|
1
|
Lorenzetto E, Brenca M, Boeri M, Verri C,
Piccinin E, Gasparini P, Facchinetti F, Rossi S, Salvatore G,
Massimino M, et al: YAP1 acts as oncogenic target of 11q22
amplification in multiple cancer subtypes. Oncotarget. 5:2608–2621.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen Z and Stanger BZ: YAP regulates
S-Phase entry in endothelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01175222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao B, Li L, Lei Q and Guan KL: The
Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: An
updated version. Genes Dev. 24:862–874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, Yagi
R, Hall RA, Donowitz M, Hisaminato A, Fujiwara T, Ito Y, Cantley LC
and Yaffe MB: TAZ: A novel transcriptional co-activator regulated
by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J.
19:6778–6791. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shimomura T, Miyamura N, Hata S, Miura R,
Hirayama J and Nishina H: The PDZ-binding motif of Yes-associated
protein is required for its co-activation of TEAD-mediated CTGF
transcription and oncogenic cell transforming activity. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 17:917–931. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Espanel X and Sudol M: Yes-associated
protein and p53-binding protein-2 interact through their WW and SH3
domains. J Biol Chem. 276:14514–14523. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moroishi T, Hansen CG and Guan KL: The
emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 276:73–79.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhou X, Wang Z, Huang W and Lei QY: G
protein-coupled receptors: Binding the gap from the extracellular
signals to the Hippo pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
47:10–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E,
Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Frasson C, et
al: YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex
orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell. 158:157–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitamura T, Watari H, Wang L, Kanno H,
Kitagawa M, Hassan MK, Kimura T, Tanino M, Nishihara H, Tanaka S
and Sakuragi N: MicroRNA 31 functions as an endometrial cancer
oncogene by suppressing Hippo tumor suppressor pathway. Mol Cancer.
13:972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Tang F, Terracciano L, Hynx D,
Kohler R, Bichet S, Hess D, Cron P, Hemmings BA, Hergovich A and
Schmitz-Rohmer D: NDR functions as a physiological YAP1 kinase in
the intestinal epithelium. Curr Biol. 25:296–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Basu S, Totty NF, Irwin MS, Sudol M and
Downward J: Akt phosphorylates the Yes-associated protein, YAP, to
induce interaction with 14-3-3 and attenuation of p73-mediated
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 11:11–23. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Llado V, Nakanishi Y, Duran A, ReinaCampos
M, Shelton PM, Linares JF, Yajima T, Campos A, AzaBlanc P, Leitges
M, et al: Repression of intestinal stem cell function and
tumorigenesis through direct phosphorylation of β-catenin andYap by
PKCζ. Cell Rep. pii:S2211–1247. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Oudhoff MJ, Freeman SA, Couzens AL,
Antignano F, Kuznetsova E, Min PH, Northrop JP, Lehnertz B,
BarsyteLovejoy D, Vedadi M, et al: Control of the hippo pathway by
Set7-dependent methylation of Yap. Dev Cell. 26:188–194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hergovich A and Hemmings BA: Mammalian
NDR/LATS protein kinases in hippo tumor suppressor signaling.
Biofactors. 35:338–345. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sorrentino G, Ruggeri N, Specchia V,
Cordenonsi M, Mano M, Dupont S, Manfrin A, Ingallina E, Sommaggio
R, Vedadi M, et al: Metabolic control of YAP and TAZ by the
mevalonate pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 16:357–366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Low BC, Pan CQ, Shivashankar GV,
Bershadsky A, Sudol M and Sheetz M: YAP/TAZ as mechanosensors and
mechanotransducers in regulating organ size and tumor growth. FEBS
Lett. 588:2663–2670. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Halder G, Dupont S and Piccolo S:
Transduction of mechanical and cytoskeletal cues by YAP and TAZ.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:591–600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
ManaCapelli S, Paramasivam M, Dutta S and
McCollum D: Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway
signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 25:1676–1685. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johnson R and Halder G: The two faces of
Hippo: Targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and
cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:63–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mori M, Triboulet R, Mohseni M,
Schlegelmilch K, Shrestha K, Camargo FD and Gregory RI: Hippo
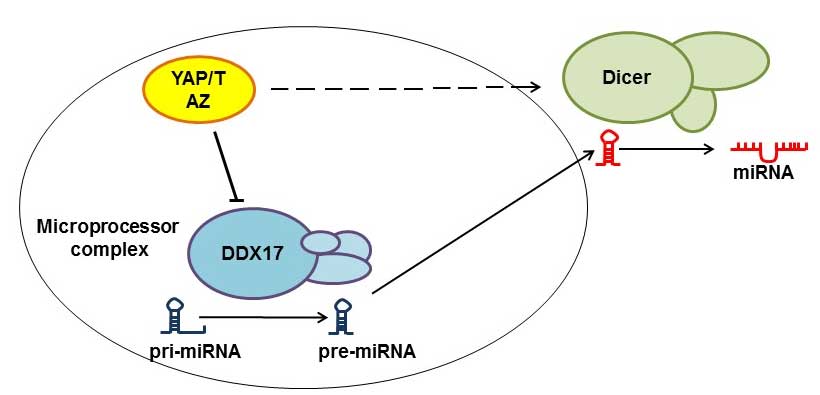
signaling regulates Microprocessor and links cell density-dependent
miRNA biogenesis to cancer. Cell. 156:893–906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chaulk SG, Lattanzi VJ, Hiemer SE, Fahlman
RP and Varelas X: The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ/YAP regulate
dicer expression and microRNA biogenesis through Let-7. J Biol
Chem. 289:1886–1891. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
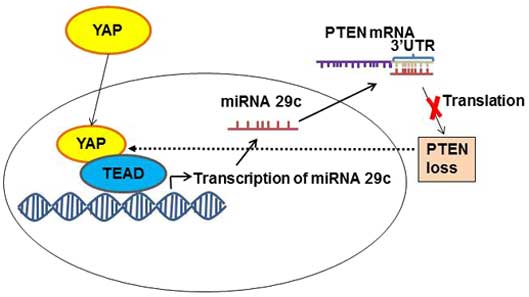
Tumaneng K, Schlegelmilch K, Russell RC,
Yimlamai D, Basnet H, Mahadevan N, Fitamant J, Bardeesy N, Camargo
FD and Guan KL: YAP mediates crosstalk between the Hippo and PI
(3)K-TOR pathways by suppressing PTEN via miR-29. Nat Cell Biol.
14:1322–1329. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fausti FI, Di Agostino S, Cioce M, Bielli
P, Sette C, Pandolfi PP, Oren M, Sudol M, Strano S and Blandino G:
ATM kinase enables the functional axis of YAP, PML and p53 to
ameliorate loss of Werner protein-mediated oncogenic senescence.
Cell Death Differ. 20:1498–1509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie Q, Chen J, Feng H, Peng S, Adams U,
Bai Y, Huang L, Li J, Huang J, Meng S, et al: YAP/TEAD-mediated
transcription controls cellular senescence. Cancer Res.
73:3615–3624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kapoor A, Yao W, Ying H, Hua S, Liewen A,
Wang Q, Zhong Y, Wu CJ, Sadanandam A, Hu B, et al: Yap1 activation
enables bypass of oncogenic Kras addiction in pancreatic cancer.
Cell. 158:185–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shao DD, Xue W, Krall EB, Bhutkar A,
Piccioni F, Wang X, Schinzel AC, Sood S, Rosenbluh J, Kim JW, et
al: KRAS and YAP1 converge to regulate EMT and tumor survival.
Cell. 158:171–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Greten FR: YAP1 takes over when oncogenic
K-Ras slumbers. Cell. 158:11–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alptekin A, Abali GK, Wang Q and Bekir C:
Regulation of androgenic signaling by yes-associated protein, YAP,
in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 73(8): Supplement. 7592013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Yang S, Chen X, Stauffer S, Yu F,
Lele SM, Fu K, Datta K, Palermo N, Chen Y and Dong J: The hippo
pathway effector, YAP, regulates motility, invasion and
castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cell
Biol. 35:1350–1362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie Y, Lu W, Liu S, Yang Q, Carver BS, Li
E, Wang Y, Fazli L, Gleave M and Chen Z: Crosstalk between nuclear
MET and SOX9/β-catenin correlates with castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Mol Endocrinol. 28:1629–1639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wanjala J, Taylor BS, Chapinski C,
Hieronymus H, Wongvipat J, Chen Y, Nanjangud GJ, Schultz N, Xie Y,
Liu Sr, et al: Identifying actionable targets through integrative
analyses of GEM model and human prostate cancer genomic profiling.
Mol Cancer Ther. 14:278–288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiao S, Wang H, Shi Z, Dong A, Zhang W,
Song X, He F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wang W, et al: A peptide mimicking
VGLL4 function acts as a YAP antagonist therapy against gastric
cancer. Cancer Cell. 25:166–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fitamant J, Kottakis F, Benhamouche S,
Tian HS, Chuvin N, Parachoniak CA, Nagle JM, Perera RM, Lapouge M,
Deshpande V, et al: YAP inhibition restores hepatocyte
differentiation in advanced HCC, leading to tumor regression. Cell
Rep. pii:S2211–S1247. 2015.
|
|
36
|
Lin L, Sabnis AJ, Chan E, Olivas V, Cade
L, Pazarentzos E, Asthana S, Neel D, Yan JJ, Lu X, et al: The Hippo
effector YAP promotes resistance to RAF- and MEK-targeted cancer
therapies. Nat Genet. 47:250–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eroglu Z and Ribas A: Combination therapy
with BRAF and MEK inhibitors for melanoma: Latest evidence and
place in therapy. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 8:48–56. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|