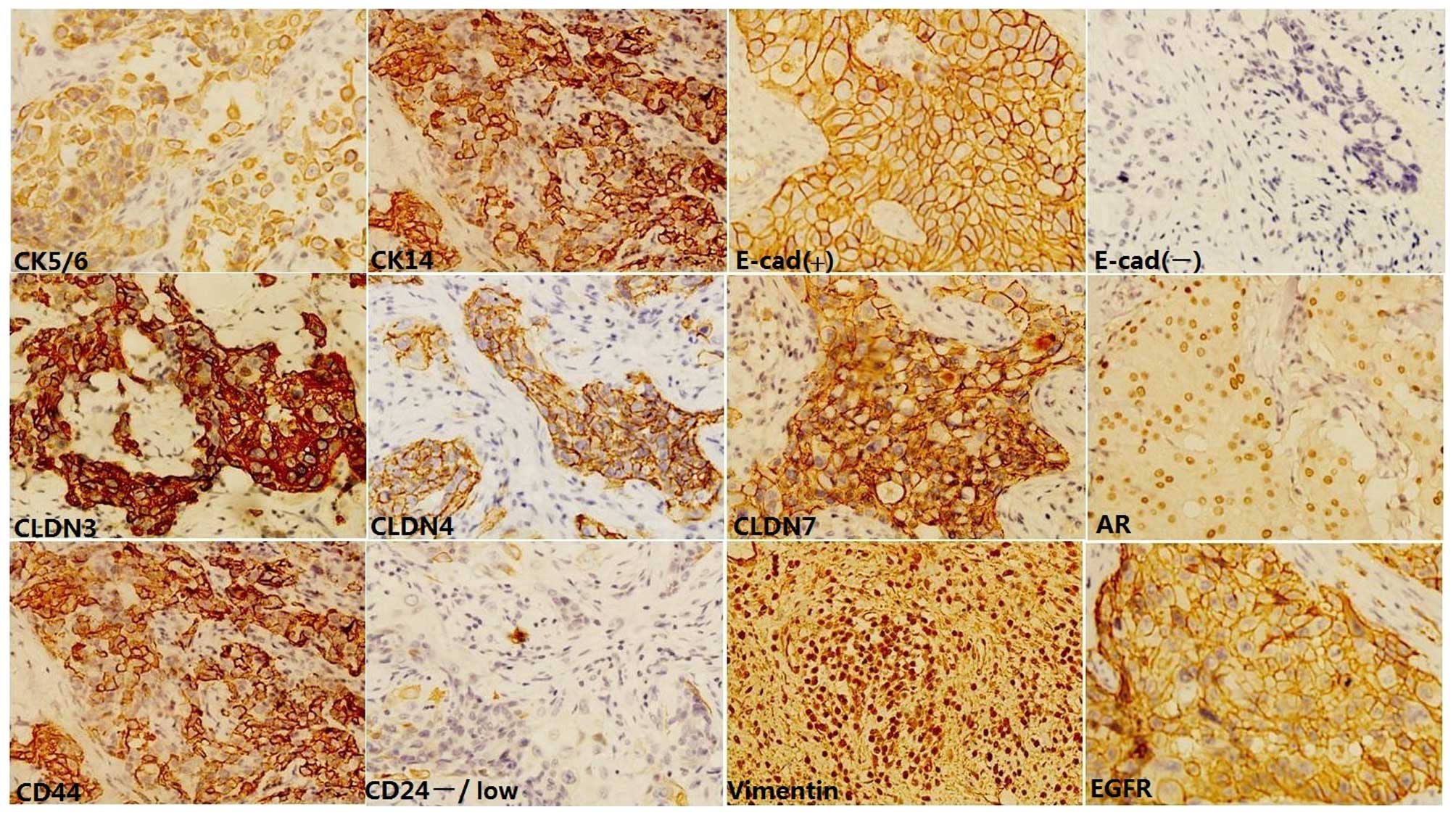
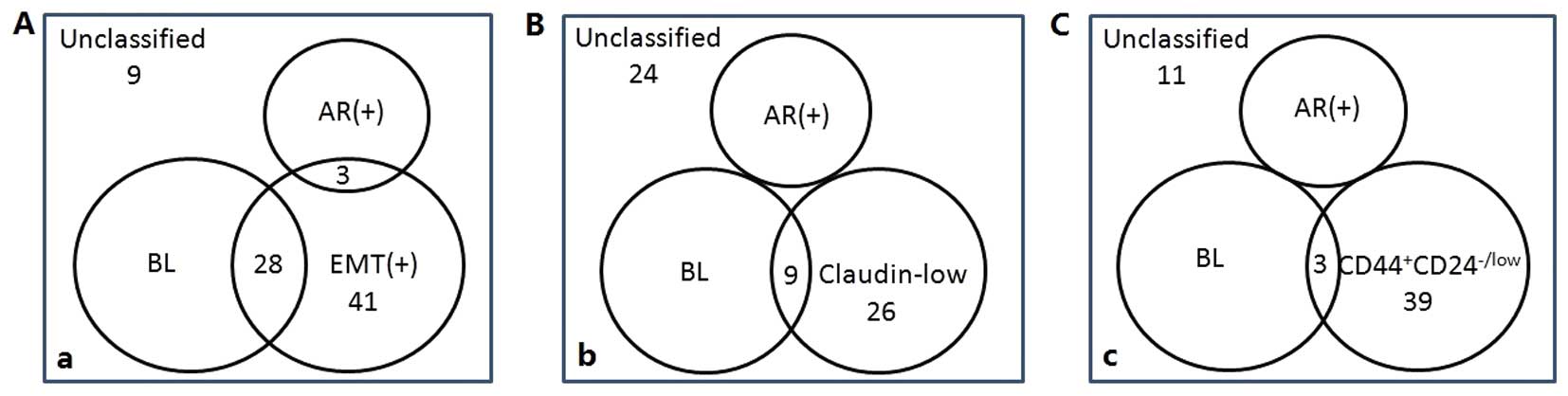
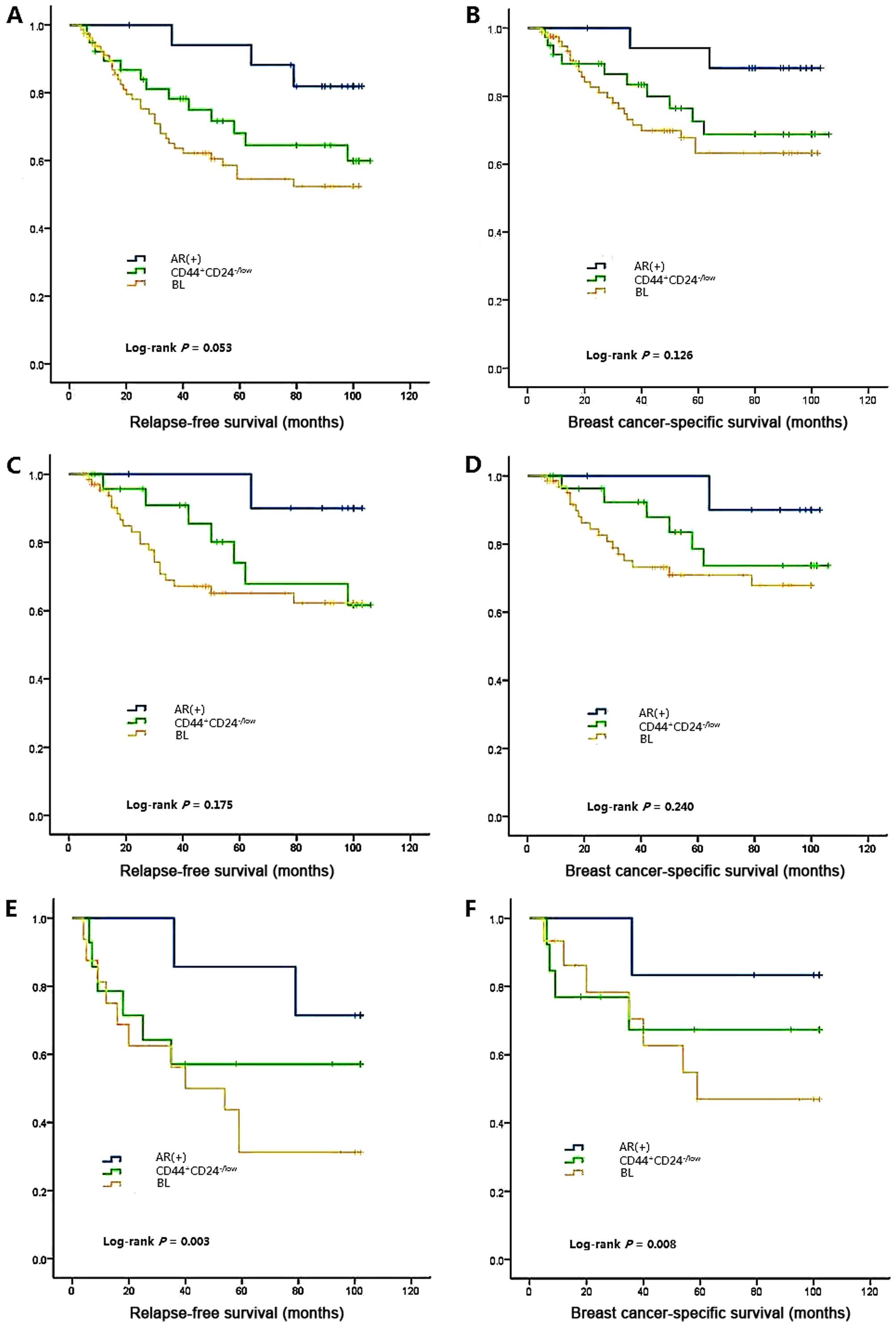
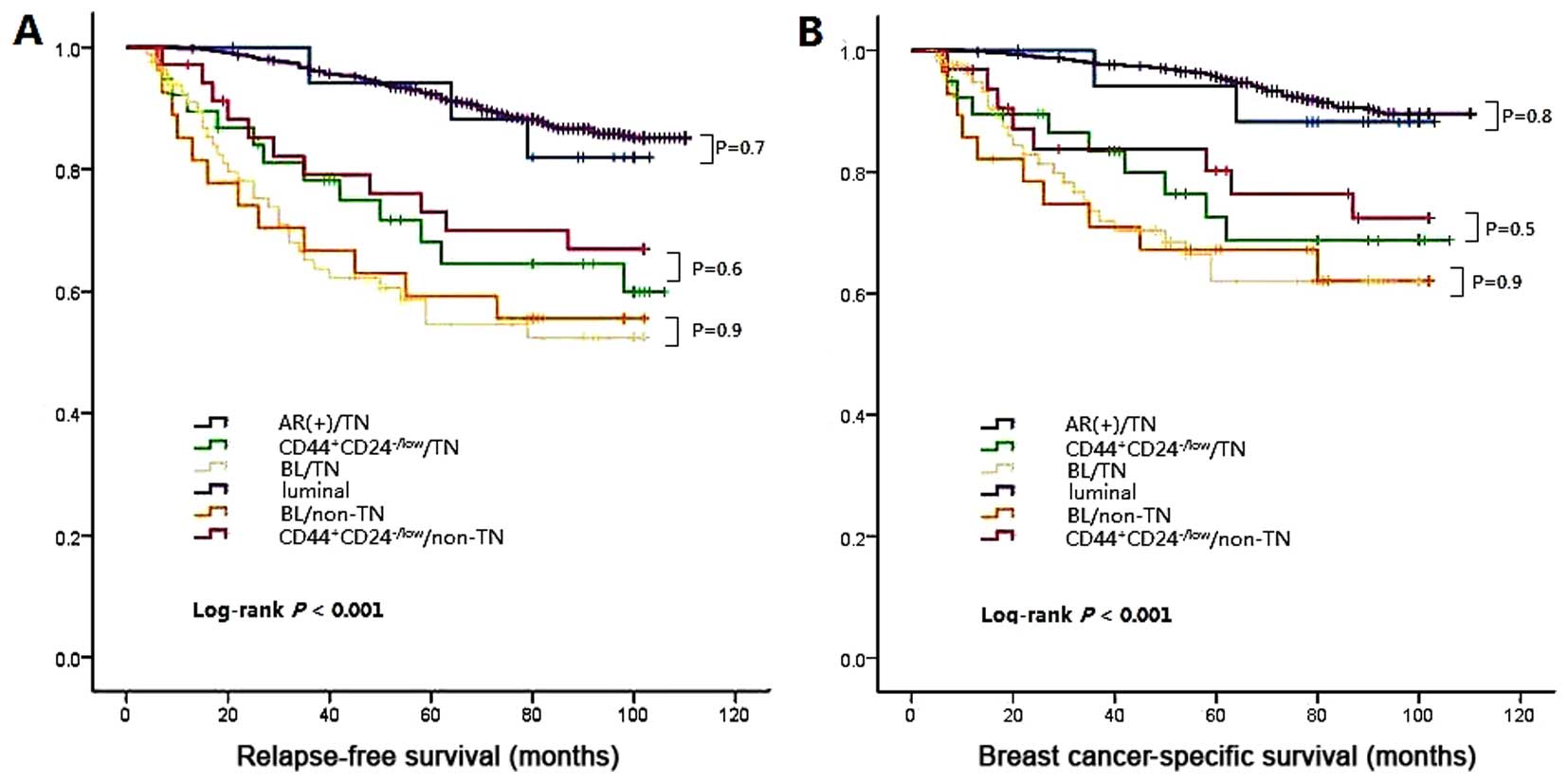
|
1
|
Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, Leung S,
McKinney S, Chia SK, Perou CM and Nielsen TO: Basal-like breast
cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value
than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1368–1376.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aguiar FN, Mendes HN, Cirqueira CS, Bacchi
CE and Carvalho FM: Basal cytokeratin as a potential marker of low
risk of invasion in ductal carcinoma in situ. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
