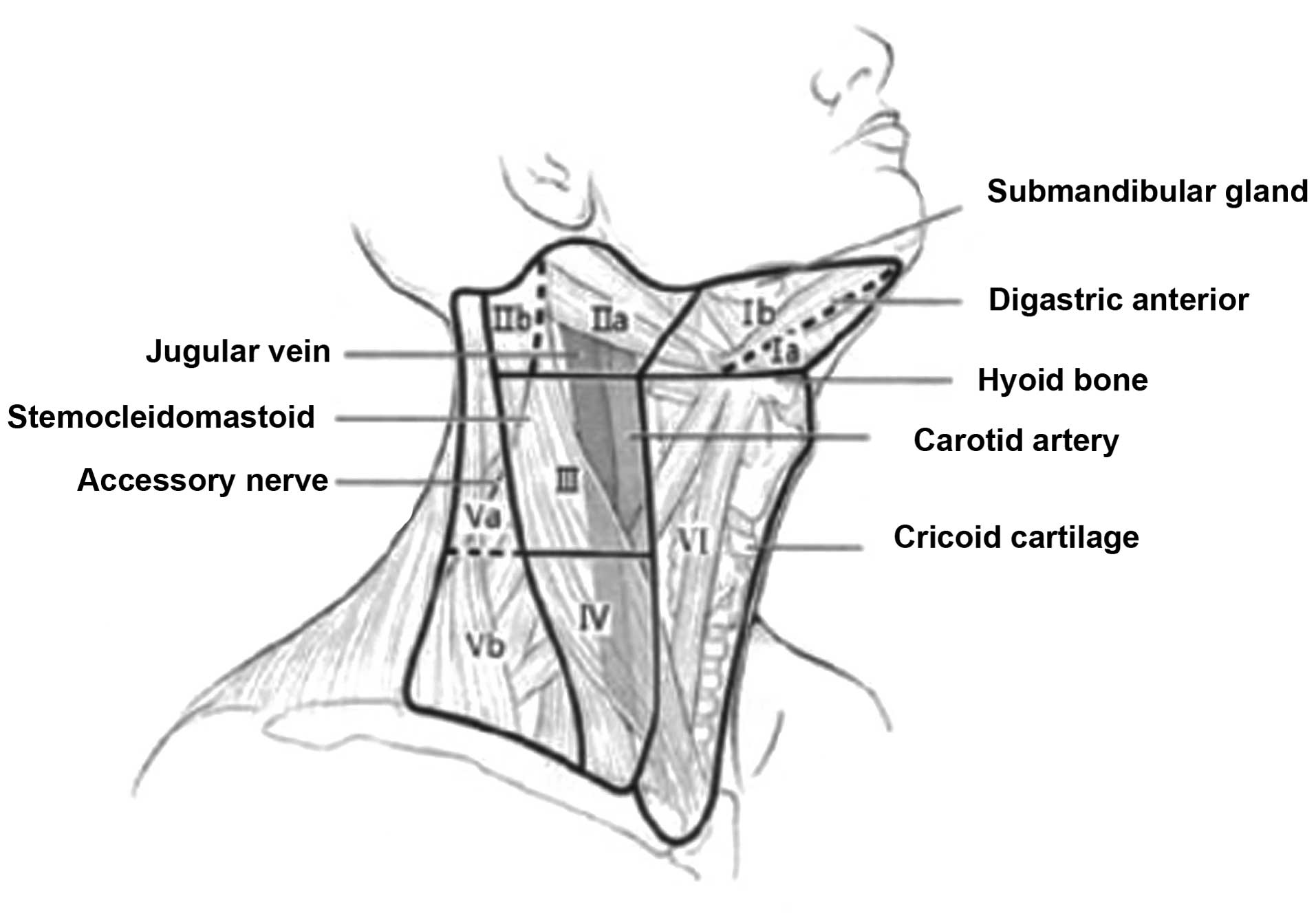
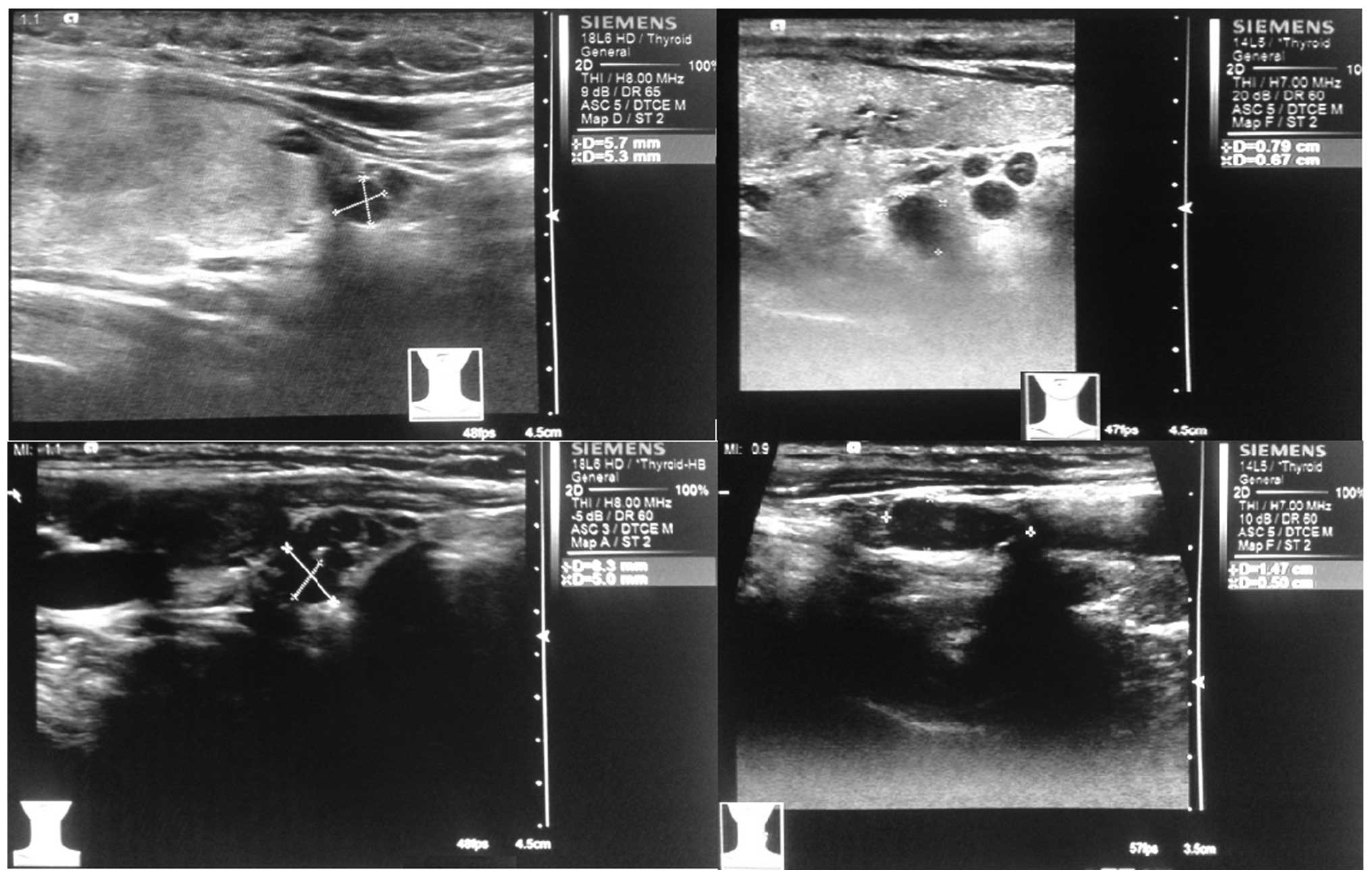
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carty SE, Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Duh QY,
Kloos RT, Mandel SJ, Randolph GW, Stack BC Jr, Steward DL, Terris
DJ, et al: American Thyroid Association Surgery Working Group;
American Association of Endocrine Surgeons; American Academy of
Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery; American Head and Neck
Society: Consensus statement on the terminology and classification
of central neck dissection for thyroid cancer. Thyroid.
