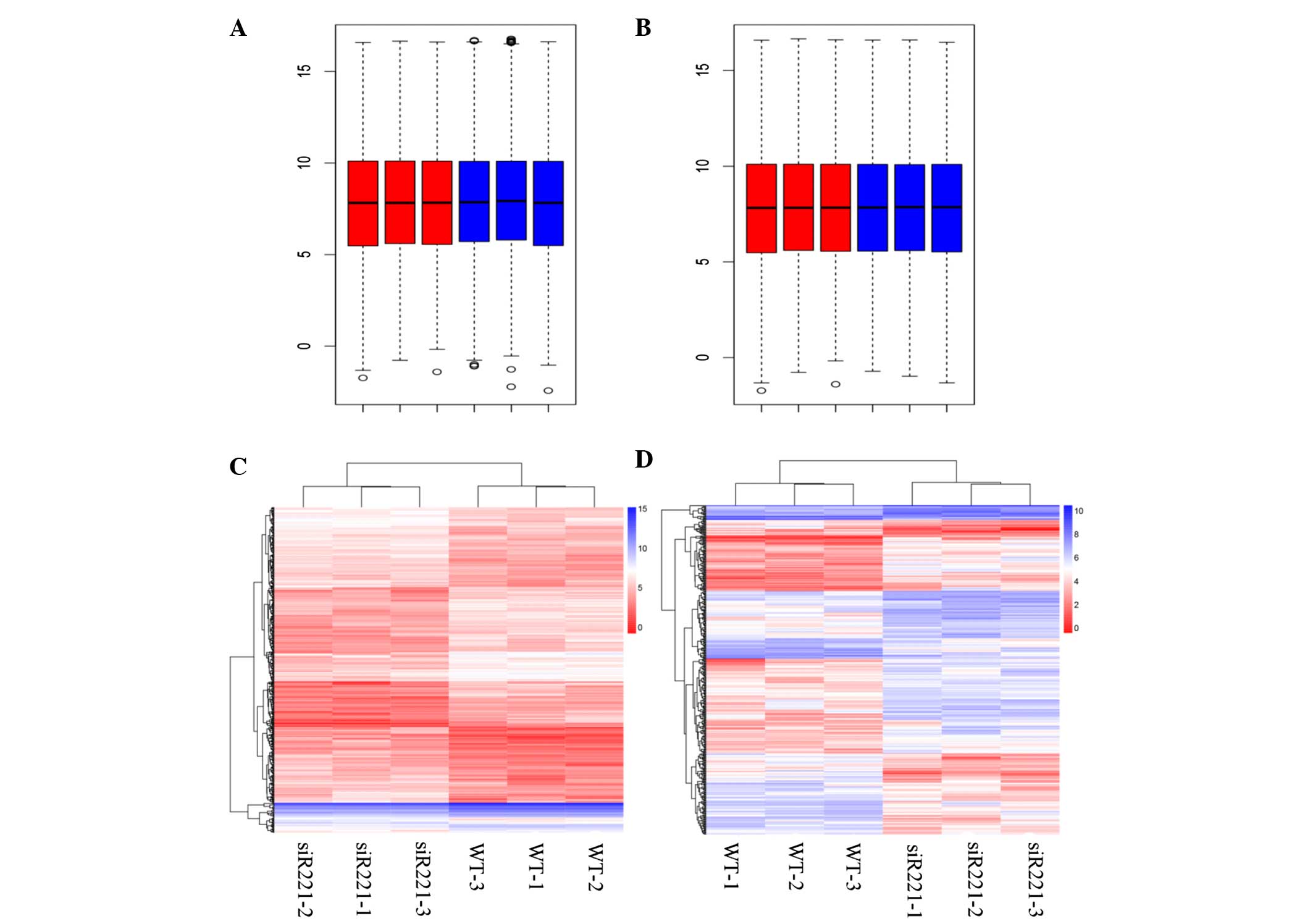
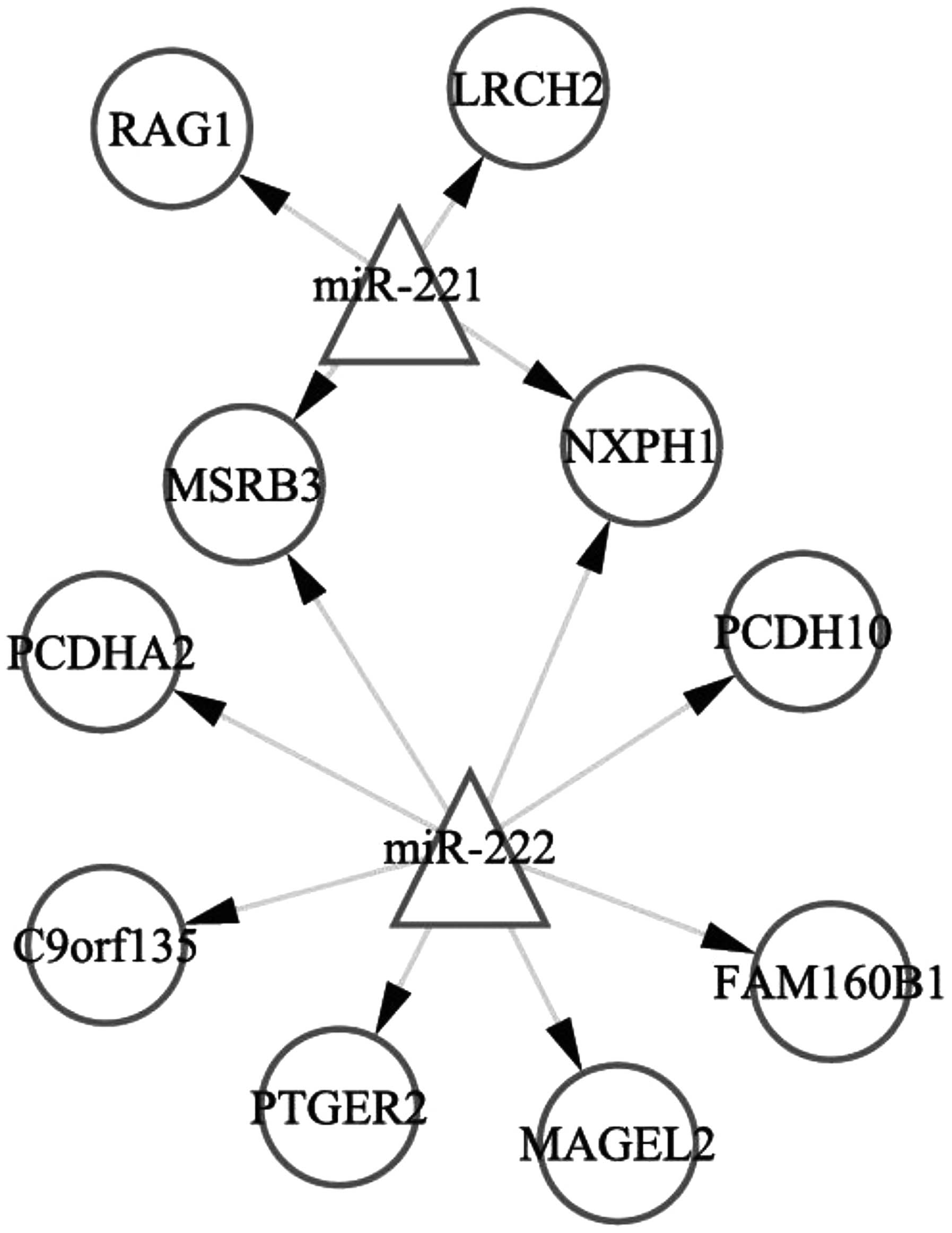
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ariazi EA, Ariazi JL, Cordera F and Jordan
VC: Estrogen receptors as therapeutic targets in breast cancer.
Curr Top Med Chem. 6:181–202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Howell A: Fulvestrant (‘Faslodex’):
Current and future role in breast cancer management. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 57:265–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baumgarten SC and Frasor J: Minireview:
Inflammation: An instigator of more aggressive estrogen receptor
(ER) positive breast cancers. Mol Endocrinol. 26:360–371. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xin F, Li M, Balch C, Thomson M, Fan MY,
Liu Y, Hammond SM, Kim S and Nephew KP: Computational analysis of
microRNA profiles and their target genes suggests significant
involvement in breast cancer antiestrogen resistance.
