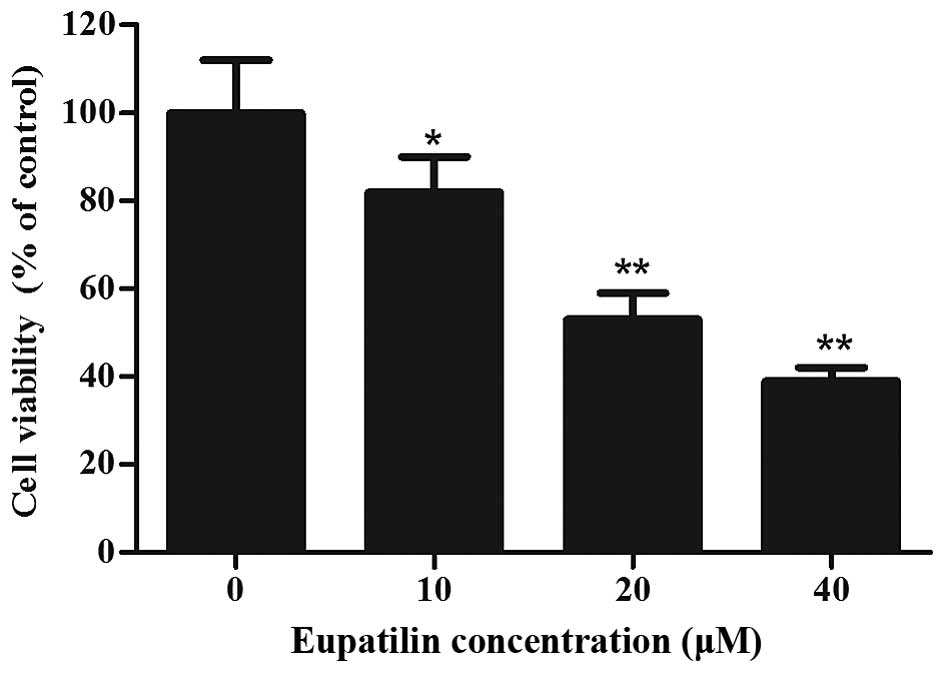
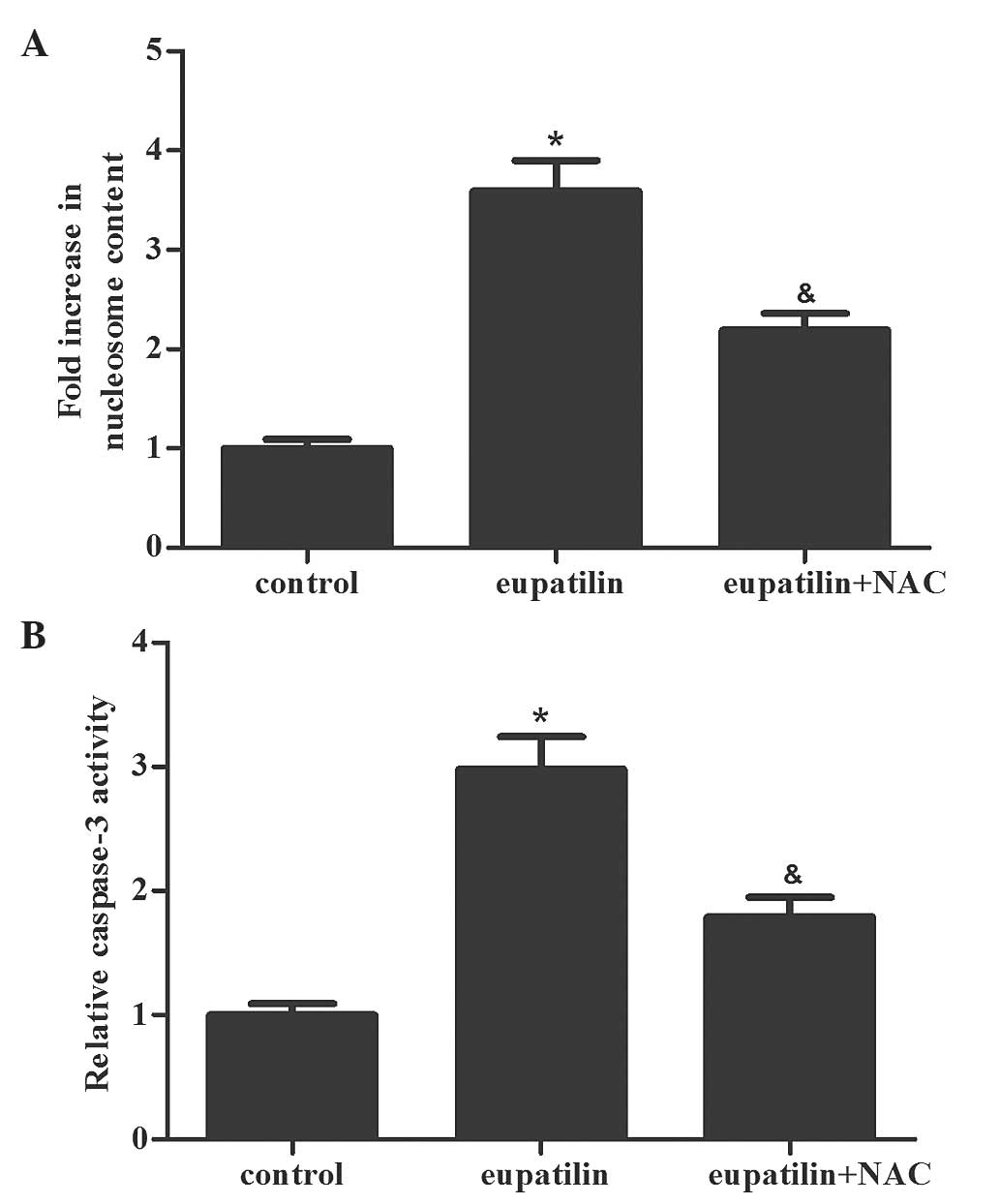
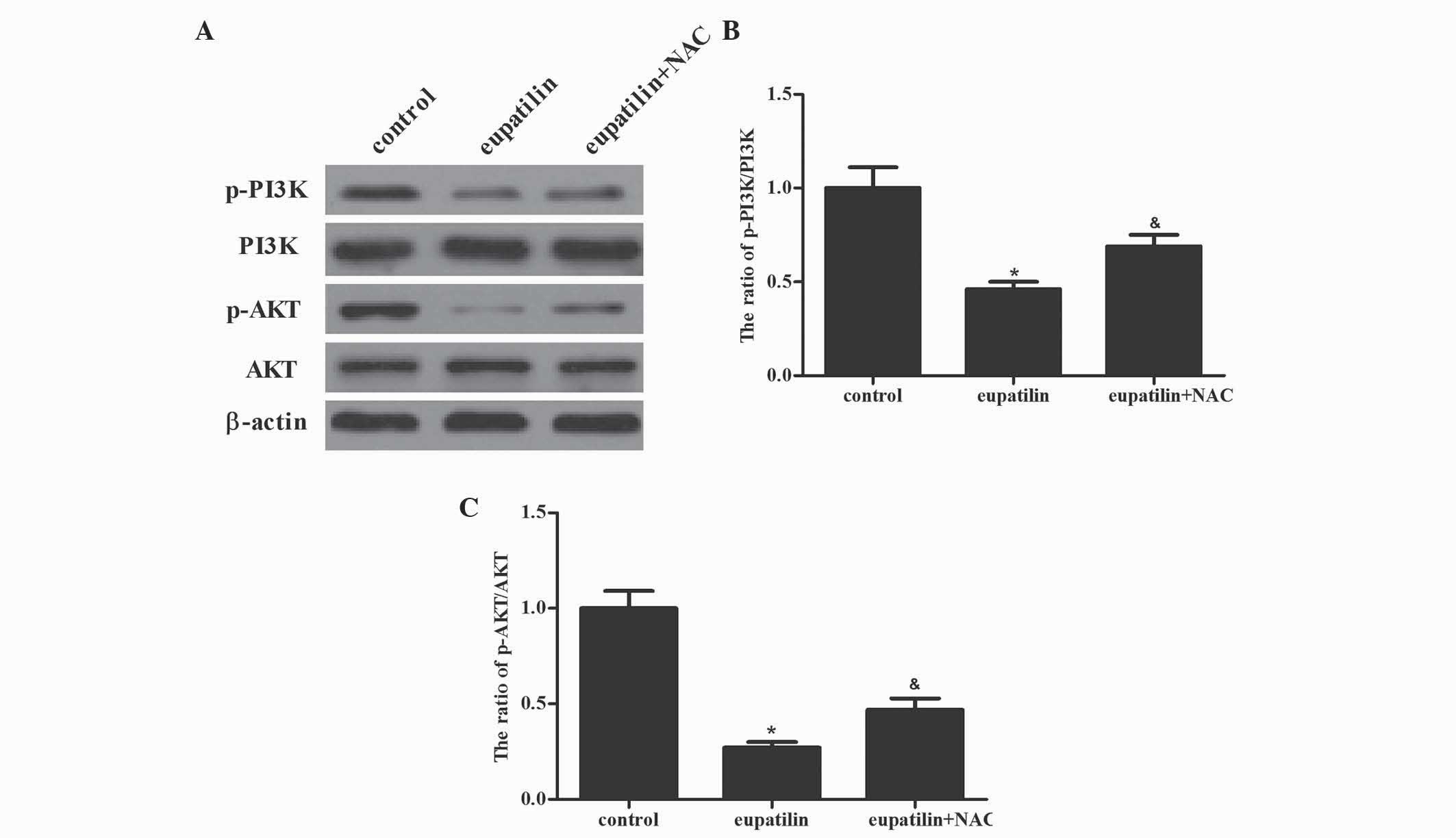
|
1
|
Larkin J, Goh XY, Vetter M, Pickering L
and Swanton C: Epigenetic regulation in RCC: Opportunities for
therapeutic intervention? Nat Rev Urol. 9:147–155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Penticuff JC and Kyprianou N: Therapeutic
challenges in renal cell carcimoma. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 3:77–90.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Salmeen A and Barford D: Functions and
mechanisms of redox regulation of cysteine-based phosphatases.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:560–577. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Waris G and Ahsan H: Reactive oxygen
species: Role in the development of cancer and various chronic
