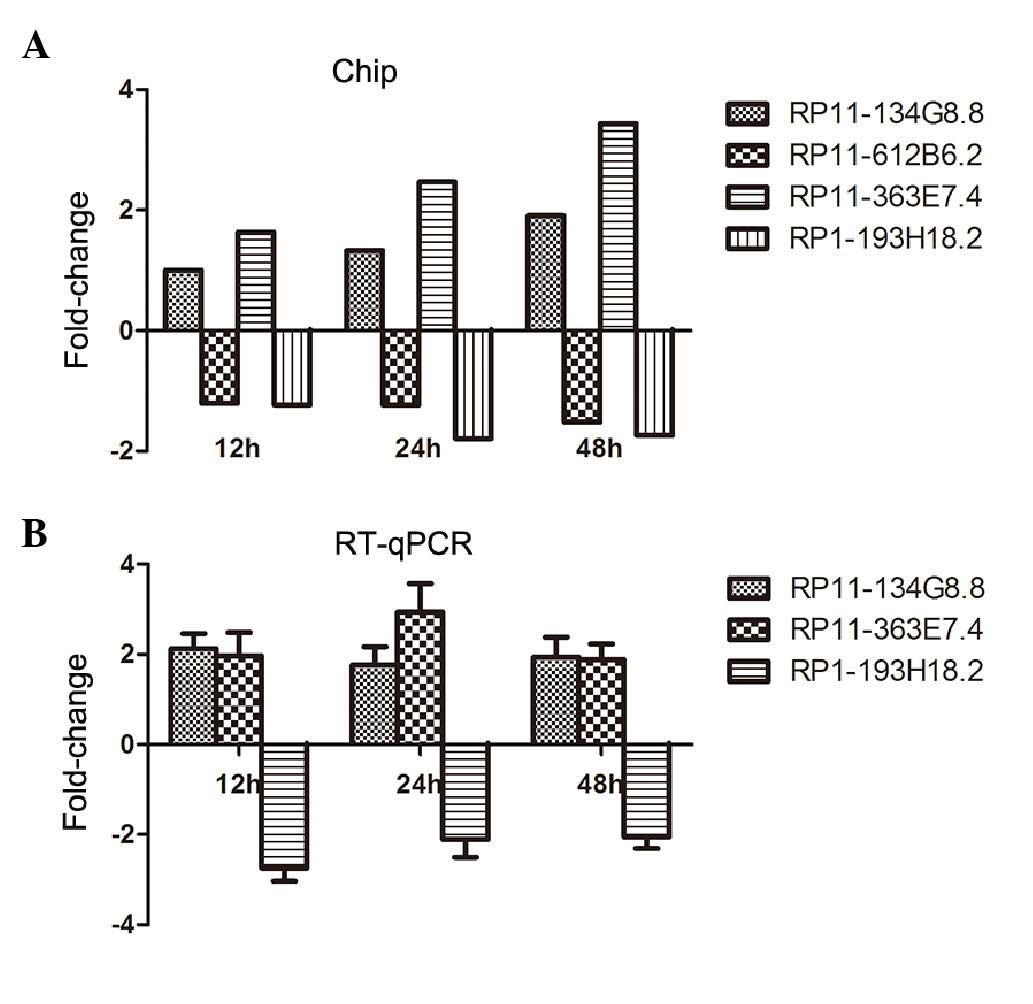
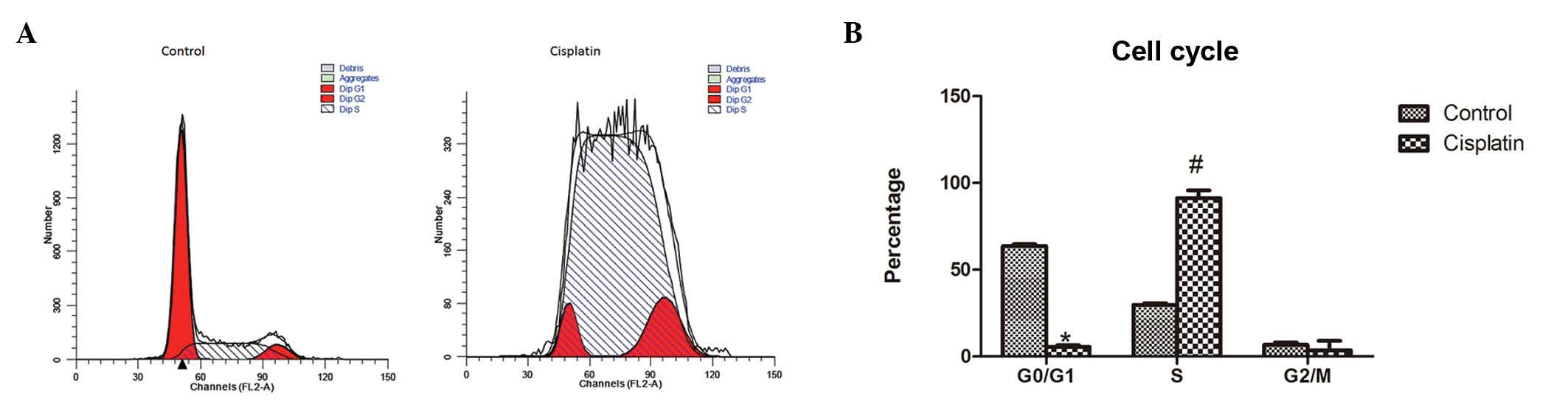
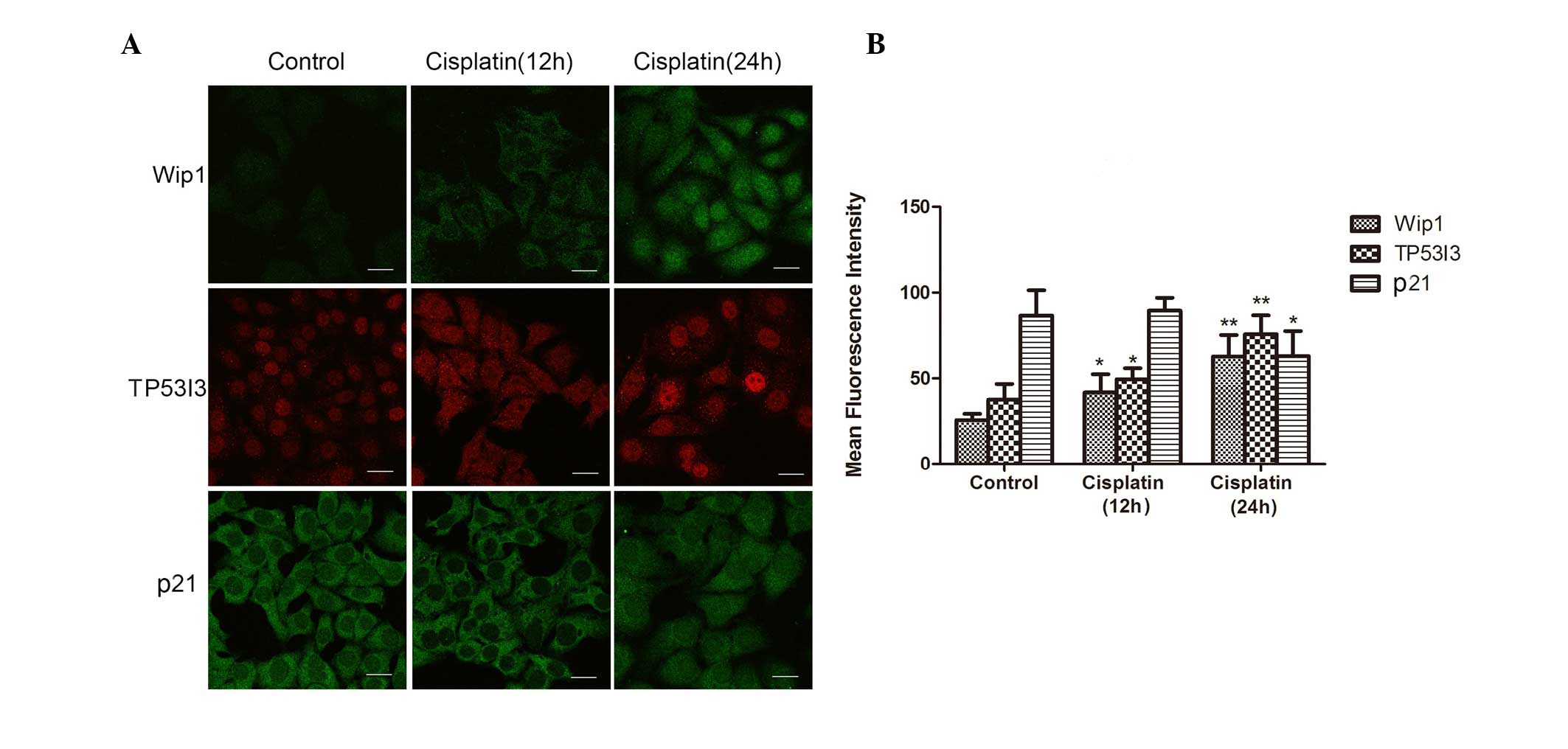
|
1
|
Hou JK, Huang Y, He W, Yan ZW, Fan L, Liu
MH, Xiao WL, Sun HD and Chen GQ: Adenanthin targets peroxiredoxin
I/II to kill hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang X, Xie X, Xiao YF, Xie R, Hu CJ, Tang
B, Li BS and Yang SM: The emergence of long non-coding RNAs in the
tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
360:119–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marullo R, Werner E, Degtyareva N, Moore
B, Altavilla G, Ramalingam SS and Doetsch PW: Cisplatin induces a
mitochondrial-ROS response that contributes to cytotoxicity
depending on mitochondrial redox status and bioenergetic functions.
