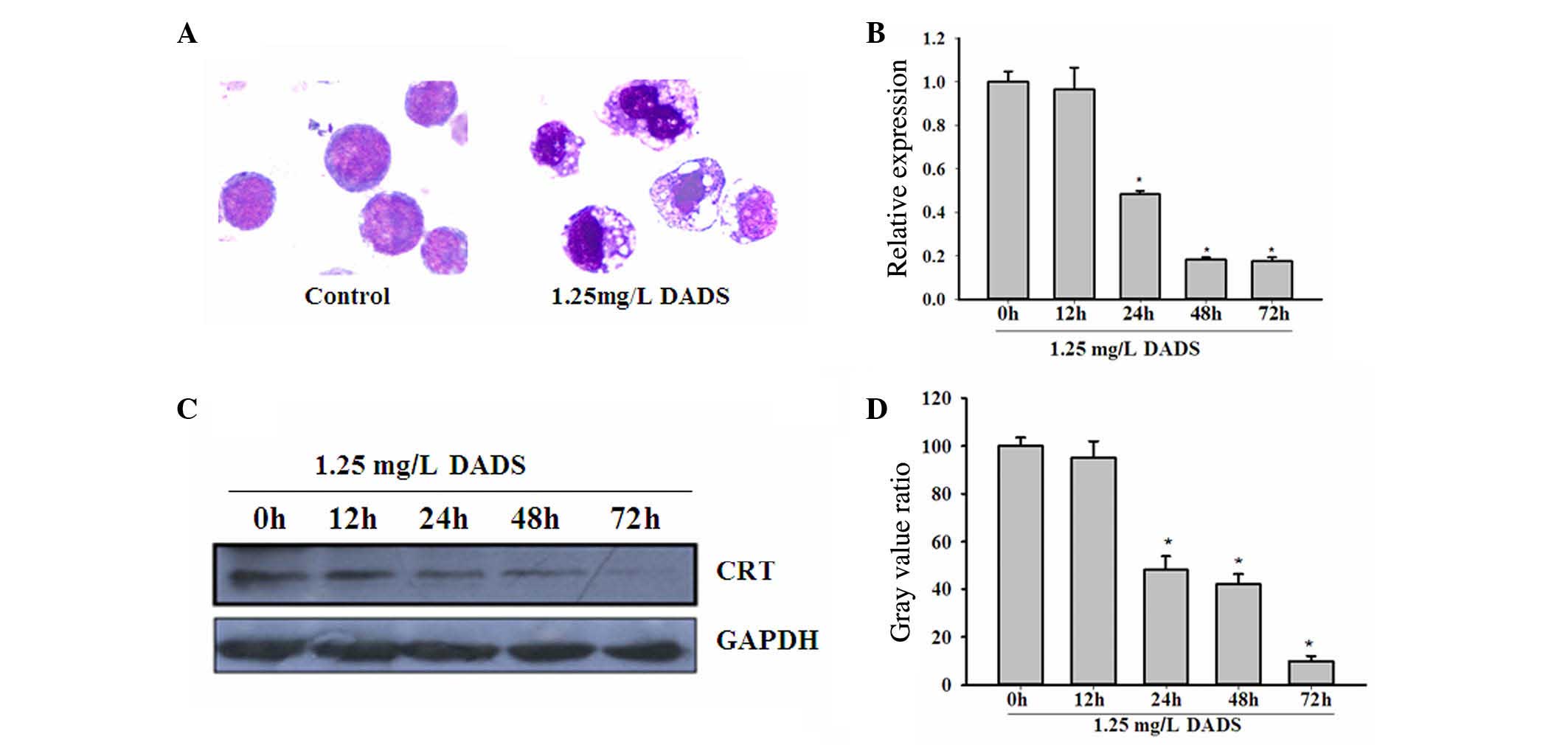
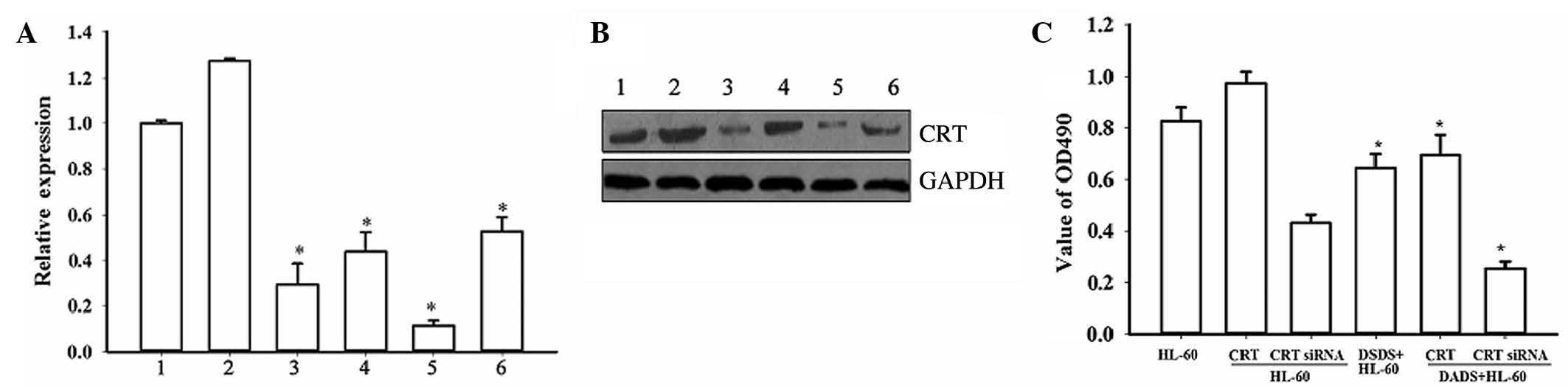
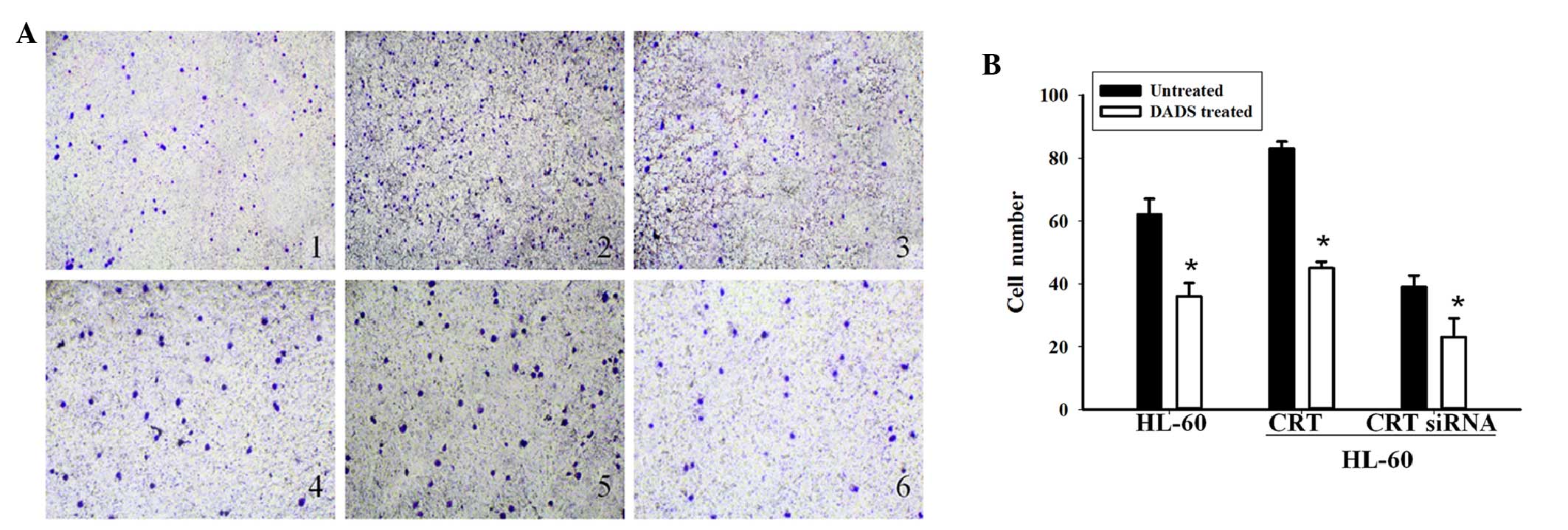
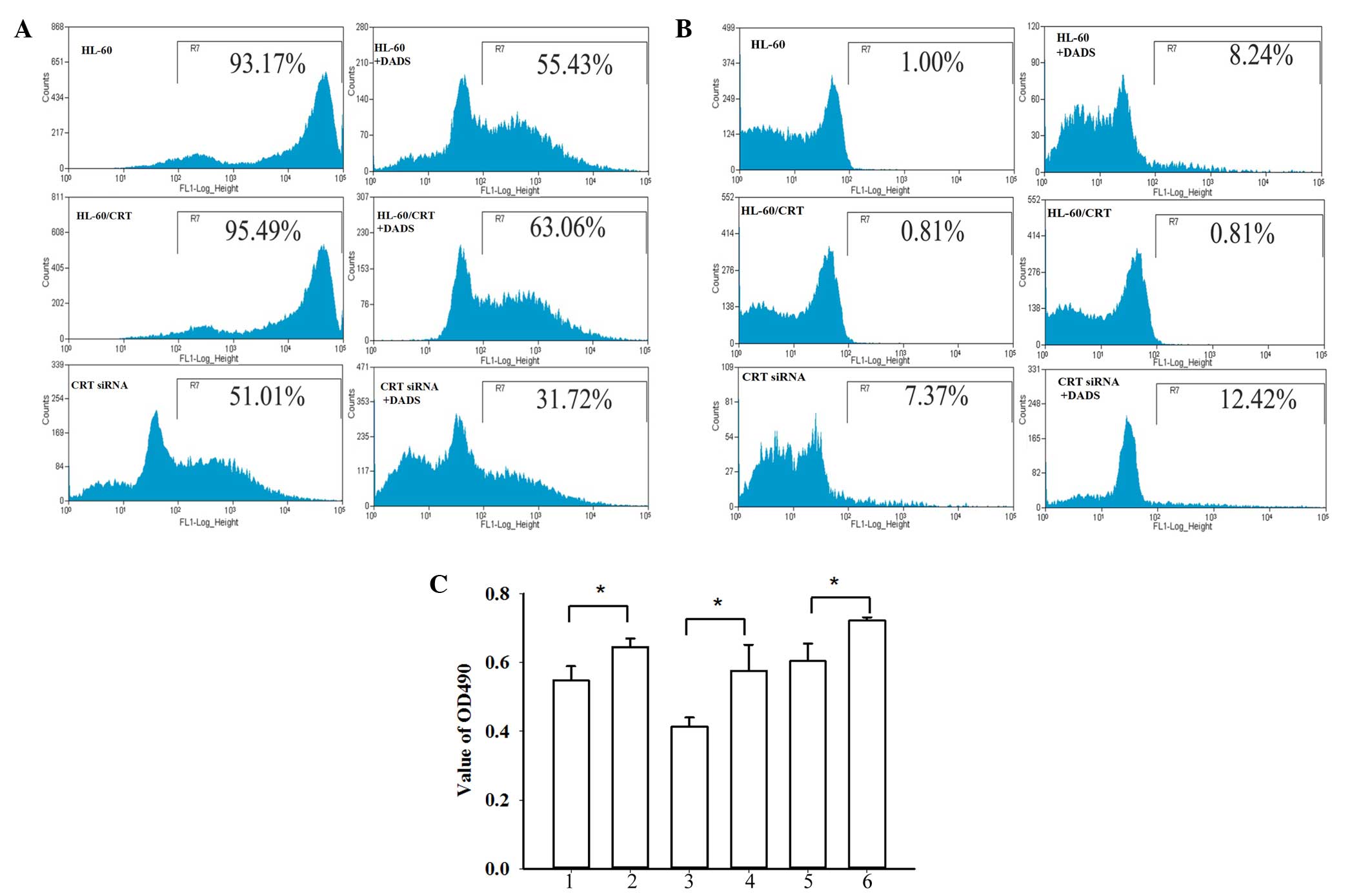
|
1
|
Rubnitz JE and Inaba H: Childhood acute
myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 159:259–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iland HJ, Bradstock K, Supple SG, Catalano
A, Collins M, Hertzberg M, Browett P, Grigg A, Firkin F, Hugman A,
et al: Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group:
All-trans-retinoic acid, idarubicin, and IV arsenic trioxide as
initial therapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML4). Blood.
