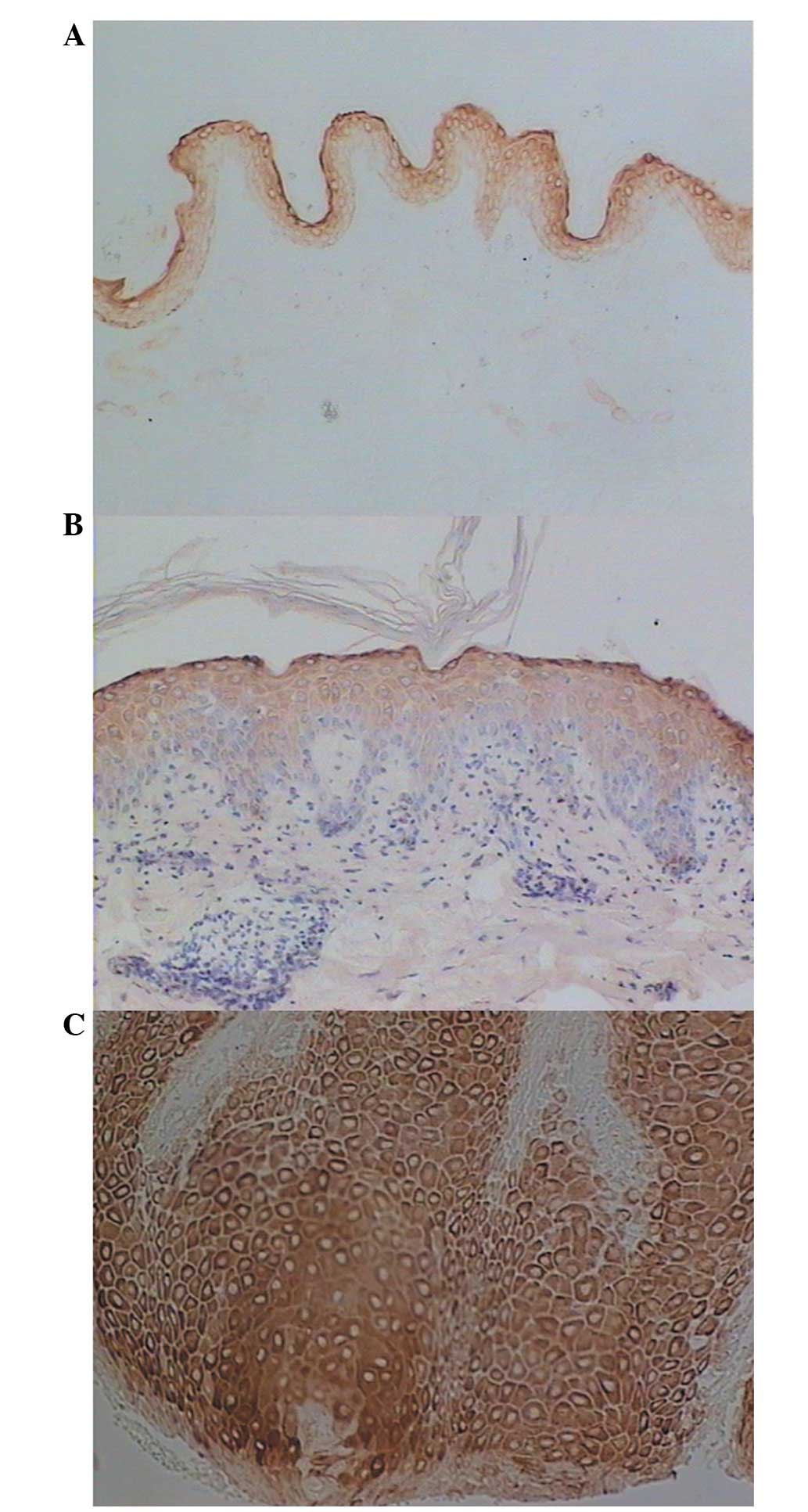
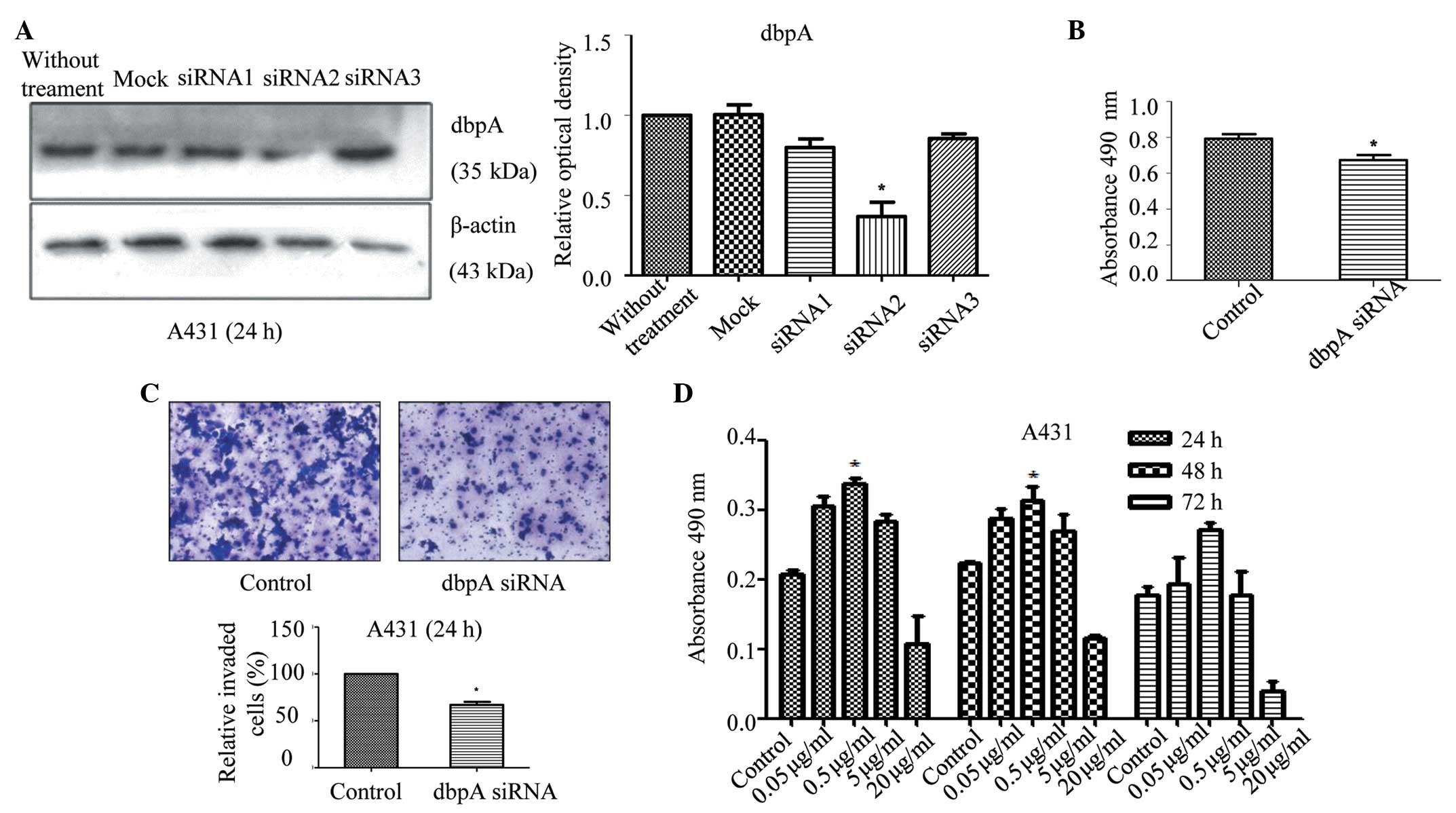
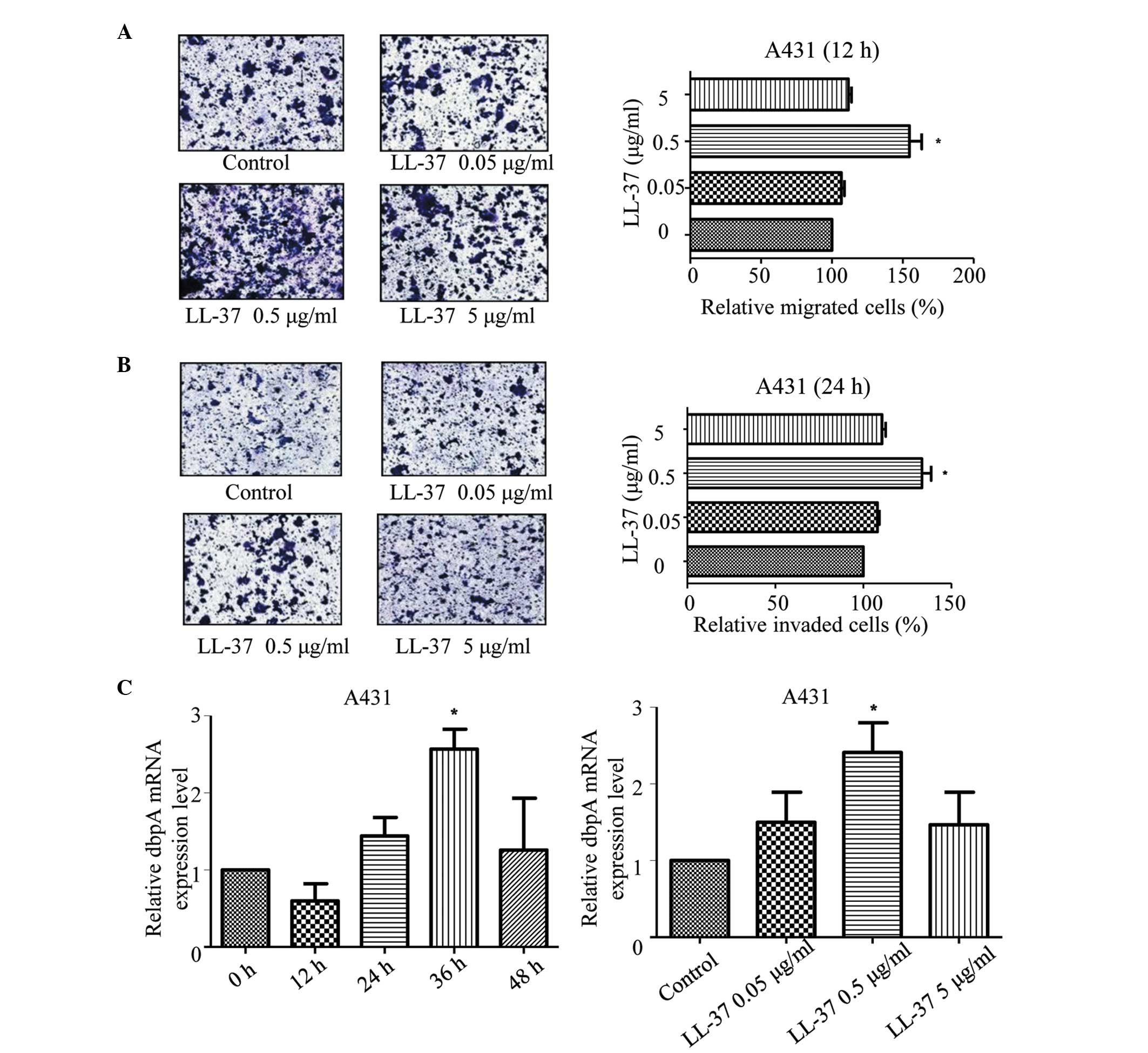
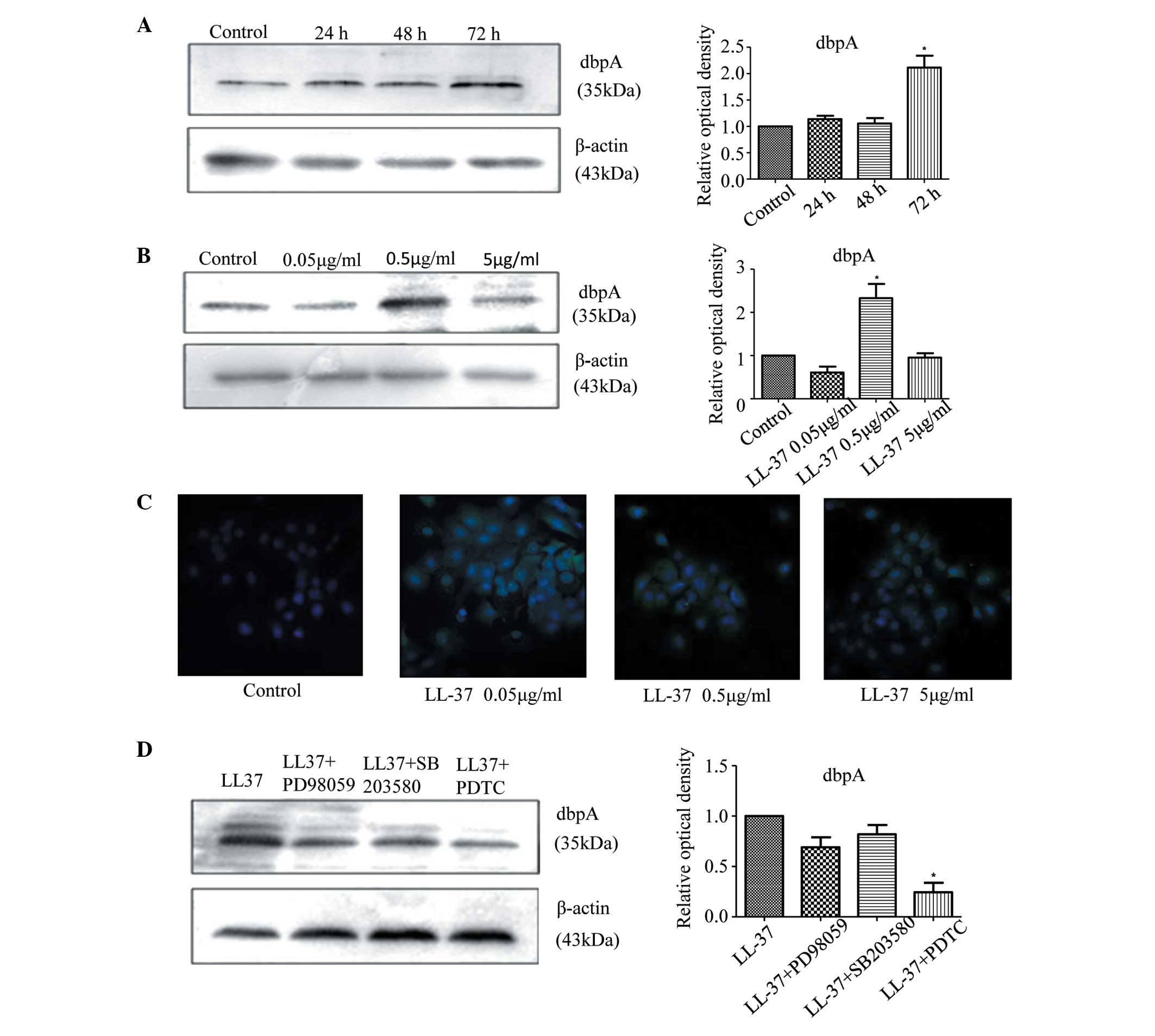
|
1
|
Knackstedt TJ, Brennick JB, Perry AE, Li
Z, Quatrano NA and Samie FH: Frequency of squamous cell carcinoma
(SCC) invasion in transected SCC in situ referred for Mohs surgery:
The Dartmouth-Hitchcock experience. Int J Dermatol. 54:830–833.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR and
Coldiron BM: Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer
(keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA
Dermatol. 151:1081–1086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sapijaszko M, Zloty D, Bourcier M, Poulin
Y, Janiszewski P and Ashkenas J: Canadian Non-melanoma Skin Cancer
Guidelines Committee: Non-melanoma skin cancer in Canada chapter 5:
Management of squamous cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg.
