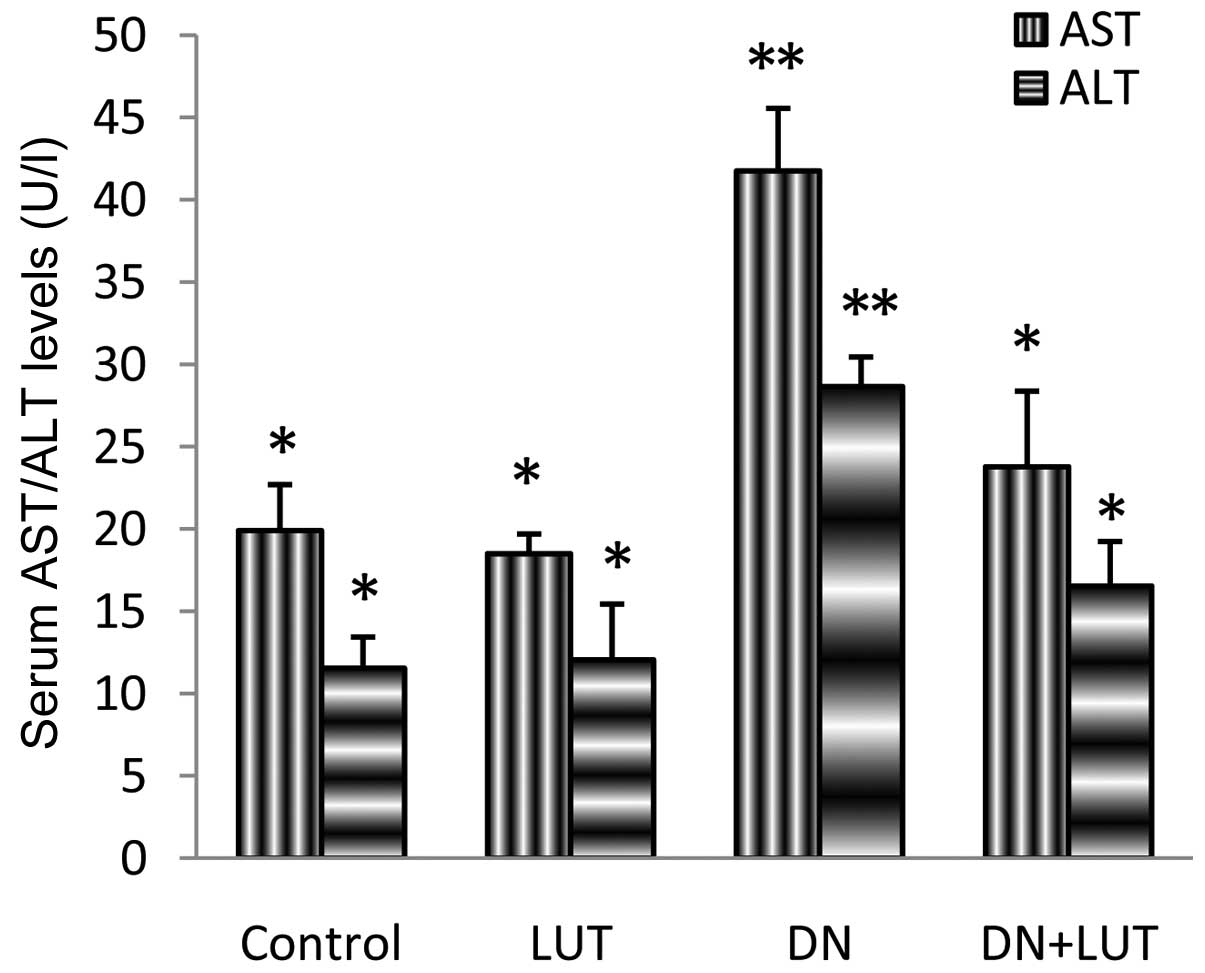
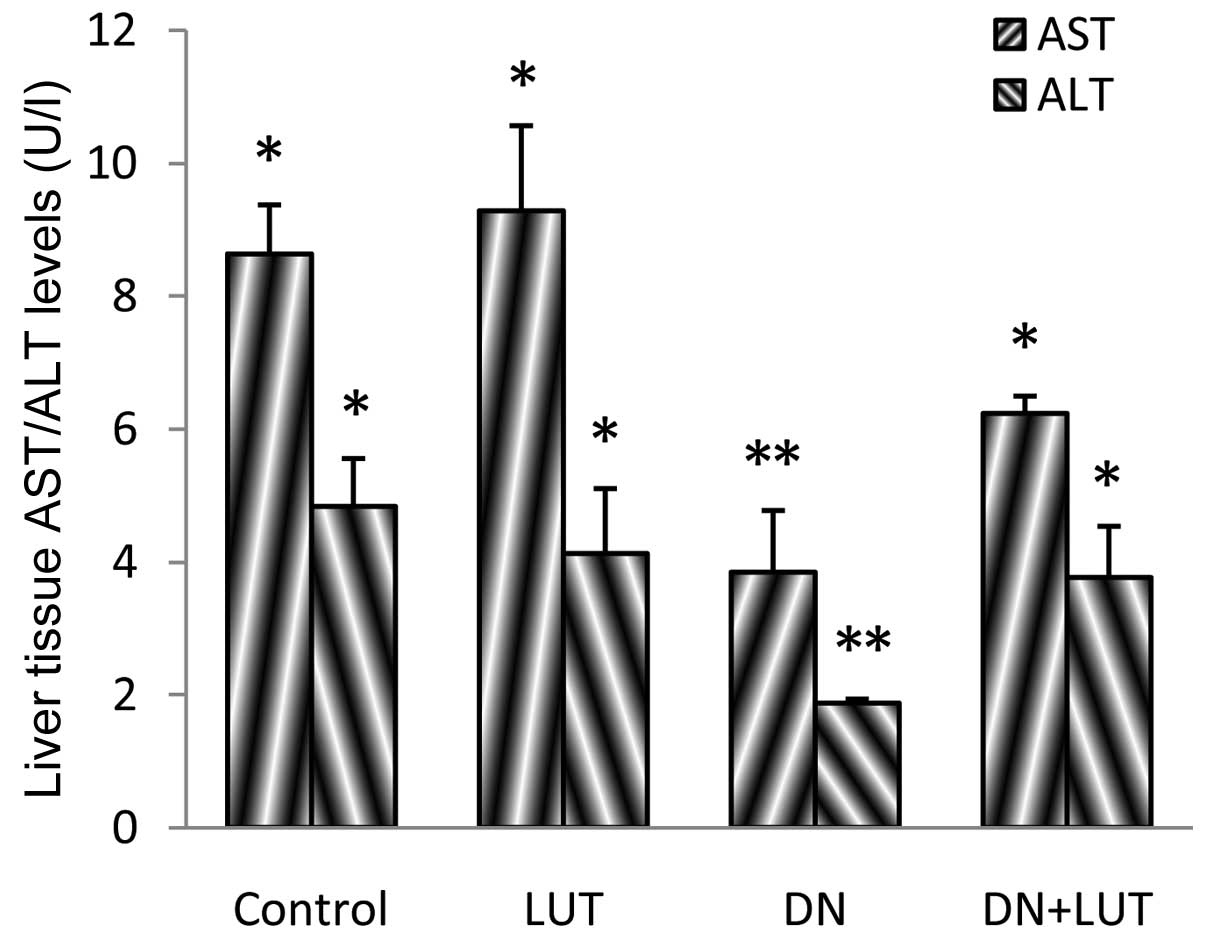
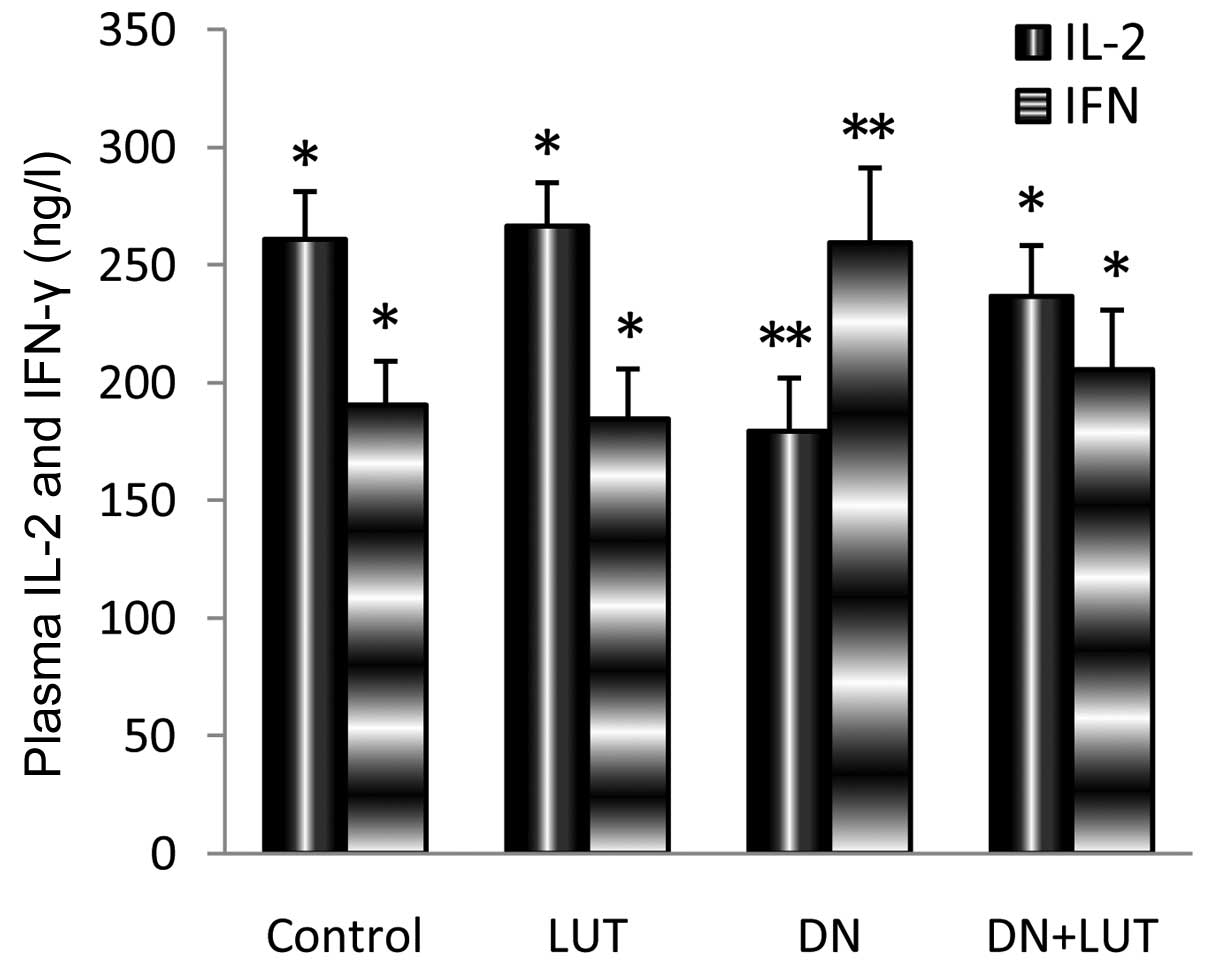
|
1
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality and survival trends
in the United States from 1995 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I and
Donato F: Hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis: Incidence and
risk factors. Gastroenterology. 127(5): Suppl 1. S35–S50. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Faloppi L, Scartozzi M, Maccaroni E, Di
Pietro Paolo M, Berardi R, Del Prete M and Cascinu S: Evolving
strategies for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: From
clinical-guided to molecularly-taylored therapeutic options. Cancer