conditions. J Carcinog. 5:142006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jang HJ, Jeong EK, Kim SS, Lee JH, Oh MY,
Kang KS, Kwan HC, Song KI, Eom DW and Han DJ: Protective effect of
Artemisia asiatica extract against renal ischemia-reperfusion
injury in mice. Exp Clin Transplant Suppl. 1:377–82. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Park BB, Yoon JS, Kim ES, Choi J, Won YW,
Choi JH and Lee YY: Inhibitory effects of eupatilin on tumor
invasion of human gastric cancer MKN-1 cells. Tumor Biol.
34:875–885. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim YD, Choi SC, Oh TY, Chun JS and Jun
CD: Eupatilin inhibits T-cell activation by modulation of
intracellular calcium flux and NF-kappaB and NF-AT activity. J Cell
Biochem. 108:225–236. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choi EJ, Lee S, Chae JR, Lee HS, Jun CD
and Kim SH: Eupatilin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
expression of inflammatory mediators in macrophages. Life Sci.
88:1121–1126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoon KD, Chin YW, Yang MH and Kim J:
Separation of anti-ulcer flavonoids from Artemisia extracts by
high-speed countercurrent chromatography. Food Chem. 129:679–683.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Choi EJ, Oh HM, Na BR, Ramesh TP, Lee HJ,
Choi CS, Choi SC, Oh TY, Choi SJ, Chae JR, et al: Eupatilin
protects gastric epithelial cells from oxidative damage and
down-regulates genes responsible for the cellular oxidative stress.
Pharm Res. 25:1355–1364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho JH, Lee JG, Yang YI, Kim JH, Ahn JH,
Baek NI, Lee KT and Choi JH: Eupatilin, a dietary flavonoid,
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in human endometrial cancer cells.
