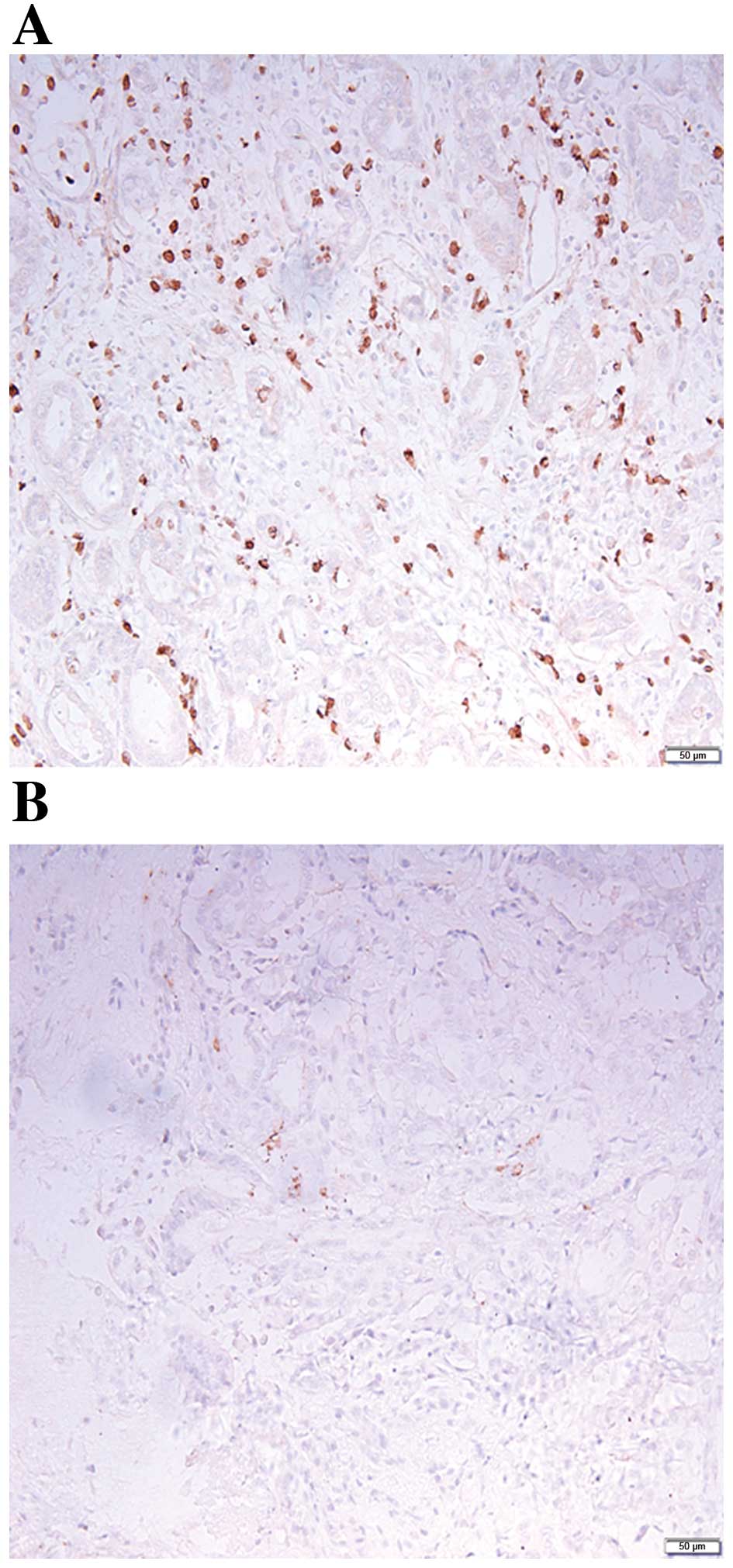
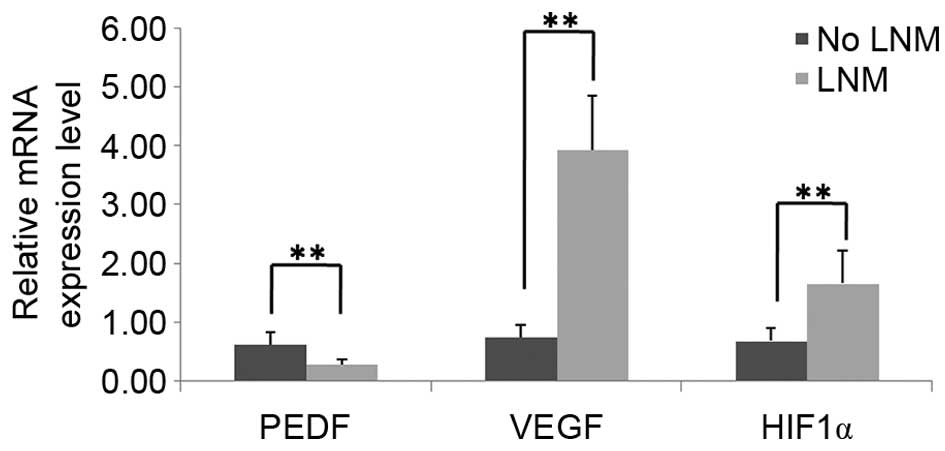
|
1
|
Udelsman R and Chen H: The current
management of thyroid cancer. Adv Surg. 33:1–27. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paterson IC, Greenlee R and Jones D Adams:
Thyroid cancer in Wales, 1985–1996: A cancer registry-based study.
Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 44:245–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Davies L and Welch HG: Increasing
incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973–2002. JAMA.
295:2164–2167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De Lellis R, Lloyd R, Heitz PU and Eng C:
Pathology and genetics of tumors of the endocrine organs. IARC;
Lyon: 2004
|
|
5
|
Mazzaferri EL and Jhiang SM: Long-term
impact of initial surgical and medical therapy on papillary and
follicular thyroid cancer. Am J Med. 97:418–428. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schlumberger MJ: Papillary and follicular
thyroid carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 338:297–306. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Desgrosellier JS and Cheresh DA: Integrins
in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:9–22. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kohn EC and Liotta LA: Molecular insights
into cancer invasion: Strategies for prevention and intervention.
Cancer Res. 55:1856–1862. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nucera C, Lawler J and Parangi S:
BRAF(V600E) and microenvironment in thyroid cancer: A functional
link to drive cancer progression. Cancer Res. 71:2417–2422. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Zhai Z, Liu D, Zhong X, Meng X, Yang
Q, Liu J and Li H: CD105 promotes hepatocarcinoma cell invasion and
metastasis through VEGF. Tumour Biol. 36:737–745. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tombran-Tink J, Chader GG and Johnson LV:
PEDF: A pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal
differentiative activity. Exp Eye Res. 53:411–414. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Becerra SP and Notario V: The effects of
PEDF on cancer biology: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic
potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:258–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Filleur S, Volz K, Nelius T, Mirochnik Y,
Huang H, Zaichuk TA, Aymerich MS, Becerra SP, Yap R, Veliceasa D,
et al: Two functional epitopes of pigment epithelial-derived factor
block angiogenesis and induce differentiation in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:5144–5152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Crawford SE, Stellmach V, Ranalli M, Huang
X, Huang L, Volpert O, De Vries GH, Abramson LP and Bouck N:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in neuroblastoma: A
multifunctional mediator of Schwann cell antitumor activity. J Cell
Sci. 114:4421–4428. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tanimoto S, Kanamoto T, Mizukami M, Aoyama
H and Kiuchi Y: Pigment epithelium-derived factor promotes neurite
outgrowth of retinal cells. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 55:109–116.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Unterlauft JD, Eichler W, Kuhne K, Yang
XM, Yafai Y, Wiedemann P, Reichenbach A and Claudepierre T: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor released by Muller glial cells exerts
neuroprotective effects on retinal ganglion cells. Neurochem Res.
