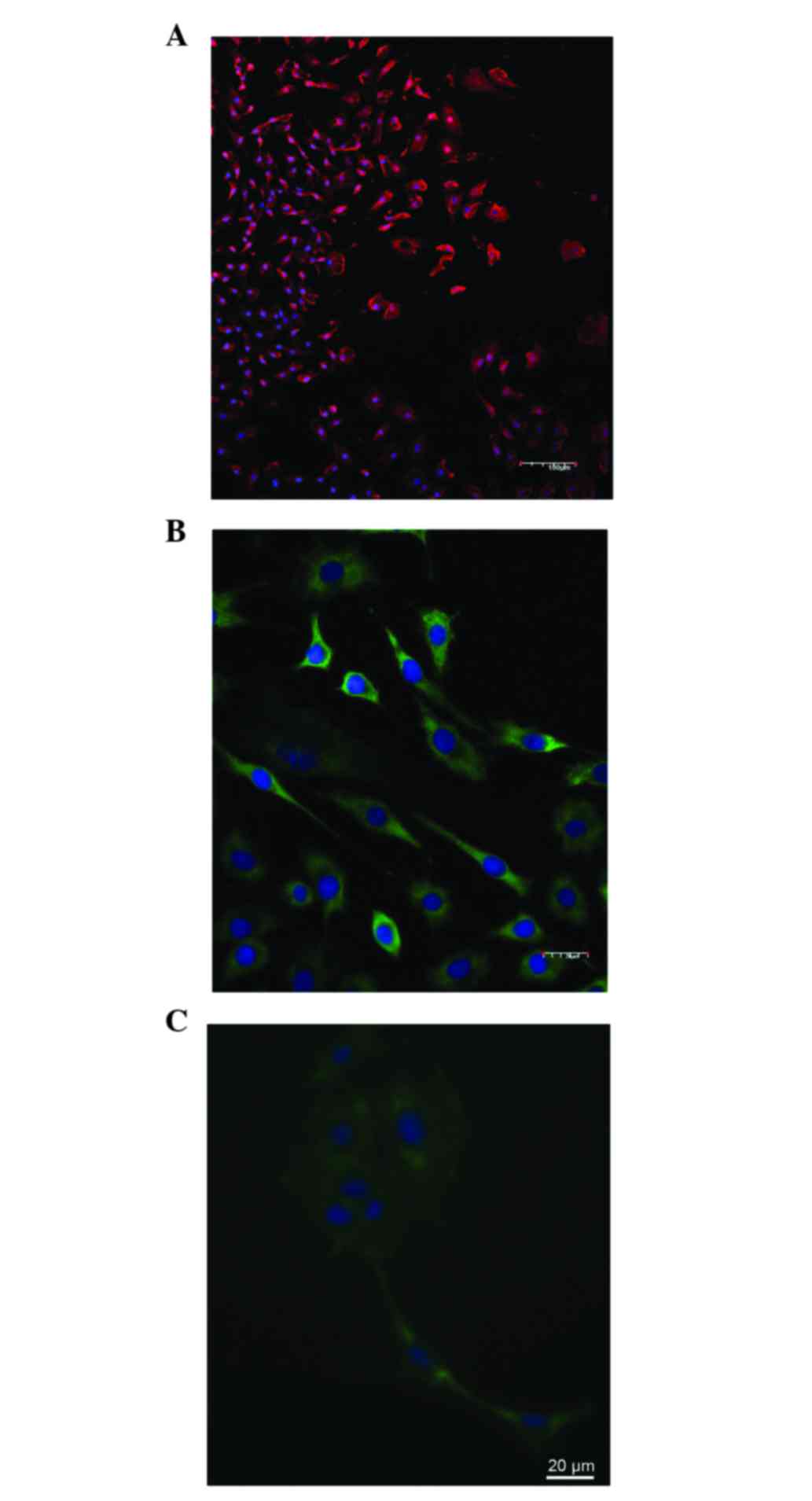
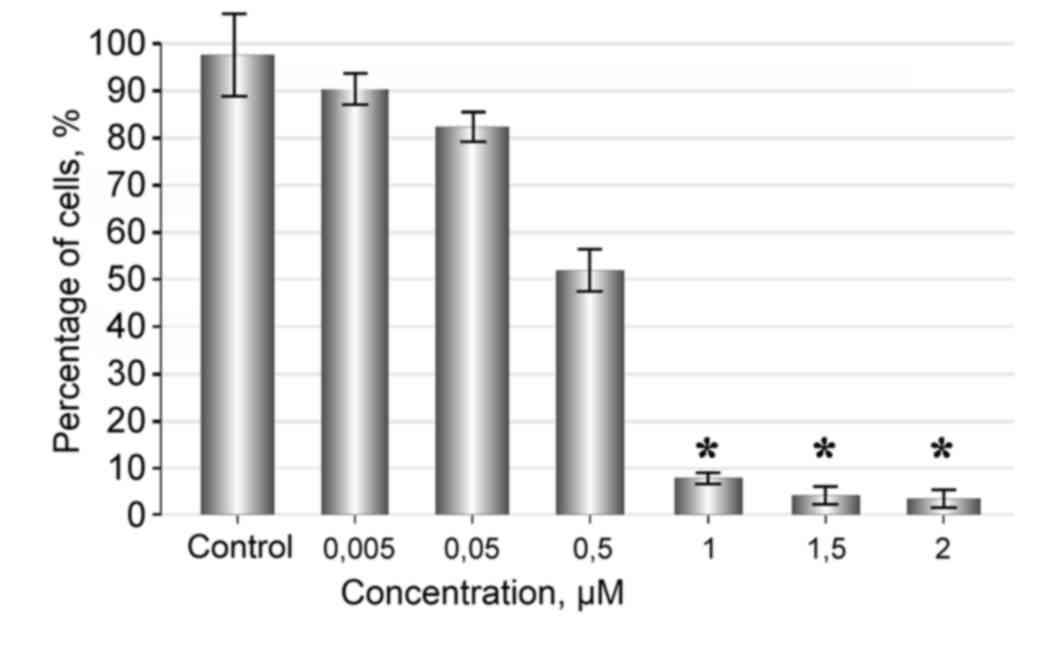
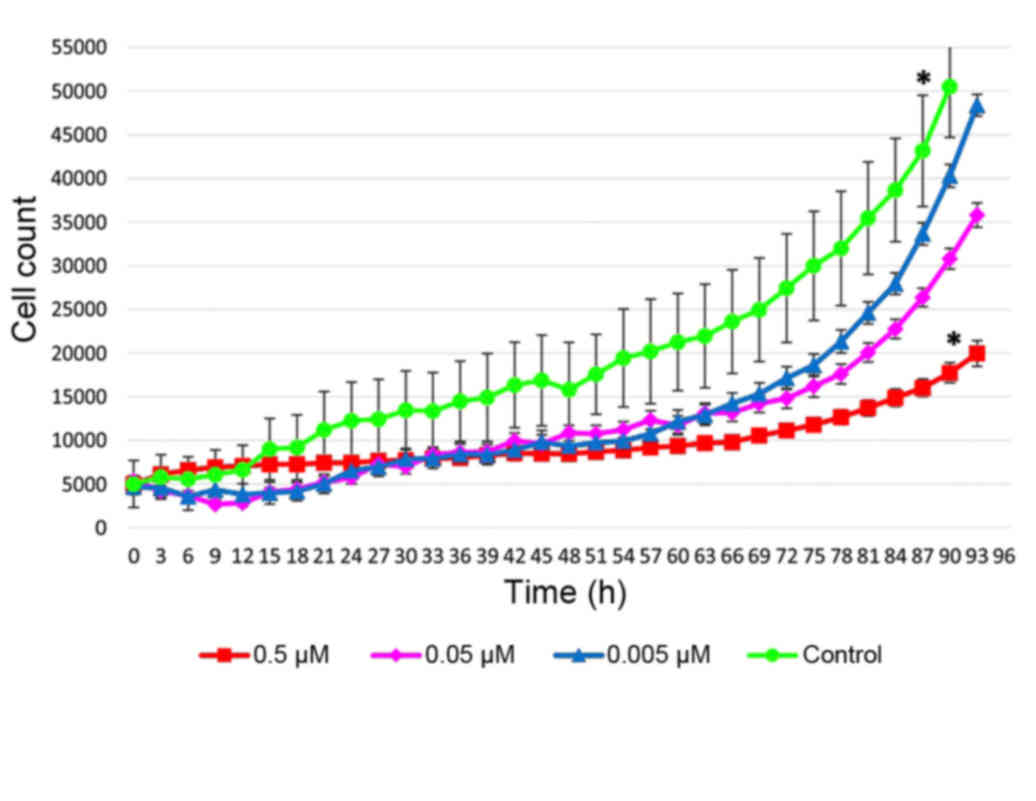
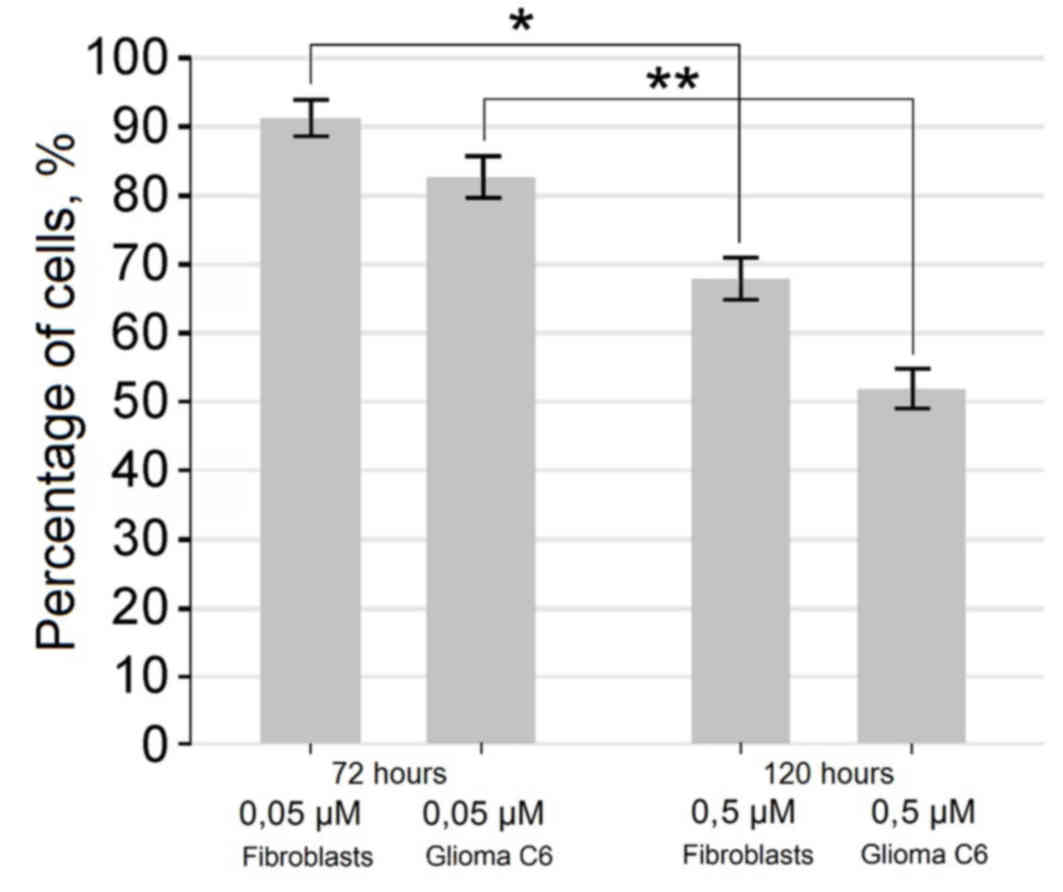
|
1
|
Carlsson SK, Brothers SP and Wahlestedt C:
Emerging treatment strategies for glioblastoma multiforme. EMBO Mol
Med. 6:1359–1370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Omuro