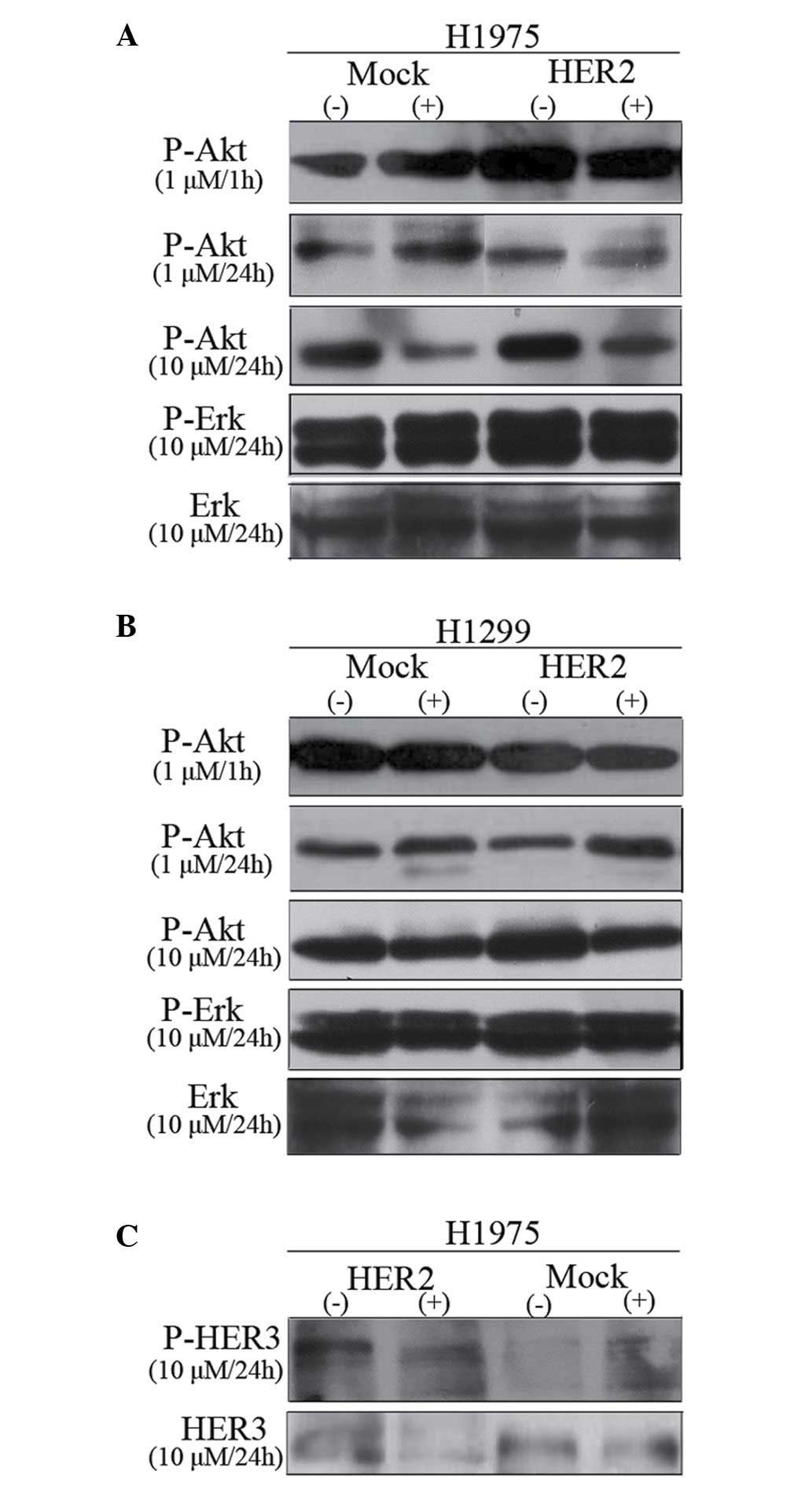
|
1
|
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett
TP, Ward CW and Burgess AW: Epidermal growth factor receptor:
Mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res. 284:31–53.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hynes NE and Lane HA: ERBB receptors and
cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:341–354. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arora A and Scholar EM: Role of tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
315:971–979. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xue C, Hu Z, Jiang W, Zhao Y, Xu F, Huang
Y, Zhao H, Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhao L, et al: National survey of the
medical treatment status for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
China. Lung Cancer. 77:371–375. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shepherd FA, Pereira J Rodrigues, Ciuleanu
T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S,
Smylie M, Martins R, et al: Erlotinib in previously treated
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:123–132. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anido J, Matar P, Albanell J, Guzmán M,
Rojo F, Arribas J, Averbuch S and Baselga J: ZD1839, a specific
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
induces the formation of inactive EGFR/HER2 and EGFR/HER3
heterodimers and prevents heregulin signaling in
HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
9:1274–1283. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T,
Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S,
Rischin D, et al: Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of
gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin
Oncol. 21:2237–2246. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ
Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H,
Sandler A, et al: Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic
patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized trial. JAMA.
290:2149–2158. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arcila ME, Oxnard GR, Nafa K, Riely GJ,
Solomon SB, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Pao W, Miller VA and Ladanyi M:
Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR
inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a
locked nucleic acid-based assay. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1169–1180.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Landi L, Tiseo M, Chiari R, Ricciardi S,
Rossi E, Galetta D, Novello S, Milella M, D'Incecco A, Minuti G, et
al: Activity of the EGFR-HER2 dual inhibitor afatinib in
EGFR-mutant lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to
reversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer.
