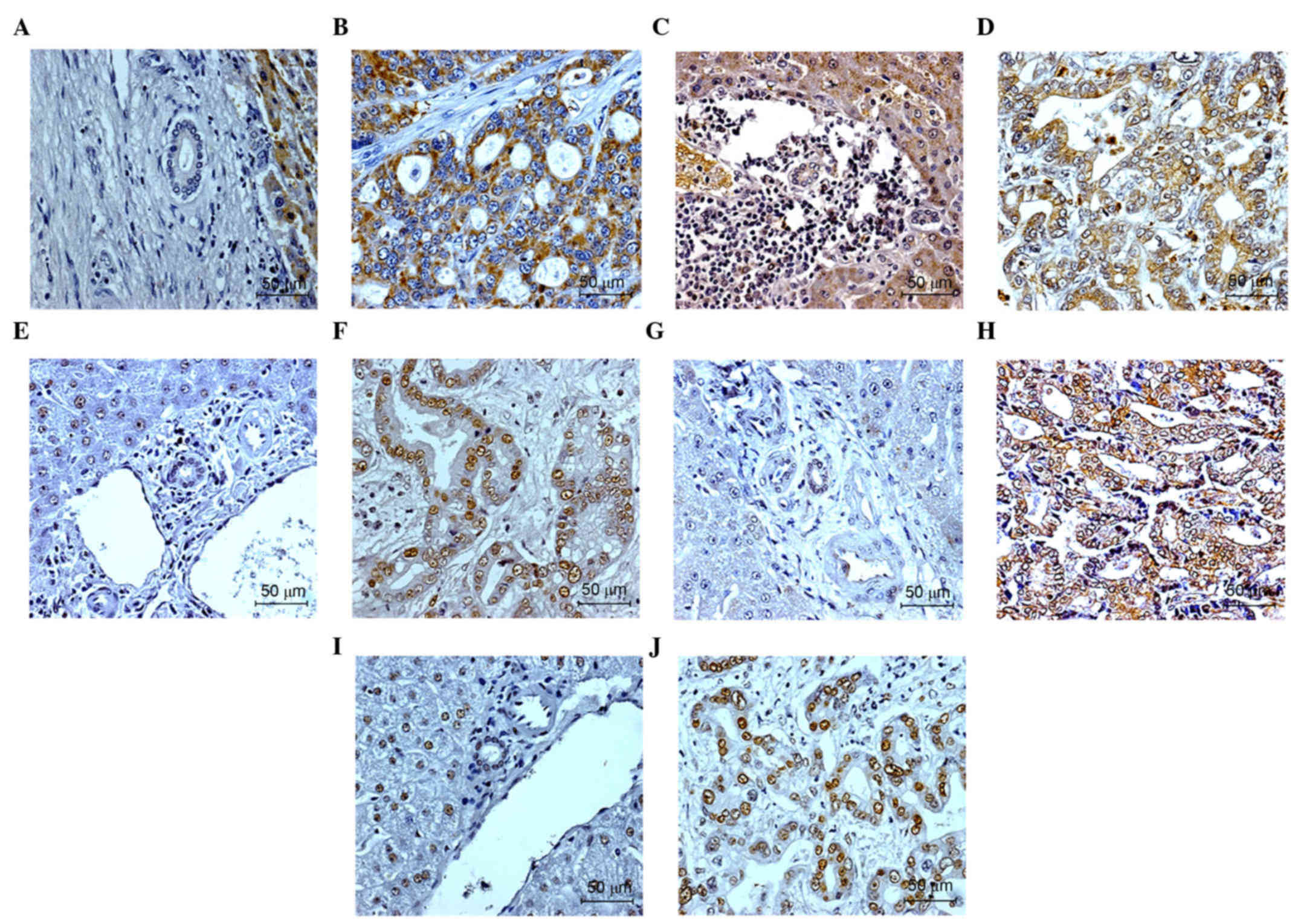
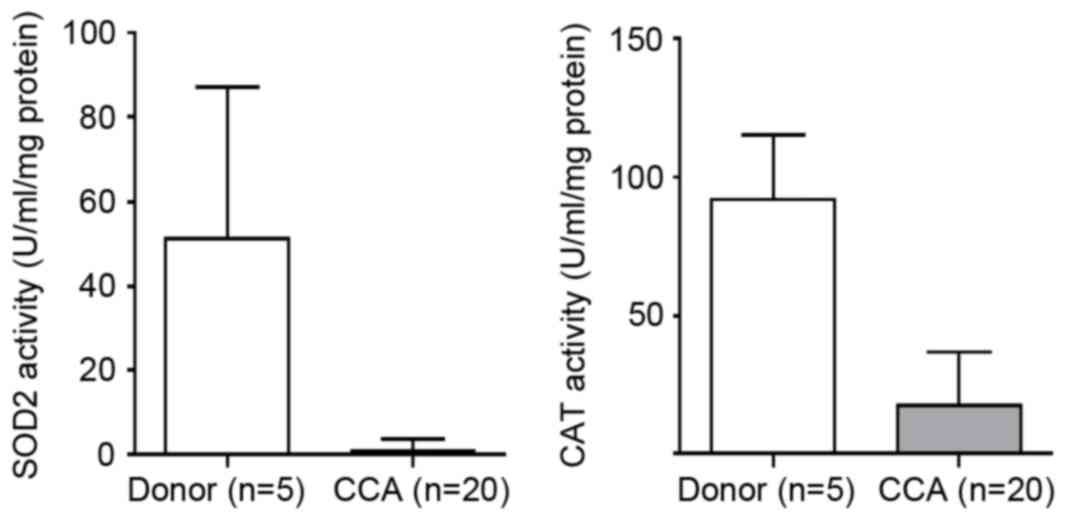
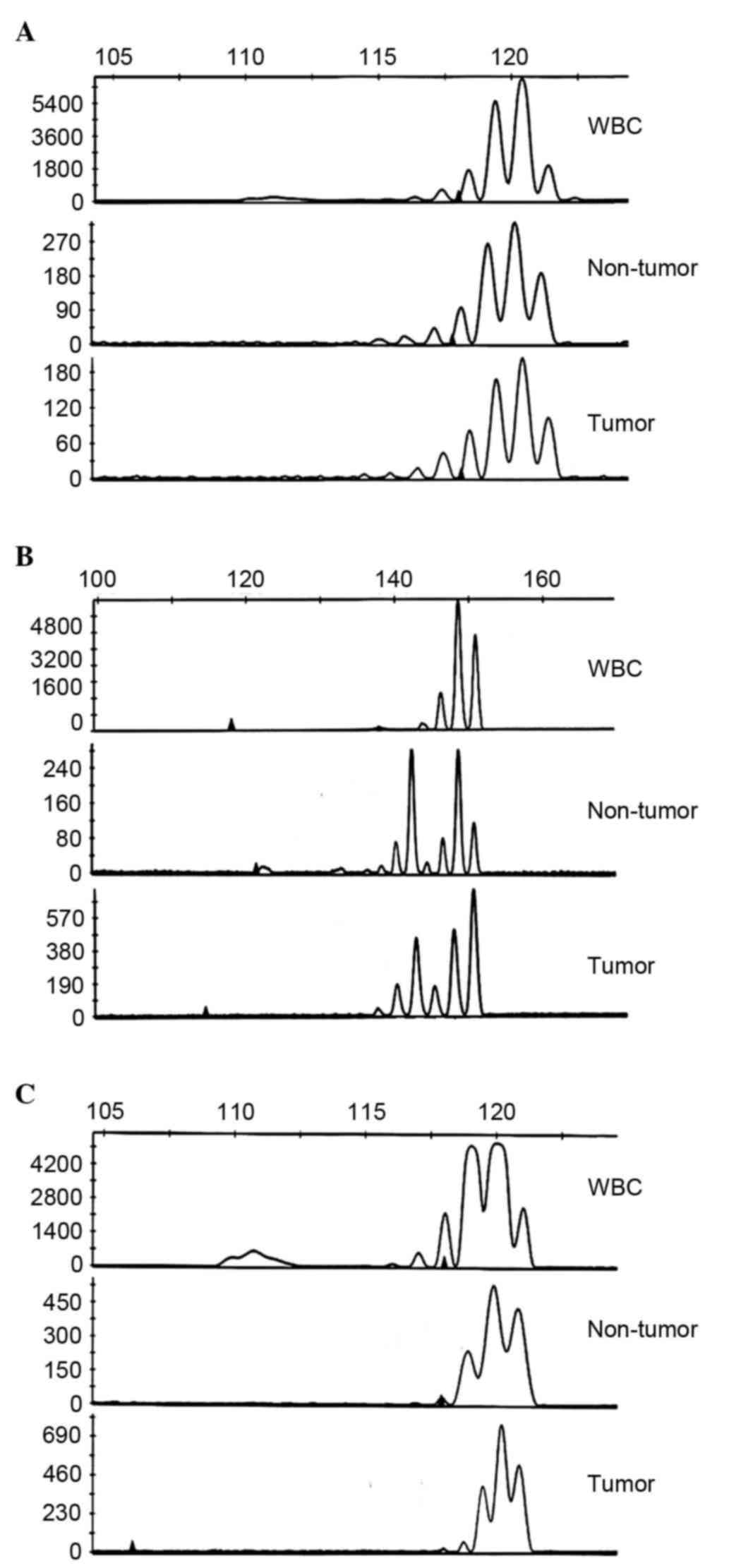
|
1
|
Khuntikeo N, Chamadol N, Yongvanit P, et
al: CASCAP investigators: Cohort profile: Cholangiocarcinoma
screening and care program (CASCAP). BMC Cancer. 15:4592015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Flavell DJ and Lucas SB: Promotion of
N-nitrosodimethylamine-initiated bile duct carcinogenesis in the
hamster by the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.
Carcinogenesis. 4:927–930. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ohshima H and Bartsch H: Chronic
infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors:
Possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res.
305:253–264. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thamavit W, Bhamarapravati N, Sahaphong S,
et al: Effects of dimethylnitrosamine on induction of
cholangiocarcinoma in Opisthorchis viverrini-infected Syrian golden
hamsters. Cancer Res. 38:4634–4639. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yongvanit P, Pinlaor S and Bartsch H:
Oxidative and nitrative DNA damage: Key events in
opisthorchiasis-induced carcinogenesis. Parasitol Int. 61:130–135.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pinlaor S, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Yongvanit P,
Semba R, Oikawa S, Murata M, Sripa B, Sithithaworn P and Kawanishi
S: Mechanism of NO-mediated oxidative and nitrative DNA damage in