37:1524–1533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao W, Tombran-Tink J, Chen W, Mrazek D,
Elias R and McGinnis JF: Pigment epithelium-derived factor protects
cultured retinal neurons against hydrogen peroxide -induced cell
death. J Neurosci Res. 57:789–800. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Gillis P, Crawford
SE, Xu H, Benedict W and Bouck NP: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor: A potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science. 285:245–248.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stellmach V, Crawford SE, Zhou W and Bouck
N: Prevention of ischemia-induced retinopathy by the natural ocular
antiangiogenic agent pigment epithelium-derived factor. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:2593–2597. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Browne M, Stellmach V, Cornwell M, Chung
C, Doll JA, Lee EJ, Jameson JL, Reynolds M, Superina RA, Abramson
LP and Crawford SE: Gene transfer of pigment epithelium-derived
factor suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis in a hepatoblastoma
xenograft model. Pediatr Res. 60:282–287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garcia M, Fernandez-Garcia NI, Rivas V,
Carretero M, Escamez MJ, Gonzalez-Martin A, Medrano EE, Volpert O,
Jorcano JL, Jimenez B, et al: Inhibition of xenografted human
melanoma growth and prevention of metastasis development by dual
antiangiogenic/antitumor activities of pigment epithelium-derived
factor. Cancer Res. 64:5632–5642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu QJ, Gong CY, Luo ST, Zhang DM, Zhang S,
Shi HS, Lu L, Yan HX, He SS, Li DD, et al: AAV-mediated human PEDF
inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in murine colorectal
peritoneal carcinomatosis model. BMC Cancer. 12:1292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maik-Rachline G, Shaltiel S and Seger R:
Extracellular phosphorylation converts pigment epithelium-derived
factor from a neurotrophic to an antiangiogenic factor. Blood.
105:670–678. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang H, Cheng R, Liu G, Zhong Q, Li C, Cai
W, Yang Z, Ma J, Yang X and Gao G: PEDF inhibits growth of
retinoblastoma by anti-angiogenic activity. Cancer Sci.
2100:2419–2425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang J, Chen S, Huang X, Han J, Wang Q,
Shi D, Cheng R, Gao G and Yang X: Growth suppression of cervical
carcinoma by pigment epithelium-derived factor via
anti-angiogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:967–974. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Han J, Yang X, Shao C, Xu Z,
Cheng R, Cai W, Ma J, Yang Z and Gao G: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor inhibits angiogenesis and growth of gastric carcinoma by
down-regulation of VEGF. Oncol Rep. 26:681–686. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu Z, Fang S, Zuo Y, Zhang Y, Cheng R,
Wang Q, Yang Z, Cai W, Ma J, Yang X and Gao G: Combination of
pigment epithelium-derived factor with radiotherapy enhances the
Anti-tumor effects on nasopharyngeal carcinoma by down-regulating
vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis.
Cancer Sci. 102:1789–1798. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A, Plank C,
Breitenecker G and Oberhuber G: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1alpha is a marker for an unfavorable prognosis in
early-stage invasive cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 60:4693–4696.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schindl M, Schoppmann SF, Samonigg H,
Hausmaninger H, Kwasny W, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Kubista E, Birner P
and Oberhuber G: Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group:
Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is associated
with an unfavorable prognosis in lymph node-positive breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 8:1831–1837. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koperek O, Akin E, Asari R, Niederle B and
Neuhold N: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in
papillary thyroid carcinoma is associated with desmoplastic stromal
reaction and lymph node metastasis. Virchows Arch. 463:795–802.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hedinger C, Williams ED and Sobin LH: The
WHO histological classification of thyroid tumors: A commentary on
the second edition. Cancer. 63:908–911. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stratmann M, Sekulla C, Dralle H and
Brauckhoff M: Current TNM system of the UICC/AJCC: The prognostic
significance for differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Chirurg.
83:646–651. 2012.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Liu R, Li W, Chen C, Katoh H, Chen
GY, McNally B, Lin L, Zhou P, Zuo T, et al: Somatic single hits
inactivate the X-linked tumor suppressor FOXP3 in the prostate.
Cancer Cell. 16:336–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cai J, Parr C, Watkins G, Jiang WG and
Boulton M: Decreased pigment epithelium-derived factor expression
in human breast cancer progression. Clinical Cancer Res.
12:3510–3517. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Orgaz JL, Ladhani O, Hoek KS,
Fernández-Barral A, Mihic D, Aguilera O, Seftor EA, Bernad A,
Rodríguez-Peralto JL, Hendrix MJ, et al: Loss of pigment
epithelium-derived factor enables migration, invasion and
metastatic spread of human melanoma. Oncogene. 28:4147–4161. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lan L, Luo Y, Cui D, Shi BY, Deng W, Huo
LL, Chen HL, Zhang GY and Deng LL: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition triggers cancer stem cell generation in human thyroid
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:113–120. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Koperek O, Bergner O, Pichlhöfer B,
Oberndorfer F, Hainfellner JA, Kaserer K, Horvat R, Harris AL,
Niederle B and Birner P: Expression of hypoxia-associated proteins
in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer is associated with
desmoplastic stroma reaction and lymph node metastasis and may
indicate somatic mutations in the VHL gene. J Pathol. 225:63–72.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|