A and DeAngeles LM: Glioblastoma and
others malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Anton K, Baehring JM and Mayer T:
Glioblastoma multiforme: Overview of current treatment and future
perspectives. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 26:825–853. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
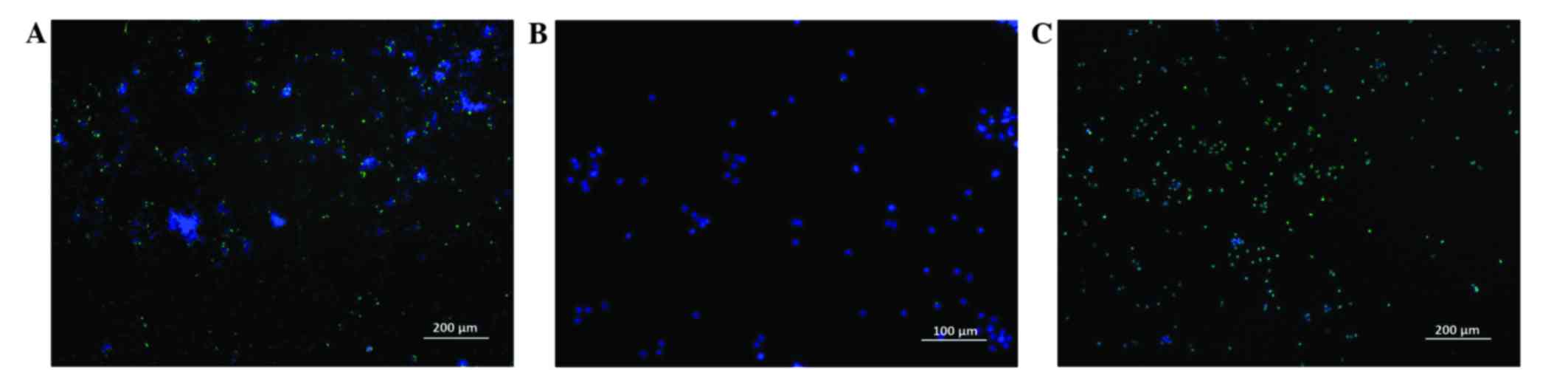
4
|
Konovalov AN, Potapov AA, Loshakov VA,
Olyushin VE, Ulitin AY, Kornienko VN, Pronin IN, Shishkina LV,
Golanov AV, Tanqskiu SV, Urakov SV and Kobqkov GL: Association of
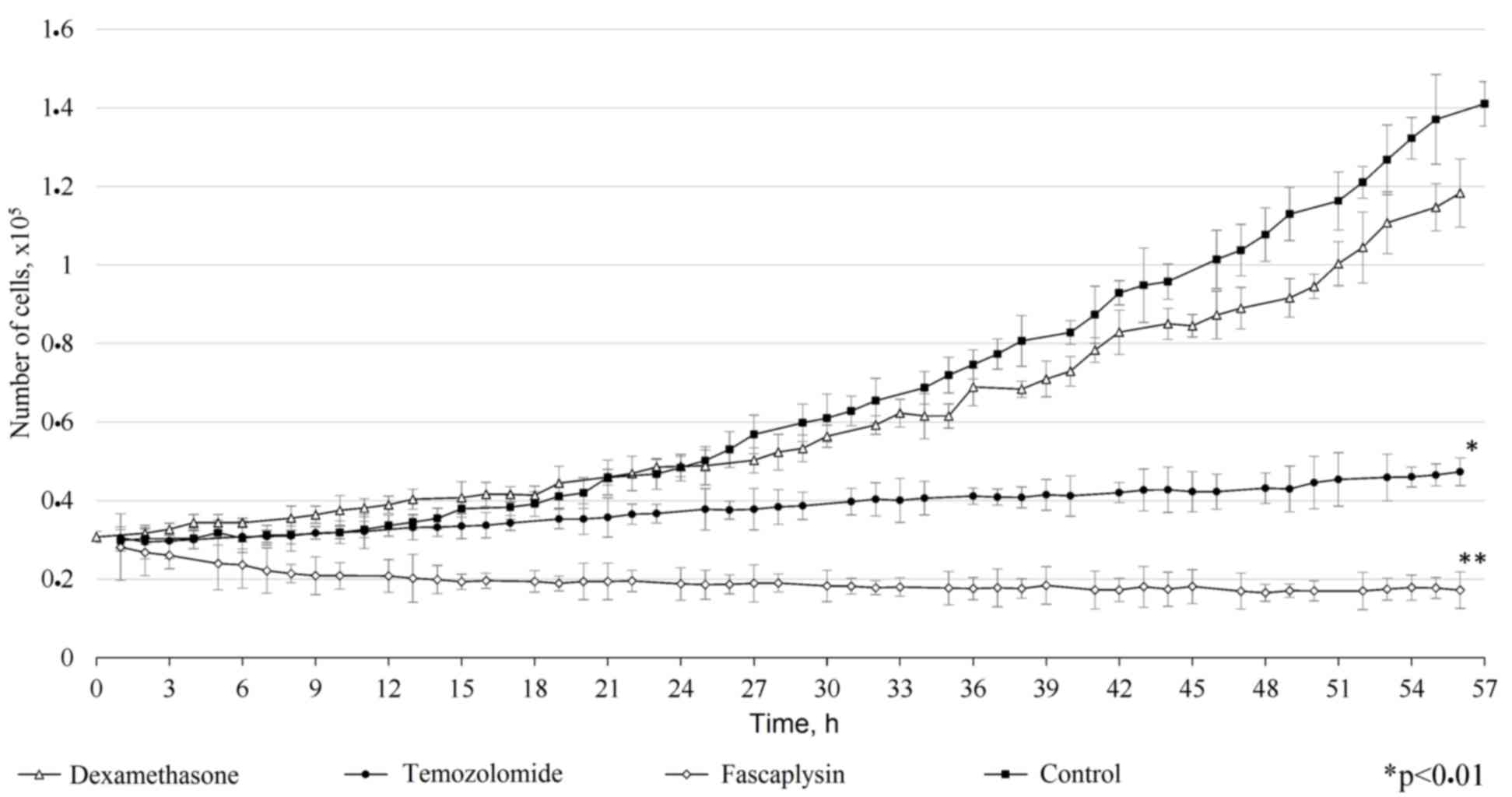
Neurosurgeons of Russia: The standards, guidelines and options in