68:638–643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fadare O, Wang SA and Hileeto D: The
expression of cytokeratin 5/6 in invasive lobular carcinoma of the
breast: evidence of a basal-like subset? Hum Pathol. 39:331–336.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee HJ, Seo AN, Kim EJ, Jang MH, Kim YJ,
Kim JH, Kim SW, Ryu HS, Park IA, Im SA, et al: Prognostic and
predictive values of EGFR overexpression and EGFR copy number
alteration in HER2-positive breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
112:103–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Park HS, Jang MH, Kim EJ, Kim HJ, Lee HJ,
Kim YJ, Kim JH, Kang E, Kim SW, Kim IA and Park SY: High EGFR gene
copy number predicts poor outcome in triple-negative breast cancer.
Mod Pathol. 27:1212–1222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH,
Robertson JF and Ellis IO: Prognostic markers in triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer. 109:25–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sood N and Nigam JS: Correlation of CK5
and EGFR with clinicopathological profile of triple-negative breast
cancer. Patholog Res Int. 2014:1418642014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Niemeier LA, Dabbs DJ, Beriwal S, Striebel
JM and Bhargava R: Androgen receptor in breast cancer: expression
in estrogen receptor-positive tumors and in estrogen
receptor-negative tumors with apocrine differentiation. Mod Pathol.
23:205–212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C,
Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X and Perou CM: Phenotypic and
molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Turner NC and Reis-Filho JS: Tackling the
diversity of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
19:6380–6388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lehmann BD and Pietenpol JA:
Identification and use of biomarkers in treatment strategies for
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes. J Pathol. 232:142–150.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prat A, Adamo B, Cheang MC, Anders CK,
Carey LA and Perou CM: Molecular characterization of basal-like and
non-basal-like triple-negative breast cancer. Oncologist.