19:249–259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakura H, Maekawa T, Imamoto F, Yasuda K
and Ishii S: Two human genes isolated by a novel method encode
DNA-binding proteins containing a common region of homology. Gene.
73:499–507. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kudo S, Mattei MG and Fukuda M:
Characterization of the gene for dbpA, a family member of the
nucleic-acid-binding proteins containing a cold-shock domain. Eur J
Biochem. 231:72–82. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Balda MS and Matter K: The tight junction
protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate
ErbB-2 expression. EMBO J. 19:2024–2033. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wolffe AP: Structural and functional
properties of the evolutionarily ancient Y-box family of nucleic
acid binding proteins. Bioessays. 16:245–251. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kohno K, Izumi H, Uchiumi T, Ashizuka M
and Kuwano M: The pleiotropic functions of the Y-box-binding
protein, YB-1. Bioessays. 25:691–698. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uramoto H, Izumi H, Ise T, Tada M, Uchiumi
T, Kuwano M, Yasumoto K, Funa K and Kohno K: p73 Interacts with
c-Myc to regulate Y-box-binding protein-1 expression. J Biol Chem.
277:31694–31702. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sourisseau T, Georgiadis A, Tsapara A, Ali
RR, Pestell R, Matter K and Balda MS: Regulation of PCNA and cyclin
D1 expression and epithelial morphogenesis by the ZO-1-regulated
transcription factor ZONAB/DbpA. Mol Cell Biol. 26:2387–2398. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tobita H, Kajino K, Inami K, Kano S, Yasen
M, Imamura O, Kinoshita Y and Hino O: Gene expression profile of
DNA binding protein A transgenic mice. Int J Oncol. 29:673–679.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dürr UH, Sudheendra US and Ramamoorthy A:
LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of
antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1758:1408–1425. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bucki R, Leszczynska K, Namiot A and
Sokolowski W: Cathelicidin LL-37: A multitask antimicrobial
peptide. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 58:15–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu WK, Wang G, Coffelt SB, Betancourt AM,
Lee CW, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J, Sung JJ and Cho CH: Emerging roles of
the host defense peptide LL-37 in human cancer and its potential
therapeutic applications. Int J Cancer. 127:1741–1747. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Coffelt SB and Scandurro AB: Tumors sound
the alarmin(s). Cancer Res. 68:6482–6485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hensel JA, Chanda D, Kumar S, Sawant A,
Grizzle WE, Siegal GP and Ponnazhagan S: LL-37 as a therapeutic
target for late stage prostate cancer. Prostate. 71:659–670. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gill K, Mohanti BK, Singh AK, Mishra B and
Dey S: The over expression of cathelicidin peptide LL37 in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma: The peptide marker for the prognosis
of cancer. Cancer Biomark. 10:125–134. 2011.2012. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim JE, Kim HJ, Choi JM, Lee KH, Kim TY,
Cho BK, Jung JY, Chung KY, Cho D and Park HJ: The antimicrobial
peptide human cationic antimicrobial protein-18/cathelicidin LL-37
as a putative growth factor for malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol.
163:959–967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heilborn JD, Nilsson MF, Jimenez CI,
Sandstedt B, Borregaard N, Tham E, Sørensen OE, Weber G and Ståhle
M: Antimicrobial protein hCAP18/LL-37 is highly expressed in breast
cancer and is a putative growth factor for epithelial cells. Int J
Cancer. 114:713–719. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Coffelt SB, Waterman RS, Florez L, Höner
zu Bentrup K, Zwezdaryk KJ, Tomchuck SL, LaMarca HL, Danka ES,
Morris CA and Scandurro AB: Ovarian cancers overexpress the
antimicrobial protein hCAP-18 and its derivative LL-37 increases
ovarian cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Int J Cancer.
