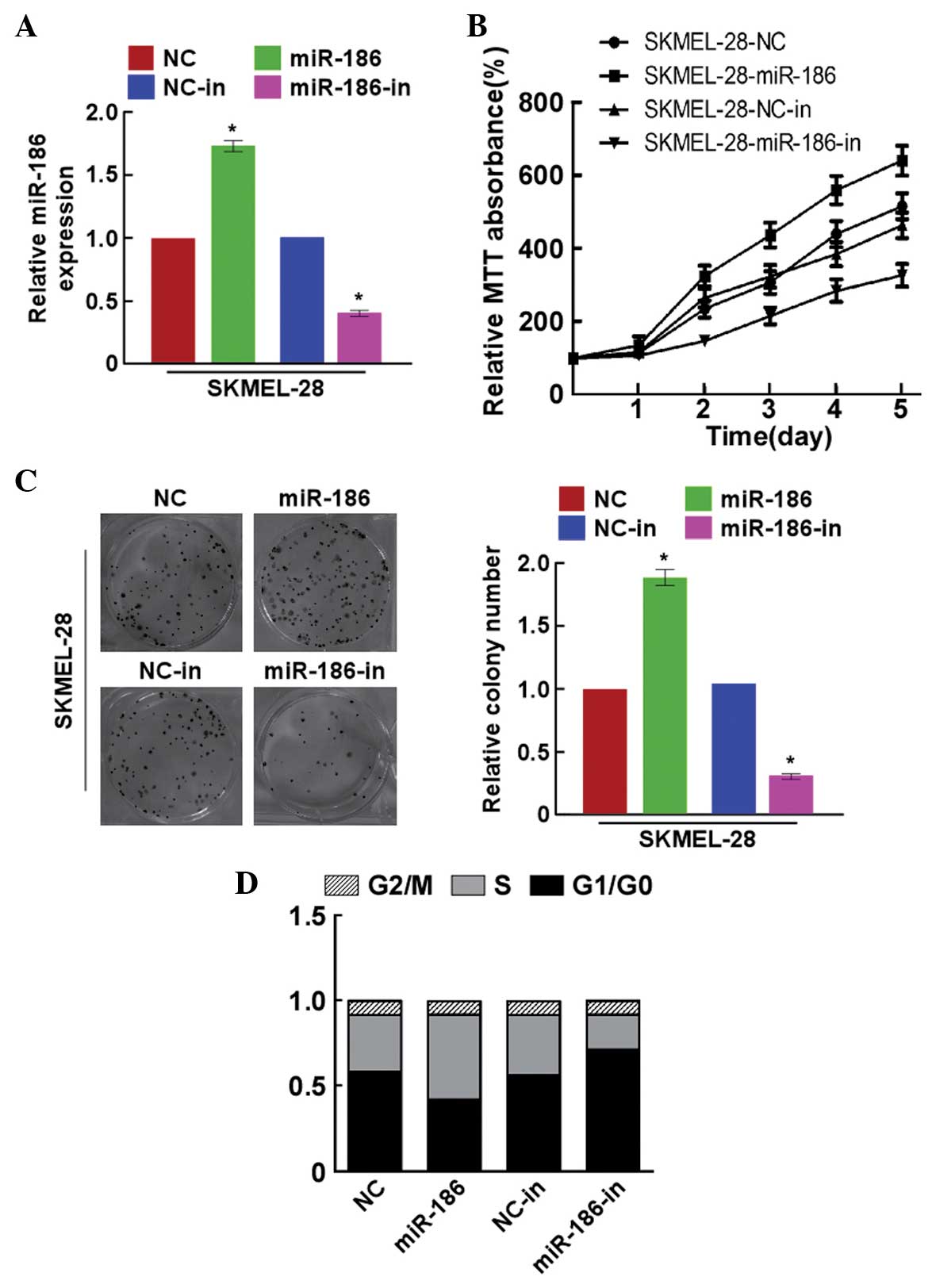
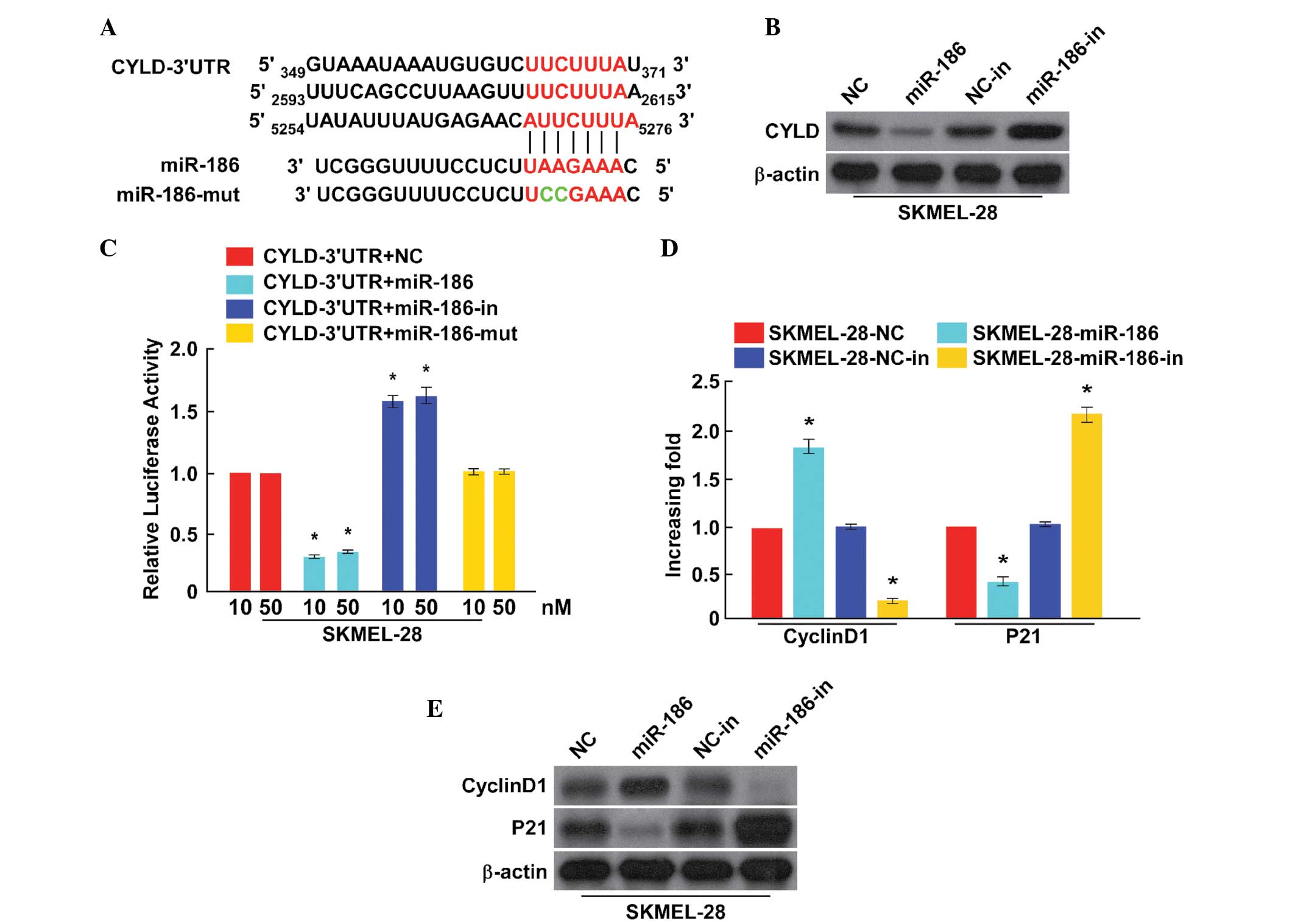
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baroudjian B, Pagès C and Lebbé C:
Melanoma, from diagnosis to treatment. Rev Infirm. 65:16–18. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Luo C, Weber CE, Osen W, Bosserhoff AK and
Eichmuller SB: The role of microRNAs in melanoma. Eur J Cell Biol.