18:123–133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abramson VG, Lehmann BD, Ballinger TJ and
Pietenpol JA: Subtyping of triple-negative breast cancer:
implications for therapy. Cancer. 121:8–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schmadeka R, Harmon BE and Singh M:
Triple-negative breast carcinoma: current and emerging concepts. Am
J Clin Pathol. 141:462–477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choo JR and Nielsen TO: Biomarkers for
basal-like breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2:1040–1065. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mylona E, Giannopoulou I, Fasomytakis E,
Nomikos A, Magkou C, Bakarakos P and Nakopoulou L: The
clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of
CD44+/CD24(−/low) and
CD44−/CD24+ tumor cells in invasive breast
carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 39:1096–1102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mayer IA, Abramson VG, Lehmann BD and
Pietenpol JA: New strategies for triple-negative breast cancer -
deciphering the heterogeneity. Clin Cancer Res. 20:782–790. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J,
Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F, et al: A
collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of
functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell. 10:515–527.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kao J, Salari K, Bocanegra M, Choi YL,
Girard L, Gandhi J, Kwei KA, Hernandez-Boussard T, Wang P, Gazdar
AF, et al: Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines
relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene
discovery. PLoS One. 4:e61462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu T, Zhang X, Shang M, Zhang Y, Xia B,
Niu M, Liu Y and Pang D: Dysregulated expression of Slug, vimentin
and E-cadherin correlates with poor clinical outcome in patients
with basal-like breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 107:188–194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee J, Hahm ER, Marcus AI and Singh SV:
Withaferin A inhibits experimental epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in MCF-10A cells and suppresses vimentin protein level
in vivo in breast tumors. Mol Carcinog. 54:417–429. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rito M, Schmitt F, Pinto AE and André S:
Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma of the breast has a
claudin-low immunohistochemical phenotype. Virchows Arch.
465:185–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Toy KA and Kleer CG: Metaplastic
breast carcinomas are enriched in markers of tumor-initiating cells
and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Mod Pathol. 25:178–184.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A and
Koukourakis MI: The CD44+/CD24- phenotype relates to
‘triple-negative’ state and unfavorable prognosis in breast cancer
patients. Med Oncol. 28:745–752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Honeth G, Bendahl PO, Ringner M, Ringnér
M, Saal LH, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Lövgren K, Grabau D, Fernö M, Borg
A and Hegardt C: The CD44+/CD24-phenotype is enriched in basal-like
breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R532008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Wolff AC, Mangu PB
and Temin S: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of
American Pathologists guideline recommendations for
immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors
in breast cancer. J Oncol Pract. 6:195–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Barry WT, Kernagis DN, Dressman HK,
Griffis RJ, Hunter JD, Olson JA, Marks JR, Ginsburg GS, Marcom PK,
Nevins JR, et al: Intratumor heterogeneity and precision of
microarray-based predictors of breast cancer biology and clinical
outcome. J Clin Oncol. 28:2198–2206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Fan C and Perou CM:
PAM50 assay and the three-gene model for identifying the major and
clinically relevant molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 135:301–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M,
Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler
L, et al: Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the
basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5367–5374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Badve S, Dabbs DJ, Schnitt SJ, Baehner FL,
Decker T, Eusebi V, Fox SB, Ichihara S, Jacquemier J, Lakhani SR,
et al: Basal-like and triple-negative breast cancers: a critical
review with an emphasis on the implications for pathologists and
oncologists. Mod Pathol. 24:157–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi YL, Oh E, Park S, Kim Y, Park YH,
Song K, Cho EY, Hong YC, Choi JS, Lee JE, et al: Triple-negative,
basal-like and quintuple-negative breast cancers: better prediction
model for survival. BMC Cancer. 10:5072010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Won JR, Gao D, Chow C, Cheng J, Lau SY,
Ellis MJ, Perou CM, Bernard PS and Nielsen TO: A survey of
immunohistochemical biomarkers for basal-like breast cancer against
a gene expression profile gold standard. Mod Pathol. 26:1438–1450.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Safarpour D, Pakneshan S and Tavassoli FA:
Androgen receptor (AR) expression in 400 breast carcinomas: is
routine AR assessment justified? Am J Cancer Res. 4:353–368.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McNamara KM, Yoda T, Miki Y, Chanplakorn
N, Wongwaisayawan S, Incharoen P, Kongdan Y, Wang L, Takagi K, Mayu
T, et al: Androgenic pathway in triple negative invasive ductal
tumors: its correlation with tumor cell proliferation. Cancer Sci.