19:1153–1158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos
RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Pacini F,
Schlumberger M, et al: American Thyroid Association (ATA)
Guidelines Taskforce on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid
Cancer: Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines
for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid
cancer. Thyroid. 19:1167–1214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rotstein L: The role of lymphadenectomy in
the management of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. J Surg Oncol.
99:186–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yüce I, Cağli S, Bayram A, Karasu F and
Güney E: Regional metastatic pattern of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 267:437–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pisello F, Geraci G, Lo Nigro C, Li Volsi
F, Modica G and Sciumè C: Neck node dissection in thyroid cancer. A
review. G Chir. 31:112–118. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vergez S, Sarini J, Percodani J, Serrano E
and Caron P: Lymph node management in clinically node-negative
patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol.
36:777–782. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferlito A, Robbins KT, Silver CE, Hasegawa
Y and Rinaldo A: Classification of neck dissections: An evolving
system. Auris Nasus Larynx. 36:127–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hughes DT and Doherty GM: Central neck
dissection for papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer Control. 18:83–88.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moo TA and Fahey TJ III: Lymph node
dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Semin Nucl Med.
41:84–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clark OH: Thyroid cancer and lymph node
metastases. J Surg Oncol. 103:615–618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang B, Niu HM, Wu Q, Zhou J, Jiang YX,
Yang X, Li JC, Zhao RN, Wang M, Li KN, et al: Comparison of
clinical and ultrasonographic features of poorly differentiated
thyroid carcinoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma. Chin Med J
(Engl). 129:169–173. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barbu CG, Florin A, Neamţu MC, Avramescu
ET, Terzea D, Miron A, Dănciulescu Miulescu R, Poiană C and Fica S:
Papillary thyroid carcinoma with anaplastic dedifferentiation in
the lymph node metastasis - a rare form of presentation even for a
tall cell variant. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 56:527–531.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Q, Zhu X and Tan Z: The clinical
significance of the Delphian lymph node metastasis in papillary
thyroid carcinoma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
29:378–381. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang XN, Guo RJ, Li S, Zheng ZM and Liang
HD: Binary logistic regression analysis of solid thyroid nodules
imaged by high-frequency ultrasonography, acoustic radiation force
impulse, and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 18:3601–3610. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ying M, Bhatia KS, Lee YP, Yuen HY and
Ahuja AT: Review of ultrasonography of malignant neck nodes:
Greyscale, Doppler, contrast enhancement and elastography. Cancer
Imaging. 13:658–669. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isik S, Akbaba G, Berker D, Tutuncu YA,
Ozuguz U, Aydin Y, Peksoy I and Guler S: Thyroid-related factors
that influence preoperative localization of parathyroid adenomas.
Endocr Pract. 18:26–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee CW, Gong G and Roh JL: Intraoperative
diagnosis of central compartment lymph node metastasis predicts
recurrence of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma and
clinically node-negative lateral neck and may guide extent of
initial surgery. World J Surg. 39:194–202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li ZJ, An CM, Yan DG, Zhang XW, Zhang ZM,
Xu ZG and Tang PZ: Significance of selective neck dissection in
patients with cN0 thyroid carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
35:783–786. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chaojie Z, Shanshan L, Zhigong Z, Jie H,
Shuwen X, Peizhi F, Jing X, Xiaowen G, Yang L and Wei Z: Evaluation
of the clinical value of carbon nanoparticles as lymph node tracer
in differentiated thyroid carcinoma requiring reoperation. Int J
Clin Oncol. 17:32–34. 2015.
|