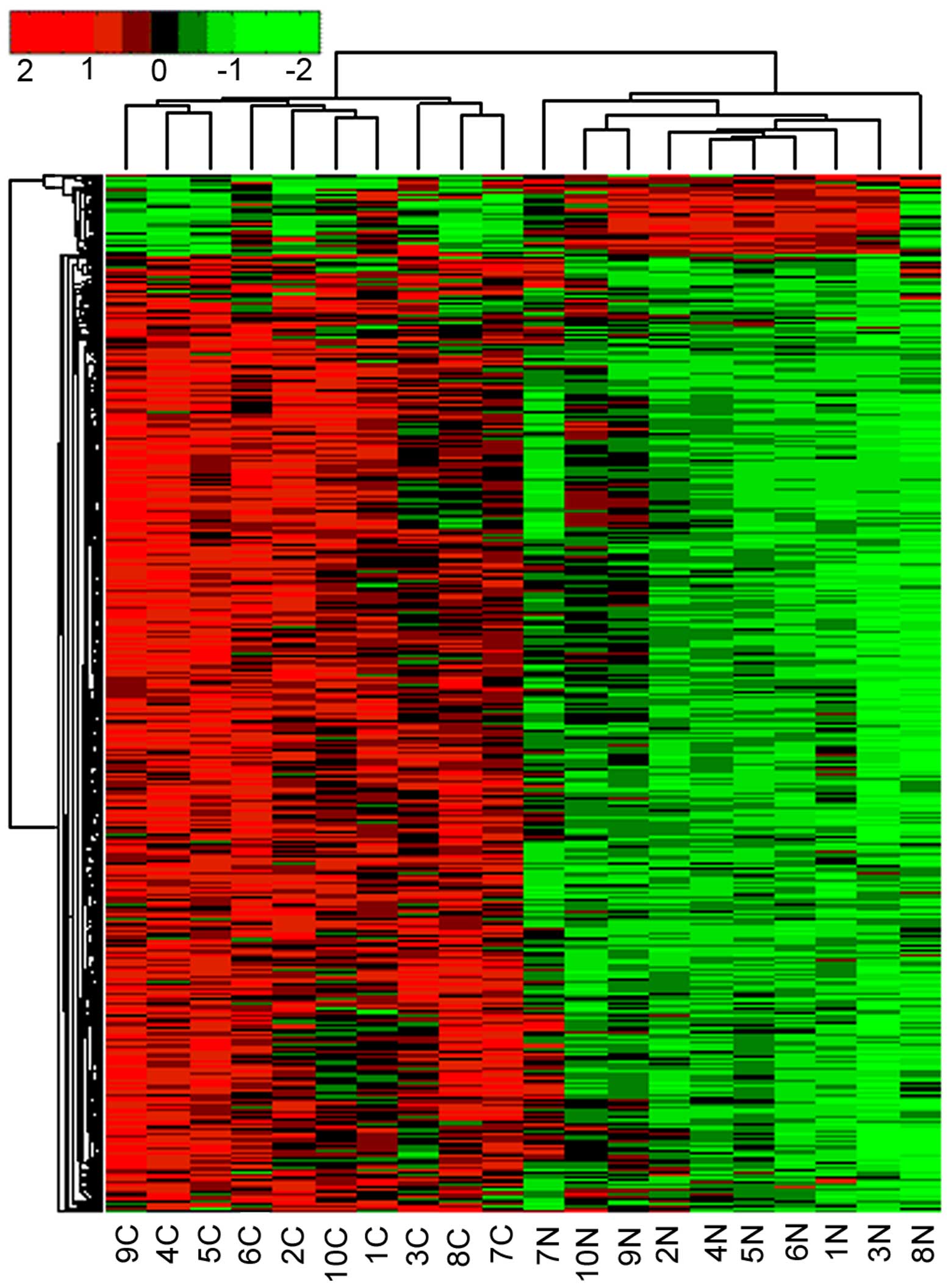
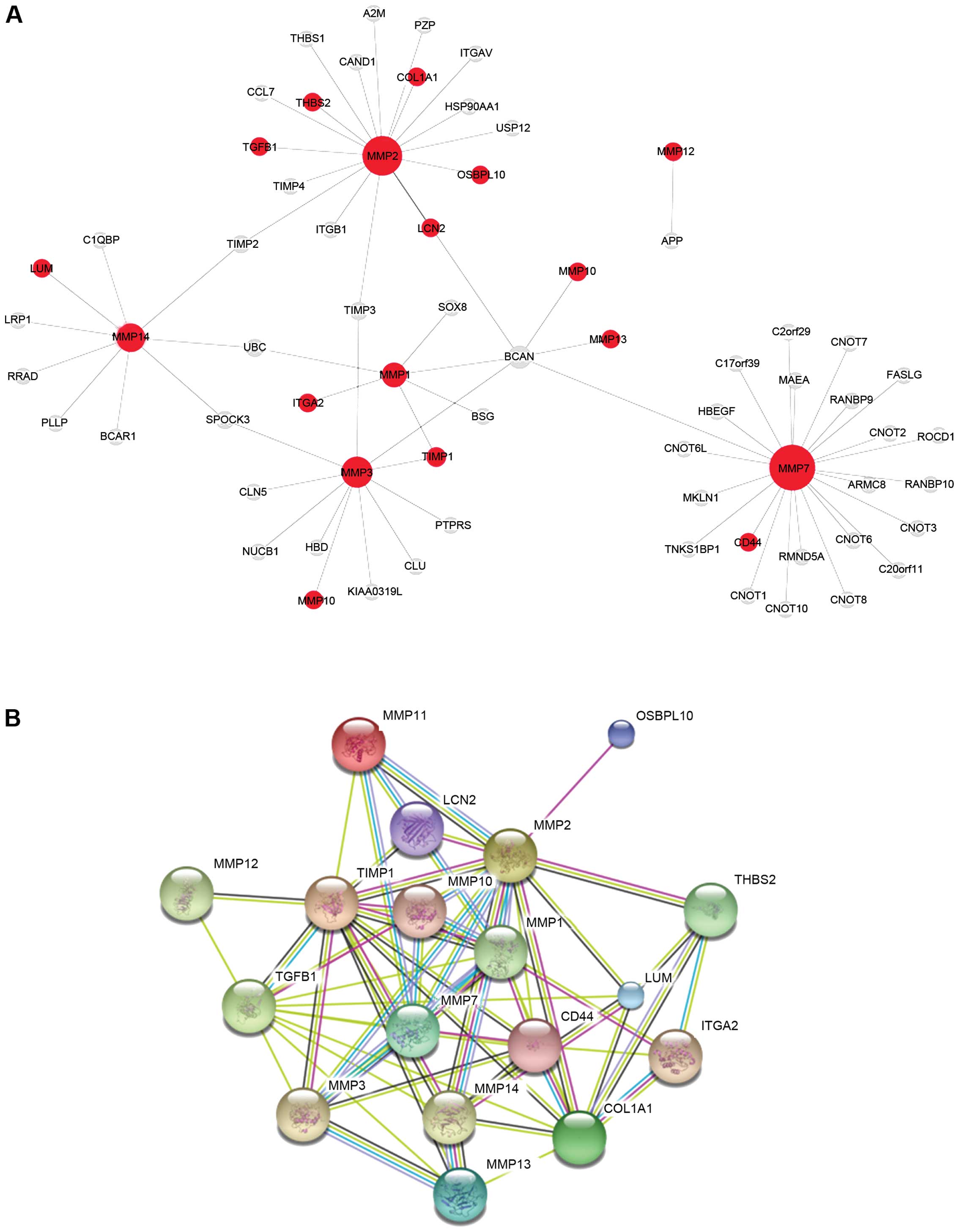
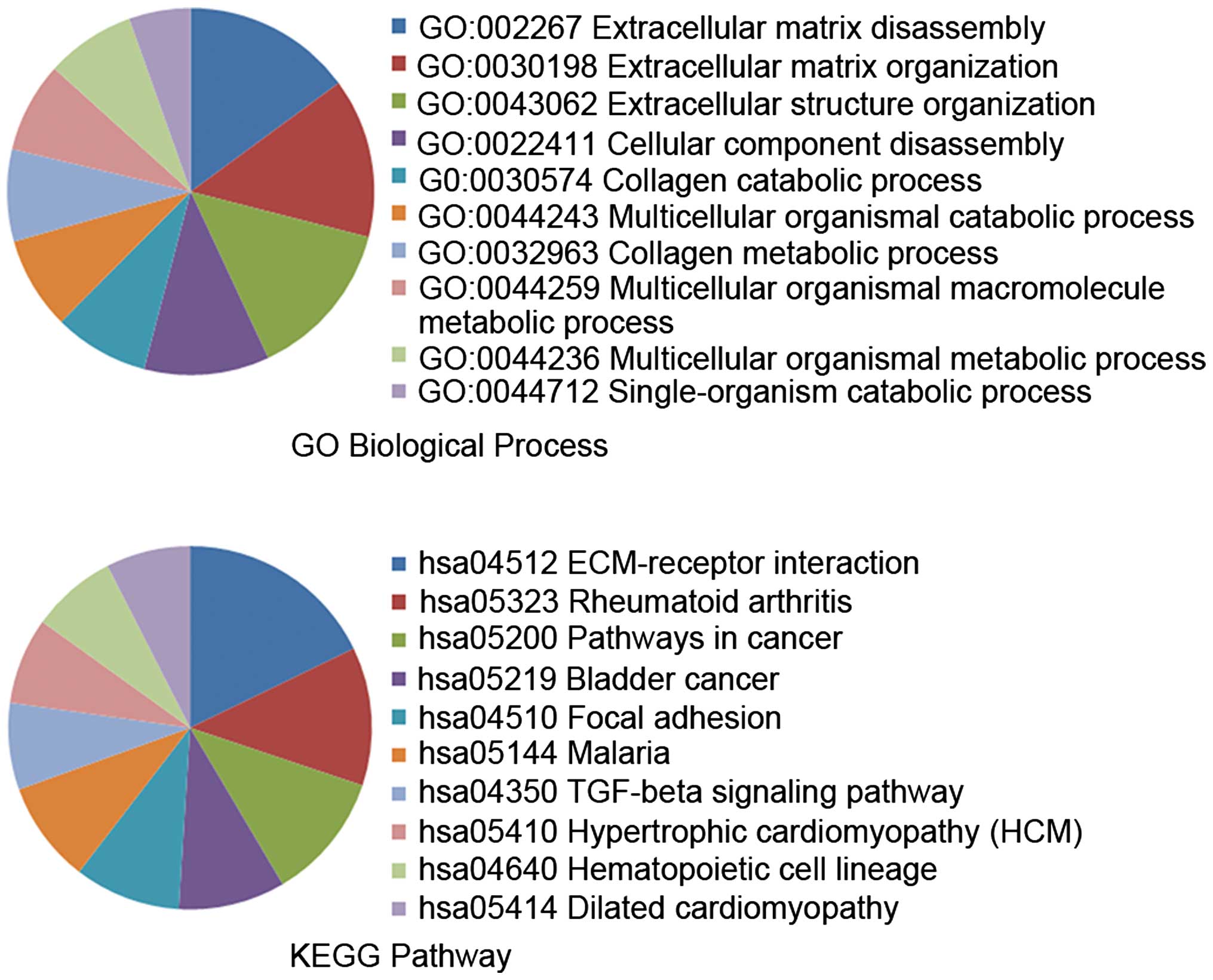
|
1
|
He YT, Hou J, Chen ZF, Qiao CY, Song GH,
Meng FS, Jin HX and Chen C: Trends in incidence of esophageal and
gastric cardia cancer in high-risk areas in China. Eur J Cancer
Prev. 17:71–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Worm K, Weaver DG, Green RC, Saeui CT,
Dulay DM, Barker WM, Cassel JA, Stabley GJ, DeHaven RN, LaBuda CJ,
et al: Discovery of N-(3-(morpholinomethyl)-phenyl)-amides as
potent and selective CB2 agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
19:5004–5008. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jin X, Zhu Z and Shi Y: Metastasis
mechanism and gene/protein expression in gastric cancer with