Treat Rev. 37:169–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Borzio M, Fargion S, Borzio F, Fracanzani
AL, Croce AM, Stroffolini T, Oldani S, Cotichini R and Roncalli M:
Impact of large regenerative, low grade and high grade dysplastic
nodules in hepatocellular carcinoma development. J Hepatol.
39:208–214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pawlik TM, Poon RT, Abdalla EK, Ikai I,
Nagorney DM, Belghiti J, Kianmanesh R, Ng IO, Curley SA, Yamaoka Y,
et al: Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal
or hepatic vein invasion: Results of a multicenter study. Surgery.
137:403–410. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Irtan S, Chopin-Laly X, Ronot M, Faivre S,
Paradis V and Belghiti J: Complete regression of locally advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma induced by sorafenib allowing curative
resection. Liver Int. 31:740–743. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Petersen FB, Buckner CD, Appelbaum FR,
Clift RA, Sanders JE, Bensinger WI, Storb R, Witherspoon RP,
Sullivan KM and Bearman SI: Busulfan, cyclophosphamide and
fractionated total body irradiation as a preparatory regimen for
marrow transplantation in patients with advanced hematological
malignancies: A phase I study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 4:617–623.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Senthilkumar S, Devaki T, Manohar BM and
Babu MS: Effect of squalene on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity.