hamsters infected with Opisthorchis viverrini: A model of
inflammation-mediated carcinogenesis. Nitric Oxide. 11:175–183.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pinlaor S, Ma N, Hiraku Y, Yongvanit P,
Semba R, Oikawa S, Murata M, Sripa B, Sithithaworn P and Kawanishi
S: Repeated infection with Opisthorchis viverrini induces
accumulation of 8-nitroguanine and
8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanine in the bile duct of hamsters via
inducible nitric oxide synthase. Carcinogenesis. 25:1535–1542.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pinlaor S, Sripa B, Sithithaworn P and
Yongvanit P: Hepatobiliary changes, antibody response, and
alteration of liver enzymes in hamsters re-infected with
Opisthorchis viverrini. Exp Parasitol. 108:32–39. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pinlaor S, Yongvanit P, Hiraku Y, Ma N,
Semba R, Oikawa S, Murata M, Sripa B, Sithithaworn P and Kawanishi
S: 8-nitroguanine formation in the liver of hamsters infected with
Opisthorchis viverrini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 309:567–571.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thanan R, Murata M, Pinlaor S,
Sithithaworn P, Khuntikeo N, Tangkanakul W, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S,
Yongvanit P and Kawanishi S: Urinary
8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine in patients with parasite
infection and effect of antiparasitic drug in relation to
cholangiocarcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:518–524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dechakhamphu S, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn
P, Bartsch H and Yongvanit P: Accumulation of miscoding etheno-DNA
adducts and highly expressed DNA repair during liver fluke-induced
cholangiocarcinogenesis in hamsters. Mutat Res. 691:9–16. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dechakhamphu S, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn
P, Nair J, Bartsch H and Yongvanit P: Lipid peroxidation and etheno
DNA adducts in white blood cells of liver fluke-infected patients:
Protection by plasma alpha-tocopherol and praziquantel. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:310–318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dechakhamphu S, Yongvanit P, Nair J,
Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn P and Bartsch H: High excretion of etheno
adducts in liver fluke-infected patients: Protection by
praziquantel against DNA damage. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:1658–1664. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thanan R, Oikawa S, Yongvanit P, Hiraku Y,
Ma N, Pinlaor S, Pairojkul C, Wongkham C, Sripa B, Khuntikeo N, et
al: Inflammation-induced protein carbonylation contributes to poor
prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma. Free Radic Biol Med.
