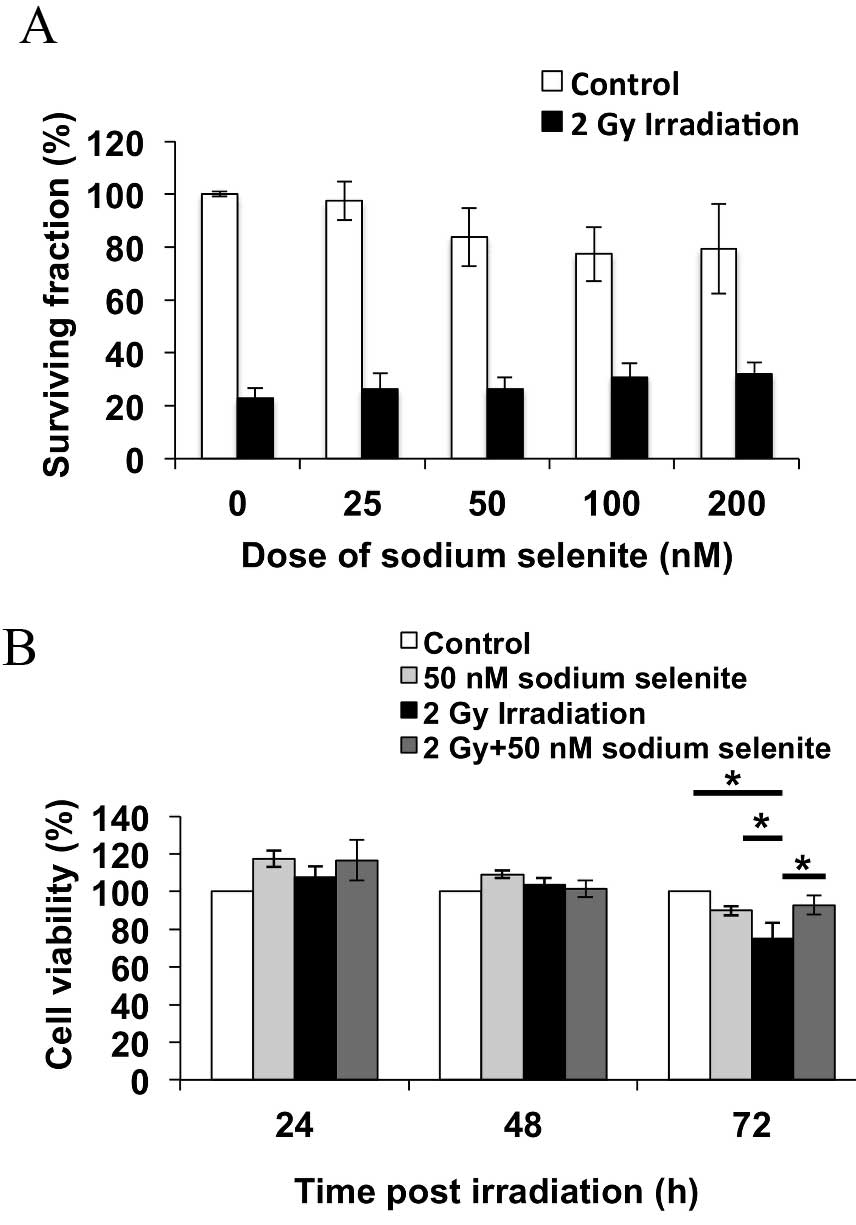
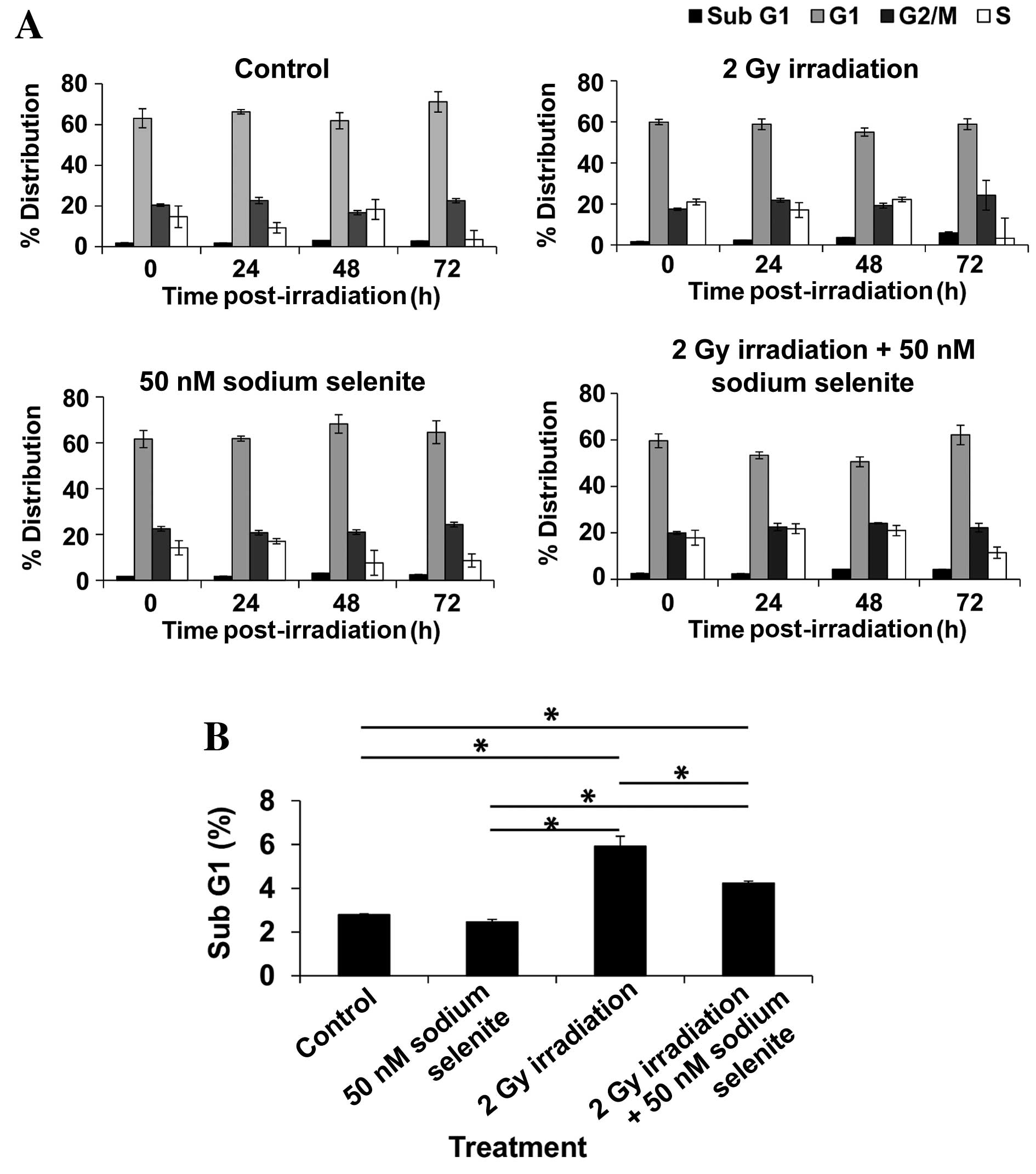
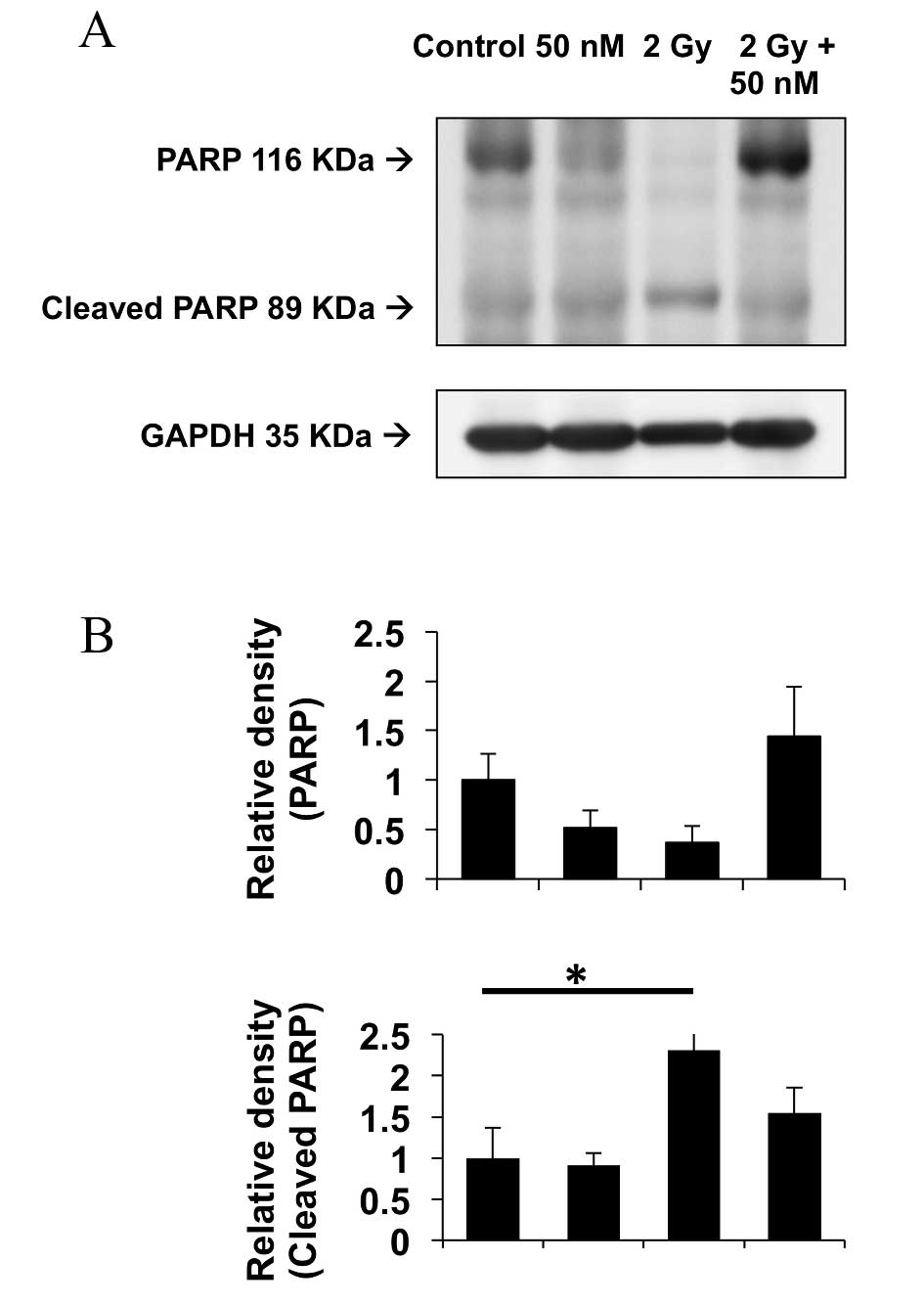
|
1
|
Shirazi A, Ghobadi G and Ghazi-Khansari M:
A radiobiological review on melatonin: A novel radioprotector. J
Radiat Res. 48:263–272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greenberger JS: Radioprotection. Vivo.
23:323–336. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Nair CK, Parida DK and Nomura T:
Radioprotectors in radiotherapy. J Radiat Res. 42:21–37. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dörr W: Effects of selenium on radiation
responses of tumor cells and tissue. Strahlenther Onkol.