PLoS One. 8:e811622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu Y, Zhou W, Wang H, Wan
G, Sun D, Zhang N and Wang Y: A polymeric prodrug of cisplatin
based on pullulan for the targeted therapy against hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Pharm. 483:89–100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ziko L, Riad S, Amer M, Zdero R,
Bougherara H and Amleh A: Mechanical stress promotes
cisplatin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell death. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:4305692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bose RN: Biomolecular targets for platinum
antitumor drugs. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2:103–111. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chu G: Cellular responses to cisplatin.
The roles of DNA-binding proteins and DNA repair. J Biol Chem.
269:787–790. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels
J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms
of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 31:1869–1883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bonasio R and Shiekhattar R: Regulation of
transcription by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 48:433–455.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kung JT, Colognori D and Lee JT: Long
noncoding RNAs: Past, present and future. Genetics. 193:651–669.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi D, Zheng H, Zhuo C, Peng J, Li D, Xu
Y, Li X, Cai G and Cai S: Low expression of novel lncRNA
RP11-462C24.1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal
cancer. Med Oncol. 31:312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun M and Kraus WL: From discovery to
function: The expanding roles of long noncoding RNAs in physiology
and disease. Endocr Rev. 36:25–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan Y, Shen B, Tan M, Mu X, Qin Y, Zhang F
and Liu Y: Long non-coding RNA UCA1 increases chemoresistance of
bladder cancer cells by regulating Wnt signaling. FEBS J.
281:1750–1758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
George J and Patel T: Noncoding RNA as
therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis.
35:63–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liao Q, Xiao H, Bu D, Xie C, Miao R, Luo
H, Zhao G, Yu K, Zhao H, Skogerbø G, et al: ncFANs: A web server
for functional annotation of long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:W118–W124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou Z, Xu C, Xie H, Xu H, Zhan P, Yu L and
Fang X: Long noncoding RNAs expression patterns associated with
chemo response to cisplatin based chemotherapy in lung squamous
cell carcinoma patients. PLoS One. 9:e1081332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sui W, Yan Q, Li H, Liu J, Chen J, Li L
and Dai Y: Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA expression in
peripheral blood mononuclear cells of uremia patients. J Nephrol.
26:731–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
da W Huang, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hall JR, Messenger ZJ, Tam HW, Phillips
SL, Recio L and Smart RC: Long noncoding RNA lincRNA-p21 is the
major mediator of UVB-induced and p53-dependent apoptosis in
keratinocytes. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Foo JB, Yazan LS, Tor YS, Wibowo A, Ismail
N, How CW, Armania N, Loh SP, Ismail IS, Cheah YK and Abdullah R:
Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by betulinic acid-rich
fraction from Dillenia suffruticosa root in MCF-7 cells involved
p53/p21 and mitochondrial signalling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
166:270–278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma X, Han J, Wu Q, Liu H, Shi S, Wang C,
Wang Y, Xiao J, Zhao J, Jiang J and Wan C: Involvement of
dysregulated Wip1 in manganese-induced p53 signaling and neuronal
apoptosis. Toxicol Lett. 235:17–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Flatt PM, Polyak K, Tang LJ, Scatena CD,
Westfall MD, Rubinstein LA, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Hill DE
and Pietenpol JA: p53-dependent expression of PIG3 during
proliferation, genotoxic stress and reversible growth arrest.