52:1465–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guner G, Islekel H, Oto O, Hazan E and
Açikel U: Evaluation of some antioxidant enzymes in lung carcinoma
tissue. Cancer Lett. 103:233–239. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hofseth LJ, Khan MA, Ambrose M, Nikolayeva
O, Xu-Welliver M, Kartalou M, Hussain SP, Roth RB, Zhou X, Mechanic
LE, et al: The adaptive imbalance in base excision-repair enzymes
generates microsatellite instability in chronic inflammation. J
Clin Invest. 112:1887–1894. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loilome W, Kadsanit S, Namwat N, Techasen
A, Puapairoj A, Dechakhamphu A, Pinitsoontorn C and Yongvanit P:
Impaired antioxidant enzyme activity and increased DNA repair
enzyme expression in hamster liver tissues related to
cholangiocarcinoma development. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (13
Suppl). S59–S64. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR,
Sidransky D, Eshleman JR, Burt RW, Meltzer SJ, Rodriguez-Bigas MA,
Fodde R, Ranzani GN and Srivastava S: A National Cancer Institute
Workshop on Microsatellite Instability for cancer detection and
familial predisposition: Development of international criteria for
the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 58:5248–5257. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scibior D, Skrzycki M, Podsiad M and
Czeczot H: Glutathione level and glutathione-dependent enzyme
activities in blood serum of patients with gastrointestinal tract
tumors. Clin Biochem. 41:852–858. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baker AM, Oberley LW and Cohen MB:
Expression of antioxidant enzymes in human prostatic
adenocarcinoma. Prostate. 32:229–233. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jaruga P, Zastawny TH, Skokowski J,
Dizdaroglu M and Olinski R: Oxidative DNA base damage and
antioxidant enzyme activities in human lung cancer. FEBS Lett.
341:59–64. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beevi SS, Rasheed AM and Geetha A:
Evaluation of oxidative stress and nitric oxide levels in patients
with oral cavity cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 34:379–385. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Itatsu K, Sasaki M, Yamaguchi J, Ohira S,
Ishikawa A, Ikeda H, Sato Y, Harada K, Zen Y, Sato H, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 is involved in the up-regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in cholangiocarcinoma induced by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. Am J Pathol. 174:829–841. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinlaor S, Hiraku Y, Yongvanit P,
Tada-Oikawa S, Ma N, Pinlaor P, Sithithaworn P, Sripa B, Murata M,
Oikawa S and Kawanishi S: iNOS-dependent DNA damage via NF-kappaB
expression in hamsters infected with Opisthorchis viverrini and its
suppression by the antihelminthic drug praziquantel. Int J Cancer.