120:1570–1580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DiNardo CD and Cortes JE: New treatment
for acute myelogenous leukemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
16:95–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arunkumar R, Sharmila G, Elumalai P,
Senthilkumar K, Banudevi S, Gunadharini DN, Benson CS, Daisy P and
Arunakaran J: Effect of diallyl disulfide on insulin-like growth
factor signaling molecules involved in cell survival and
proliferation of human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in silico
approach through docking analysis. Phytomedicine. 19:912–923. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yi L and Su Qi: Molecular mechanisms for
the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide. Food Chem Toxicol.
57:362–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Altonsy MO, Habib TN and Andrews SC:
Diallyl disulfide-induced apoptosis in a breast-cancer cell line
(MCF-7) may be caused by inhibition of histone deacetylation. Nutr
Cancer. 64:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou Y, Su J, Shi L, Liao Q and Su Q: DADS
downregulates the Rac1-ROCK1/PAK1-LIMK1-ADF/cofilin signaling
pathway, inhibiting cell migration and invasion. Oncol Rep.
29:605–612. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan H, Ling H, He J, Yi L, Zhou J, Lin M
and Su Q: Inhibition of ERK and activation of p38 are involved in
diallyl disulfide induced apoptosis of leukemia HL-60 cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 31:786–793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yi L, Ji XX, Tan H, Lin M, Tang Y, Wen L,
Ma YH and Su Q: Role of Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2
(Rac2), NADPH oxidase and reactive oxygen species in diallyl
disulphide-induced apoptosis of human leukaemia HL-60 cells. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:1147–1153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yi L, Ji XX, Tan H, Feng MY, Tang Y, Wen L
and Su Q: Involvement of Mcl1 in diallyl disulfide-induced G2/M
cell cycle arrest in HL-60 cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1911–1917.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu MH, Huang WG, Tan H, He J and Su Q:
Induction of differentiation by diallyl disulfide through
inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Zhong Guo
Yao Li Xue Tong Bao. 21:580–583. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Zhao J, Huang WG, He J, Tan H, Liao QJ and
Su Q: Diallyl disulfide suppresses growth of HL-60 cell through
increasing histone acetylation and p21WAF1 expression in
vivo and in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:1459–1466.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He J, Su Q, Huang WG, Xie HL, Liang SP,
Song Y, Xie JY, Zhou XT, Tan H, Zhao J and Wu MH: Proteomic initial
analysis of differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells induced
by diallyl disulfide. FEBS J. 272(Suppl 1): S4402005.
|
|
14
|
Wang WA, Groenendyk J and Michalak M:
Calreticulin signaling in health and disease. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 44:842–846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zamanian M, Veerakumarasivam A, Abdullah S
and Rosli R: Calreticulin and Cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:149–154.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu R, Gong J, Chen J, Li Q, Song C, Zhang
J, Li Y, Liu Z, Dong Y, Chen L and Jin B: Calreticulin as a
potential diagnostic biomarker for lung cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 61:855–864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kageyama S, Isono T, Matsuda S, Ushio Y,
Satomura S, Terai A, Arai Y, Kawakita M, Okada Y and Yoshiki T:
Urinary calreticulin in the diagnosis of bladder urothelial
carcinoma. Int J Urol. 16:481–486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen CN, Chang CC, Su TE, Hsu WM, Jeng YM,
Ho MC, Hsieh FJ, Lee PH, Kuo ML, Lee H and Chang KJ: Identification
of calreticulin as a prognosis marker and angiogenic regulator in
human gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:524–533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsu WM, Hsieh FJ, Jeng YM, Kuo ML, Chen
CN, Lai DM, Hsieh LJ, Wang BT, Tsao PN, Lee H, et al: Calreticulin
expression in neuroblastoma-a novel independent prognostic factor.