Bioinformatics. 25:430–434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rao X, Di Leva G, Li M, Fang F, Devlin C,
Hartman-Frey C, Burow ME, Lvan M, Croce CM and Nephew KP:
MicroRNA-221/222 confers breast cancer fulvestrant resistance by
regulating multiple signaling pathways. Oncogene. 30:1082–1097.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perey L, Paridaens R, Hawle H, Zaman K,
Nolé F, Wildiers H, Fiche M, Dietrich D, Clément P, Köberle D, et
al: Clinical benefit of fulvestrant in postmenopausal women with
advanced breast cancer and primary or acquired resistance to
aromatase inhibitors: Final results of phase II Swiss Group for
Clinical Cancer Research Trial (SAKK 21/00). Ann Oncol. 18:64–69.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tangkeangsirisin W and Serrero G: GP88
(Progranulin) confers fulvestrant (Faslodex, ICI 182,780)
resistance to human breast cancer cells. Adv Breast Cancer Res.
3:68–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kirkegaard T, Yde CW, Kveiborg M and
Lykkesfeldt AE: The broad-spectrum metalloproteinase inhibitor
BB-94 inhibits growth, HER3 and Erk activation in
fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol.
45:393–400. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Afsari B, Geman D and Fertig EJ: Learning
dysregulated pathways in cancers from differential variability
analysis. Cancer Inform. 13(Suppl 5): S61–S67. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Troyanskaya O, Cantor M, Sherlock G, Brown
P, Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Botstein D and Altman RB: Missing value
estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics. 17:520–525.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Székely GJ and Rizzo ML: Hierarchical
clustering via joint between-within distances: Extending Ward's
minimum variance method. J Classif. 22:151–183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Deza E and Deza MM: Encyclopedia of
distances. 3rd. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shi J and Walker MG: Gene Set Enrichment
Analysis (GSEA) for Interpreting Gene Expression Profiles. Curr
Bioinform. 2:133–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gotea V and Ovcharenko I: DiRE:
Identifying distant regulatory elements of co-expressed genes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:(Web Server Issue). W133–W139. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ldeker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tian WN, Braunstein LD, Apse K, Pang J,
Rose M, Tian X and Stanton RC: Importance of glucose-6-phosphate
dehydrogenase activity in cell death. Am J Physiol.
276:C1121–C1131. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Riganti C, Gazzano E, Polimeni M, Aldieri
E and Ghigo D: The pentose phosphate pathway: An antioxidant
defense and a crossroad in tumor cell fate. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:421–436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Richardson AD, Yang C, Osterman A and
Smith JW: Central carbon metabolism in the progression of mammary
carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 110:297–307. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu X, Bennet B, Mu E, Rabinowitz J and
Kang Y: Metabolomic changes accompanying transformation and
acquisition of metastatic potential in a syngeneic mouse mammary
tumor model. J Biol Chem. 285:9317–9321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai J, Guan H, Fang L, Yang Y, Zhu X, Yuan
J, Wu J and Li M: MicroRNA-374a activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling
to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 123:566–579.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bilir B, Kucuk O and Moreno CS: Wnt
signaling blockage inhibits cell proliferation and migration, and
induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Transl
Med. 11:2802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li DM and Feng YM: Signaling mechanism of
cell adhesion molecules in breast cancer metastasis: Potential
therapeutic targets. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:7–21. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saadatmand S, de Kruijf EM, Sajet A,
Dekker-Ensink NG, van Nes JG, Putter H, Smit VT, van de Velde CJ,
Liefers GJ and Kuppen JK: Expression of cell adhesion molecules and
prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 100:252–260. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pines J, Toldo L and Lafont F: Cell to
cell contact and extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
10:5611998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ying J, Li H, Seng TJ, Langford C,
Srivastava G, Tsao SW, Putti T, Murray P, Chan AT and Tao Q:
Functional epigenetics identifies a protocadherin PCDH10 as a
candidate tumor suppressor for nasopharyngeal, esophageal and
multiple other carcinomas with frequent methylation. Oncogene.
25:1070–1080. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|