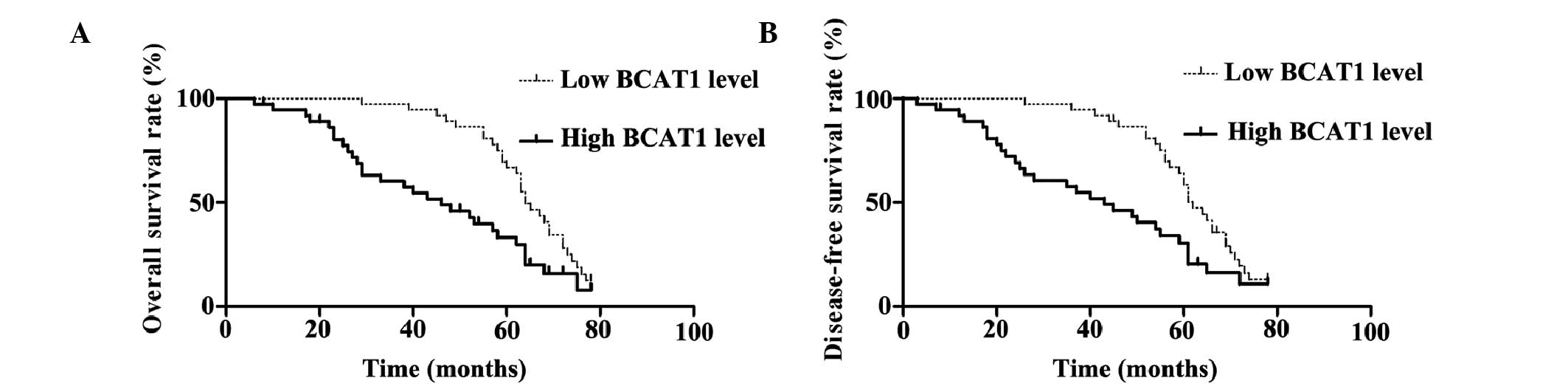
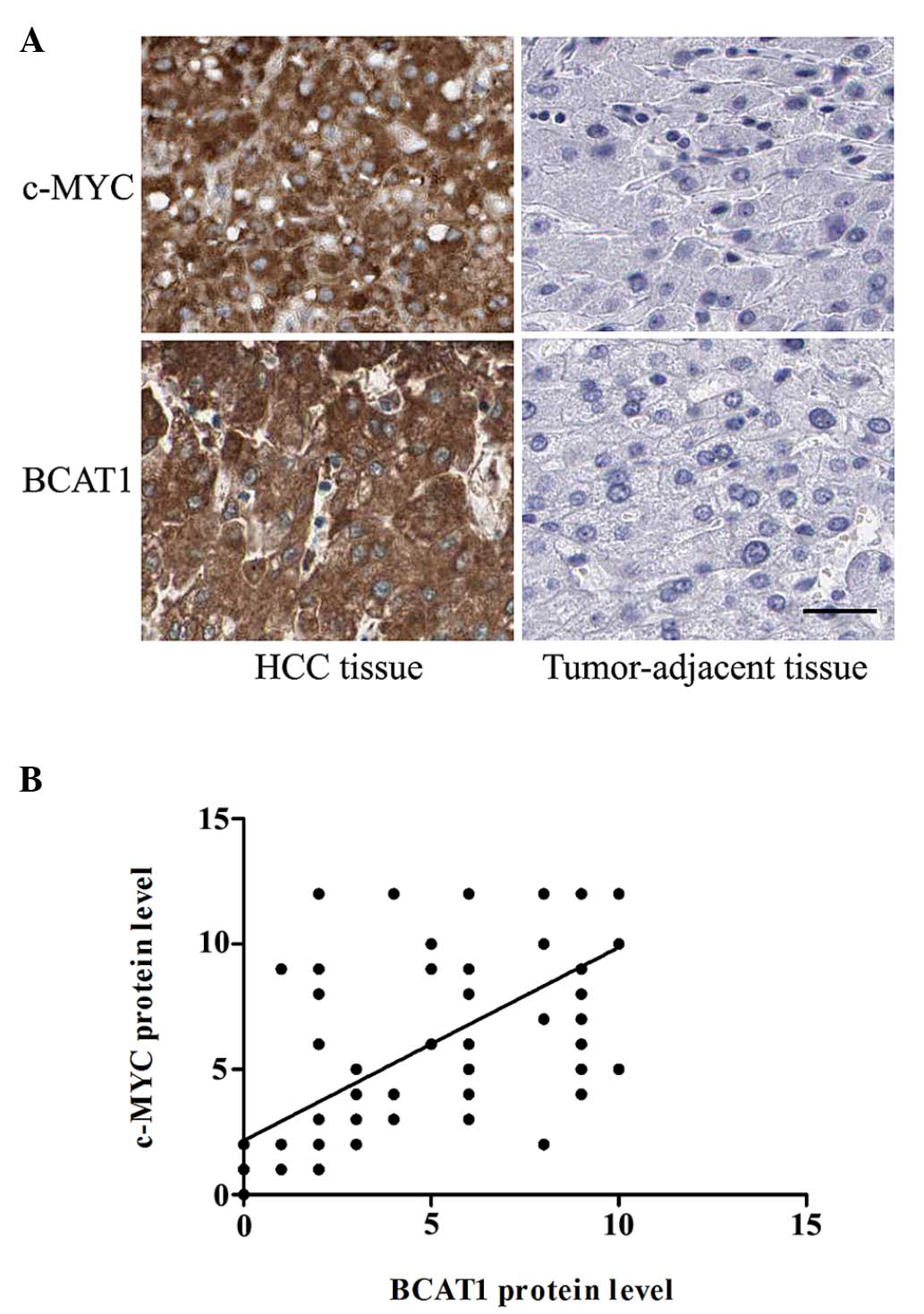
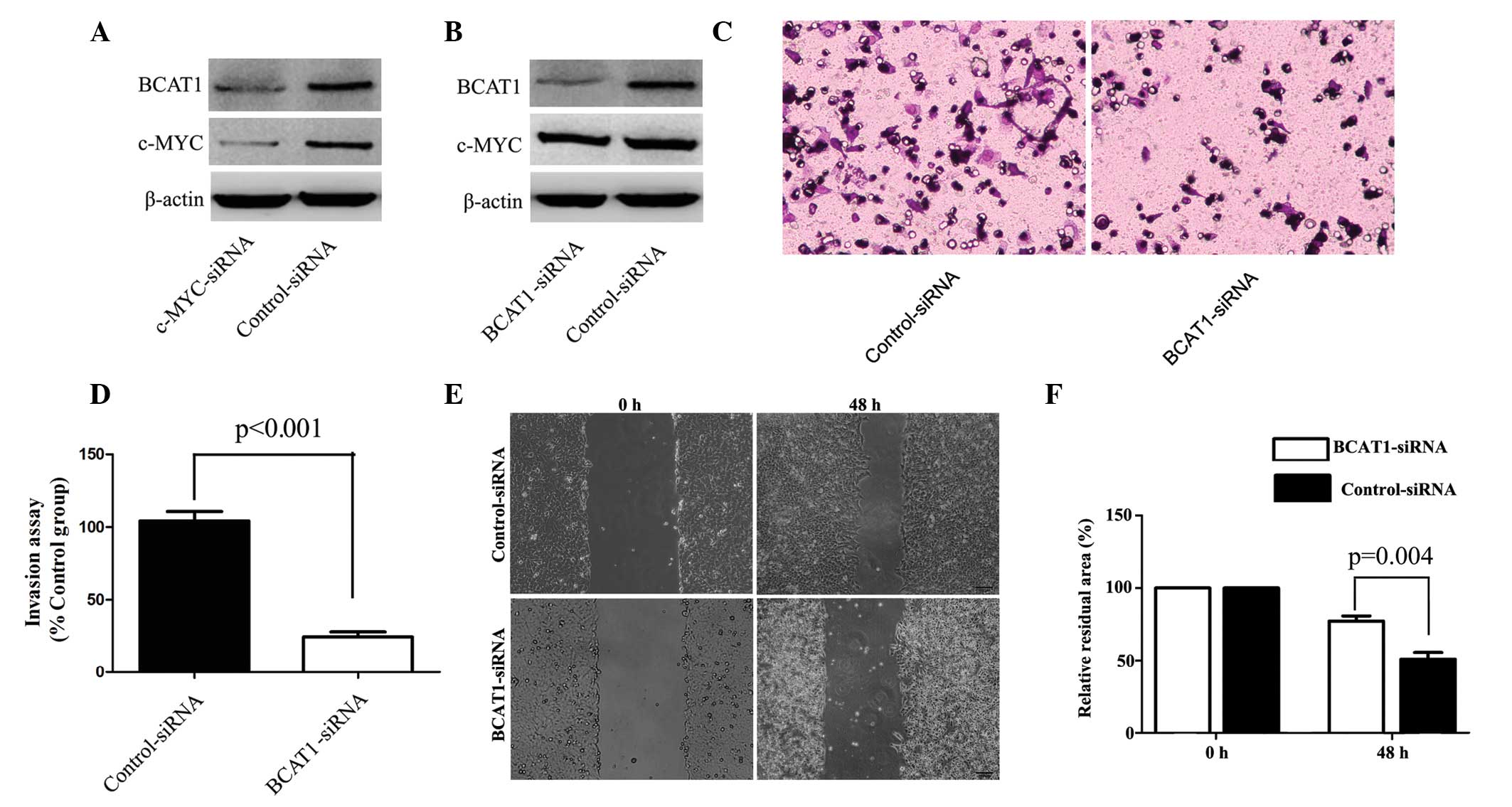
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ and
McGlynn KA: The continuing increase in the incidence of
hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: An update. Ann
Intern Med. 139:817–823. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shariff MI, Cox IJ, Gomaa AI, Khan SA,
Gedroyc W and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and
therapeutics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:353–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dhanasekaran R, Limaye A and Cabrera R:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends in worldwide epidemiology,
risk factors, diagnosis, and therapeutics. Hepat Med. 4:19–37.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng X, Song T, Dou C, Jia Y and Liu Q:
CtBP2 is an independent prognostic marker that promotes GLI1
induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:3752–3769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoshikawa R, Yanagi H, Shen CS, Fujiwara
Y, Noda M, Yagyu T, Gega M, Oshima T, Yamamura T, Okamura H, et al:
ECA39 is a novel distant metastasis-related biomarker in colorectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 12:5884–5889. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schuldiner O, Eden A, Ben-Yosef T, Yanuka
O, Simchen G and Benvenisty N: ECA39, a conserved gene regulated by
c-Myc in mice, is involved in G1/S cell cycle regulation in yeast.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:7143–7148. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eden A and Benvenisty N: Involvement of
branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase (Bcat1/Eca39) in
apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 457:255–261. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bledsoe RK, Dawson PA and Hutson SM:
Cloning of the rat and human mitochondrial branched chain
aminotransferases (BCATm). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1339:9–13. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eden A, Simchen G and Benvenisty N: Two
yeast homologs of ECA39, a target for c-Myc regulation, code for
