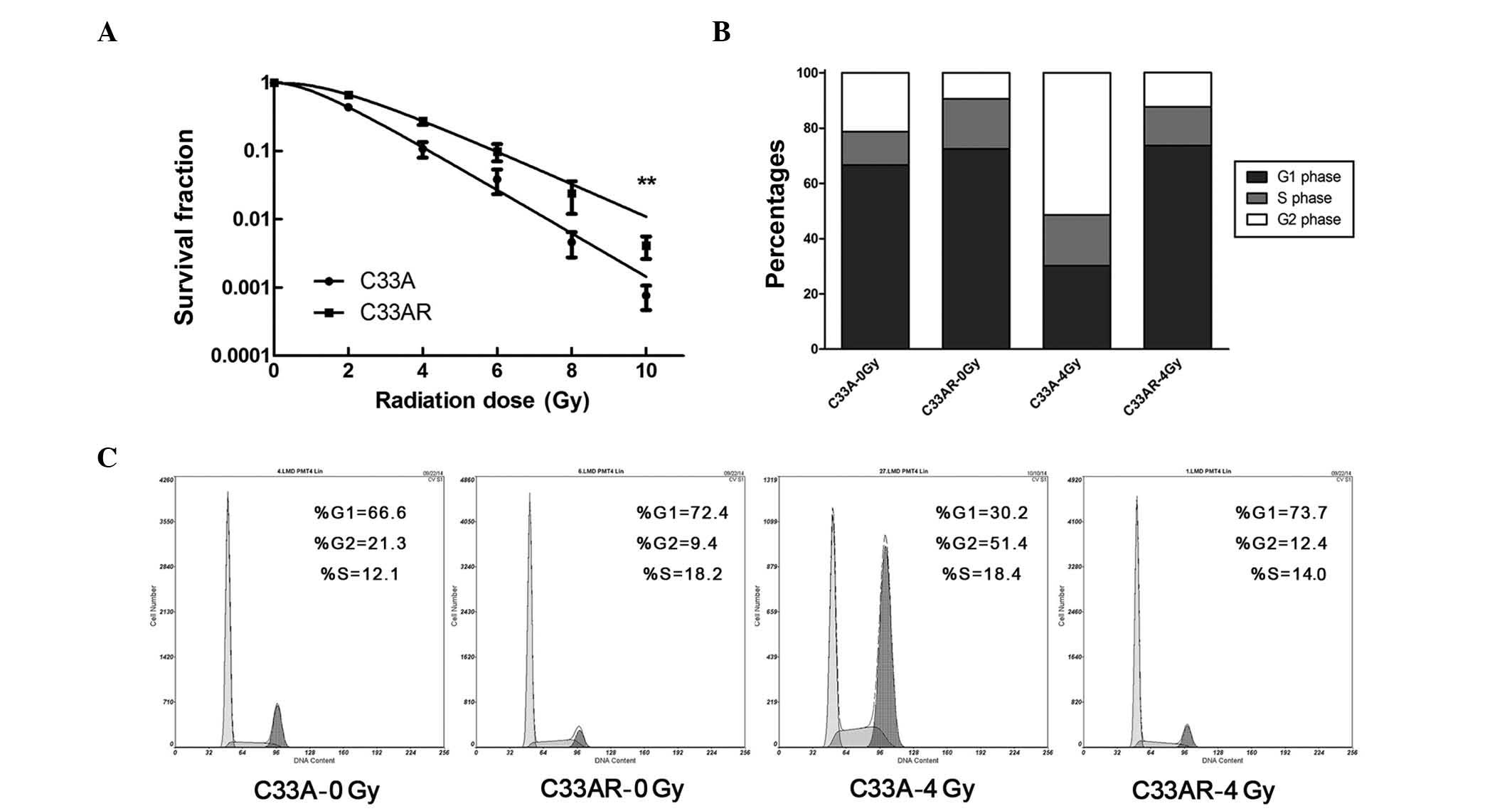
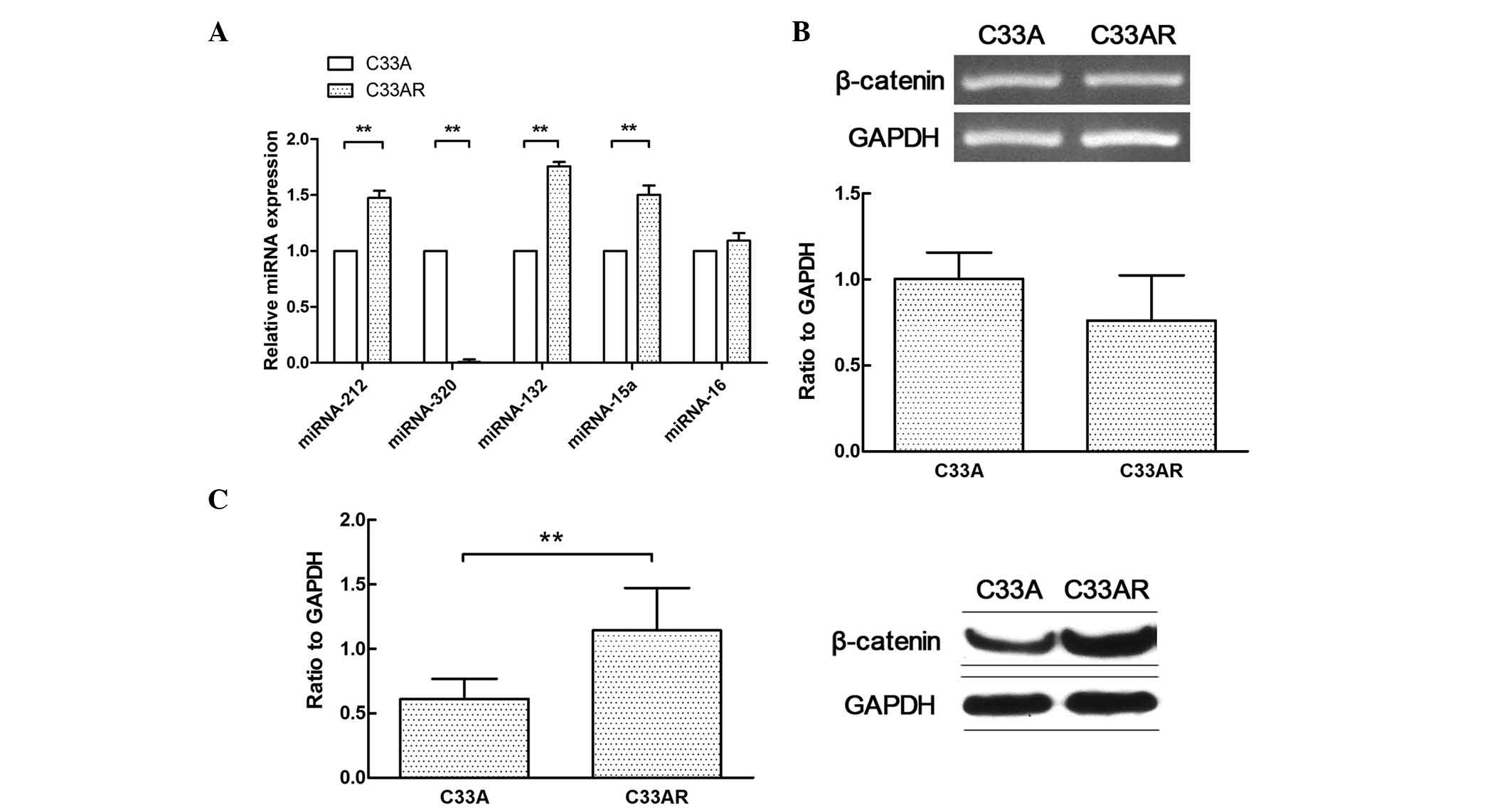
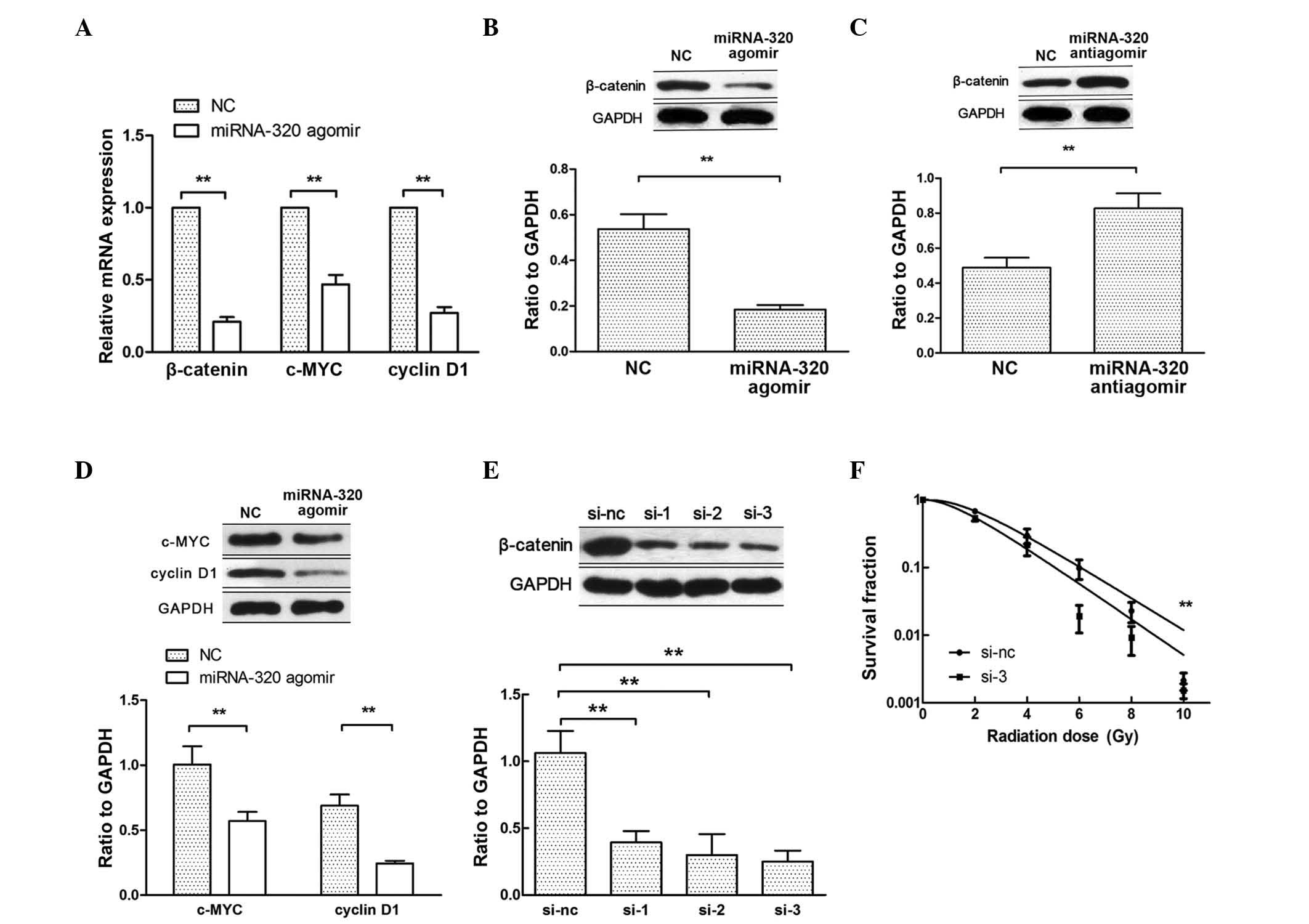
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Waggoner SE: Cervical cancer. Lancet.
361:2217–2225. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM and
Hannon GJ: Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step
of RNA interference. Nature. 409:363–366. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sevignani C, Calin GA, Siracusa LD and
Croce CM: Mammalian microRNAs: A small world for fine-tuning gene
expression. Mamm Genome. 17:189–202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang B, Wang Q and Pan X: MicroRNAs and
their regulatory roles in animals and plants. J Cell Physiol.
