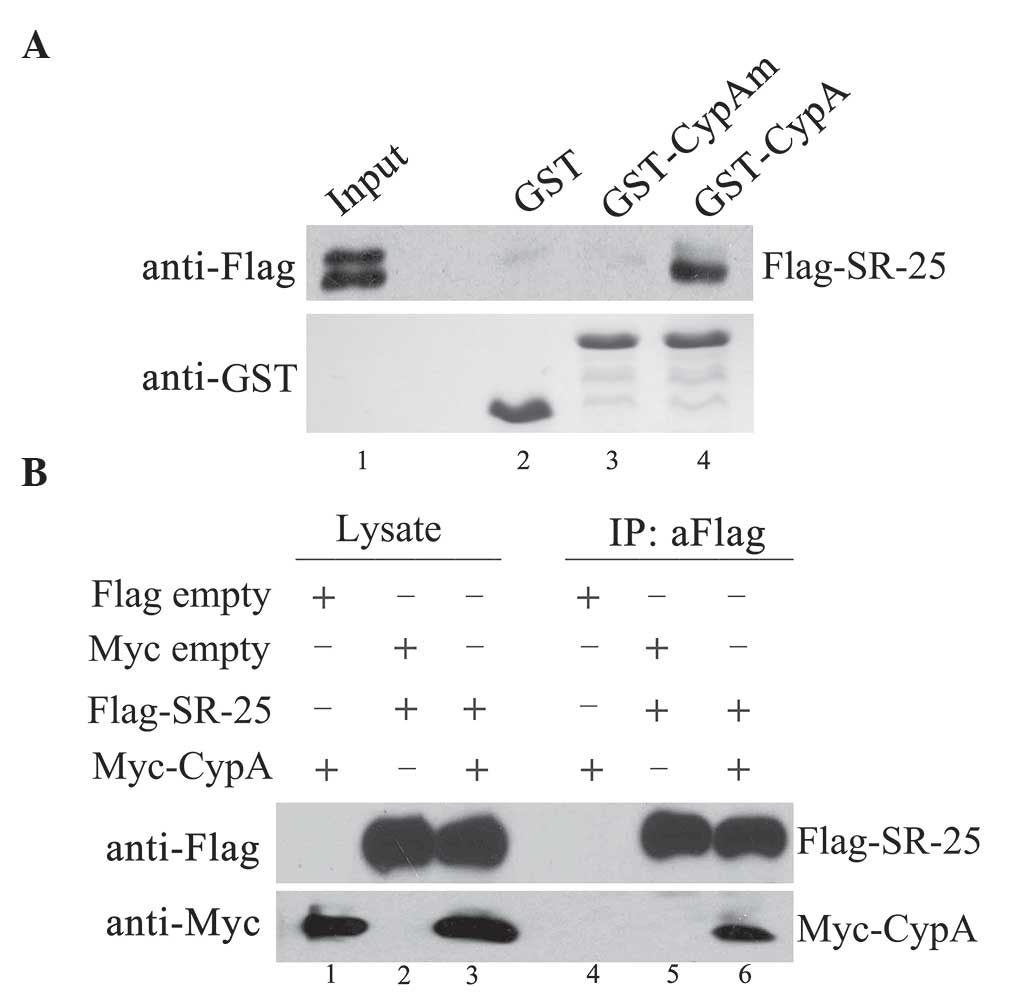
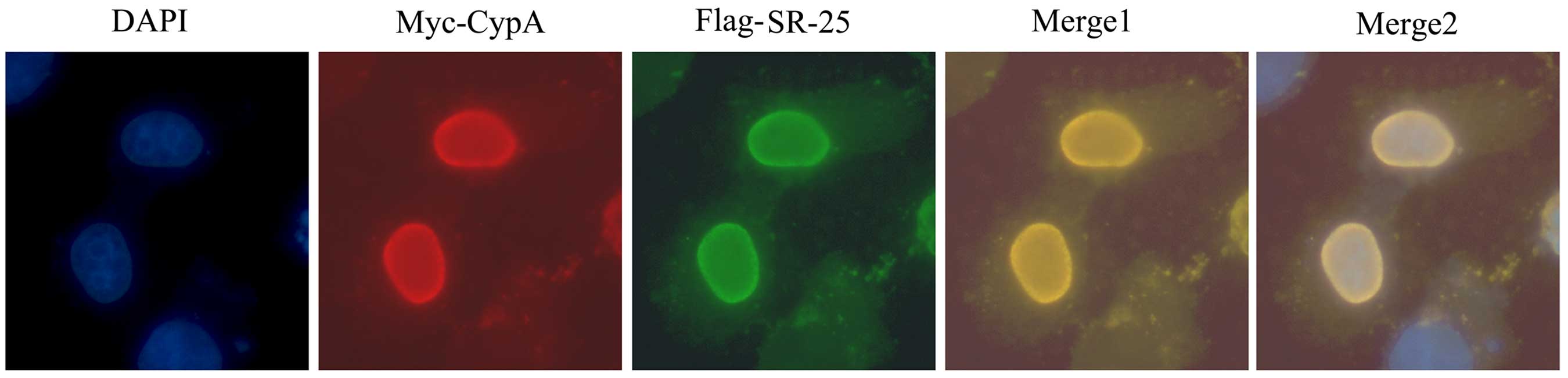
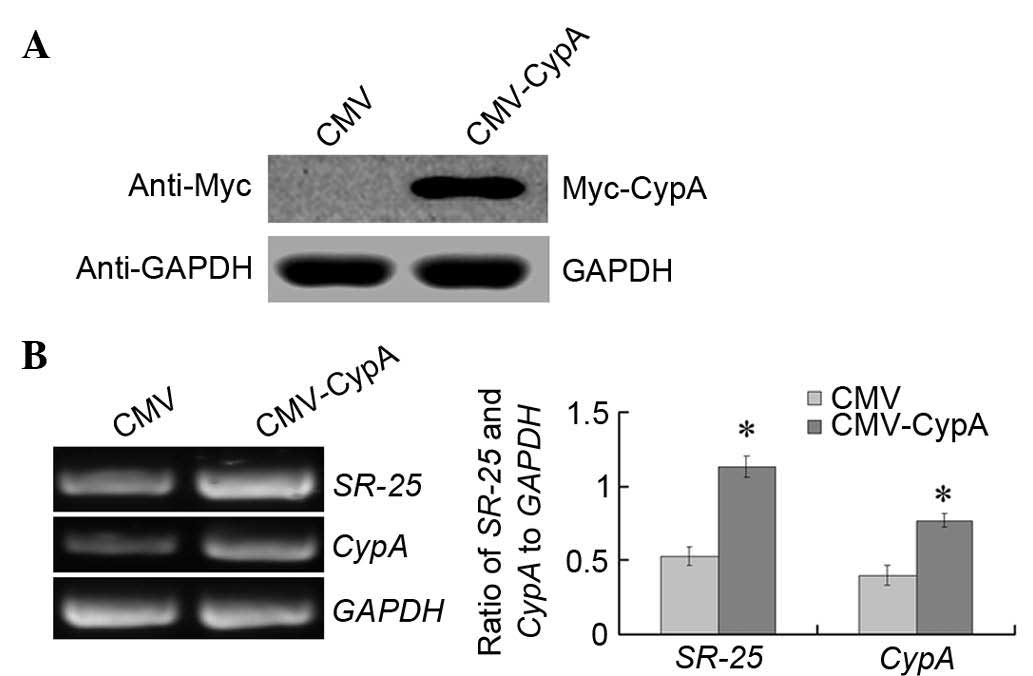
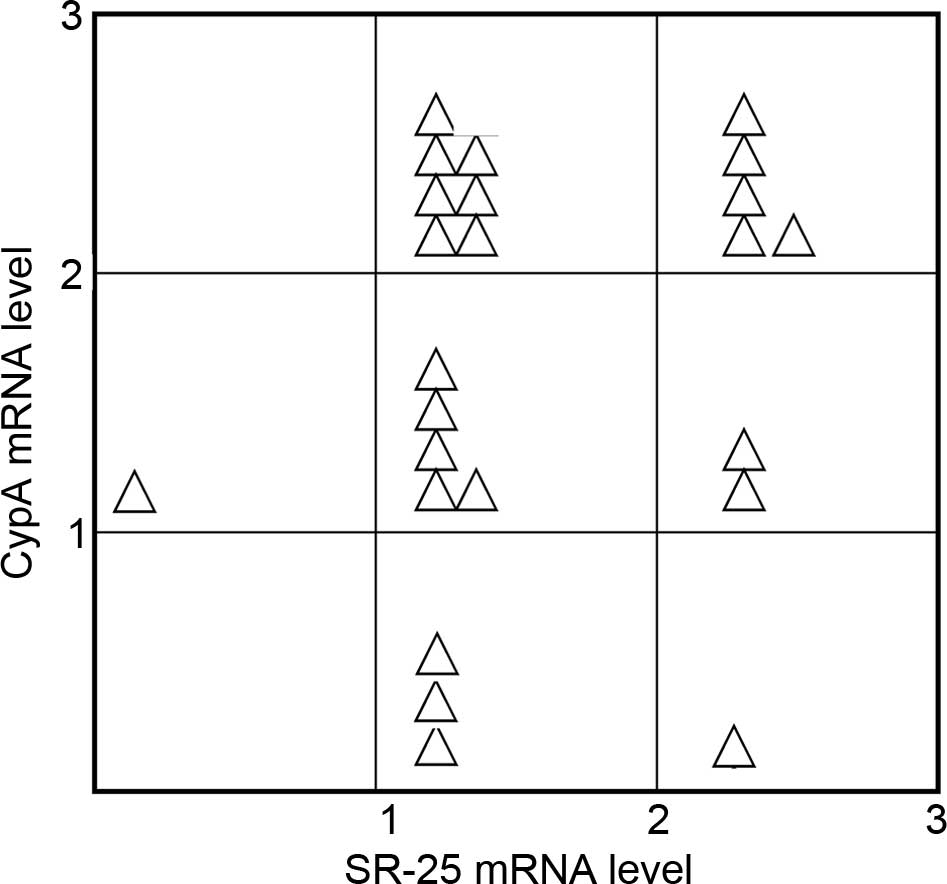
|
1
|
Davis TL, Walker JR, Campagna-Slater V,
Finerty PJ, Paramanathan R, Bernstein G, MacKenzie F, Tempel W,
Ouyang H, Lee WH, et al: Structural and biochemical
characterization of the human cyclophilin family of peptidyl-prolyl
isomerases. PLoS Biol. 8:e10004392010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Naoumov NV: Cyclophilin inhibition as
potential therapy for liver diseases. J Hepatol. 61:1166–1174.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee J: Cyclophilin A as a new therapeutic
target for hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 17:375–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nigro P, Pompilio G and Capogrossi MC:
Cyclophilin A: A key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis.
