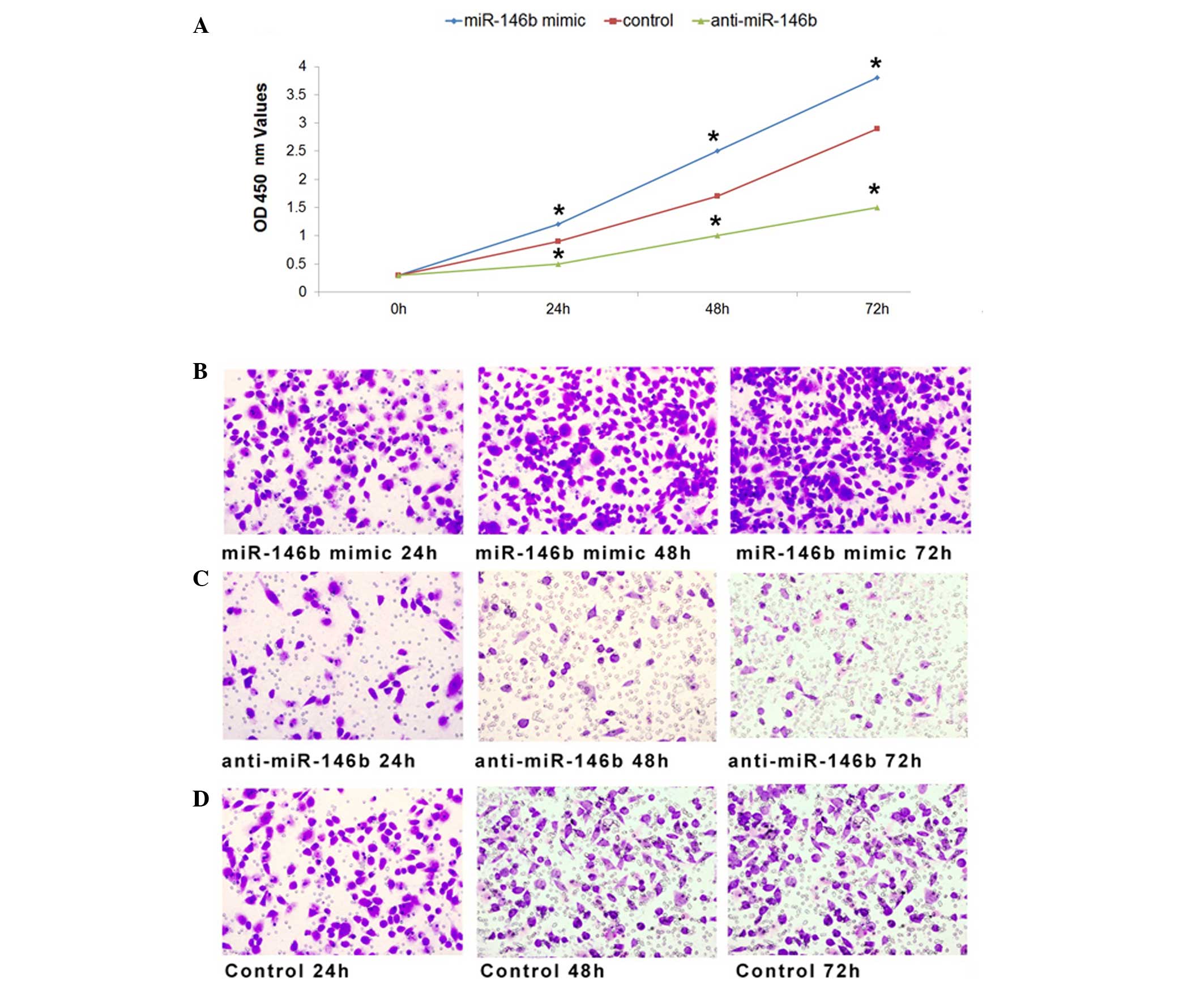
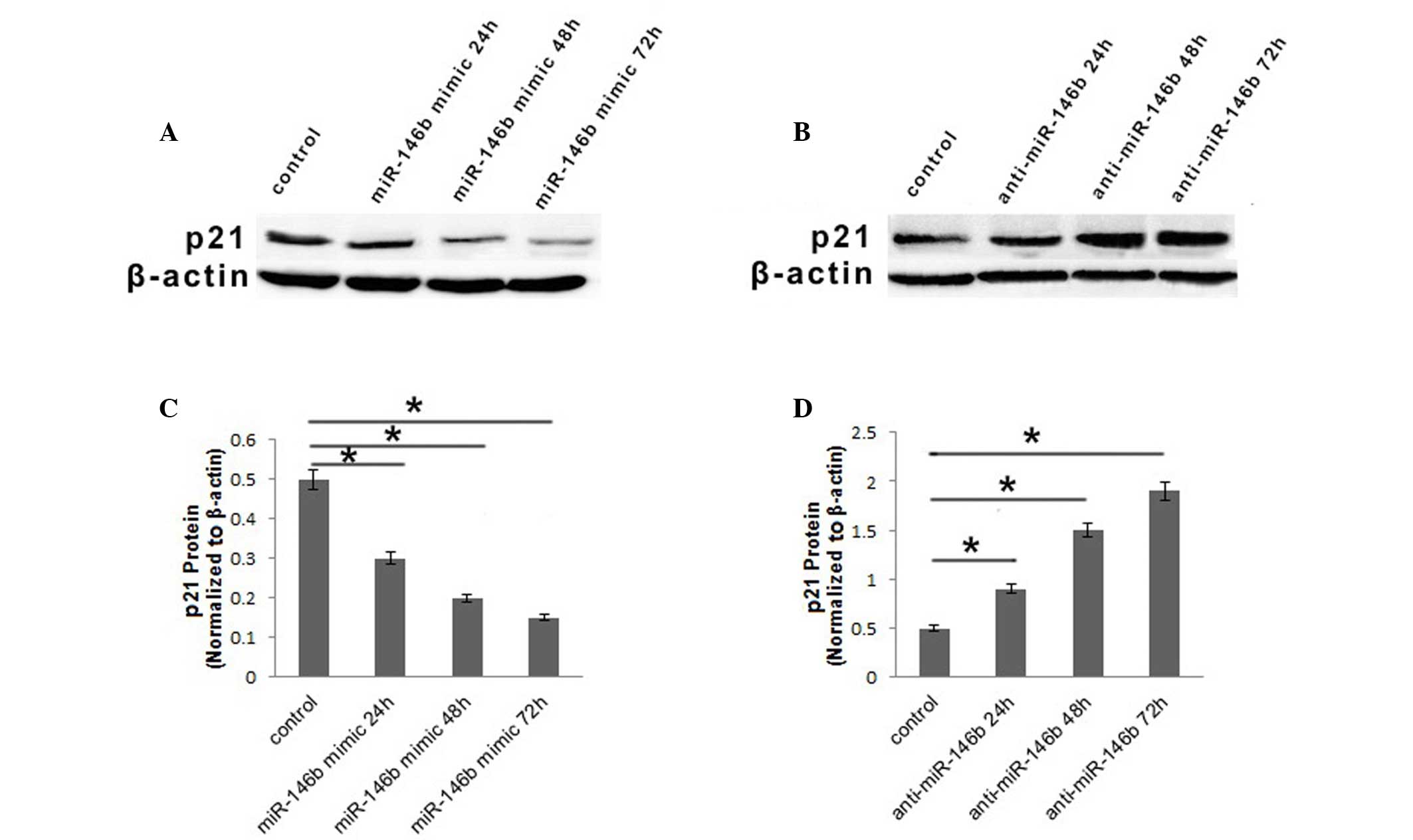
|
1
|
Viola D, Valerio L, Molinaro E, Agate L,
Bottici V, Biagini A, Lorusso L, Cappagli V, Pieruzzi L, Giani C,
et al: Treatment of advanced thyroid cancer with targeted
therapies: Ten years of experience. Endocr Relat Cancer.
23:R185–R205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Likhterov I, Tuttle RM, Haser GC, Su HK,
Bergman D, Alon EE, Bernet V, Brett E, Cobin R, Dewey EH, et al:
Improving the adoption of thyroid cancer clinical practice
guidelines. Laryngoscope. April 14–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Smallridge RC, Ain KB, Asa SL, Bible KC,
Brierley JD, Burman KD, Kebebew E, Lee NY, Nikiforov YE, Rosenthal
MS, et al: American Thyroid Association Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
Guidelines Taskforce: American Thyroid Association guidelines for
management of patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer. Thyroid.
22:1104–1139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, Diorio
D and Nikiforov YE: MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid
tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:1600–1608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kebebew E: Hereditary non-medullary
thyroid cancer: World. J Surg. 32:678–682. 2008.
