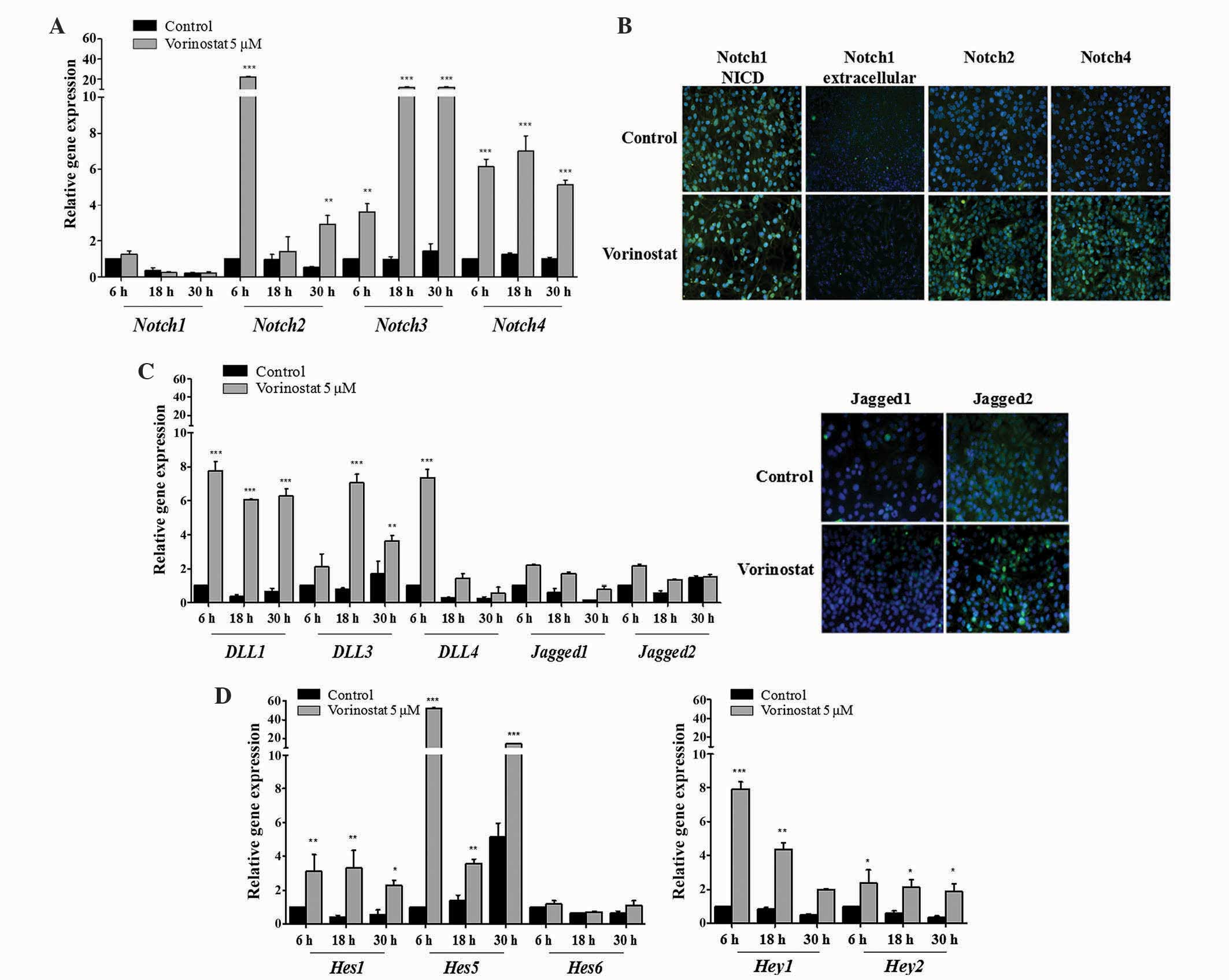
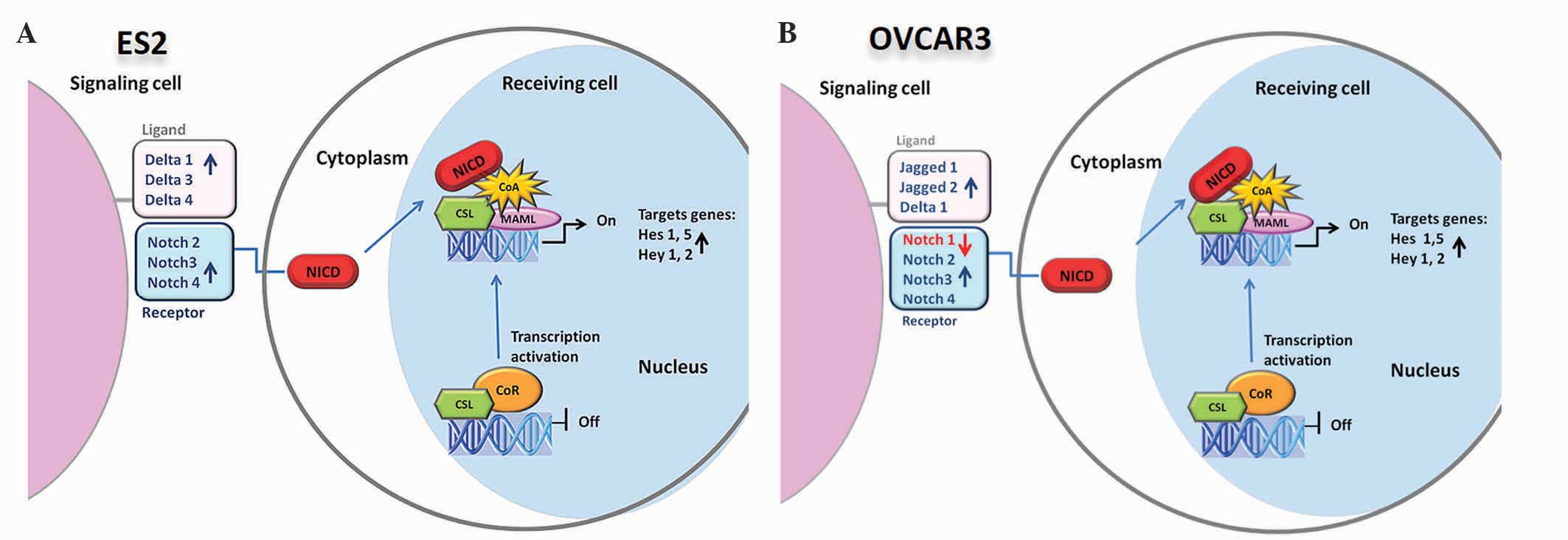
|
1
|
Reinhardt MJ: Gynecologic tumorsPET in
Oncology. Dresel S: 170. Springer; Berlin: pp. 141–150. 2008,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bast RC, Hennessy B and Mills GB: The
biology of ovarian cancer: New opportunities for translation. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:415–428. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smolle E, Taucher V, Pichler M, Petru E,
Lax S and Haybaeck J: Targeting signaling pathways in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:9536–9555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.
Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature.
474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
DelCarmen MG, Birrer M and Schorge JO:
Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary: A review of the literature.
Gynecol Oncol. 126:481–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ayhan A, Mao TL, Seckin T, Wu CH, Guan B,
Ogawa H, Futagami M, Mizukami H, Yokoyama Y, Kurman RJ and Shih
IeM: Loss of ARID1A expression is an early molecular event in tumor
progression from ovarian endometriotic cyst to clear cell and
endometrioid carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:1310–1305. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guan B, Wang TL and Shih IM: ARID1A, a
factor that promotes formation of SWI/SNF-mediated chromatin
remodeling, is a tumor suppressor in gynecologic cancers. Cancer
Res. 71:6718–6727. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kotsopoulos IC, Papanikolaou A,
Lambropoulos AF, Papazisis KT, Tsolakidis D, Touplikioti P and
Tarlatzis BC: Serous ovarian cancer signaling pathways. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 24:410–417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin KL, Pak JH, Park JY, Choi WH, Lee JY,
Kim JH and Nam JH: Expression profile of histone deacetylases 1, 2
and 3 in ovarian cancer tissues. J Gynecol Oncol. 19:185–190. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takebe N, Nguyen D and Yang SX: Targeting
notch signaling pathway in cancer: Clinical development advances
and challenges. Pharmacol Ther. 141:140–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nickoloff BJ, Osborne BA and Miele L:
Notch signaling as a therapeutic target in cancer: A new approach
to the development of cell fate modifying agents. Oncogene.
22:6598–6608. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aster JC and Blacklow SC: Targeting the
Notch pathway: Twists and turns on the road to rational
therapeutics. J Clin Oncol. 30:2418–2420. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li JL and Harris AL: Notch signaling from
tumor cells: A new mechanism of angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 8:1–3.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dufraine J, Funahashi Y and Kitajewski J:
Notch signaling regulates tumor angiogenesis by diverse mechanisms.