the treatment of brain tumors in adults (2009). Association of
Neurosurgeons of Russia; Moscow, Russia: 2009, (In Russian).
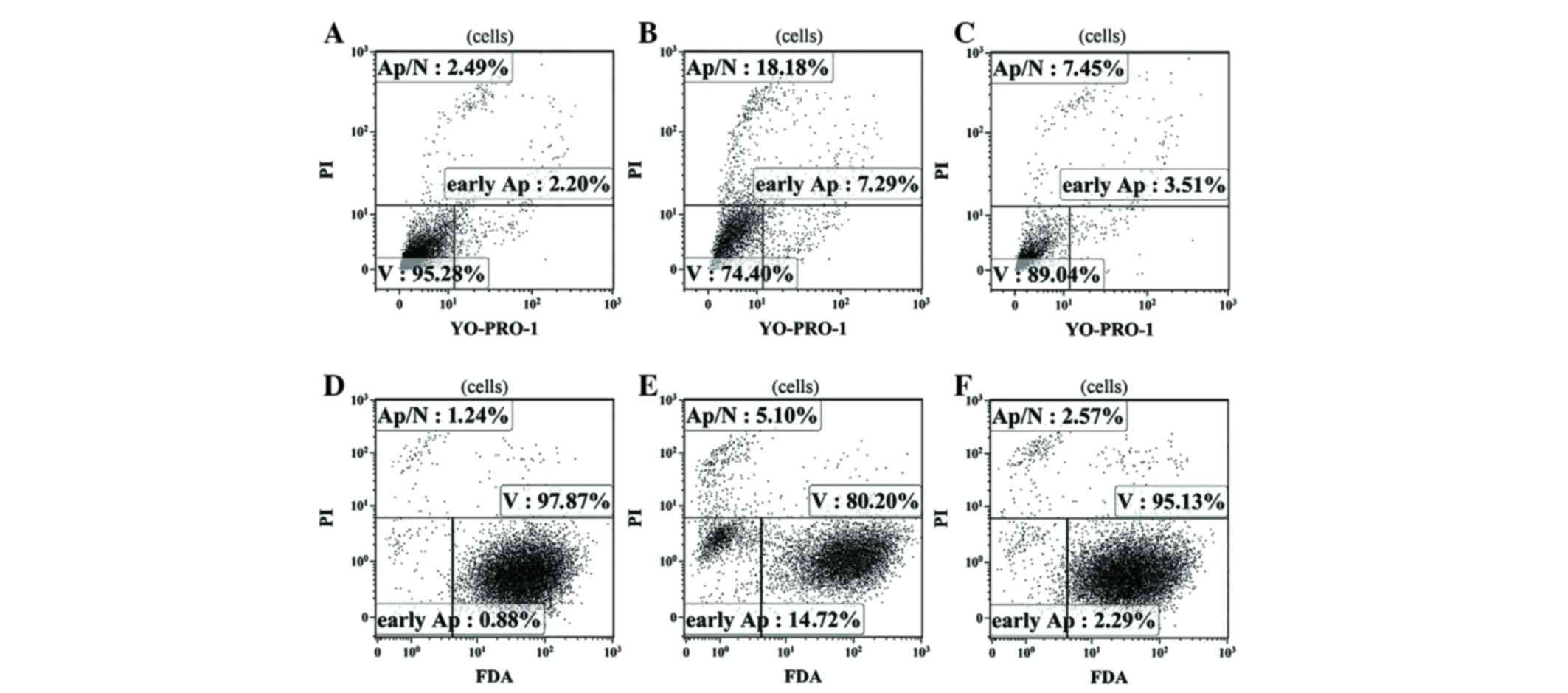
|
|
5
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Burger P, Ellison DW,
Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Aldape K, Brat D, Collins VP,
Eberhart C, et al: International Society of Neuropathology -
Haarlem consensus guidelines for nervous system tumor
classification and grading. Brain Pathol. 24:429–435. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paw I, Carpenter RC, Watabe K, Debinski W
and Lo HW: Mechanisms regulating glioma invasion. Cancer Lett.
362:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Molina JR, Hayashi Y, Stephens C and
Georgescu MM: Invasive glioblastoma cells acquire stemness and
increased Akt activation. Neoplasia. 12:453–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barani IJ and Larson DA: Radiation therapy
of glioblastoma. Cancer Treat Res. 163:49–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mitchison TJ: The proliferation rate
paradox in antimitotic chemotherapy. Mol Biol Cell. 23:1–6. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu YY, Gao P, Sun Y and Duan YR:
Development of targeted therapies in treatment of glioblastoma.
Cancer Biol Med. 12:223–237. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tiwari G, Tiwari R, Sriwastawa B, Bhati L,
Pandey S, Pandey P and Bannerjee SK: Drug delivery systems: An
updated review. Int J Pharm Investig. 2:2–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aboody KS, Brown A, Rainov NG, Bower KA,
Liu S, Yang W, Small JE, Herrlinger U, Ourednik V, Black PM, et al:
Neural stem cells display extensive tropism for pathology in adult
brain: Evidence from intracranial gliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:12846–12851. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou J, Atsina KB, Himes BT, Strohbehn GW
and Saltzman WM: Novel delivery strategies for glioblastoma. Cancer
J. 18:89–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barber FA: Complications of Biodegradable
Materials: Anchors and Interference Screws. Sports Med Arthrosc.
23:149–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roll DM, Ireland CM, Lu HSM and Clardy J:
Fascaplysin, an unusual antimicrobial pigment from the marine
sponge Fascaplysinopsis sp. J Org Chem. 53:3276–3278. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bharate SB, Manda S, Mupparapu N, Battini
N and Vishwakarma RA: Chemistry and biology of fascaplysin, a
potent marine-derived CDK-4 inhibitor. Mini Rev Med Chem.
12:650–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuzmich AS, Fedorov SN, Shastina VV,
Shubina LK, Radchenko OS, Balaneva NN, Zhidkov ME, Park JI, Kwak JY
and Stonik VA: The anticancer activity of 3- and
10-bromofascaplysins is mediated by caspase-8, −9, −3-dependent
apoptosis. Bioorg Med Chem. 18:3834–3840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu XL, Zheng YL, Chen HM, Yan XJ, Wang F
and Xu WF: Anti-proliferation of human cervical cancer HeLa cell
line by fascaplysin through apoptosis induction. Yao Xue Xue Bao.
44:980–986. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamilton G: Cytotoxic effects of
fascaplysin against small cell lung cancer cell lines. Mar Drugs.
12:1377–1389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Phillips MA, Gran ML and Peppas NA:
Targeted nanodelivery of drugs and diagnostics. Nano Today.
5:143–159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhidkov ME and Kaminskii VA: A new method
for the synthesis of marine alkaloid fascaplysin based on the
microwave-assisted Minisci reaction. Tetrahedron Lett.
54:3530–3532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kirsch G, Köng GM, Wright AD and Kaminsky
R: A new bioactive sesterterpene and antiplasmodial alkaloids from
the marine sponge hyrtios cf. erecta. J Nat Prod. 63:825–829. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Idziorek T, Estaquier J, De Bels F and
Ameisen JC: YOPRO-1 permits cytofluorometric analysis of programmed
cell death (apoptosis) without interfering with cell viability. J
Immunol Methods. 185:249–258. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fujisawa S, Romin Y, Barlas A, Petrovic
LM, Turkekul M, Fan N, Xu K, Garcia AR, Monette S, Klimstra DS, et
al: Evaluation of YO-PRO-1 as an early marker of apoptosis
following radiofrequency ablation of colon cancer liver metastases.
