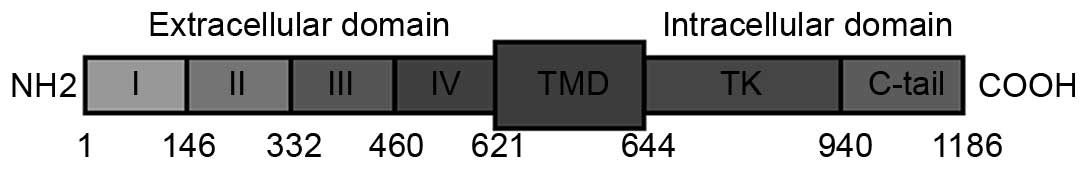
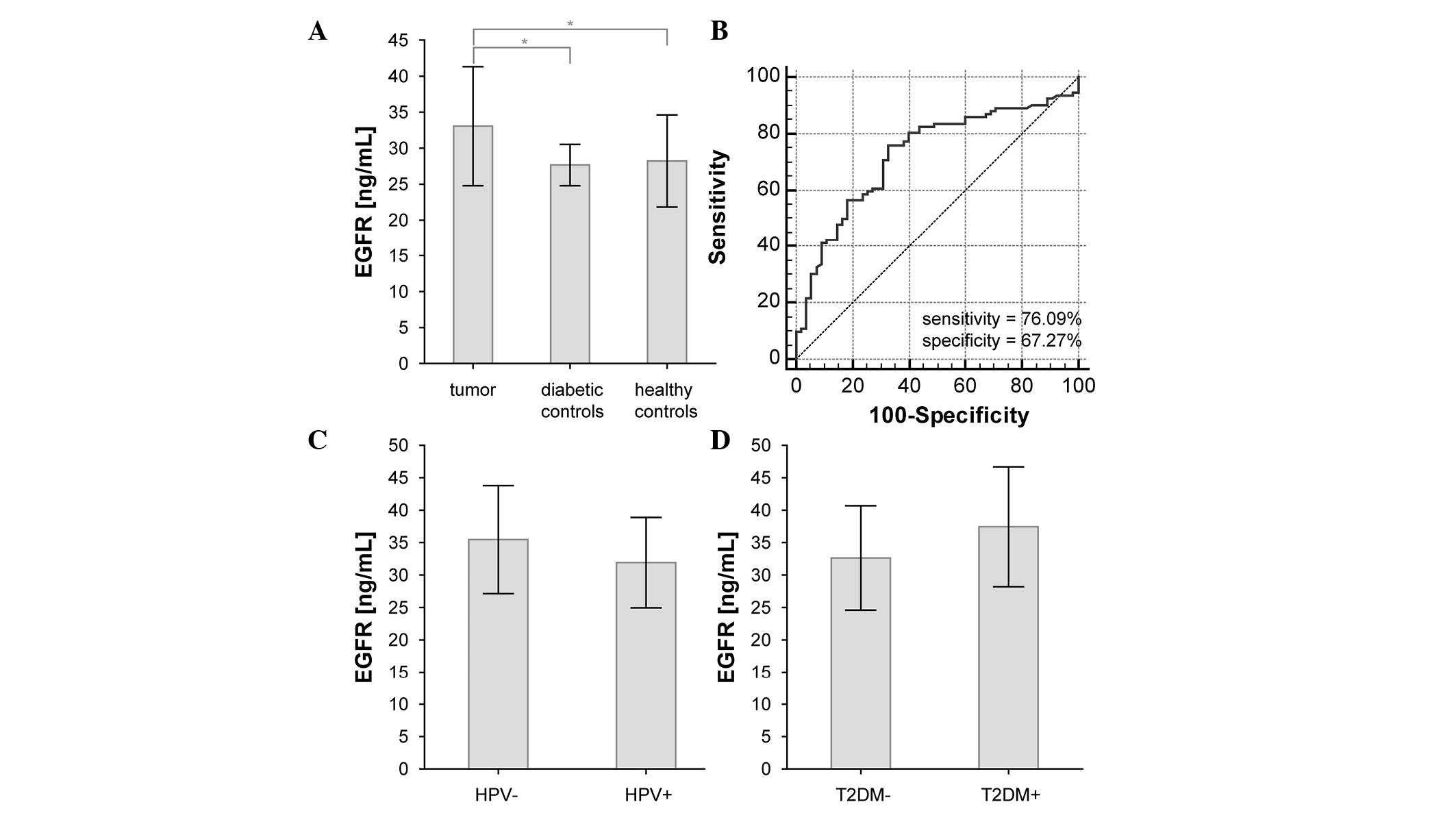
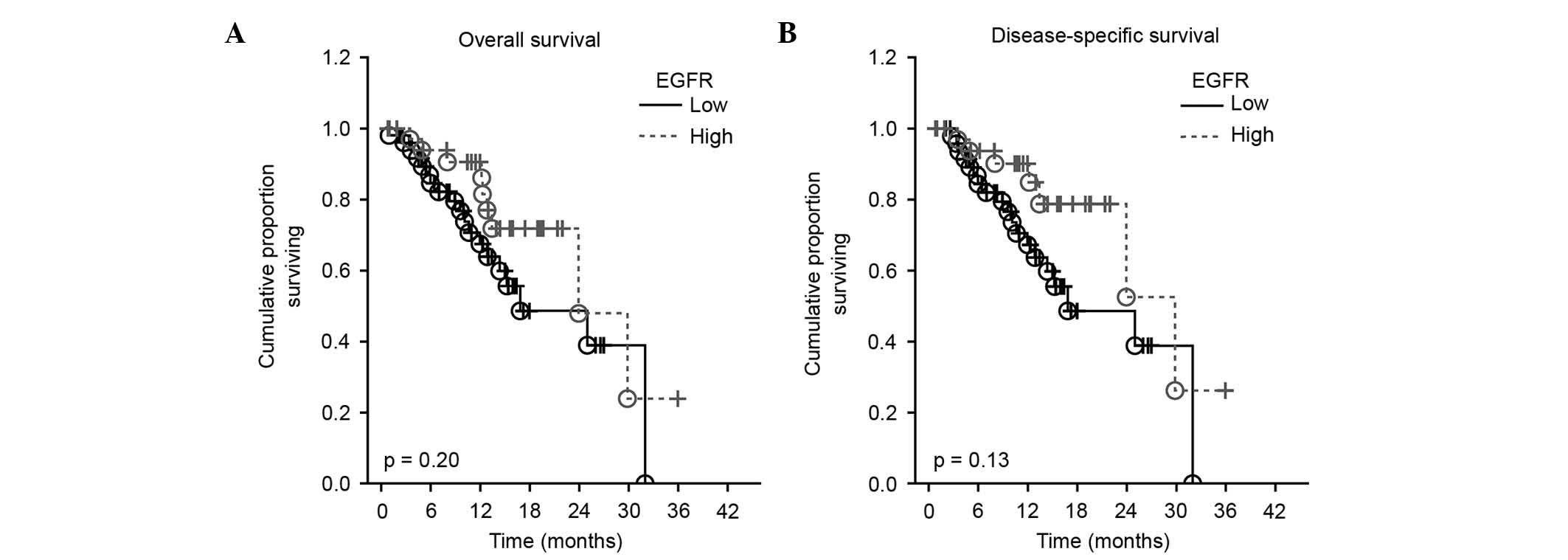
|
1
|
Albitar L, Pickett G, Morgan M, Wilken JA,
Maihle NJ and Leslie KK: EGFR isoforms and gene regulation in human
endometrial cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 9:1662010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick JS, Dull
TJ, Gray A, Tam AW, Lee J, Yarden Y, Libermann TA, Schlessinger J,
et al: Human epidermal growth-factor receptor cDNA sequence and
aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid
carcinoma-cells. Nature. 309:418–425. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ciardiello F and Tortora G: Epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a target in cancer therapy:
Understanding the role of receptor expression and other molecular
determinants that could influence the response to anti-EGFR drugs.
Eur J Cancer. 39:1348–1354. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Psyrri A, Seiwert TY and Jimeno A:
Molecular pathways in head and neck cancer: EGFR, PI3K, and more.
Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 246–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sartor CI: Biological modifiers as
potential radiosensitizers: Targeting the epidermal growth factor
receptor family. Semin Oncol. 27(6 Suppl 11): S15–S20; discussion
92–100. 2000.
|
|
6
|
Woodburn JR: The epidermal growth factor
receptor and its inhibition in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther.