93:11–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Novel biomarkers
and therapeutic targets for optimizing the therapeutic management
of melanomas. World J Clin Oncol. 3:32–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui G, Cui M, Li Y, Liang Y, Li W, Guo H
and Zhao S: MiR-186 targets ROCK1 to suppress the growth and
metastasis of NSCLC cells. Tumour Biol. 35:8933–8937. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim SY, Lee YH and Bae YS: MiR-186,
miR-216b, miR-337-3p and miR-760 cooperatively induce cellular
senescence by targeting α subunit of protein kinase CKII in human
colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 429:173–179.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cai J, Wu J, Zhang H, Fang L, Huang Y,
Yang Y, Zhu X, Li R and Li M: miR-186 downregulation correlates
with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma, where it interferes with
cell-cycle regulation. Cancer Res. 73:756–766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ries J, Vairaktaris E, Agaimy A, Kintopp
R, Baran C, Neukam FW and Nkenke E: miR-186, miR-3651 and miR-494:
Potential biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma extracted
from whole blood. Oncol Rep. 31:1429–1436. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mathis BJ, Lai Y, Qu C, Janicki JS and Cui
T: CYLD-mediated signaling and diseases. Curr Drug Targets.
16:284–294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhong Q, Wang T, Lu P, Zhang R, Zou J and
Yuan S: miR-193b promotes cell proliferation by targeting Smad3 in
human glioma. J Neurosci Res. 92:619–626. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi L, Wang Z, Sun G, Wan Y, Guo J and Fu
X: miR-145 inhibits migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by
targeting ABCG2. Neuromolecular Med. 16:517–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang HF, Chen H, Ma MW, Wang JA, Tang TT,
Ni LS, Yu JL, Li YZ and Bai BX: miR-573 regulates melanoma
progression by targeting the melanoma cell adhesion molecule. Oncol
Rep. 30:520–526. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prasad R and Katiyar SK: Down-regulation
of miRNA-106b inhibits growth of melanoma cells by promoting
G1-phase cell cycle arrest and reactivation of p21/WAF1/Cip1
protein. Oncotarget. 5:10636–10649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu SM, Lu J, Lee HC, Chung FH and Ma N:
miR-524-5p suppresses the growth of oncogenic BRAF melanoma by
targeting BRAF and ERK2. Oncotarget. 5:9444–9459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Babapoor S, Fleming E, Wu R and Dadras SS:
A novel miR-451a isomiR, associated with amelanotypic phenotype,
acts as a tumor suppressor in melanoma by retarding cell migration
and invasion. PLoS One. 9:e1075022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rico-Rosillo MG, Vega-Robledo GB and
Oliva-Rico D: The role and importance of the microRNAs in the
diagnosis and development of diseases. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc.
52:302–307. 2014.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deng LL, Shao YX, Lv HF, Deng HB and Lv
FZ: Over-expressing CYLD augments antitumor activity of TRAIL by
inhibiting the NF-κB survival signaling in lung cancer cells.
Neoplasma. 59:18–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Massoumi R: CYLD: A deubiquitination
enzyme with multiple roles in cancer. Future Oncol. 7:285–297.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lim JH, Jono H, Komatsu K, Woo CH, Lee J,
Miyata M, Matsuno T, Xu X, Huang Y, Zhang W, et al: CYLD negatively
regulates transforming growth factor-β-signalling via
deubiquitinating Akt. Nat Commun. 3:7712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blake PW and Toro JR: Update of
cylindromatosis gene (CYLD) mutations in Brooke-Spiegler syndrome:
Novel insights into the role of deubiquitination in cell signaling.
Hum Mutat. 30:1025–1036. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|