distant organs metastasis. Bull Cancer. 2014.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Wang Y, Dong S, Ge C, Xiao Y, Li R,
Ma X, Xue Y, Zhang Q, Lv J, et al: Association of CXCR1 and 2
expressions with gastric cancer metastasis in ex vivo and tumor
cell invasion in vitro. Cytokine. 69:6–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Steinestel K, Brüderlein S, Lennerz JK,
Steinestel J, Kraft K, Pröpper C, Meineke V and Möller P:
Expression and Y435-phosphorylation of Abelson interactor 1 (Abi1)
promotes tumour cell adhesion, extracellular matrix degradation and
invasion by colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 13:1452014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu P, Wang X, Hu CH and Hu TH:
Bioinformatics analysis with graph-based clustering to detect
gastric cancer-related pathways. Genet Mol Res. 11:3497–3504. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hansmann F, Herder V, Kalkuhl A, Haist V,
Zhang N, Schaudien D, Deschl U, Baumgärtner W and Ulrich R: Matrix
metalloproteinase-12 deficiency ameliorates the clinical course and
demyelination in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis. Acta
Neuropathol. 124:127–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Griner SE, Joshi JP and Nahta R: Growth
differentiation factor 15 stimulates rapamycin-sensitive ovarian
cancer cell growth and invasion. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:46–58. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Theocharis AD, Gialeli C, Bouris P,
Giannopoulou E, Skandalis SS, Aletras AJ, Iozzo RV and Karamanos
NK: Cell-matrix interactions: focus on proteoglycan-proteinase
interplay and pharmacological targeting in cancer. FEBS J.