4:e8882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Satoh K, Nigro P, Matoba T, O'Dell MR, Cui
Z, Shi X, Mohan A, Yan C, Abe J, Illig KA and Berk BC: Cyclophilin
A enhances vascular oxidative stress and the development of
angiotensin II-induced aortic aneurysms. Nat Med. 15:649–656. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Satoh K, Matoba T, Suzuki J, O'Dell MR,
Nigro P, Cui Z, Mohan A, Pan S, Li L, Jin ZG, et al: Cyclophilin A
mediates vascular remodeling by promoting inflammation and vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation. 117:3088–3098. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sokolskaja E and Luban J: Cyclophilin,
TRIM5, and innate immunity to HIV-1. Curr Opin Microbiol.
9:404–408. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Lu N, Zhou J, Chen ZN and Zhu P:
Cyclophilin A up-regulates MMP-9 expression and adhesion of
monocytes/macrophages via CD147 signalling pathway in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:1299–1310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hussain SA, Ferry DR, El-Gazzaz G, Mirza
DF, James ND, McMaster P and Kerr DJ: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann
Oncol. 12:161–172. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ and Cressman EN:
Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
48:2047–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
142:1264–1273.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bouchard MJ and Navas-Martin S: Hepatitis
B and C virus hepatocarcinogenesis: Lessons learned and future
challenges. Cancer Lett. 305:123–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Towers GJ, Hatziioannou T, Cowan S, Goff
SP, Luban J and Bieniasz PD: Cyclophilin A modulates the
sensitivity of HIV-1 to host restriction factors. Nat Med.