cytosolic and mitochondrial branched-chain amino acid
aminotransferases. J Biol Chem. 271:20242–20245. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou W, Feng X, Ren C, Jiang X, Liu W,
Huang W, Liu Z, Li Z, Zeng L, Wang L, et al: Over-expression of
BCAT1, a c-Myc target gene, induces cell proliferation, migration
and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 12:532013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bible E: Neuro-oncology: BCAT1 promotes
cell proliferation in aggressive gliomas. Nat Rev Neurol.
9:4202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zerban H, Radig S, Kopp-Schneider A and
Bannasch P: Cell proliferation and cell death (apoptosis) in
hepatic preneoplasia and neoplasia are closely related to
phenotypic cellular diversity and instability. Carcinogenesis.
15:2467–2473. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tönjes M, Barbus S, Park YJ, Wang W,
Schlotter M, Lindroth AM, Pleier SV, Bai AH, Karra D, Piro RM, et
al: BCAT1 promotes cell proliferation through amino acid catabolism
in gliomas carrying wild-type IDH1. Nat Med. 19:901–908. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greco D, Kotronen A, Westerbacka J, Puig
O, Arkkila P, Kiviluoto T, Laitinen S, Kolak M, Fisher RM, Hamsten
A, et al: Gene expression in human NAFLD. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 294:G1281–G1287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsumura T, Morinaga Y, Fujitani S,
Takehana K, Nishitani S and Sonaka I: Oral administration of
branched-chain amino acids activates the mTOR signal in cirrhotic
rat liver. Hepatol Res. 33:27–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Honda M, Takehana K, Sakai A, Tagata Y,
Shirasaki T, Nishitani S, Muramatsu T, Yamashita T, Nakamoto Y,
Mizukoshi E, et al: Malnutrition impairs interferon signaling
through mTOR and FoxO pathways in patients with chronic hepatitis
C. Gastroenterology. 141:128–140, 140.e1-e2. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ben-Yosef T, Yanuka O, Halle D and
Benvenisty N: Involvement of Myc targets in c-myc and N-myc induced
human tumors. Oncogene. 17:165–171. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ben-Yosef T, Eden A and Benvenisty N:
Characterization of murine BCAT genes: Bcat1, a c-Myc target, and
its homolog, Bcat2. Mamm Genome. 9:595–597. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng SY, Lai PL and Hsu HC: Amplification
of the c-myc gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma: Biologic
significance. J Formos Med Assoc. 92:866–870. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Q, Tu K, Zhang H, Zheng X, Yao Y and
Liu Q: TPX2 as a novel prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:906–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Edmondson HA and Steiner PE: Primary
carcinoma of the liver: A study of 100 cases among 48,900
necropsies. Cancer. 7:462–504. 1954. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Colombo M and Sangiovanni A: Treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Beyond international guidelines. Liver
Int. 35(Suppl 1): S129–S138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roberts LR and Gores GJ: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Molecular pathways and new therapeutic targets. Semin
Liver Dis. 25:212–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scaggiante B, Kazemi M, Pozzato G, Dapas
B, Farra R, Grassi M, Zanconati F and Grassi G: Novel
hepatocellular carcinoma molecules with prognostic and therapeutic
potentials. World J Gastroenterol. 20:1268–1288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Satow R, Shitashige M, Kanai Y, Takeshita
F, Ojima H, Jigami T, Honda K, Kosuge T, Ochiya T, Hirohashi S and
Yamada T: Combined functional genome survey of therapeutic targets
for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2518–2528. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schattenberg JM, Schuchmann M and Galle
PR: Cell death and hepatocarcinogenesis: Dysregulation of apoptosis
signaling pathways. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26(Suppl 1):
S213–S219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Elsemman IE, Mardinoglu A, Shoaie S,
Solima TH and Nielsen J: Systems biology analysis of hepatitis C
virus infection reveals the role of copy number increases in
regions of chromosome 1q in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism.
Mol Biosyst. 12:1496–1506. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|