281:5023–5042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Long ZW, Wang JL and Wang YN: Matrix
metalloproteinase-7 mRNA and protein expression in gastric
carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:11415–11426. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang BG, Du T, Zang MD, Chang Q, Fan ZY,
Li JF, Yu BQ, Su LP, Li C, Yan C, et al: Androgen receptor promotes
gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via AKT-phosphorylation
dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9. Oncotarget.
5:10584–10595. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang L, Ren Y, Yu X, Qian F, Bian BS, Xiao
HL, Wang WG, Xu SL, Yang J, Cui W, et al: ALDH1A1 defines invasive
cancer stem-like cells and predicts poor prognosis in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 27:775–783. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruiz-Morales JM, Dorantes-Heredia R,
Arrieta O, Chávez-Tapia NC and Motola-Kuba D: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) prognostic value in lung
adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:3601–3610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heinke J, Kerber M, Rahner S, Mnich L,
Lassmann S, Helbing T, Werner M, Patterson C, Bode C and Moser M:
Bone morphogenetic protein modulator BMPER is highly expressed in
malignant tumors and controls invasive cell behavior. Oncogene.
31:2919–2930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen J, Chen LJ, Zhou HC, Yang RB, Lu Y,
Xia YL, Werner M, Patterson C, Bode C and Moser M: Prognostic value
of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.
Hepatogastroenterology. 61:518–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ibrahim ZM and Ngom A: The relative vertex
clustering value - a new criterion for the fast discovery of
functional modules in protein interaction networks. BMC
Bioinformatics. 16(Suppl 4): S32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anwar S, Dikhit MR, Singh KP, Kar RK,
Zaidi A, Sahoo GC, Roy AK, Nozaki T, Das P and Ali V: Interaction
between Nbp35 and Cfd1 proteins of cytosolic Fe-S cluster assembly
reveals a stable complex formation in Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS
One. 9:e1089712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chatr-Aryamontri A, Breitkreutz BJ,
Heinicke S, et al: The BioGRID interaction database: 2013 update.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:(Database Issue). D816–D823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . The Gene
Ontology project in 2008. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:(Database Issue).
D440–D448. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu A, Wang C and Sun S: Screening
candidate genes associated with bladder cancer using DNA
microarray. Mol Med Rep. 10:3087–3091. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim SO and Kim MR: [6]-gingerol prevents
disassembly of cell junctions and activities of MMPs in invasive
human pancreas cancer cells through ERK/NF-kappa B/snail signal
transduction pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:7618522013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong J, Baquiran JB, Bonakdar N, Lees J,
Ching YW, Pugacheva E, Fabry B and O'Neill GM: NEDD9 stabilizes
focal adhesions, increases binding to the extra-cellular matrix and
differentially effects 2D versus 3D cell migration. PLoS One.
7:e350582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Okazaki I, Noro T, Tsutsui N, Yamanouchi
E, Kuroda H, Nakano M, Yokomori H and Inagaki Y: Fibrogenesis and
carcinogenesis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): involvement
of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinase (TIMPs). Cancers. 6:1220–1255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fiorentini C, Bodei S, Bedussi F, Fragni
M, Bonini SA, Simeone C, Zani D, Berruti A, Missale C, Memo M, et
al: GPNMB/OA protein increases the invasiveness of human metastatic
prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC3 through MMP-2 and MMP-9
activity. Exp Cell Res. 323:100–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Dai C, Zhu H, Chen S, Wu Y, Li Q,
Zeng X, Wang W, Zuo J, Zhou M, et al: Cyclophilin A promotes human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell metastasis via regulation of MMP3 and
MMP9. Mol Cell Biochem. 357:387–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Campbell NE, Kellenberger L, Greenaway J,
Moorehead RA, Linnerth-Petrik NM and Petrik J: Extracellular matrix
proteins and tumor angiogenesis. J Oncol. 2010:5869052010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng D, Ye X, Zhu Z, Wei Z, Cai Q and Wang
Y: Comparative transcriptome analysis between metastatic and
non-metastatic gastric cancer reveals potential biomarkers. Mol Med
Rep. 11:386–392. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang Y, Shu Y, Shi Y, Li LP, Yuan F and
Ren H: Identifying gastric cancer related genes using the shortest
path algorithm and protein-protein interaction network. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:3713972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Huang Z, Zhu Z, Liu J, Zheng X
and Zhang Y: Network analysis of ChIP-Seq data reveals key genes in
prostate cancer. Eur J Med Res. 19:472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|