Ann Oncol. 16:314–321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alfonso P, Núñez A, Madoz-Gurpide J,
Lombardia L, Sánchez L and Casal JI: Proteomic expression analysis
of colorectal cancer by two-dimensional differential gel
electrophoresis. Proteomics. 5:2602–2611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen CN, Su TE, Lu YC and Lee H:
Calreticulin regulates cell proliferation and migration in gastric
cancer cell line AGS. FASEB J. 21:A13182007.
|
|
22
|
Kabbage M, Trimeche M, Bergaoui S, Hammann
P, Kuhn L, Hamrita B, ben Nasr H, Chaieb A, Chouchane L and Chahed
K: Calreticulin expression in infiltrating ductal breast
carcinomas: Relationships with disease progression and humoral
immune responses. Tumour Biol. 34:1177–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park S, Huh HJ, Mun YC, Seong CM, Chung
WS, Chung HS and Huh J: Calreticulin mRNA expression and
clinicopathological characteristics in acute myeloid leukemia.
Cancer Genet. 208:630–635. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kourie HR, Ameye L, Paesmans M and Bron D:
Improved Survival of Calreticulin-Mutated Patients Compared With
Janus Kinase 2 in Primary Myelofibrosis: A Meta-Analysis. Clin
Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 16:264–268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mans S, Banz Y, Mueller BU and Pabst T:
The angiogenesis inhibitor vasostatin is regulated by neutrophil
elastase-dependent cleavage of calreticulin in AML patients. Blood.
120:2690–2699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao H and Shockey JM: Comparison of TaqMan
and SYBR Green qPCR methods for quantitative gene expression in
tung tree tissues. J Agric Food Chem. 60:12296–12303. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J:
Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol.
731:237–245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu MH, Su Q, Cheng AL, Tan H and Song Y:
Experimental study of HL-60 cell differentiation induced by diallyl
disulfide. Zhong Guo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao. 19:319–322. 2003.(In
Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Ling H, Zhang LY, Su Q, Song Y, Luo ZY,
Zhou XT, Zeng X, He J, Tan H and Yuan JP: Erk is involved in the
differentiation induced by diallyl disulfide in the human gastric
cancer cell line MGC803. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 11:408–423. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He J, Su Q, Huang WG, Xie HL, Liang SP,
Song Y, Xie JY, Zhou XT, Tan H, Zhao J and Wu MH: Proteomic initial
analysis of differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells induced
by diallyl disulfide. FEBS J. 272:4402005.
|
|
31
|
Michalak M, Groenendyk J, Szabo E, Gold LI
and Opas M: Calreticulin, a multi-process calcium-buffering
chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 417:651–666.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Walter RB, Appelbaum FR, Estey EH and
Bernstein ID: Acute myeloid leukemia stem cells and CD33-targeted
immunotherapy. Blood. 119:6198–6208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ayadi L, Abid N, Makni S, Bahri I, Frikha
I and Sellami-Boudawara T: An unusual tumour of the lung.
Pathologica. 107:14–18. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jurcic JG: What happened to anti-CD33
therapy for acute myeloid leukemia? Curr Hematol Malig Rep.
7:65–73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arora M, Poe SL, Ray A and Ray P:
LPS-induced CD11b+Gr1(int)F4/80+ regulatory myeloid cells suppress
allergen-induced airway inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:827–832. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Heo SK, Noh EK, Yoon DJ, Jo JC, Koh S,
Baek JH, Park JH, Min YJ and Kim H: Rosmarinic acid potentiates
ATRA-induced macrophage differentiation in acute promyelocytic
leukemia NB4 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 747:36–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|