15:411–417.e4. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han SW, Kim TY, Jeon YK, Hwang PG, Im SA,
Lee KH, Kim JH, Kim DW, Heo DS, Kim NK, et al: Optimization of
patient selection for gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer by
combined analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation,
K-ras mutation, and Akt phosphorylation. Clin Cancer Res.
12:2538–2544. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cappuzzo F, Varella-Garcia M, Shigematsu
H, Domenichini I, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Rossi E, Ludovini V,
Gregorc V, Toschi L, et al: Increased HER2 gene copy number is
associated with response to gefitinib therapy in epidermal growth
factor receptor-positive non-small-cell lung cancer patients. J
Clin Oncol. 23:5007–5018. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takezawa K, Pirazzoli V, Arcila ME, Nebhan
CA, Song X, de Stanchina E, Ohashi K, Janjigian YY, Spitzler PJ,
Melnick MA, et al: HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of
acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers
that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov.
2:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, Miller VA, Pan
Q, Ladanyi M, Zakowski MF, Heelan RT, Kris MG and Varmus HE: KRAS
mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to
gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2:e172005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei Q, Chen L, Sheng L, Nordgren H, Wester
K and Carlsson J: EGFR, HER2 and HER3 expression in esophageal
primary tumours and corresponding metastases. Int J Oncol.
31:493–499. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Cappuzzo F,
McCoy J, Bemis L, Xavier AC, Dziadziuszko R, Gumerlock P, Chansky
K, West H, et al: Combination of EGFR gene copy number and protein
expression predicts outcome for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
patients treated with gefitinib. Ann Oncol. 18:752–760. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mendelsohn J and Baselga J: The EGF
receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene.
19:6550–6565. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moulder SL, Yakes FM, Muthuswamy SK,
Bianco R, Simpson JF and Arteaga CL: Epidermal growth factor
receptor (HER1) tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa) inhibits
HER2/neu (erbB2)-overexpressing breast cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Cancer Res. 61:8887–8895. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Normanno N, Maiello MR and De Luca A:
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(EGFR-TKIs): Simple drugs with a complex mechanism of action? J
Cell Physiol. 194:13–19. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ono M, Hirata A, Kometani T, Miyagawa M,
Ueda S, Kinoshita H, Fujii T and Kuwano M: Sensitivity to gefitinib
(Iressa, ZD1839) in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
correlates with dependence on the epidermal growth factor (EGF)
receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and EGF
receptor/Akt pathway for proliferation. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:465–472.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Soh J, Toyooka S, Ichihara S, Fujiwara Y,
Hotta K, Suehisa H, Kobayashi N, Ichimura K, Aoe K, Aoe M, et al:
Impact of HER2 and EGFR gene status on gefitinib-treated patients
with nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 121:1162–1167. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moasser MM, Basso A, Averbuch SD and Rosen
N: The tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (‘Iressa’) inhibits
HER2-driven signaling and suppresses the growth of
HER2-overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Res. 61:7184–7188.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Noro R, Gemma A, Kosaihira S, Kokubo Y,
Chen M, Seike M, Kataoka K, Matsuda K, Okano T, Minegishi Y, et al:
Gefitinib (IRESSA) sensitive lung cancer cell lines show
phosphorylation of Akt without ligand stimulation. BMC Cancer.
6:2772006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shigematsu H, Takahashi T, Nomura M,
Majmudar K, Suzuki M, Lee H, Wistuba II, Fong KM, Toyooka S,
Shimizu N, et al: Somatic mutations of the HER2 kinase domain in
lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 65:1642–1646. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cohen EE, Lingen MW, Martin LE, Harris PL,
Brannigan BW, Haserlat SM, Okimoto RA, Sgroi DC, Dahiya S, Muir B,
et al: Response of some head and neck cancers to epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be linked to
mutation of ERBB2 rather than EGFR. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8105–8108.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y and Dennis PA:
Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell
lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to
chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 61:3986–3997.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han SW, Hwang PG, Chung DH, Kim DW, Im SA,
Kim YT, Kim TY, Heo DS, Bang YJ and Kim NK: Epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR) downstream molecules as response predictive markers
for gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) in chemotherapy-resistant non-small
cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 113:109–115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lurje G and Lenz HJ: EGFR signaling and
drug discovery. Oncology. 77:400–410. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ricciardi GR, Russo A, Franchina T,
Ferraro G, Zanghì M, Picone A, Scimone A and Adamo V: NSCLC and
HER2: Between lights and shadows. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1750–1762.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garrido-Castro AC and Felip E: HER2 driven
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Potential therapeutic
approaches. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2:122–127. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fuller SJ, Sivarajah K and Sugden PH: ErbB
receptors, their ligands, and the consequences of their activation
and inhibition in the myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 44:831–854.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chandarlapaty S, Sawai A, Scaltriti M,
Rodrik-Outmezguine V, Grbovic-Huezo O, Serra V, Majumder PK,
Baselga J and Rosen N: AKT inhibition relieves feedback suppression
of receptor tyrosine kinase expression and activity. Cancer Cell.
19:58–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rho JK, Choi YJ, Ryoo BY, Na II, Yang SH,
Kim CH and Lee JC: p53 enhances gefitinib-induced growth inhibition
and apoptosis by regulation of Fas in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Res. 67:1163–1169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Strobel T, Swanson L, Korsmeyer S and
Cannistra SA: BAX enhances paclitaxel-induced apoptosis through a
p53-independent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:14094–14099.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dudek AZ, Kmak KL, Koopmeiners J and
Keshtgarpour M: Skin rash and bronchoalveolar histology correlates
with clinical benefit in patients treated with gefitinib as a
therapy for previously treated advanced or metastatic non-small
cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 51:89–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|