Cancer Lett. 156:63–72. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gartel AL and Radhakrishnan SK: Lost in
transcription: p21 repression, mechanisms and consequences. Cancer
Res. 65:3980–3985. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ando T, Kawabe T, Ohara H, Ducommun B,
Itoh M and Okamoto T: Involvement of the interaction between p21
and proliferating cell nuclear antigen for the maintenance of G2/M
arrest after DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 276:42971–42977. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yadav V, Sultana S, Yadav J and Saini N:
Gatifloxacin induces S and G2-phase cell cycle arrest in pancreatic
cancer cells via p21/p27/p53. PLoS One. 7:e477962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qu K, Lin T, Wei J, Meng F, Wang Z, Huang
Z, Wan Y, Song S, Liu S, Chang H, et al: Cisplatin induces cell
cycle arrest and senescence via upregulating P53 and P21 expression
in HepG2 cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 33:1253–1259.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Chen Z, Ge Q, Hu J, Li F, Hu J, Xu
H, Ye Z and Li LC: Up-regulation of p21 (WAF1/CIP1) by miRNAs and
its implications in bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 588:4654–4664.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Zhang X, Ji S, Hao C, Mu Y, Sun J
and Hao J: Sohlh2 inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation by
upregulation of p21 and downregulation of cyclin D1.
Carcinogenesis. 35:1863–1871. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Z, Sun M, Lu K, Liu J, Zhang M, Wu W,
De W, Wang Z and Wang R: The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes
to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via
downregualtion of p21 (WAF1/CIP1) expression. PLoS One.
8:e772932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Contente A, Dittmer A, Koch MC, Roth J and
Dobbelstein M: A polymorphic microsatellite that mediates induction
of PIG3 by p53. Nat Genet. 30:315–320. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guan X, Liu Z, Wang L, Wang LE, Sturgis EM
and Wei Q: Functional repeats (TGYCC)n in the p53-inducible gene 3
(PIG3) promoter and susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. Carcinogenesis. 34:812–817. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li B, Shang ZF, Yin JJ, Xu QZ, Liu XD,
Wang Y, Zhang SM, Guan H and Zhou PK: PIG3 functions in DNA damage
response through regulating DNA-PKcs homeostasis. Int J Biol Sci.
9:425–434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shaltiel IA, Aprelia M, Saurin AT,
Chowdhury D, Kops GJ, Voest EE and Medema RH: Distinct phosphatases
antagonize the p53 response in different phases of the cell cycle.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:7313–7318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lowe J, Cha H, Lee MO, Mazur SJ, Appella E
and Fornace AJ Jr: Regulation of the Wip1 phosphatase and its
effects on the stress response. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
17:1480–1498. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang W, Zhu H, Zhang H, Zhang L, Ding Q
and Jiang H: Targeting PPM1D by lentivirus-mediated RNA
interference inhibits the tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:1044–1049. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li GB, Zhang XL, Yuan L, Jiao QQ, Liu DJ
and Liu J: Protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1delta (PPM1D)
mRNA expression is a prognosis marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
PLoS One. 8:e607752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yagi H, Chuman Y, Kozakai Y, Imagawa T,
Takahashi Y, Yoshimura F, Tanino K and Sakaguchi K: A small
molecule inhibitor of p53-inducible protein phosphatase PPM1D.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:729–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tan DS, Lambros MB, Rayter S, Natrajan R,
Vatcheva R, Gao Q, Marchio C, Geyer FC, Savage K, Parry S, et al:
PPM1D is a potential therapeutic target in ovarian clear cell
carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2269–2280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng TS, He YH, Nie T, Hu XD, Lu HY, Yi J,
Shuai YF and Luo M: PPM1D is a prognostic marker and therapeutic
target in colorectal cancer. Exp Ther Med. 8:430–434.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ali AY, Kim JY, Pelletier JF, Vanderhyden
BC, Bachvarov DR and Tsang BK: Akt confers cisplatin
chemoresistance in human gynecological carcinoma cells by
modulating PPM1D stability. Mol Carcinog. 54:1301–1314. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park HK, Panneerselvam J, Dudimah FD, Dong
G, Sebastian S, Zhang J and Fei P: Wip1 contributes to cell
homeostasis maintained by the steady-state level of Wtp53. Cell
Cycle. 10:2574–2582. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cao R, Zhang J, Zhang M and Chen X: PPM1D
regulates p21 expression via dephoshporylation at serine 123. Cell
Cycle. 14:641–647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|