Oncogene. 27:5132–5137. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fleming RJ, Purcell K and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: The NOTCH receptor and its ligands. Trends
Cell Biol. 7:437–441. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lendahl U: A growing family of Notch
ligands. Bioessays. 20:103–107. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gray GE, Mann RS, Mitsiadis E, Henrique D,
Carcangiu ML, Banks A, Leiman J, Ward D, IshHorowitz D and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Human ligands of the Notch receptor. Am J
Pathol. 154:785–794. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamaguchi E, Chiba S, Kumano K, Kunisato
A, Takahashi T, Takahashi T and Hirai H: Expression of Notch
ligands, Jagged1, 2 and Delta1 in antigen presenting cells in mice.
Immunol Lett. 81:59–64. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kao HY, Ordentlich P, KoyanoNakagawa N,
Tang Z, Downes M, Kintner CR, Evans RM and Kadesch T: A histone
deacetylase corepressor complex regulates the Notch signal
transduction pathway. Genes Dev. 12:2269–2277. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ronchini C and Capobianco AJ: Induction of
cyclin D1 transcription and CDK2 activity by Notch (ic):
Implication for cell cycle disruption in transformation by Notch
(ic). Mol Cell Biol. 21:5925–5934. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weng AP, Millholland JM, YashiroOhtani Y,
Arcangeli ML, Lau A, Wai C, Del Bianco C, Rodriguez CG, Sai H,
Tobias J, et al: c-Myc is an important direct target of Notch1 in
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Genes Dev.
20:2096–2109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hirose H, Ishii H, Mimori K, Ohta D,
Ohkuma M, Tsujii H, Saito T, Sekimoto M, Doki Y and Mori M: Notch
pathway as candidate therapeutic target in Her2/Neu/ErbB2
receptor-negative breast tumors. Oncol Rep. 23:35–43.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takai N and Narahara H: Histone
deacetylase inhibitor therapy in epithelial ovarian cancer. J
Oncol. 2010:4584312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bolden JE, Peart MJ and Johnstone RW:
Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 5:769–784. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Richon VM: Cancer biology: mechanism of
antitumour action of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid),
a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Br J Cancer. 95(Suppl 1):
S2–S6. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cooper AL, Greenberg VL, Lancaster PS, Van
Nagell JR Jr, Zimmer SG and Modesitt SC: In vitro and in vivo
histone deacetylase inhibitor therapy with suberoylanilide
hydroxamic acid (SAHA) and paclitaxel in ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 104:596–601. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bolós V, Grego-Bessa J and de la Pompa JL:
Notch signaling in development and cancer. Endocr Rev. 28:339–363.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McAuliffe SM, Morgan SL, Wyant GA, Tran
LT, Muto KW, Chen YS, Chin KT, Partridge JC, Poole BB, Cheng KH, et
al: Targeting Notch, a key pathway for ovarian cancer stem cells,
sensitizes tumors to platinum therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:E2939–E2948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rose SL, Kunnimalaiyaan M, Drenzek J and
Seiler N: Notch 1 signaling is active in ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 117:130–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hopfer O, Zwahlen D, Fey MF and Aebi S:
The Notch pathway in ovarian carcinomas and adenomas. Br J Cancer.
93:709–718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Capaccione KM and Pine SR: The Notch
signaling pathway as a mediator of tumor survival. Carcinogenesis.
34:1420–1430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park JT, Li M, Nakayama K, Mao TL,
Davidson B, Zhang Z, Kurman RJ, Eberhart CG, Shih IeM and Wang TL:
Notch3 gene amplification in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
66:6312–6387. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park JT, Chen X, Tropè CG, Davidson B,
Shih IM and Wang TL: Notch3 overexpression is related to the
recurrence of ovarian cancer and confers resistance to carboplatin.
Am J Pathol. 177:1087–1094. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tan DSP, Miller RE and Kaye SB: New
perspectives on molecular targeted therapy in ovarian clear cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:1553–1559. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jung SG, Kwon YD, Song JA, Back MJ, Lee
SY, Lee C, Hwang YY and An HJ: Prognostic significance of Notch 3
gene expression in ovarian serous carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
101:1977–1983. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iso T, Kedes L and Hamamori Y: HES and
HERP families: Multiple effectors of the Notch signaling pathway. J
Cell Physiol. 194:237–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|