210:279–289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mendell JT and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nikitina EG, Urazova LN and Stegny VN:
MicroRNAs and human cancer. Exp Oncol. 34:2–8. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie H, Zhao Y, Caramuta S, Larsson C and
Lui WO: miR-205 expression promotes cell proliferation and
migration of human cervical cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e469902012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aigner A: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer
invasion and metastasis: Therapeutic approaches based on
metastasis-related miRNAs. J Mol Med (Berl). 89:445–457. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Zhang J, Wu J, Luo D, Su K, Shi W,
Liu J, Tian Y and Wei L: MicroRNA-610 inhibits the migration and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing the expression of
vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein. Eur J Cancer. 48:1904–1913.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang LY, Ho-Fun Lee V, Wong AM, Kwong DL,
Zhu YH, Dong SS, Kong KL, Chen J, Tsao SW, Guan XY and Fu L:
MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN.
Carcinogenesis. 34:454–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lynam-Lennon N, Reynolds JV, Marignol L,
Sheils OM, Pidgeon GP and Maher SG: MicroRNA-31 modulates tumour
sensitivity to radiation in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. J Mol Med
(Berl). 90:1449–1458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen G, Zhu W, Shi D, Lv L, Zhang C, Liu P
and Hu W: MicroRNA-181a sensitizes human malignant glioma U87MG
cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. 23:997–1003.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li G, Liu Y, Su Z, Ren S, Zhu G, Tian Y
and Qiu Y: MicroRNA-324-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma
radioresistance by directly targeting WNT2B. Eur J Cancer.
49:2596–2607. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salim H, Akbar NS, Zong D, Vaculova AH,
Lewensohn R, Moshfegh A, Viktorsson K and Zhivotovsky B: miRNA-214
modulates radiotherapy response of non-small cell lung cancer cells
through regulation of p38MAPK, apoptosis and senescence. Br J
Cancer. 107:1361–1373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shinohara A, Yokoyama Y, Wan X, Takahashi
Y, Mori Y, Takami T, Shimokawa K and Tamaya T: Cytoplasmic/nuclear
expression without mutation of exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene is
frequent in the development of the neoplasm of the uterine cervix.
Gynecol Oncol. 82:450–455. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mei Z, Su T, Ye J, Yang C, Zhang S and Xie
C: The miR-15 family enhances the radiosensitivity of breast cancer
cells by targeting G2 checkpoints. Radiat Res. 183:196–207. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang X, Chen X, Chen L, Ma Y, Zhou L, Qi
Q, Liu Y, Zhang S, Luo J and Zhou X: Upregulation of the
miR-212/132 cluster suppresses proliferation of human lung cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 33:705–712. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsieh IS, Chang KC, Tsai YT, Ke JY, Lu PJ,
Lee KH, Yeh SD, Hong TM and Chen YL: MicroRNA-320 suppresses the
stem cell-like characteristics of prostate cancer cells by
downregulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 34:530–538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Valenta T, Hausmann G and Basler K: The
many faces and functions of β-catenin. Embo J. 31:2714–2736. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao L, Lu X and Cao Y: MicroRNA and
signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response. Cell
Signal. 25:1625–1634. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
López J, Poitevin A, Mendoza-Martínez V,
Pérez-Plasencia C and García-Carrancá A: Cancer-initiating cells
derived from established cervical cell lines exhibit stem-cell
markers and increased radioresistance. BMC Cancer. 12:482012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ke G, Liang L, Yang JM, Huang X, Han D,
Huang S, Zhao Y, Zha R, He X and Wu X: MiR-181a confers resistance
of cervical cancer to radiation therapy through targeting the
pro-apoptotic PRKCD gene. Oncogene. 32:3019–3027. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu XM, Wang XB, Chen MM, Liu T, Li YX, Jia
WH, Liu M, Li X and Tang H: MicroRNA-19a and −19b regulate cervical
carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting CUL5. Cancer
Lett. 322:148–158. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang T, Wong HK, Gu W, Yu MY, To KF, Wang
CC, Wong YF, Cheung TH, Chung TK and Choy KW: MicroRNA-182 plays an
onco-miRNA role in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 129:199–208.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pawlik TM and Keyomarsi K: Role of cell
cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 59:928–942. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shiiba M, Shinozuka K, Saito K, Fushimi K,
Kasamatsu A, Ogawara K, Uzawa K, Ito H, Takiguchi Y and Tanzawa H:
MicroRNA-125b regulates proliferation and radioresistance of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:1817–1821. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
John-Aryankalayil M, Palayoor ST, Makinde
AY, Cerna D, Simone CB II, Falduto MT, Magnuson SR and Coleman CN:
Fractionated radiation alters oncomir and tumor suppressor miRNAs
in human prostate cancer cells. Radiat Res. 178:105–117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kagan J, Stein J, Babaian RJ, Joe YS,
Pisters LL, Glassman AB, von Eschenbach AC and Troncoso P:
Homozygous deletions at 8p22 and 8p21 in prostate cancer implicate
these regions as the sites for candidate tumor suppressor genes.