122:1030–1039. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
von Haussen J, Koczulla R, Shaykhiev R,
Herr C, Pinkenburg O, Reimer D, Wiewrodt R, Biesterfeld S, Aigner
A, Czubayko F, et al: The host defence peptide LL-37/hCAP-18 is a
growth factor for lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 59:12–23. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coffelt SB, Tomchuck SL, Zwezdaryk KJ,
Danka ES and Scandurro AB: Leucine leucine-37 uses formyl peptide
receptor-like 1 to activate signal transduction pathways, stimulate
oncogenic gene expression, and enhance the invasiveness of ovarian
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:907–915. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coffelt SB, Marini FC, Watson K, Zwezdaryk
KJ, Dembinski JL, LaMarca HL, Tomchuck SL, Honer zu Bentrup K,
Danka ES, Henkle SL and Scandurro AB: The pro-inflammatory peptide
LL-37 promotes ovarian tumor progression through recruitment of
multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:3806–3811. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Girnita A, Zheng H, Grönberg A, Girnita L
and Ståhle M: Identification of the cathelicidin peptide LL-37 as
agonist for the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor.
Oncogene. 31:352–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choi KY, Napper S and Mookherjee N: Human
cathelicidin LL-37 and its derivative IG-19 regulate
interleukin-32-induced inflammation. Immunology. 143:68–80. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chuang CM, Monie A, Wu A, Mao CP and Hung
CF: Treatment with LL-37 peptide enhances antitumor effects induced
by CpG oligodeoxynucleotides against ovarian cancer. Hum Gene Ther.
20:303–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li D, Wang X, Wu JL, Quan WQ, Ma L, Yang
F, Wu KY and Wan HY: Tumor-produced versican V1 enhances
hCAP18/LL-37 expression in macrophages through activation of TLR2
and vitamin D3 signaling to promote ovarian cancer progression in
vitro. PLoS One. 8:e566162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kittaka M, Shiba H, Kajiya M, Ouhara K,
Takeda K, Kanbara K, Fujita T, Kawaguchi H, Komatsuzawa H and
Kurihara H: Antimicrobial peptide LL37 promotes vascular
endothelial growth factor-A expression in human periodontal
ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 48:228–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yasen M, Kajino K, Kano S, Tobita H,
Yamamoto J, Uchiumi T, Kon S, Maeda M, Obulhasim G, Arii S and Hino
O: The up-regulation of Y-box binding proteins (DNA binding protein
A and Y-box binding protein-1) as prognostic markers of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7354–7361. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang LL, He DL, Li X, Li L, Zhu GD, Zhang
D and Wang XY: Overexpression of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor
inhibit growth of human bladder cancer cell in vitro and in vivo.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:895–900. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guay D, Garand C, Reddy S, Schmutte C and
Lebel M: The human endonuclease III enzyme is a relevant target to
potentiate cisplatin cytotoxicity in Y-box-binding protein-1
overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 99:762–769. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang GR, Zheng Y, Che XM, Wang XY, Zhao
JH, Wu KJ, Zeng J, Pan CE and He DL: Upregulation of human DNA
binding protein A (dbpA) in gastric cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 30:1436–1442. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koike K, Uchiumi T, Ohga T, Toh S, Wada M,
Kohno K and Kuwano M: Nuclear translocation of the Y-box binding
protein by ultraviolet irradiation. FEBS Lett. 417:390–394. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arakawa Y, Kajino K, Kano S, Tobita H,
Hayashi J, Yasen M, Moriyama M, Arakawa Y and Hino O: Transcription
of dbpA, a Y box binding protein, is positively regulated by E2F1:
Implications in hepatocarcinogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
322:297–302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bandurska K, Berdowska A,
Barczyńska-Felusiak R and Krupa P: Unique features of human
cathelicidin LL-37. Biofactors. 41:289–300. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu J and Du L: PERK pathway is involved
in oxygen-glucose-serum deprivation-induced NF-κB activation via
ROS generation in spinal cord astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 467:197–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|