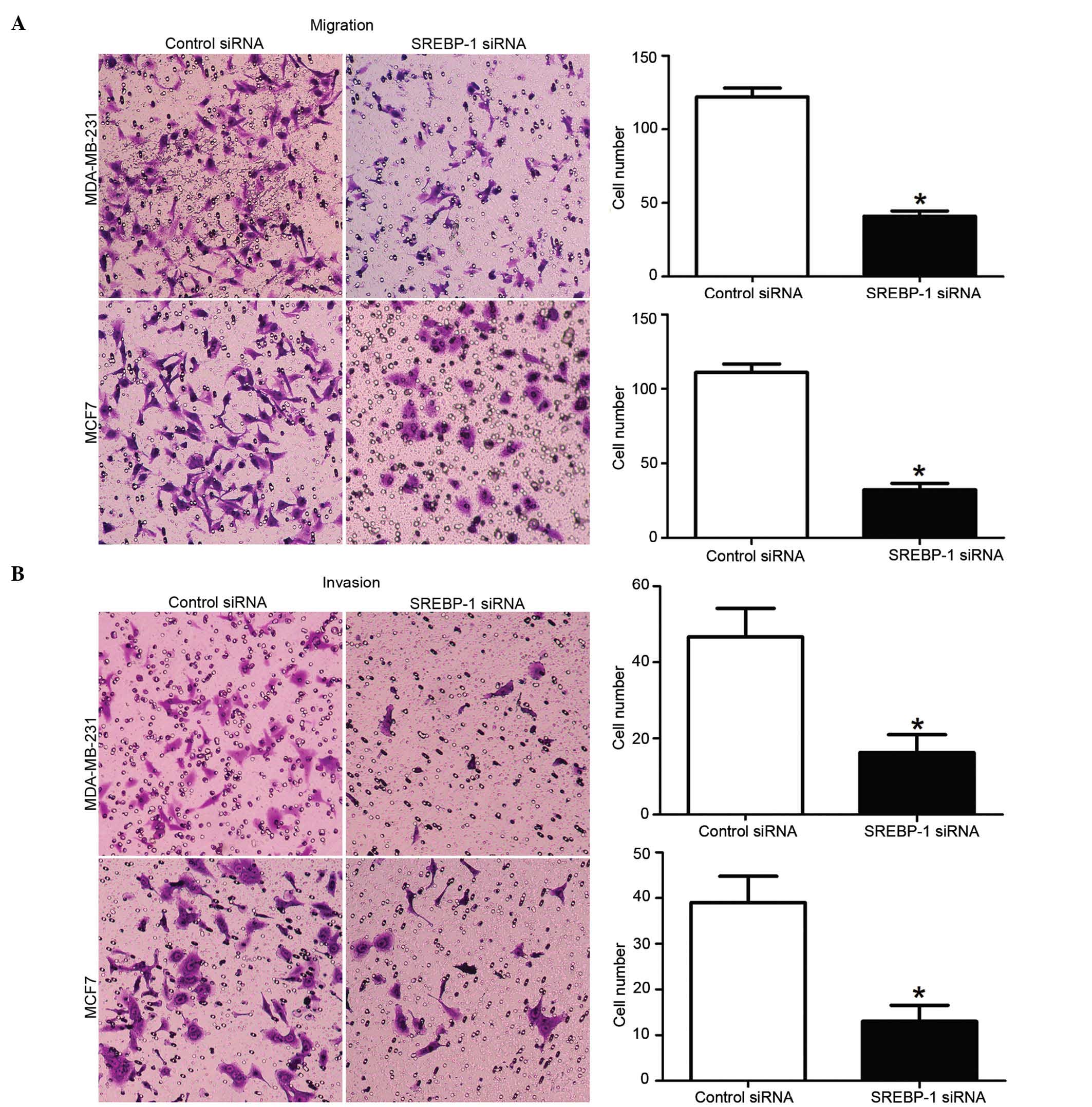
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giordano SH, Buzdar AU, Smith TL, Kau SW,
Yang Y and Hortobagyi GN: Is breast cancer survival improving?
Cancer. 100:44–52. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hurvitz SA, Hu Y, O'Brien N and Finn RS:
Current approaches and future directions in the treatment of
HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:219–229. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Almendro V, Kim HJ, Cheng YK, Gönen M,
Itzkovitz S, Argani P, van Oudenaarden A, Sukumar S, Michor F and
Polyak K: Genetic and phenotypic diversity in breast tumor
metastases. Cancer Res. 74:1338–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J and Gallo KA: MLK3 regulates
paxillin phosphorylation in chemokine-mediated breast cancer cell
migration and invasion to drive metastasis. Cancer Res.
72:4130–4140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nature
Rev Cancer. 7:763–777. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuhajda FP: Fatty-acid synthase and human
cancer: New perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition.