Cytotechnology. 66:259–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rieger AM, Nelson KL, Konowalchuk JD and
Barreda DR: Modified annexin V/propidium iodide apoptosis assay for
accurate assessment of cell death. J Vis Exp. 50:2512011.
|
|
26
|
Kudryavtsev IV, Khaidukov SV, Zurochka AV
and Chereshev VA: Flow cytometry in experimental biology. RIO Ural
Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences; Yekaterinburg, Russia:
2012, (In Russian).
|
|
27
|
Hughes D and Mehmet H: Cell Proliferation
and Apoptosis. 1st. Taylor and Francis; Abingdon, UK: 2002
|
|
28
|
Kostaras X, Cusano F, Kline GA, Roa W and
Easaw J: Use of dexamethasone in patients with high-grade glioma: A
clinical practice guideline. Curr Oncol. 21:e493–e503. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chamberlain MC: Temozolomide: Therapeutic
limitations in the treatment of adult high-grade gliomas. Expert
Rev Neurother. 10:1537–1544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen TC, Cho HY, Wang W, Wetzel SJ, Singh
A, Nguyen J, Hofman FM and Schönthal AH: Chemotherapeutic effect of
a novel temozolomide analog on nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro
and in vivo. J Biomed Sci. 22:712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zeiss CJ: The apoptosis-necrosis
continuum: Insights from genetically altered mice. Vet Pathol.
40:481–495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, Zhang W, Cao WD, Cheng G and
Zhang YQ: Glioblastoma multiforme: Molecular characterization and
current treatment strategy (Review). Exp Ther Med. 3:9–14.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kalkan R: Glioblastoma stem cells as a new
therapeutic target for glioblastoma. Clin Med Insights Oncol.
9:95–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bryukhovetskiy A, Shevchenko V, Kovalev S,
Chekhonin V, Baklaushev V, Bryukhovetskiy I and Zhukova M: To the
novel paradigm of proteome-based cell therapy of tumors: Through
comparative proteome mapping of tumor stem cells and
tissue-specific stem cells of humans. Cell Transplant. 23:(Suppl
1). S151–S170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Khalili AA and Ahmad MR: A Review of Cell
Adhesion Studies for Biomedical and Biological Applications. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:18149–18184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park D, Xiang AP, Mao FF, Zhang L, Di CG,
Liu XM, Shao Y, Ma BF, Lee JH, Ha KS, et al: Nestin is required for
the proper self-renewal of neural stem cells. Stem Cells.
28:2162–2171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barth RF and Kaur B: Rat brain tumor
models in experimental neuro-oncology: The C6, 9L, T9, RG2, F98,
BT4C, RT-2 and CNS-1 gliomas. J Neurooncol. 94:299–312. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang PY, Yang YJ, Xue Y, Fu J, Zhang CX,
Wang Y, Yang Y and Shi H: Cancer stem cells: Targeting tumors at
the source. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:1821–1828.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xie Q, Mittal S and Berens ME: Targeting
adaptive glioblastoma: An overview of proliferation and invasion.
Neuro Oncol. 16:1575–1584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Paltsev MA, Ivanov AA and Severin SE:
Cellular interactions (2nd). Medicine. Moscow: 2003.(In
Russian).
|
|
41
|
Wolinsky JB, Colson YL and Grinstaff MW:
Local drug delivery strategies for cancer treatment: gels,
nanoparticles, polymeric films, rods, and wafers. J Control
Release. 159:14–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meng XG and Yue SW: Dexamethasone disrupts
cytoskeleton organization and migration of T47D human breast cancer
cells by modulating the AKT/mTOR/RhoA pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:10245–10250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Laquintana V, Trapani A, Denora N, Wang F,
Gallo JM and Trapani G: New strategies to deliver anticancer drugs
to brain tumors. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 6:1017–1032. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Friedman HS, Kerby T and Calvert H:
Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res.
6:2585–2597. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang J, Stevens MF and Bradshaw TD:
Temozolomide: Mechanisms of action, repair and resistance. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 5:102–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bryukhovetsky IS: The effectiveness in
vivo of a stem cell drug on glioblastoma rat's model after
chemotherapy. Russian Journal of Biotherapy. 13:51–58. 2014.(In
Russian).
|