|
|
6
|
Vriens MR, Suh I, Moses W and Kebebew E:
Clinical features and genetic predisposition to hereditary
nonmedullary thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 19:1343–1349. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smallridge RC and Copland JA: Anaplastic
thyroid carcinoma: Pathogenesis and emerging therapies. Clin Oncol
(R Coll Radiol). 22:486–497. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Azizian A, Gruber J, Ghadimi BM and
Gaedcke J: MicroRNA in rectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
8:416–426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Endzeliņš E, Melne V, Kalniņa Z,
Lietuvietis V, Riekstiņa U, Llorente A and Linē A: Diagnostic,
prognostic and predictive value of cell-free miRNAs in prostate
cancer: A systematic review. Mol Cancer. 15:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sheu SY, Grabellus F, Schwertheim S, Worm
K, Broecker-Preuss M and Schmid KW: Differential miRNA expression
profiles in variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma and
encapsulated follicular thyroid tumours. Br J Cancer. 102:376–382.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, Magnus JF,
Kibukawa M, Schelter JM, Kobayashi SV, Lim L, Burchard J, Jackson
AL, et al: MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and
promote cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2167–2174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiong Y, Zhang L and Kebebew E: MiR-20a is
upregulated in anaplastic thyroid cancer and targets LIMK1. PLoS
One. 9:e961032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen YT, Kitabayashi N, Zhou XK, Fahey TJ
III and Scognamiglio T: MicroRNA analysis as a potential diagnostic
tool for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 21:1139–1146.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vriens MR, Weng J, Suh I, Huynh N,
Guerrero MA, Shen WT, Duh QY, Clark OH and Kebebew E: MicroRNA
expression profiling is a potential diagnostic tool for thyroid
cancer. Cancer. 118:3426–3432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lodewijk L, Prins AM, Kist JW, Valk GD,
Kranenburg O, Rinkes IH and Vriens MR: The value of miRNA in
diagnosing thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Biomark.
11:229–238. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fuziwara CS and Kimura ET: MicroRNA
deregulation in anaplastic thyroid cancer biology. Int J
Endocrinol. 2014:7434502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Visone R, Pallante P, Vecchione A,
Cirombella R, Ferracin M, Ferraro A, Volinia S, Coluzzi S, Leone V,
Borbone E, et al: Specific microRNAs are downregulated in human
thyroid anaplastic carcinomas. Oncogene. 26:7590–7595. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Braun J, Hoang-Vu C, Dralle H and
Hüttelmaier S: Downregulation of microRNAs directs the EMT and
invasive potential of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene.
29:4237–4244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fassina A, Cappellesso R, Simonato F, Siri
M, Ventura L, Tosato F, Busund LT, Pelizzo MR and Fassan M: A
4-MicroRNA signature can discriminate primary lymphomas from
anaplastic carcinomas in thyroid cytology smears. Cancer
Cytopathol. 122:274–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Löhr K, Möritz C, Contente A and
Dobbelstein M: p21/CDKN1A mediates negative regulation of
transcription by p53. J Biol Chem. 278:32507–32516. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rohaly G, Chemnitz J, Dehde S, Nunez AM,
Heukeshoven J, Deppert W and Dornreiter I: A novel human p53
isoform is an essential element of the ATR-intra-S phase
checkpoint. Cell. 122:21–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gupta R, Dong Y, Solomon PD, Wettersten
HI, Cheng CJ, Min JN, Henson J, Dogra SK, Hwang SH, Hammock BD, et
al: Synergistic tumor suppression by combined inhibition of
telomerase and CDKN1A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E3062–E3071.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Minami Y, Kohsaka S, Tsuda M, Yachi K,
Hatori N, Tanino M, Kimura T, Nishihara H, Minami A, Iwasaki N and
Tanaka S: SS18-SSX-regulated miR-17 promotes tumor growth of
synovial sarcoma by inhibiting p21WAF1/CIP1. Cancer Sci.
105:1152–1159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Zhu LJ, Yang YC, Wang ZX and Wang
R: MiR-224 promotes the chemoresistance of human lung
adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin via regulating G1/S
transition and apoptosis by targeting p21(WAF1/CIP1). Br J Cancer.
111:339–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yi C, Wang Q, Wang L, Huang Y, Li L, Liu
L, Zhou X, Xie G, Kang T, Wang H, et al: MiR-663, a microRNA
targeting p21(WAF1/CIP1), promotes the proliferation and
tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 31:4421–4433.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schweppe RE, Klopper JP, Korch C,
Pugazhenthi U, Benezra M, Knauf JA, Fagin JA, Marlow LA, Copland
JA, Smallridge RC and Haugen BR: Deoxyribonucleic acid profiling
analysis of 40 human thyroid cancer cell lines reveals
cross-contamination resulting in cell line redundancy and
misidentification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 93:4331–4341. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abbas T and Dutta A: p21 in cancer:
Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nature Review Cancer.
9:400–414. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Borgdorff V, Lleonart ME, Bishop CL,
Fessart D, Bergin AH, Overhoff MG and Beach DH: Multiple microRNAs
rescue from Ras-induced senescence by inhibiting p21(Waf1/Cip1).
Oncogene. 29:2262–2271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|