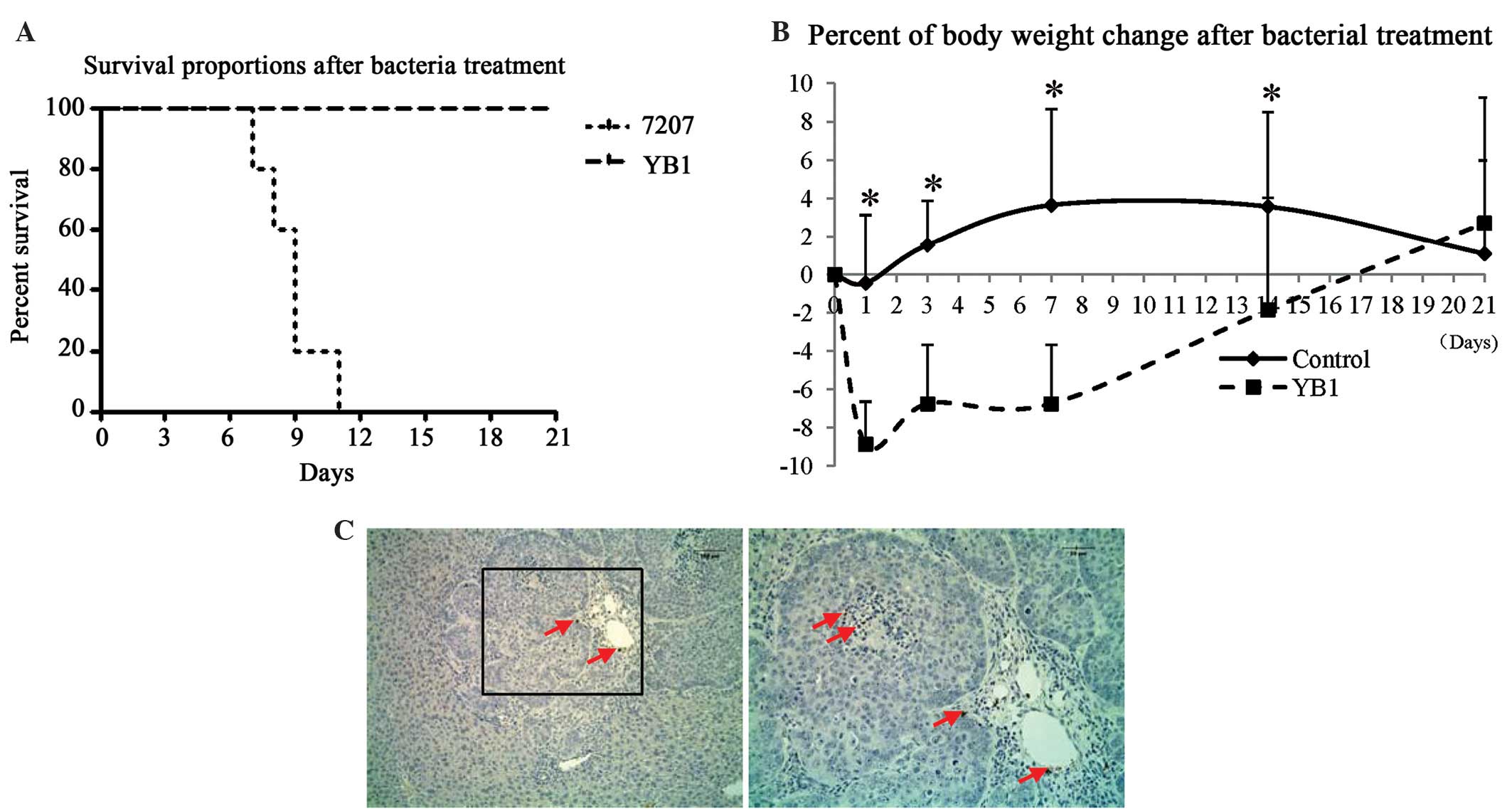
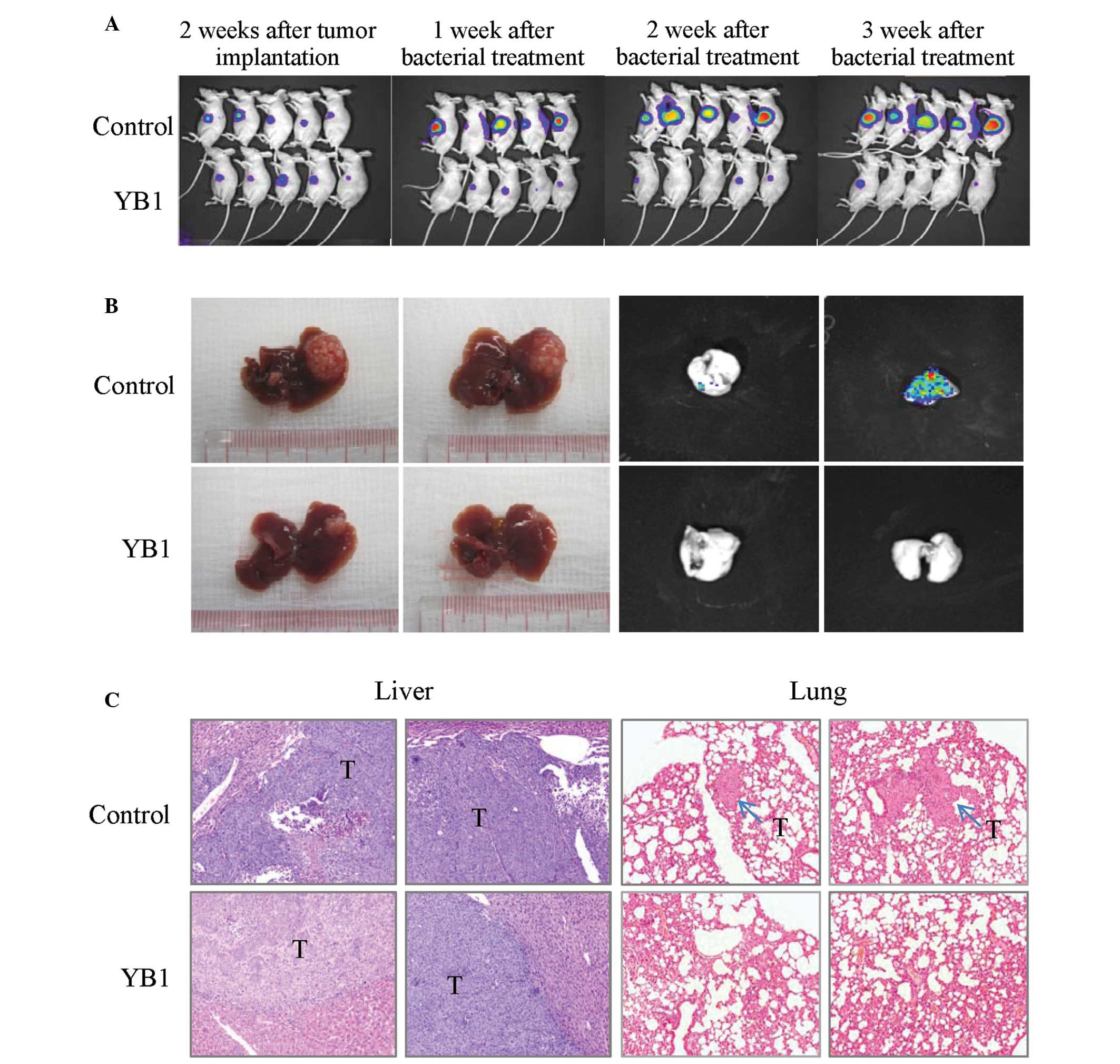
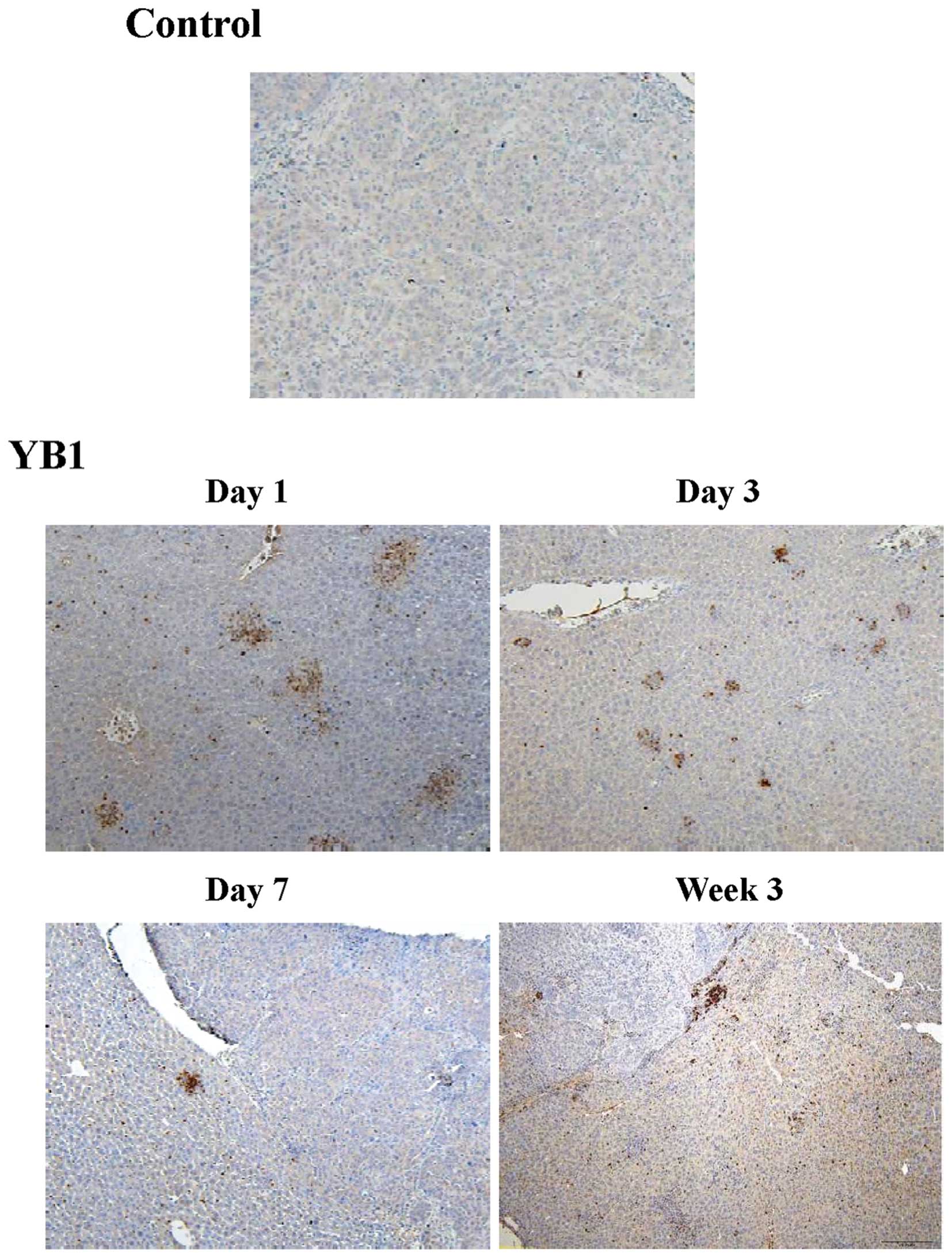
|
1
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127:S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doi K, Horiuchi T, Uchinami M, Tabo T,
Kimura N, Yokomachi J, Yoshida M and Tanaka K: Hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion promotes liver metastasis of colon cancer. J
Surg Res. 105:243–247. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Bilt JD, Kranenburg O, Nijkamp MW,
Smakman N, Veenendaal LM, Te Velde EA, Voest EE, van Diest PJ and
Rinkes IH Borel: Ischemia/reperfusion accelerates the outgrowth of
hepatic micrometastases in a highly standardized murine model.
Hepatology. 42:165–175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bruix J, Llovet JM, Castells A, Montañá X,
Brú C, Ayuso MC, Vilana R and Rodés J: Transarterial embolization
versus symptomatic treatment in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a randomized, controlled trial
in a single institution. Hepatology. 27:1578–1583. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ahn J and Flamm SL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dis Mon. 50:556–573. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wall DM, Srikanth CV and McCormick BA:
Targeting tumors with salmonella Typhimurium - potential for
therapy. Oncotarget. 1:721–728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pawelek JM, Low KB and Bermudes D:
Tumor-targeted Salmonella as a novel anticancer vector. Cancer Res.
57:4537–4544. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nauts HC, Fowler GA and Bogatko FH: A
review of the influence of bacterial infection and of bacterial
products (Coley's toxins) on malignant tumors in man; a critical
analysis of 30 inoperable cases treated by Coley's mixed toxins, in
which diagnosis was confirmed by microscopic examination selected
for special study. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 276:1–103. 1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barbé S, Van Mellaert L and Anné J: The
use of clostridial spores for cancer treatment. J Appl Microbiol.
101:571–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Van Mellaert L, Barbé S and Anné J:
Clostridium spores as anti-tumour agents. Trends Microbiol.
