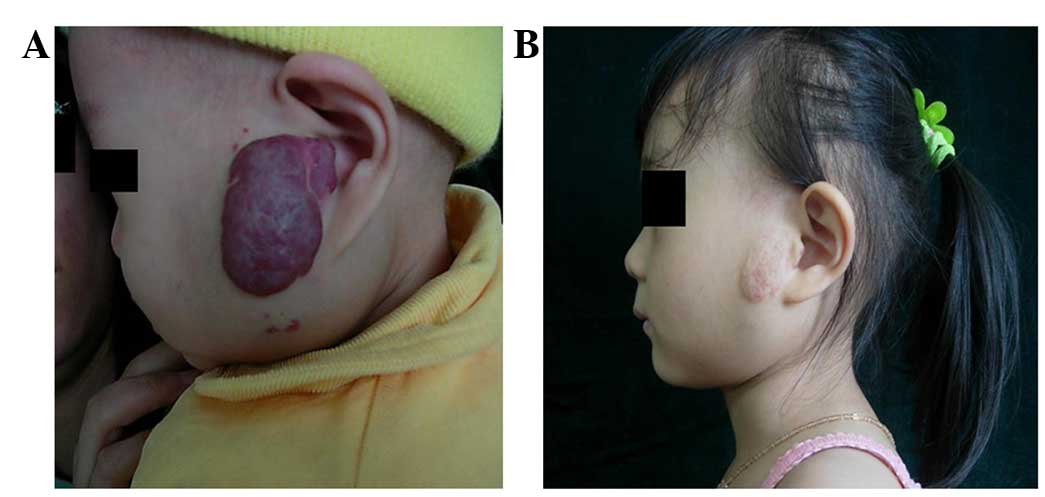
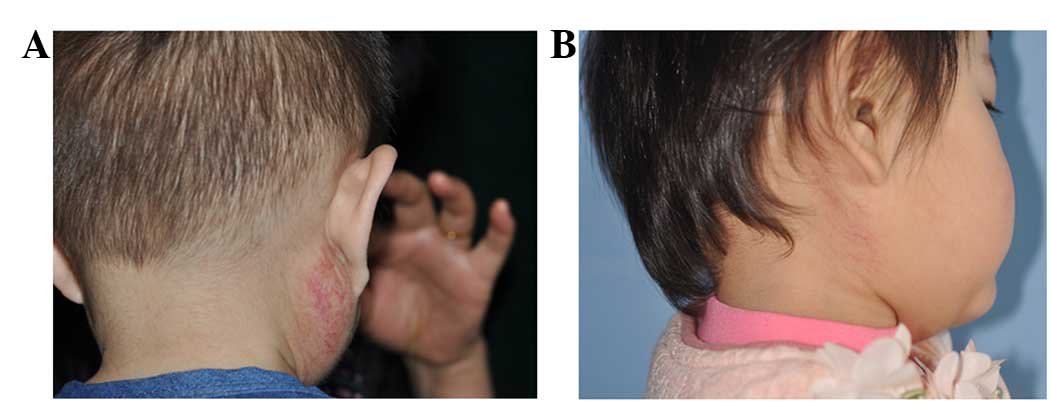
|
1
|
Phung TL, Hochman M and Mihm MC: Current
knowledge of the pathogenesis of infantile hemangiomas. Arch Facial
Plast Surg. 7:319–321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yuan WL, Jin ZL, Wei JJ, Liu ZY, Xue L and
Wang XK: Propranolol given orally for proliferating infantile
haemangiomas: Analysis of efficacy and serological changes in
vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial nitric oxide
synthase in 35 patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 51:656–661.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mulliken JB and Glowacki J: Hemangiomas
and vascular malformations in infants and children: A
classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 69:412–422. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buckmiller LM, Richter GT and Suen JY:
Diagnosis and management of hemangiomas and vascular malformations
of the head and neck. Oral Dis. 16:405–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Enjolras O and Gelbert F: Superficial
hemangiomas: Associations and management. Pediatr Dermatol.
14:173–179. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu X, Tai M, Qin Z, Li K and Ge C:
Clinical analysis for treatment of 1,080 cases of infantile
hemangiomas with oral propranolol. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
94:1878–1881. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Waner M and Suen JY: Management of
congenital vascular lesions of the head and neck. Oncology
(Williston Park). 9:989–994, 997; discussion 998 passim.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malik MA, Menon P, Rao KL and Samujh R:
Effect of propranolol vs prednisolone vs. propranolol with
prednisolone in the management of infantile hemangioma: A
randomized controlled study. J Pediatr Surg. 48:2453–2459. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E,
Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW,
Newell B, et al: Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas:
Clinical characteristics predicting complications and treatment.
Pediatrics. 118:882–887. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Achauer BM, Chang CJ and Vander Kam VM:
Management of hemangioma of infancy: Review of 245 patients. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 99:1301–1308. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mantadakis E, Tsouvala E, Deftereos S,
Danielides V and Chatzimichael A: Involution of a large parotid
hemangioma with oral propranolol: An illustrative report and review
of the literature. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012:3538122012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng JW: Infantile hemangiomas: Seldom
wait and see. China Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.
