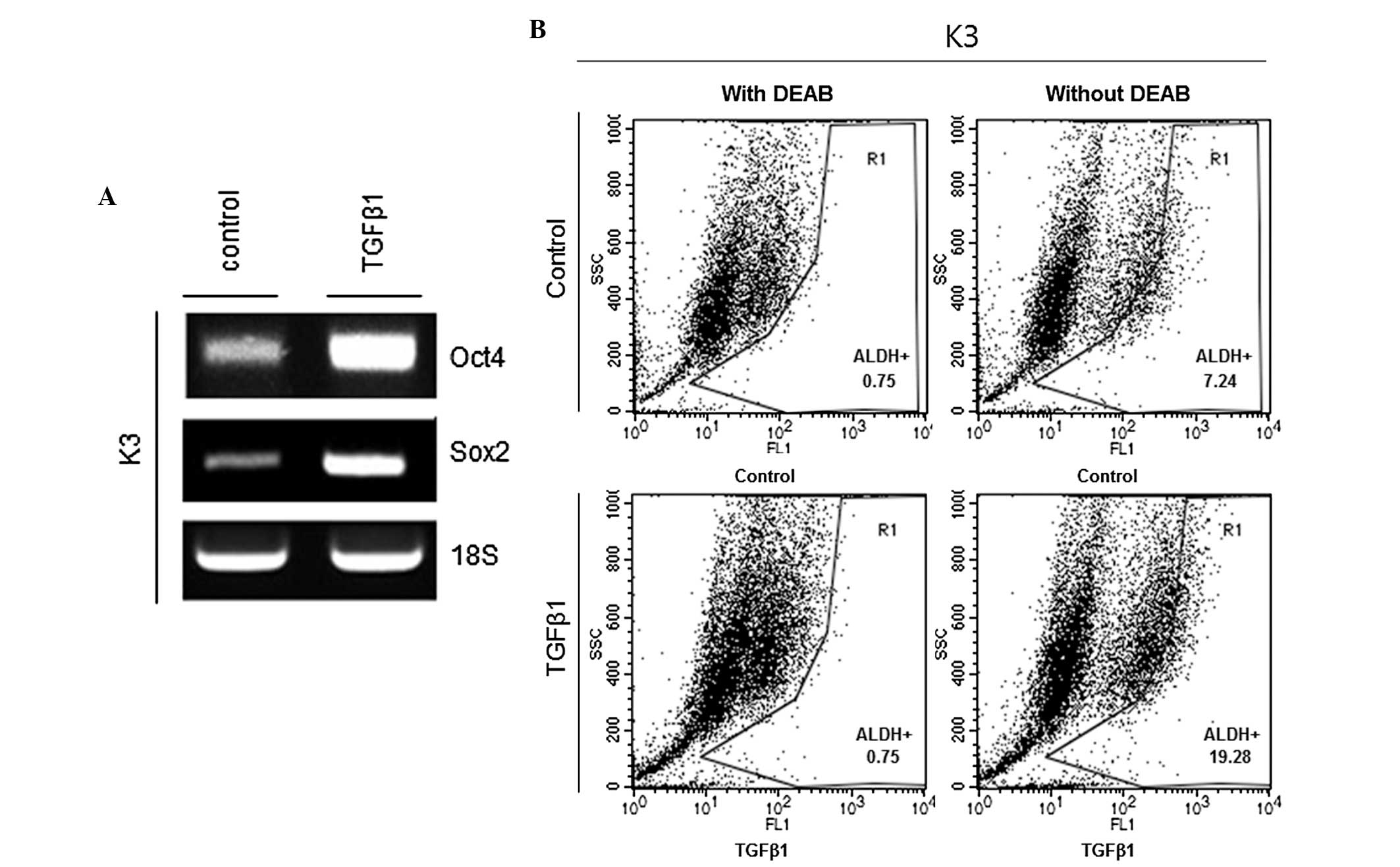
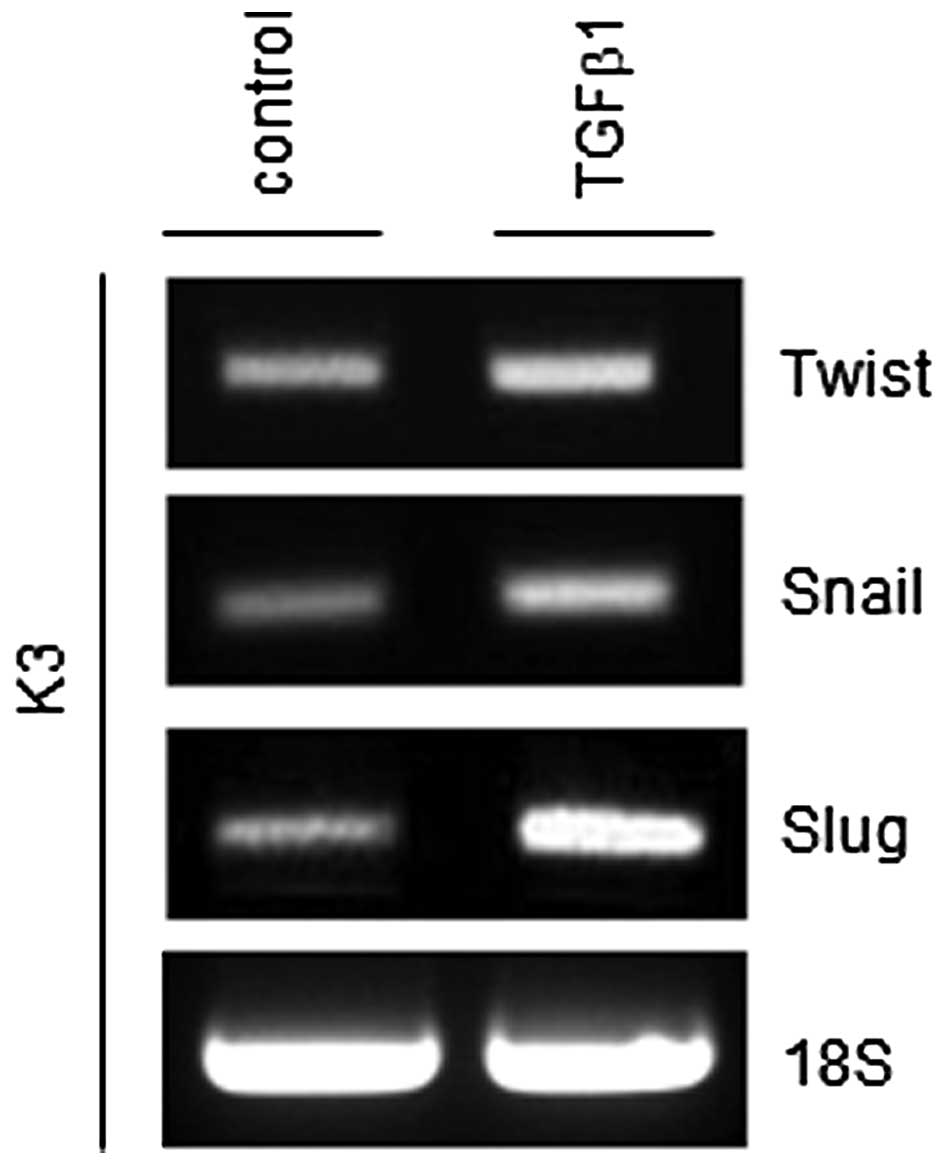
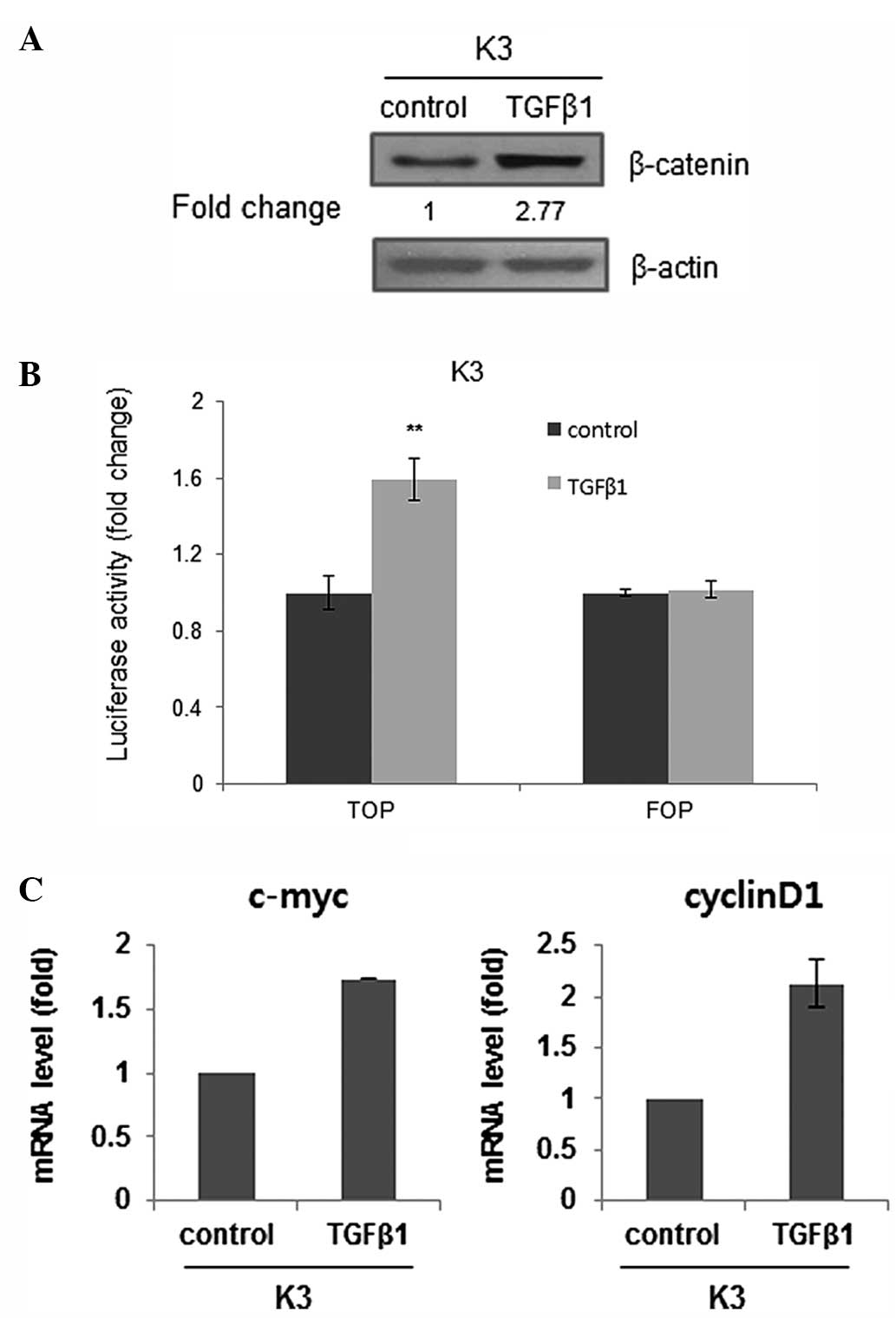
|
1
|
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A,
Ward E and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin.