14:190–196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sasaki T, Fujimori M, Hamaji Y, Hama Y,
Ito K, Amano J and Taniguchi S: Genetically engineered
Bifidobacterium longum for tumor-targeting enzyme-prodrug therapy
of autochthonous mammary tumors in rats. Cancer Sci. 97:649–657.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Fu GF, Fan YR, Liu WH, Liu XJ, Wang
JJ and Xu GX: Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a delivery system of
endostatin for cancer gene therapy: selective inhibitor of
angiogenesis and hypoxic tumor growth. Cancer Gene Ther.
10:105–111. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patyar S, Joshi R, Byrav DS, Prakash A,
Medhi B and Das BK: Bacteria in cancer therapy: a novel
experimental strategy. J Biomed Sci. 17:212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Minton NP: Clostridia in cancer therapy.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 1:237–242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bacon GA, Burrows TW and Yates M: The
effects of biochemical mutation on the virulence of bacterium
typhosum: the induction and isolation of mutants. Br J Exp Pathol.
31:702–713. 1950.
|
|
16
|
Forbes NS, Munn LL, Fukumura D and Jain
RK: Sparse initial entrapment of systemically injected Salmonella
typhimurium leads to heterogeneous accumulation within tumors.
Cancer Res. 63:5188–5193. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loessner H, Endmann A, Leschner S,
Westphal K, Rohde M, Miloud T, Hämmerling G, Neuhaus K and Weiss S:
Remote control of tumour-targeted Salmonella enterica serovar
Typhimurium by the use of L-arabinose as inducer of bacterial gene
expression in vivo. Cell Microbiol. 9:1529–1537. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Royo JL, Becker PD, Camacho EM, Cebolla A,
Link C, Santero E and Guzmán CA: In vivo gene regulation in
Salmonella spp. by a salicylate-dependent control circuit. Nat
Methods. 4:937–942. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Westphal K, Leschner S, Jablonska J,
Loessner H and Weiss S: Containment of tumor-colonizing bacteria by
host neutrophils. Cancer Res. 68:2952–2960. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu B, Yang M, Shi L, Yao Y, Jiang Q, Li X,
Tang LH, Zheng BJ, Yuen KY, Smith DK, et al: Explicit hypoxia
targeting with tumor suppression by creating an ‘obligate’
anaerobic Salmonella Typhimurium strain. Sci Rep. 2:4362012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hoiseth SK and Stocker BA:
Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and
effective as live vaccines. Nature. 291:238–239. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li CX, Shao Y, Ng KT, Liu XB, Ling CC, Ma
YY, Geng W, Fan ST, Lo CM and Man K: FTY720 suppresses liver tumor
metastasis by reducing the population of circulating endothelial
progenitor cells. PLoS One. 7:e323802012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saccheri F, Pozzi C, Avogadri F, Barozzi
S, Faretta M, Fusi P and Rescigno M: Bacteria-induced gap junctions
in tumors favor antigen cross-presentation and antitumor immunity.
Sci Transl Med. 2:44ra57. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishikawa H, Sato E, Briones G, Chen LM,
Matsuo M, Nagata Y, Ritter G, Jäger E, Nomura H, Kondo S, et al: In
vivo antigen delivery by a Salmonella typhimurium type III
secretion system for therapeutic cancer vaccines. J Clin Invest.
116:1946–1954. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
al-Ramadi BK, Fernandez-Cabezudo MJ,
El-Hasasna H, Al-Salam S, Bashir G and Chouaib S: Potent anti-tumor
activity of systemically-administered IL2-expressing Salmonella
correlates with decreased angiogenesis and enhanced tumor
apoptosis. Clin Immunol. 130:89–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Avogadri F, Martinoli C, Petrovska L,
Chiodoni C, Transidico P, Bronte V, Longhi R, Colombo MP, Dougan G
and Rescigno M: Cancer immunotherapy based on killing of
Salmonella-infected tumor cells. Cancer Res. 65:3920–3927. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al-Ramadi BK, Fernandez-Cabezudo MJ,
El-Hasasna H, Al-Salam S, Attoub S, Xu D and Chouaib S: Attenuated
bacteria as effectors in cancer immunotherapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1138:351–357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wall DM, Nadeau WJ, Pazos MA, Shi HN,
Galyov EE and McCormick BA: Identification of the Salmonella
enterica serotype typhimurium SipA domain responsible for inducing
neutrophil recruitment across the intestinal epithelium. Cell
Microbiol. 9:2299–2313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Srikanth CV, Wall DM, Maldonado-Contreras
A, Shi HN, Zhou D, Demma Z, Mumy KL and McCormick BA: Salmonella
pathogenesis and processing of secreted effectors by caspase-3.
Science. 330:390–393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B,
Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ and
Los M: Apoptosis and cancer: mutations within caspase genes. J Med
Genet. 46:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|