Clin Chim Acta. 364:335–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clemens MR, Ladner C, Schmidt H, Ehninger
G, Einsele H, Bühler E, Waller HD and Gey KF: Decreased essential
antioxidants and increased lipid hydroperoxides following high-dose
radiochemotherapy. Free Radic Res Commun. 7:227–232. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hosakote YM, Liu T, Castro SM, Garofalo RP
and Casola A: Respiratory syncytial virus induces oxidative stress
by modulating antioxidant enzymes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
41:348–357. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Li J, Cao L, Xu W and Yin Z:
Circulating tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: Detection
techniques, clinical implications and future perspectives. Semin
Oncol. 39:449–460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lopez-Lazaro M: Distribution and
biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:31–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai X, Lu W, Ye T, Lu M, Wang J, Huo J,
Qian S, Wang X and Cao P: The molecular mechanism of
luteolin-induced apoptosis is potentially related to inhibition of
angiogenesis in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
28:1353–1361. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Merfort I, Heilmann J, Hagedorn-Leweke U
and Lippold BC: In vivo skin penetration studies on chamomile
flavones. Pharmazie. 49:509–511. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Plaschke K: Composition comprising one or
more flavonoids, method of obtaining such composition and use there
of as UV-absorbing agent. US Patent 6,409,996 B1. Filed November
19, 1998; issued June 25. 2002.
|
|
16
|
Graefe EU, Derendorf H and Veit M:
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the flavonols quercetin in
humans. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 37:219–233. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N and Yagi K: Assay for
lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction.
Anal Biochem. 95:351–358. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ellman GL: Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 82:70–77. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morota K, Komori M, Fujinami R, Yamada K,
Kuribayashi K, Watanabe N, Sokoll LJ, Elliott D, Chan DW, Martens
F, et al: Improvement and multicenter evaluation of the analytical
performance of an automated chemiluminescent immunoassay for alpha
fetoprotein. Int J Biol Markers. 27:39–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rice-Evans CA, Miller NJ and Paganga G:
Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and
phenolic acids. Free Radic Biol Med. 20:933–956. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Halliwell B and Gutteridge JM: Lipid
peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage and antioxidant therapy.
Lancet. 1:1396–1397. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Senthilkumar S, Ebenezar KK, Sathish V,
Yogeeta S and Devaki T: Modulation of tissue defense system by
squalene in cyclophosphamide induced toxicity in rats. Arch Med
Sci. 2:94–100. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Quinlan GJ and Gutteridege JM: Hydroxyl
radical generation by the tetracycline antibodies with free radical
damage to DNA, lipids, carbohydrates in the presence of iron and
copper salts. Free Radic Biol Med. 5:341–348. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Van Poppel G, Verhoeven DT, Verhagen H and
Goldbohm RA: Brassica vegetables and cancer prevention.
Epidemiology and mechanisms. Adv Exp Med Biol. 472:159–168. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Østergaard H, Tachibana C and Winther JR:
Monitoring disulfide bond formation in the eukaryotic cytosol. J
Cell Biol. 166:337–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Senthilkumar S, Yogeeta SK, Subashini R
and Devaki T: Attenuation of cyclophosphamide induced toxicity by
squalene in experimental rats. Chem Biol Interact. 160:252–260.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tafazoli S and O'Brien PJ: Peroxidases: A
role in the metabolism and side effects of drugs. Drug Discov
Today. 10:617–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trevisani F, D'Intino PE, Morselli-Labate
AM, Mazzella G, Accogli E, Caraceni P, Domenicalli M, De Notariis
S, Roda E and Bernardi M: Serum alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease:
Influence of HBsAg and anti- HCV status. J Hepatol. 34:570–575.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wright LM, Kreikemeier JT and Fimmel CJ: A
concise review of serum markers for hepatocellular cancer. Cancer
Detect Prev. 31:35–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chiappini F: Circulating tumor cells
measurements in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Hepatol.
2012:6848022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang Gui-zhen: Boundary immunology.
Beijing: Science Press; 2002, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tagawa M: Cytokine therapy for cancer.
Curr Pharm Des. 6:681–699. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kusters S, Gantner F, Künstle G and Tiegs
G: Interferon-ã plays a critical role in T cell-dependent liver
injury in mice initiated by concanavalin A. Gastroenterology.
111:462–471. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Haqqi TM, Anthony DD, Gupta S, Ahmad N,
Lee MS, Kumar GK and Mukhtar H: Prevention of collagen-induced
arthritis in mice by a polyphenolic fraction from green tea. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:4524–4529. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|