53:5–26. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forastiere A, Koch W, Trotti A and
Sidransky D: Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 345:1890–1900.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamano Y, Uzawa K, Saito K, Nakashima D,
Kasamatsu A, Koike H, Kouzu Y, Shinozuka K, Nakatani K, Negoro K,
et al: Identification of cisplatin-resistance related genes in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:437–449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haddad RI and Shin DM: Recent advances in
head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1143–1154. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lim YC, Oh SY, Cha YY, Kim SH, Jin X and
Kim H: Cancer stem cell traits in squamospheres derived from
primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol.
47:83–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mannelli G and Gallo O: Cancer stem cells
hypothesis and stem cells in head and neck cancers. Cancer Treat
Rev. 38:515–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu L, Jiao J, Wang Y, Wu J, Huang D, Teng
W and Chen L: TGF-beta1 gene polymorphism in association with
diabetic retinopathy susceptibility: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e941602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
White RA, Malkoski SP and Wang XJ: TGFβ
signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene.
29:5437–5446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Siegel PM and Massagué J: Cytostatic and
apoptotic actions of TGF-beta in homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:807–821. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu SL, Herrington H, Reh D, Weber S,
Bornstein S, Wang D, Li AG, Tang CF, Siddiqui Y, Nord J, et al:
Loss of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor promotes
metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Dev.
20:1331–1342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu SL, Reh D, Li AG, Woods J, Corless CL,
Kulesz-Martin M and Wang XJ: Overexpression of transforming growth
factor beta1 in head and neck epithelia results in inflammation,
angiogenesis, and epithelial hyperproliferation. Cancer Res.
64:4405–4410. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
You H, Ding W and Rountree CB: Epigenetic
regulation of cancer stem cell marker CD133 by transforming growth
factor-beta. Hepatology. 51:1635–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kashyap V, Rezende NC, Scotland KB,
Shaffer SM, Persson JL, Gudas LJ and Mongan NP: Regulation of stem
cell pluripotency and differentiation involves a mutual regulatory
circuit of the NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 pluripotency transcription
factors with polycomb repressive complexes and stem cell microRNAs.
Stem Cells Dev. 18:1093–1108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zou B, Sun S, Qi X and Ji P: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase activity is a cancer stem cell marker of tongue
squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 5:1116–1120. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee SH, Koo BS, Kim JM, Huang S, Rho YS,
Bae WJ, Kang HJ, Kim YS, Moon JH and Lim YC: Wnt/β-catenin
signalling maintains self-renewal and tumourigenicity of head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma stem-like cells by activating Oct4. J
Pathol. 234:99–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dalerba P and Clarke MF: Cancer stem cells
and tumor metastasis: First steps into uncharted territory. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:241–242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Campelo MR Garcia, Curbera G Alonso,
Gallego G Aparicio, Pulido E Grande and Antón Aparicio LM: Stem
cell and lung cancer development: Blaming the Wnt, Hh and Notch
signalling pathway. Clin Transl Oncol. 13:77–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Piccirillo SG, Reynolds BA, Zanetti N,
Lamorte G, Binda E, Broggi G, Brem H, Olivi A, Dimeco F and Vescovi
AL: Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential
of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature. 444:761–765. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K, Donin NM, Li A,
Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, et al:
Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein
pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:69–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seoane J: TGFbeta and cancer initiating
cells. Cell Cycle. 8:3787–3788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Levy L and Hill CS: Alterations in
components of the TGF-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:41–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Lathia JD, Wu Q, Wang J, Li Z,
Heddleston JM, Eyler CE, Elderbroom J, Gallagher J, Schuschu J, et
al: Targeting interleukin 6 signaling suppresses glioma stem cell
survival and tumor growth. Stem Cells. 27:2393–2404. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Serra R, Easter SL, Jiang W and Baxley SE:
Wnt5a as an effector of TGFβ in mammary development and cancer. J
Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 16:157–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|