119:1067–1072. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu T: Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin
signaling in cholangiocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1755:135–150. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Prawan A, Buranrat B, Kukongviriyapan U,
Sripa B and Kukongviriyapan V: Inflammatory cytokines suppress NAD
(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase-1 and induce oxidative stress in
cholangiocarcinoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 135:515–522.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yongvanit P, Thanan R, Pinlaor S,
Sithithaworn P, Loilome W, Namwat N, Techasen A and Dechakhamphu S:
Increased expression of TLR-2, COX-2 and SOD-2 genes in the
peripheral blood leukocytes of opisthorchiasis patients induced by
Opisthorchis viverrini antigen. Parasitol Res. 110:1969–1977. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Z, Boonmars T, Boonjaraspinyo S, Nagano
I, Pinlaor S, Puapairoj A, Yongvanit P and Takahashi Y: Candidate
genes involving in tumorigenesis of cholangiocarcinoma induced by
Opisthorchis viverrini infection. Parasitol Res. 109:657–673. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kolodziejczyk L, Siemieniuk E and
Skrzydlewska E: Antioxidant potential of rat liver in experimental
infection with Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res. 96:367–372. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
el Ghissassi F, Barbin A, Nair J and
Bartsch H: Formation of 1,N6-ethenoadenine and 3, N4-ethenocytosine
by lipid peroxidation products and nucleic acid bases. Chem Res
Toxicol. 8:278–283. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nair J, De Flora S, Izzotti A and Bartsch
H: Lipid peroxidation-derived etheno-DNA adducts in human
atherosclerotic lesions. Mutat Res. 621:95–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Singer B and Hang B: Mammalian enzymatic
repair of etheno and para-benzoquinone exocyclic adducts derived
from the carcinogens vinyl chloride and benzene. IARC Sci Publ.
233–247. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bohr VA: Repair of oxidative DNA damage in
nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and some changes with aging in
mammalian cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 32:804–812. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liengswangwong U, Nitta T, Kashiwagi H,
Kikukawa H, Kawamoto T, Todoroki T, Uchida K, Khuhaprema T, Karalak
A, Srivatanakul P and Miwa M: Infrequent microsatellite instability
in liver fluke infection-associated intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinomas from Thailand. Int J Cancer. 107:375–380. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Losso GM, Rda S Moraes, Gentili AC and
Messias-Reason IT: Microsatellite instability-MSI markers (BAT26,
BAT25, D2S123, D5S346, D17S250) in rectal cancer. Arq Bras Cir Dig.
25:240–244. 2012.(In English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saridaki Z, Souglakos J and Georgoulias V:
Prognostic and predictive significance of MSI in stages II/III
colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 20:6809–6814. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Glassner BJ, Rasmussen LJ, Najarian MT,
Posnick LM and Samson LD: Generation of a strong mutator phenotype
in yeast by imbalanced base excision repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:9997–10002. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Posnick LM and Samson LD: Imbalanced base
excision repair increases spontaneous mutation and alkylation
sensitivity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 181:6763–6771.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jones LE Jr, Ying L, Hofseth AB, Jelezcova
E, Sobol RW, Ambs S, Harris CC, Espey MG, Hofseth LJ and Wyatt MD:
Differential effects of reactive nitrogen species on DNA base
excision repair initiated by the alkyladenine DNA glycosylase.
Carcinogenesis. 30:2123–2129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zmudzka BZ, Fornace A, Collins J and
Wilson SH: Characterization of DNA polymerase beta mRNA: Cell-cycle
and growth response in cultured human cells. Nucleic Acids Res.
16:9587–9596. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Canitrot Y, Cazaux C, Fréchet M, Bouayadi
K, Lesca C, Salles B and Hoffmann JS: Overexpression of DNA
polymerase beta in cell results in a mutator phenotype and a
decreased sensitivity to anticancer drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:12586–12590. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bergoglio V, Pillaire MJ, Lacroix-Triki M,
Raynaud-Messina B, Canitrot Y, Bieth A, Garès M, Wright M, Delsol
G, Loeb LA, et al: Deregulated DNA polymerase beta induces
chromosome instability and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 62:3511–3514.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yamada NA and Farber RA: Induction of a
low level of microsatellite instability by overexpression of DNA
polymerase Beta. Cancer Res. 62:6061–6064. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|