Oncogene. 11:2121–2126. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim BM and Choi MY: Non-canonical
microRNAs miR-320 and miR-702 promote proliferation in
Dgcr8-deficient embryonic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
426:183–189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren XP, Wu J, Wang X, Sartor MA, Qian J,
Jones K, Nicolaou P, Pritchard TJ and Fan GC: MicroRNA-320 is
involved in the regulation of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury
by targeting heat-shock protein 20. Circulation. 119:2357–2366.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou FX, Xiong J, Luo ZG, Dai J, Yu HJ,
Liao ZK, Lei H, Xie CH and Zhou YF: cDNA expression analysis of a
human radiosensitive-radioresistant cell line model identifies
telomere function as a hallmark of radioresistance. Radiat Res.
174:550–557. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang M, Atkinson RL and Rosen JM:
Selective targeting of radiation-resistant tumor-initiating cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3522–3527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Theys J, Yahyanejad S, Habets R, Span P,
Dubois L, Paesmans K, Kattenbeld B, Cleutjens J, Groot AJ,
Schuurbiers OC, et al: High NOTCH activity induces radiation
resistance in non small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol.
108:440–445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huerta S, Gao X, Dineen S, Kapur P, Saha D
and Meyer J: Role of p53, Bax, p21 and DNA-PKcs in radiation
sensitivity of HCT-116 cells and xenografts. Surgery. 154:143–151.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim KH, Seol HJ, Kim EH, Rheey J, Jin JH,
Lee Y, Joo KM, Lee J and Nam DH: Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a key
downstream mediator of MET signaling in glioblastoma stem cells.
Neuro Oncol. 15:161–171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Orford K, Orford CC and Byers SW:
Exogenous expression of beta-catenin regulates contact inhibition,
anchorage-independent growth, anoikis, and radiation-induced cell
cycle arrest. J Cell Biol. 146:855–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nakashima M, Meirmanov S, Matsufuji R,
Hayashida M, Fukuda E, Naito S, Matsuu M, Shichijo K, Kondo H, Ito
M, et al: Altered expression of beta-catenin during
radiation-induced colonic carcinogenesis. Pathol Res Pract.
198:717–724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rodningen OK, Overgaard J, Alsner J,
Hastie T and Børresen-Dale AL: Microarray analysis of the
transcriptional response to single or multiple doses of ionizing
radiation in human subcutaneous fibroblasts. Radiother Oncol.
77:231–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gassler N, Herr I, Keith M, Autschbach F,
Schmitz-Winnenthal H, Ulrich A, Otto HF, Kartenbeck J and Z'graggen
K: Wnt-signaling and apoptosis after neoadjuvant short-term
radiotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 25:1543–1549.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Woodward WA, Chen MS, Behbod F, Alfaro MP,
Buchholz TA and Rosen JM: WNT/beta-catenin mediates radiation
resistance of mouse mammary progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:618–623. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Watson RL, Spalding AC, Zielske SP, Morgan
M, Kim AC, Bommer GT, Eldar-Finkelman H, Giordano T, Fearon ER,
Hammer GD, et al: GSK3beta and beta-catenin modulate radiation
cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer. Neoplasia. 12:357–365. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|