82:241–250. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nicholson RI, Gee JM and Harper ME: EGFR
and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 37(Suppl 4): S9–S15. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F and
Normanno N: Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their
receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
19:183–232. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grandis Rubin J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE,
Day R, Holst VA, Wagener MM, Drenning SD and Tweardy DJ: Levels of
TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 90:824–832. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Box C, Rogers SJ, Mendiola M and Eccles
SA: Tumour-microenvironmental interactions: Paths to progression
and targets for treatment. Semin Cancer Biol. 20:128–138. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zuo JH, Zhu W, Li MY, Li XH, Yi H, Zeng
GQ, Wan XX, He QY, Li JH, Qu JQ, et al: Activation of EGFR promotes
squamous carcinoma SCC10A cell migration and invasion via inducing
EMT-Like phenotype change and MMP-9-mediated degradation of
E-cadherin. J Cell Biochem. 112:2508–2517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Holz C, Niehr F, Boyko M, Hristozova T,
Distel L, Budach V and Tinhofer I:
Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition induced by EGFR activation
interferes with cell migration and response to irradiation and
cetuximab in head and neck cancer cells. Radiother Oncol.
101:158–164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang SJ and Bourguignon LY: Hyaluronan and
the interaction between CD44 and epidermal growth factor receptor
in oncogenic signaling and chemotherapy resistance in head and neck
cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 132:771–778. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hunts JH, Shimizu N, Yamamoto T, Toyoshima
K, Merlino GT, Xu YH and Pastan I: Translocation chromosome 7 of
A431 cells contains amplification and rearrangement of EGF receptor
gene responsible for production of variant mRNA. Somat Cell Mol
Genet. 11:477–484. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kulasinghe A, Perry C, Jovanovic L, Nelson
C and Punyadeera C: Circulating tumour cells in metastatic head and
neck cancers. Int J Cancer. 136:2515–2523. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ancot F, Foveau B, Lefebvre J, Leroy C and
Tulasne D: Proteolytic cleavages give receptor tyrosine kinases the
gift of ubiquity. Oncogene. 28:2185–2195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Perez-Torres M, Valle BL, Maihle NJ,
Negron-Vega L, Nieves-Alicea R and Cora EM: Shedding of epidermal
growth factor receptor is a regulated process that occurs with
overexpression in malignant cells. Exp Cell Res. 314:2907–2918.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sanderson MP, Keller S, Alonso A, Riedle
S, Dempsey PJ and Altevogt P: Generation of novel, secreted
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR/ErbB1) isoforms via metal
loprotease-dependent ectodomain shedding and exosome secretion. J
Cell Biochem. 103:1783–1797. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vairaktaris E, Goutzanis L, Yapijakis C,
Vassiliou S, Spyridonidou S, Vylliotis A, Nkenke E, Lazaris AC,
Strantzias P and Patsouris E: Diabetes enhances the expression of
H-ras and suppresses the expression of EGFR leading to increased
cell proliferation. Histol Histopathol. 24:531–539. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Britton DJ, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM,
Barrow D, Giles M, McClelland RA, Gee JM and Nicholson RI:
Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signalling
pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 96:131–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Levin ER: Bidirectional signaling between
the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol
Endocrinol. 17:309–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bonaccorsi L, Muratori A, Carloni V,
Marchiani S, Formigli L, Forti G and Baldi E: The androgen receptor
associates with the epidermal growth factor receptor in
androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells. Steroids. 69:549–552.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Raudenska M, Sztalmachova M, Gumulec J,
Fojtu M, Polanska H, Balvan J, Feith M, Binkova H, Horakova Z,
Kostrica R, et al: Prognostic significance of the tumour-adjacent
tissue in head and neck cancers. Tumour Biol. 36:9929–9939. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polanska H, Raudenska M, Gumulec J,
Sztalmachova M, Adam V, Kizek R and Masarik M: Clinical
significance of head and neck squamous cell cancer biomarkers. Oral
Oncol. 50:168–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Grandis JR and Tweardy DJ: Elevated levels
of transforming growth-factor-alpha and epidermal growth-factor
receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head
and neck-cancer. Cancer Res. 53:3579–3584. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Partanen R, Hemminki K, Koskinen H, Luo
JC, Carney WP and Brandtrauf PW: The detection of increased amounts
of the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth-factor receptor
in serum during carcinogenesis in asbestosis patients. J Occup Med.
36:1324–1328. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Witters LM, Curley EM, Kumar R, Chinchilli
VM, Harvey JP, Crebbin V, Harvey HA and Lipton A: Epidermal growth
factor receptor ectodomain in the urine of patients with squamous
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 1:551–557. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carney WP: Circulating oncoproteins
HER2/neu, EGFR and CAIX (MN) as novel cancer biomarkers. Expert Rev
Mol Diagn. 7:309–319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ye P, Zhao J, Wang S and Kong FM: The
plasma level of soluble epidermal growth factor Receptor (EGFR) and
overall survival (OS) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
patients. Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical
Oncology (ASCO). J Clin Oncol. 33:e190912015.
|