16:202–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Puig T, Vázquez-Martin A, Relat J, Pétriz
J, Menéndez JA, Porta R, Casals G, Marrero PF, Haro D, Brunet J and
Colomer R: Fatty acid metabolism in breast cancer cells:
Differential inhibitory effects of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
and C75. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 109:471–479. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakakuki M, Shimano H, Inoue N, Tamura M,
Matsuzaka T, Nakagawa Y, Yahagi N, Toyoshima H, Sato R and Yamada
N: A transcription factor of lipid synthesis, sterol regulatory
element-binding protein (SREBP)-1a causes G(1) cell-cycle arrest
after accumulation of cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) inhibitors.
FEBS J. 274:4440–4452. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taskinen MR: Diabetic dyslipidaemia: From
basic research to clinical practice. Diabetologia. 46:733–749.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ruiz R, Jideonwo V, Ahn M, Surendran S,
Tagliabracci VS, Hou Y, Gamble A, Kerner J, Irimia-Dominguez JM,
Puchowicz MA, et al: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1
(SREBP-1) is required to regulate glycogen synthesis and
gluconeogenic gene expression in mouse liver. J Biol Chem.
289:5510–5517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo D, Prins RM, Dang J, Kuga D, Iwanami
A, Soto H, Lin KY, Huang TT, Akhavan D, Hock MB, et al: EGFR
signaling through an Akt-SREBP-1-dependent, rapamycin-resistant
pathway sensitizes glioblastomas to antilipogenic therapy. Sci
Signal. 2:ra822009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Porstmann T, Griffiths B, Chung YL,
Delpuech O, Griffiths JR, Downward J and Schulze A: PKB/Akt induces
transcription of enzymes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid
biosynthesis via activation of SREBP. Oncogene. 24:6465–6481.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yecies JL, Zhang HH, Menon S, Liu S,
Yecies D, Lipovsky AI, Gorgun C, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hotamisligil GS,
Lee CH and Manning BD: Akt stimulates hepatic SREBP1c and
lipogenesis through parallel mTORC1-dependent and independent
pathways. Cell Metab. 14:21–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nie LY, Lu QT, Li WH, Yang N, Dongol S,
Zhang X and Jiang J: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 is
required for ovarian tumor growth. Oncology Rep. 30:1346–1354.
2013.
|
|
16
|
Guo D, Bell EH and Chakravarti A: Lipid
metabolism emerges as a promising target for malignant glioma
therapy. CNS Oncol. 2:289–299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li W, Tai Y, Zhou J, Gu W, Bai Z, Zhou T,
Zhong Z, McCue PA, Sang N, Ji JY, et al: Repression of endometrial
tumor growth by targeting SREBP1 and lipogenesis. Cell Cycle.
11:2348–2358. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang WC, Li X, Liu J, Lin J and Chung LW:
Activation of androgen receptor, lipogenesis, and oxidative stress
converged by SREBP-1 is responsible for regulating growth and
progression of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 10:133–142.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miyachi K, Sawada Y, Shida Y, Sugawara A
and Hisatomi H: Lipogenic gene expression profile in patients with
gastric cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:825–827. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mashima T, Seimiya H and Tsuruo T: De novo
fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for
cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 100:1369–1372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ameer F, Scandiuzzi L, Hasnain S,
Kalbacher H and Zaidi N: De novo lipogenesis in health and disease.
Metabolism. 63:895–902. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Calvisi DF, Wang C, Ho C, Ladu S, Lee SA,
Mattu S, Destefanis G, Delogu S, Zimmermann A, Ericsson J, et al:
Increased lipogenesis, induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 signaling,
promotes development of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 140:1071–1083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamashita T, Honda M, Takatori H, Nishino
R, Minato H, Takamura H, Ohta T and Kaneko S: Activation of
lipogenic pathway correlates with cell proliferation and poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 50:100–110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Swinnen JV, Heemers H, van de Sande T, de
Schrijver E, Brusselmans K, Heyns W and Verhoeven G: Androgens,
lipogenesis and prostate cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
92:273–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song HJ, Sneddon AA, Heys SD and Wahle KW:
Regulation of fatty acid synthase (FAS) and apoptosis in
estrogen-receptor positive and negative breast cancer cells by
conjugated linoleic acids. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty
Acids. 87:197–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee JS, Sul JY, Park JB, Lee MS, Cha EY,
Song IS, Kim JR and Chang ES: Fatty acid synthase inhibition by
amentoflavone suppresses HER2/neu (erbB2) oncogene in SKBR3 human
breast cancer cells. Phytother Res. 27:713–720. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roongta UV, Pabalan JG, Wang X, Ryseck RP,
Fargnoli J, Henley BJ, Yang WP, Zhu J, Madireddi MT, Lawrence RM,
et al: Cancer cell dependence on unsaturated fatty acids implicates
stearoyl-CoA desaturase as a target for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer
Res. 9:1551–1561. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tong L and Harwood HJ Jr: Acetyl-coenzyme
A carboxylases: Versatile targets for drug discovery. J Cell
Biochem. 99:1476–1488. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|