Food Chem Toxicol. 49:1737–1744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin Y, Yang J, Lin L, Lin Y and Zheng C:
The attenuation of Scutellariae radix extract on oxidative stress
for colon injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cell and
2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis
rats. Pharmacogn Mag. 12:153–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiong Y, Ye T, Wang M, Xia Y, Wang N, Song
X, Wang F, Liu L, Zhu Y, Yang F, et al: A novel cinnamide YLT26
induces breast cancer cells apoptosis via ROS-mitochondrial
apoptotic pathway in vitro and inhibits lung metastasis in vivo.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1863–1876. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi EK, Yeo JS, Park CY, Na HI, Lim JA,
Lee JE, Hong SW, Park SS, Lim DG and Kwak KH: Inhibition of
reactive oxygen species downregulates the MAPK pathway in rat
spinal cord after limb ischemia reperfusion injury. Int J Surg.
22:74–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Luo WM, Bender S, Qian
CN, Kort E, Zhang ZF, VandenBeldt K, Duesbery NS, Resau JH and Teh
BT: Inhibition of MAPK kinase signaling pathways suppressed renal
cell carcinoma growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res.
68:81–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo H, German P, Bai S, Barnes S, Guo W,
Qi X, Lou H, Liang J, Jonasch E, Mills GB and Ding Z: The PI3K/AKT
pathway and renal cell carcinoma. J Genet Genomics. 42:343–353.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thannickal VJ and Fanburg BL: Reactive
oxygen species in cell signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 279:L1005–L1028. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Essick EE and Sam F: Oxidative stress and
autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and
cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:168–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J and Yuan J: Caspases in apoptosis and
beyond. Oncogene. 27:6194–6206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tawa P, Hell K, Giroux A, Grimm E, Han Y,
Nicholson DW and Xanthoudakis S: Catalytic activity of caspase-3 is
required for its degradation: Stabilization of the active complex
by synthetic inhibitors. Cell Death Differ. 11:439–447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wada T and Penninger JM: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene. 23:2838–2849.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ballif BA and Blenis J: Molecular
mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase
(MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ.
12:397–408. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu J, Chang F, Li F, Fu H, Wang J, Zhang
S, Zhao J and Yin D: Palmitate promotes autophagy and apoptosis
through ROS-dependent JNK and p38 MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:262–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ki YW, Park JH, Lee JE, Shin IC and Koh
HC: JNK and p38 MAPK regulate oxidative stress and the inflammatory
response in chlorpyrifos-induced apoptosis. Toxicol Lett.
218:235–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Porras A, Zuluaga S, Black E, Valladares
A, Alvarez AM, Ambrosino C, Benito M and Nebreda AR: P38 alpha
mitogen-activated protein kinase sensitizes cells to apoptosis
induced by different stimuli. Mol Biol Cell. 15:922–933. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park EJ, Park SW, Kim HJ, Kwak JH, Lee DU
and Chang KC: Dehydrocostuslactone inhibits LPS-induced
inflammation by p38MAPK-dependent induction of hemeoxygenase-1 in
vitro and improves survival of mice in CLP-induced sepsis in vivo.
Int Immunopharmacol. 22:332–340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Porta C and Figlin RA:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway and kidney
cancer, and the therapeutic potential of
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt inhibitors. J Urol.
182:2569–2577. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Banumathy G and Cairns P: Signaling
pathways in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:658–664.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sourbier C, Lindner V, Lang H, Agouni A,
Schordan E, Danilin S, Rothhut S, Jacqmin D, Helwig JJ and
Massfelder T: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway: A new
target in human renal cell carcinoma therapy. Cancer Res.
66:5130–5142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brzezianska E and Pastuszak-Lewandoska D:
A minireview: The role of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in thyroid
follicular cell-derived neoplasm. Fronti Biosci (Landmark Ed).
16:422–439. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shi Y, Song Q, Hu D, Zhuang X, Yu S and
Teng D: Oleanolic acid induced autophagic cell death in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and ROS-dependent
pathway. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 20:237–243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mi Y, Xiao C, Du Q, Wu W, Qi G and Liu X:
Momordin Ic couples apoptosis with autophagy in human
hepatoblastoma cancer cells by reactive oxygen species
(ROS)-mediated PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Free Radic
Biol Med. 90:230–422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hao W, Yuan X, Yu L, Gao C, Sun X, Wang D
and Zheng Q: Licochalcone A-induced human gastric cancer BGC-823
cells apoptosis by regulating ROS-mediated MAPKs and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 5:103362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|