9:1138–1143. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang M, Dai C, Zhu H, Chen S, Wu Y, Li Q,
Zeng X, Wang W, Zuo J, Zhou M, et al: Cyclophilin A promotes human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell metastasis via regulation of MMP3 and
MMP9. Mol Cell Biochem. 357:387–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Zhang M, Ma H, Saiyin H, Shen S,
Xi J, Wan B and Yu L: Oligo-microarray analysis reveals the role of
cyclophilin A in drug resistance. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
61:459–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Li N, Zhu P, Wang Y, Tian Y and Wang
X: Decreased β-catenin expression in first-trimester villi and
decidua of patients with recurrent spontaneous abortion. J Obstet
Gynaecol Res. 41:904–911. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qu X, Wang C, Zhang J, Qie G and Zhou J:
The roles of CD147 and/or cyclophilin A in kidney diseases.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:7286732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seizer P, Gawaz M and May AE: Cyclophilin
A and EMMPRIN (CD147) in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc Res.
102:17–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arevalo-Rodriguez M and Heitman J:
Cyclophilin A is localized to the nucleus and controls meiosis in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eukaryot Cell. 4:17–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiu R, Rey O, Zheng JQ, Twiss JL, Song J,
Pang S and Yokoyama KK: Effects of altered expression and
localization of cyclophilin A on differentiation of p19 embryonic
carcinoma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 23:929–943. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin S and Fu XD: SR proteins and related
factors in alternative splicing. Adv Exp Med Biol. 623:107–122.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Long JC and Caceres JF: The SR protein
family of splicing factors: Master regulators of gene expression.
Biochem J. 417:15–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hertel KJ and Graveley BR: RS domains
contact the pre-mRNA throughout spliceosome assembly. Trends
Biochem Sci. 30:115–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen H, Kan JL and Green MR:
Arginine-serine-rich domains bound at splicing enhancers contact
the branchpoint to promote prespliceosome assembly. Mol Cell.
13:367–376. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bradley T, Cook ME and Blanchette M: SR
proteins control a complex network of RNA-processing events. RNA.
21:75–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guil S, Gattoni R, Carrascal M, Abián J,
Stévenin J and Bach-Elias M: Roles of hnRNP A1, SR proteins, and
p68 helicase in c-H-ras alternative splicing regulation. Mol Cell
Biol. 23:2927–2941. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ghigna C, Giordano S, Shen H, Benvenuto F,
Castiglioni F, Comoglio PM, Green MR, Riva S and Biamonti G: Cell
motility is controlled by SF2/ASF through alternative splicing of
the Ron protooncogene. Mol Cell. 20:881–890. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cartegni L, Hastings ML, Calarco JA, de
Stanchina E and Krainer AR: Determinants of exon 7 splicing in the
spinal muscular atrophy genes, SMN1 and SMN2. Am J Hum Genet.
78:63–77. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sasahara K, Yamaoka T, Moritani M, Tanaka
M, Iwahana H, Yoshimoto K, Miyagawa J, Kuroda Y and Itakura M:
Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a putative nuclear
protein, SR-25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 269:444–450. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bauer K, Kretzschmar AK, Cvijic H, Blumert
C, Löffler D, Brocke-Heidrich K, Schiene-Fischer C, Fischer G, Sinz
A, Clevenger CV and Horn F: Cyclophilins contribute to Stat3
signaling and survival of multiple myeloma cells. Oncogene.
28:2784–2795. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horowitz DS, Lee EJ, Mabon SA and Misteli
T: A cyclophilin functions in pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J.
21:470–480. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Keshwani MM, Aubol BE, Fattet L, Ma CT,
Qiu J, Jennings PA, Fu XD and Adams JA: Conserved proline-directed
phosphorylation regulates SR protein conformation and splicing
function. Biochem J. 466:311–322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lorkovic ZJ, Lopato S, Pexa M, Lehner R
and Barta A: Interactions of Arabidopsis RS domain containing
cyclophilins with SR proteins and U1 and U11 small nuclear
ribonucleoprotein-specific proteins suggest their involvement in
pre-mRNA Splicing. J Biol Chem. 279:33890–33898. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee SC, Sim N, Clement MV, Yadav SK and
Pervaiz S: Dominant negative Rac1 attenuates paclitaxel-induced
apoptosis in human melanoma cells through upregulation of heat
shock protein 27: A functional proteomic analysis. Proteomics.
7:4112–4122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Z, Min W and Gou J: Knockdown of
cyclophilin A reverses paclitaxel resistance in human endometrial
cancer cells via suppression of MAPK kinase pathways. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 72:1001–1011. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|