10:163–164. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Bennett ML, Fleischer AB Jr, Chamlin SL
and Frieden IJ: Oral corticosteroid use is effective for cutaneous
hemangiomas: An evidence-based evaluation. Arch Dermatol.
137:1208–1213. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gangopadhyay AN, Sharma SP, Gopal SC,
Gupta DK, Panjawani K and Sinha JK: Local steroid therapy in
cutaneous hemangiomas. Indian Pediatr. 33:31–33. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Muir T, Kirsten M, Fourie P, Dippenaar N
and Ionescu GO: Intralesional bleomycin injection (IBI) treatment
for haemangiomas and congenital vascular malformations. Pediatr
Surg Int. 19:766–773. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Omidvari S, Nezakatgoo N, Ahmadloo N,
Mohammadianpanah M and Mosalaei A: Role of intralesional bleomycin
in the treatment of complicated hemangiomas: Prospective clinical
study. Dermatol Surg. 31:499–501. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Enjolras O, Brevière GM, Roger G, Tovi M,
Pellegrino B, Varotti E, Soupre V, Picard A and Leverger G:
Vincristine treatment for function- and life-threatening infantile
hemangioma. Arch Pediatr. 11:99–107. 2004.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ezekowitz RA, Mulliken JB and Folkman J:
Interferon alfa-2a therapy for life-threatening hemangiomas of
infancy. N Engl J Med. 326:1456–1463. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hochman A and Mascareno A: Management of
nasal hemangiomas. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 7:295–300. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hamou C, Diner PA, Dalmonte P, Vercellino
N, Soupre V, Enjolras O, Vazquez MP and Picard A: Nasal tip
haemangiomas: Guidelines for an early surgical approach. J Plast
Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 63:934–939. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng JW, Zhou GY, Wang YA and Zhang ZY:
Management of head and neck hemangiomas in China. Chin Med J
(Engl). 121:1037–1042. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Léauté-Labrèze C, Dumas de la Roque E,
Hubiche T, Boralevi F, Thambo JB and Taïeb A: Propranolol for
severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 358:2649–2651. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Price CJ, Lattouf C, Baum B, McLeod M,
Schachner LA, Duarte AM and Connelly EA: Propranlol vs
corticosteroids for infantile hemangiomas: A multicenter
retrospective analysis. Arch Dermatol. 147:1371–1376. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Storch CH and Hoeger PH: Propranolol for
infantile haemangiomas: Insights into the molecular mechanisms of
action. Br J Dermatol. 163:269–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ribatti D: The crucial role of vascular
permeability factor/vascular endothelial factor in angiogenesis: A
historical review. Br J Haematol. 128:303–309. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ye XX, Jin YB, Lin XX, Ma G, Chen XD, Qiu
YJ, Chen H and Hu XJ: Topical timolol in the treatment of
periocular superficial infantile hemangiomas: A prospective study.
Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 28:161–164. 2012.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Coppens G, Stalmans I, Zeyen T and
Casteels I: The safety andefficacy of glaucoma medication in the
pediatric population. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 46:12–18.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo S and Ni N: Topical treatment for
capillary hemangioma of the eyelid using beta-blocker solution.
Arch Ophthalmol. 128:255–256. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Prey S, Voisard JJ, Delarue A, Lebbe G,
Taïeb A, Leaute-Labreze C and Ezzedine K: Safety of propranolol
therapy for severe infantile hemangioma. JAMA. 315:413–415. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pope E and Chakkittakandiyil A: Topical
timolol gel for infantile hemangiomas: A pilot study. Arch
Dermatol. 146:564–565. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu Y, Xue L, Wei J, Lei B, Liu Z and Wang
X: Oral propranolol treatment for infants with proliferating
hemangiomas: Clinical analysis of 35 cases. Zhongguo Kouqiang He
Mian Waike Zazhi. 10:159–162. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Zheng JW, Zhou Q, Yang XJ, Wang YA, Fan
XD, Zhou GY, Zhang ZY and Suen JY: Treatment guideline for
hemangiomas and vascular malformations of the head and neck. Head
Neck. 32:1088–1098. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng JW: Comment on efficacy and safety
of propranolol in the treatment of parotid hemangioma. Cutan Ocul
Toxicol. 30:333–334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu DP, Cao RY and Tong S: Topical timolol
maleate for superficial infantile hemangiomas: an observational
study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 73:1089–1094. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chan H, Mckay C, Adam S and Wargon O: RCT
of timolol maleate gel for superficial infantile hemangiomas in
5-to 24-week-olds. Pediatrics. 131:e1739–e1747. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li G, Xu DP, Tong S, Xue L, Sun NN and
Wang XK: Oral Propranolol With Topical Timolol Maleate Therapy for
Mixed Infantile Hemangiomas in Oral and Maxillofacial Regions. J
Craniofac Surg. 27:56–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Storch CH and Hoeger PH: Propranolol for
infantile hemangiomas: Insights into the molecular mechanisms of
action. Br J Dermatol. 163:269–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Itinteang T, Brasch HD, Tan ST and Day DJ:
Expression of components of the renin-angiotensin system in
proliferating infantile hemangioma may account for the
propranolol-induced accelerated involution. J Plast Reconstr
Aesthet. 64:759–765. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|