104:639–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsutsumi Y: Apocrine carcinoma as
triple-negative breast cancer: novel definition of apocrine-type
carcinoma as estrogen/progesterone receptor-negative and androgen
receptor-positive invasive ductal carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
42:375–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Thike AA, Yong-Zheng Chong L, Cheok PY, Li
HH, Wai-Cheong Yip G, Huat Bay B, Tse GM, Iqbal J and Tan PH: Loss
of androgen receptor expression predicts early recurrence in
triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer. Mod Pathol.
27:352–360. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tsang JY, Ni YB, Chan SK, Shao MM, Law BK,
Tan PH and Tse GM: Androgen receptor expression shows distinctive
significance in ER positive and negative breast cancers. Ann Surg
Oncol. 21:2218–2228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pistelli M, Caramanti M, Biscotti T,
Santinelli A, Pagliacci A, De Lisa M, Ballatore Z, Ridolfi F,
Maccaroni E, Bracci R, et al: Androgen receptor expression in early
triple-negative breast cancer: clinical significance and prognostic
associations. Cancers (Basel). 6:1351–1362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McNamara KM, Yoda T, Takagi K, Miki Y,
Suzuki T and Sasano H: Androgen receptor in triple negative breast
cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 133:66–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gasparini P, Fassan M, Cascione L, Guler
G, Balci S, Irkkan C, Paisie C, Lovat F, Morrison C, Zhang J, et
al: Androgen receptor status is a prognostic marker in non-basal
triple negative breast cancers and determines novel therapeutic
options. PLoS One. 9:e885252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Loibl S, Müller BM, von Minckwitz G,
Schwabe M, Roller M, Darb-Esfahani S, Ataseven B, du Bois A,
Fissler-Eckhoff A, Gerber B, et al: Androgen receptor expression in
primary breast cancer and its predictive and prognostic value in
patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 130:477–487. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Micello D, Marando A, Sahnane N, Riva C,
Capella C and Sessa F: Androgen receptor is frequently expressed in
HER2-positive, ER/PR-negative breast cancers. Virchows Arch.
457:467–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ogawa Y, Hai E, Matsumoto K, Ikeda K,
Tokunaga S, Nagahara H, Sakurai K, Inoue T and Nishiguchi Y:
Androgen receptor expression in breast cancer: relationship with
clinicopathological factors and biomarkers. Int J Clin Oncol.
13:431–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Witzel I, Graeser M, Karn T, Schmidt M,
Wirtz R, Schütze D, Rausch A, Jänicke F, Milde-Langosch K and
Müller V: Androgen receptor expression is a predictive marker in
chemotherapy-treated patients with endocrine receptor-positive
primary breast cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:809–816. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tang D, Xu S, Zhang Q and Zhao W: The
expression and clinical significance of the androgen receptor and
E-cadherin in triple-negative breast cancer. Med Oncol. 29:526–533.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hu R, Dawood S, Holmes MD, Collins LC,
Schnitt SJ, Cole K, Marotti JD, Hankinson SE, Colditz GA and Tamimi
RM: Androgen receptor expression and breast cancer survival in
postmenopausal women. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1867–1874. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu S, Singh K, Mangray S, Tavares R, Noble
L, Resnick MB and Yakirevich E: Claudin expression in high-grade
invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: correlation with the
molecular subtype. Mod Pathol. 26:485–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gerhard R, Ricardo S, Albergaria A, Gomes
M, Silva AR, Logullo ÂF, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Paredes J and
Schmitt F: Immunohistochemical features of claudin-low intrinsic
subtype in metaplastic breast carcinomas. Breast. 21:354–360. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sabatier R, Guille A, Adelaide J,
Chaffanet M, Viens P, Birnbaum D, Bertucci F and Finetti P:
Claudin-low breast cancers: clinical, pathological, molecular and
prognostic characterization. Mol Cancer. 13:2282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Masuda H, Baggerly KA, Wang Y, Zhang Y,
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Meric-Bernstam F, Valero V, Lehmann BD,
Pietenpol JA, Hortobagyi GN, et al: Differential response to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy among 7 triple-negative breast cancer
molecular subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5533–5540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|