182:693–695. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weiss JF and Landauer MR: Radioprotection
by antioxidants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 899:44–60. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rayman MP: The importance of selenium to
human health. Lancet. 356:233–241. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puspitasari IM, Abdulah R, Yamazaki C,
Kameo S, Nakano T and Koyama H: Updates on clinical studies of
selenium supplementation in radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. 9:1252014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rayman MP: Selenium in cancer prevention:
A review of the evidence and mechanism of action. Proc Nutr Soc.
64:527–542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fritz H, Kennedy D, Fergusson D, Fernandes
R, Cooley K, Seely A, Sagar S, Wong R and Seely D: Selenium and
lung cancer: A systematic review and meta analysis. PLoS One.
6:e262592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abdulah R, Miyazaki K, Nakazawa M and
Koyama H: Chemical forms of selenium for cancer prevention. J Trace
Elem Med Biol. 19:141–150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ponholzer A, Struhal G and Madersbacher S:
Frequent use of complementary medicine by prostate cancer patients.
Eur Urol. 43:604–608. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Micke O, Buntzel J, Kisters K, Schafer U,
Micke P and Mucke R: Complementary and alternative medicine in lung
cancer patients: A neglected phenomenon? Front Radiat Ther Oncol.
42:198–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schleicher UM, Cotarelo C Lopez,
Andreopoulos D, Handt S and Ammon J: Radioprotection of human
endothelial cells by sodium selenite. Med Klin (Munich). 94:(Suppl
3). 35–38. 1999.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rodemann HP, Hehr T and Bamberg M:
Relevance of the radioprotective effect of sodium selenite. Med
Klin (Munich). 94:(Suppl 3). 39–41. 1999.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Micke O, Schomburg L, Buentzel J, Kisters
K and Muecke R: Selenium in oncology: From chemistry to clinics.
Molecules. 14:3975–3988. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Diamond AM, Dale P, Murray JL and Grdina
DJ: The inhibition of radiation-induced mutagenesis by the combined
effects of selenium and the aminothiol WR-1065. Mutat Res.
356:147–154. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eckers JC, Kalen AL, Xiao W, Sarsour EH
and Goswami PC: Selenoprotein P inhibits radiation-induced late
reactive oxygen species accumulation and normal cell injury. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 87:619–625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tak JK and Park JW: The use of ebselen for
radioprotection in cultured cells and mice. Free Radic Biol Med.
46:1177–1185. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdulah R, Faried A, Kobayashi K, Yamazaki
C, Suradji EW, Ito K, Suzuki K, Murakami M, Kuwano H and Koyama H:
Selenium enrichment of broccoli sprout extract increases
chemosensitivity and apoptosis of LNCaP prostate cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 9:4142009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paglia DE and Valentine WN: Studies on the
quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte
glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 70:158–169. 1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Buch K, Peters T, Nawroth T, Sänger M,
Schmidberger H and Langguth P: Determination of cell survival after
irradiation via clonogenic assay versus multiple MTT Assay-a
comparative study. Radiat Oncol. 7:12012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rafferty TS, Green MH, Lowe JE, Arlett C,
Hunter JA, Beckett GJ and McKenzie RC: Effects of selenium
compounds on induction of DNA damage by broadband ultraviolet
radiation in human keratinocytes. Br J Dermatol. 148:1001–1019.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee JH, Kim SY, Kil IS and Park JW:
Regulation of ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis by mitochondrial
NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem.
282:13385–13341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Zhao S and Song J:
Caspase-dependent apoptosis and -independent poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase cleavage induced by transforming growth factor beta1.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:223–234. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Baker RD, Baker SS, LaRosa K, Whitney C
and Newburger PE: Selenium regulation of glutathione peroxidase in
human hepatoma cell line Hep3B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 304:53–57.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Husbeck B, Peehl DM and Knox SJ: Redox
modulation of human prostate carcinoma cells by selenite increases
radiation-induced cell killing. Free Radic Biol Med. 38:50–57.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|